Piper longum
January 15, 2020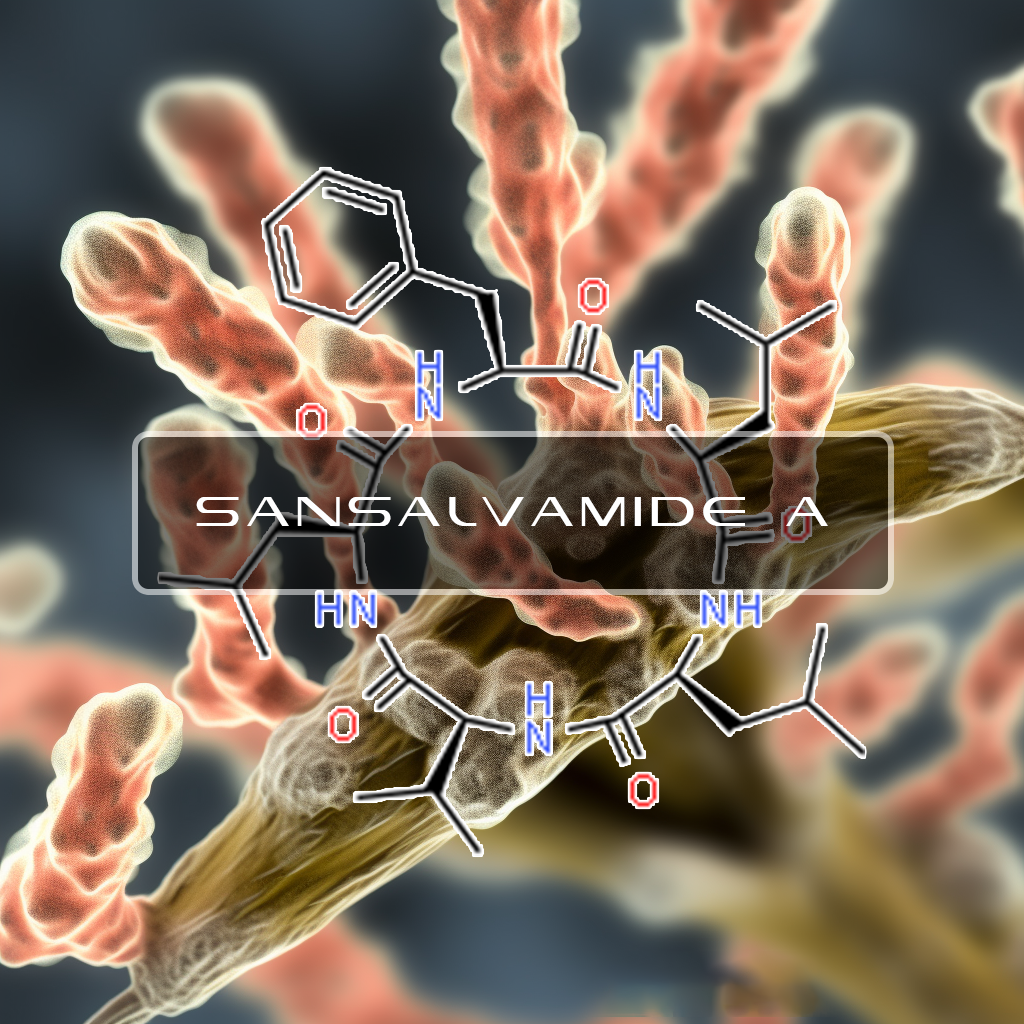
Sansalvamide A (MArine Fungi Fusarium)
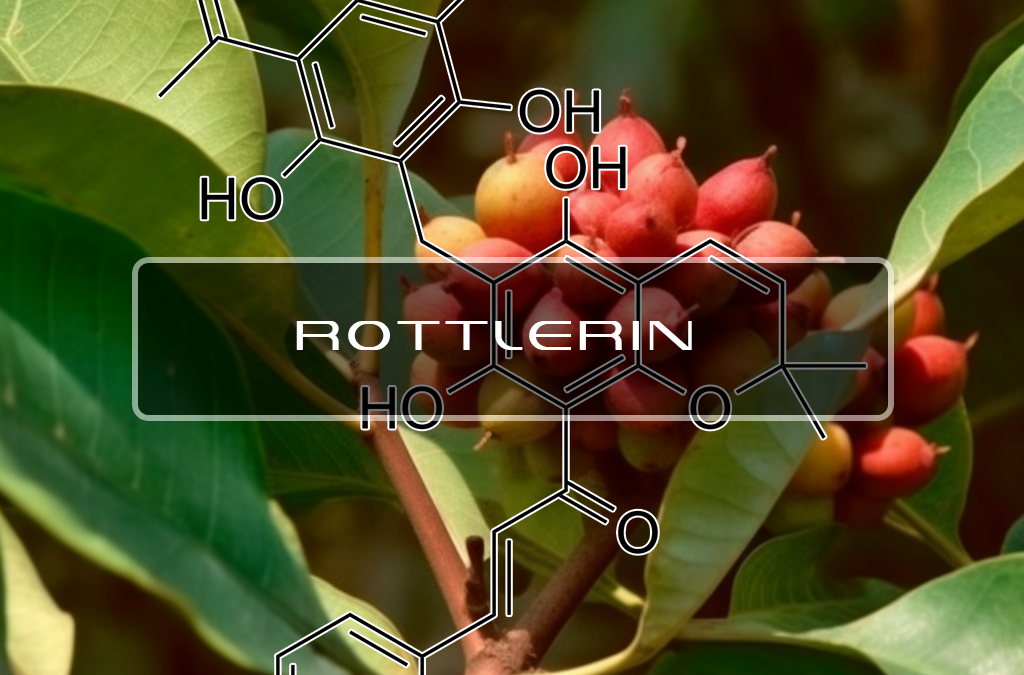
January 15, 2020Rottlerin (Asian tree Mallotus philippensis)
- … (BCR) cross-talk: the IL-4-induced alternate pathway for BCR signaling operates in parallel with the classical pathway, is sensitive to Rottlerin, and depends on Lyn
- … Receptor Crosstalk: The IL-4-induced Alternate Pathway for BCR Signaling Operates in Parallel with the Classical Pathway, Is Sensitive to Rottlerin, and Depends on …
- 303 ENHANCED THERAPY SUCCESS OF RENAL CELL CARCINOMA USING TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITORS COMBINED WITH ROTTLERIN
- 64PEffects of Rottlerin and genistein through EF2K on proliferation, invasion and cell cycle/death in neuroblastoma cells
- A polyphenolic compound Rottlerin demonstrates significant in vitro cytotoxicity against human cancer cell lines: isolation and characterization from the fruits of …
- AB161. Rottlerin-induced autophagy leads to the apoptosis in bladder cancer cells
- Abstract LB-011: PAK1 inhibitor FRAX1036 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells with amplified 11q13 to cytotoxic effect of rottlerin
- Activation of BKCa Channels With Rottlerin Greatly Improves Cardiac Functional Improvement Following Surgical Ischemia Associated With Cardioplegic Arrest.
- Alternative pathways of cancer cell death by rottlerin: apoptosis versus autophagy
- Anti-allergic actions of Rottlerin from Mallotus philippinensis in experimental mast cell-mediated anaphylactic models
- Antiproliferative effect of Rottlerin on SK-MEL-28 melanoma cells
- Arsenite-Stimulated Glucose Uptake in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Is Sensitive to Inhibition by Rottlerin and Ro-31-8220
- Biosynthesis of promatrix metalloproteinase-9/
chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan heteromer involves a Rottlerin-sensitive pathway - Coadministration of sorafenib with Rottlerin potently inhibits cell proliferation and migration in human malignant glioma cells
- Critical appraisal of the MTT assay in the presence of Rottlerin and uncouplers
- Design, synthesis and functional characterization of Rottlerin analogs
- Determination of rottlerin, a natural protein kinases C inhibitor, in pancreatic cancer cells and mouse xenografts by RP-HPLC method
- Development and validation of a RP-HPLC method for quantification of Rottlerin in Kamala (Mallotus philppinensis).
- Development and validation of a RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of Embelin, Rottlerin and Ellagic acid in Vidangadi churna
- Down-regulation of caspase-2 by Rottlerin via protein kinase C-δ–independent pathway
- Down-regulation of Caspase-2 by Rottlerin via Protein Kinase CD–Independent Pathway
- Effect of rottlerin, a PKC-δ inhibitor, on TLR-4-dependent activation of murine microglia
- Effects of Rottlerin on in vitro proliferation of and expressions of interleukin-17C, CCL20 and nuclear factor-κB in a human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT
- Effects of Rottlerin on silica-exacerbated systemic autoimmune disease in New Zealand mixed mice
- Effects of rottlerin, an inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III, on cellular proliferation, viability, and cell cycle distribution in malignant glioma cells.
- Effects of Rottlerin, an Inhibitor of Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase Ill, on Cellular Proliferation, Viability, and Cell Cycle Distribution in Malignant Glioma …
- Efficient synthesis of Rottlerin and its two subunits
- Elongation factor-2 kinase: effective inhibition by the novel protein kinase inhibitor Rottlerin and relative insensitivity towards staurosporine
- Elongation factor-2 kinase: effective inhibition by the novel protein kinase inhibitor Rottlerin and relative insensitivity towards staurosporine
- Expression of protein kinase c (pkc) isoforms and the effect of selective pkc-s inhibition by Rottlerin on the induction of apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia
- Improved synergistic anticancer efficacy of quercetin in combination with PI-103, rottlerin, and G0 6983 against MCF-7 and RAW 264.7 cells
- Inhibition of amyloid fibril formation and disassembly of pre-formed fibrils by natural polyphenol rottlerin
- Inhibition of eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase mediates Rottlerin induced effects in apoptosis and cell proliferation inhibition in human pancreatic cancer cells.
- Inhibition of Notch-1 pathway is involved in rottlerin-induced tumor suppressive function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- Inhibitions of mTORC1 and 4EBP-1 are key events orchestrated by Rottlerin in SK-Mel-28 cell killing
- Integrated in Silico Docking and MOMA Simulation Methods Reveal Rottlerin as a Potent Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) Inhibitor
- Integrin signaling and cell spreading alterations by Rottlerin treatment of chick limb bud mesenchymal cells
- Kinase inhibitors tyrphostin 9 and Rottlerin block early steps of rabies virus cycle
- Links between L-glutamate transporters, Na+/K+-ATPase and cytoskeleton in astrocytes: evidence following inhibition with rottlerin
- Mechanisms of apoptosis-induction by rottlerin: therapeutic implications for B-CLL
- Mechanisms of Rottlerin-mediated inhibition of chlamydial growth
- Mo1954 Rottlerin Promotes Apoptosis and Autophagy in Pancreatic Stellate Cells via AMPK Activation
- Multi-Functional Role of Rottlerin, PKC-Delta Inhibitor, in Immune Cells and Cancer Cells
- Multiple mechanisms of Rottlerin toxicity in A375 melanoma cells
- Neuroprotective effect of protein kinase Cδ inhibitor Rottlerin in cell culture and animal models of Parkinson’s disease
- Non-conventional Rottlerin anticancer properties
- NOX, RAS and PKC-Δ as Key Players in Kidney Diseases: A Possible Role of Rottlerin
- Phosphorylation-independent mTORC1 inhibition by the autophagy inducer Rottlerin
- Possible mechanism of Rottlerin induced modulation of ischemia reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts
- Potent stimulation of large‐conductance Ca2+‐activated K+ channels by rottlerin, an inhibitor of protein kinase C‐δ, in pituitary tumor (GH3) cells and in cortical …
- Potential in for PKC inhibitor Rottlerin in murine experimental model of asthma
- Potentiation of tumor necrosis factor-α-induced cell death by Rottlerin through a cytochrome-c-independent pathway
- Prevention of TNF-induced necrotic cell death by Rottlerin through a Nox1 NADPH oxidase
- Protection of human colon epithelial cells against deoxycholate by rottlerin
- Protein kinase C-δ inhibitor, Rottlerin inhibits growth and survival of mycobacteria exclusively through Shikimate kinase
- Protein kinase C‐delta is commonly expressed in multiple myeloma cells and its downregulation by Rottlerin causes apoptosis
- Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-icB Is Induced by a Rottlerin-sensitive and p38 MAP Kinase-dependent Pathway during Monocyte Differentiation.
- Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB is induced by a rottlerin-sensitive and p38 MAP kinase-dependent pathway during monocyte differentiation
- Research Article Alternative Pathways of Cancer Cell Death by Rottlerin: Apoptosis versus Autophagy
- Research Article Rottlerin Inhibits ROS Formation and Prevents NFκB Activation in MCF-7 and HT-29 Cells
- Reversal of the negative effects of TGFβ1 on human articular chondrocytes by PKCδ inhibition with rottlerin
- Rottlerin activates AMPK possibly through LKB1 in vascular cells and tissues
- Rottlerin and cancer: novel evidence and mechanisms
- Rottlerin and curcumin: a comparative analysis
- Rottlerin as a novel chemotherapy agent for adrenocortical carcinoma
- Rottlerin as a therapeutic approach in psoriasis: Evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies
- Rottlerin causes pulmonary edema in vivo: a possible role
- Rottlerin causes pulmonary edema in vivo: a possible role for PKCδ
- Rottlerin Derivatives and Other Compounds from Mallotus philippinensis Fruits and Their Potential Antimycobactrial Activity
- Rottlerin diminished the lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cell line and enhanced the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation in D16 cell line via LRP6 mediated pathway
- Rottlerin dissolves pre-formed protein amyloid: A study on hen egg white lysozyme
- Rottlerin enhances IL-1β-induced COX-2 expression through sustained p38 MAPK activation in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells
- Rottlerin exerts its anti-tumor activity through inhibition of Skp2 in breast cancer cells
- Rottlerin exhibits anti-cancer effect through inactivation of S phase kinase-associated protein 2 in pancreatic cancer cells
- Rottlerin Exhibits Antiangiogenic Effects In vitro
- Rottlerin exhibits antitumor activity via down-regulation of TAZ in non-small cell lung cancer
- Rottlerin greatly improves cardiac functional recovery following ischemic cardioplegic arrest (CP) in wild-type but not BKCa channel knockout mice
- Rottlerin impairs the formation and maintenance of psychostimulant-supported memory
- Rottlerin Increases Cardiac Contractile Performance and Coronary Perfusion Through BKCa++ Channel Activation After Cold Cardioplegic Arrest in Isolated Hearts
- Rottlerin induce early autophagy and late apoptosis via PKC-delta independent pathway.
- Rottlerin induced autophagy by targeting multiple sites that leads to the apoptosis in cancer stem cells
- Rottlerin induces a transformed phenotype in human keratinocytes
- Rottlerin induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through the interaction with Bcl-2 family proteins
- Rottlerin induces apoptosis of HT29 colon carcinoma cells through NAG-1 upregulation via an ERK and p38 MAPK-dependent and PKC δ-independent mechanism
- Rottlerin induces apoptosis of human blood eosinophils: A possible role for PKC-[delta] in mediating eosinophil survival
- Rottlerin induces apoptosis via death receptor 5 (DR5) upregulation through CHOP-dependent and PKC δ-independent mechanism in human malignant tumor cells
- Rottlerin Induces Apoptosis via Death Receptor5 (DR5) Up-Regulation through CHOP-Dependent and PKC d-Independent Mechanism in Human Malignant Tumor …
- Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptosis in prostate cancer stem cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptotic cell death through a PKC-delta-independent pathway in HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells: the protective role of …
- Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic cell death through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human pancreatic cancer stem cells
- Rottlerin induces calcium influx and protein degradation in cultured lenses independent of effects on protein kinase Cδ
- Rottlerin induces cyclooxygenase-2 upregulation through an ATF4 and reactive oxygen species-independent pathway in HEI-OC1 cells
- Rottlerin induces ER stress-mediated cell death in pancreatic stellate cells
- Rottlerin induces heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) up-regulation through reactive oxygen species (ROS) dependent and PKC δ-independent pathway in human colon …
- Rottlerin Induces Heme Oxygenase-1 through ROS generation, p38 and Akt Phosphorylation and Nrf2/ARE Activation in Human Colon Cancer HT29 Cells
- Rottlerin induces pro-apoptotic endoplasmic reticulum stress through the protein kinase C-δ-independent pathway in human colon cancer cells
- Rottlerin induces Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and suppresses both Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in prostate and breast cancer cells
- Rottlerin inhibitis agonist-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation (TyrP), MAPK activation, and amylase secretion by depleting intracellular ATP in rat …
- Rottlerin Inhibits (Na+, K+)-ATPase Activity in Brain Tissue and Alters d-Aspartate Dependent Redistribution of Glutamate Transporter GLAST in Cultured Astrocytes
- Rottlerin inhibits (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity in brain tissue and alters D-Aspartate dependent redistribution of glutamate transporter GLAST in cultured astrocytes
- Rottlerin inhibits cell growth and invasion via down-regulation of Cdc20 in glioma cells
- Rottlerin inhibits cell growth and invasion via down-regulation of EZH2 in prostate cancer
- Rottlerin inhibits cell growth, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, and inhibits cell invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma
- Rottlerin inhibits chlamydial intracellular growth and blocks chlamydial acquisition of sphingolipids from host cells
- Rottlerin inhibits human T cell responses
- Rottlerin inhibits insulin-stimulated glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by uncoupling mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation
- Rottlerin inhibits Lonicera japonica-induced photokilling in human lung cancer cells through cytoskeleton-related signaling cascade
- Rottlerin inhibits migration of follicular thyroid carcinoma cells by PKCδ‐independent destabilization of the focal adhesion complex
- Rottlerin inhibits migration of thyroid follicular carcinoma through destablization of the focal adhesion complex
- Rottlerin inhibits multiple steps involved in insulin-induced glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- Rottlerin inhibits P2X7 receptor‐stimulated phospholipase D activity in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia B‐lymphocytes
- Rottlerin Inhibits ROS Formation and Prevents NF 𝜅 B Activation in MCF-7 and HT-29 Cells
- Rottlerin inhibits stimulated enzymatic secretion and several intracellular signaling transduction pathways in pancreatic acinar cells by a non-PKC-δ …
- Rottlerin inhibits the nuclear factor κB/Cyclin-D1 cascade in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Rottlerin inhibits tonicity-dependent expression and action of TonEBP in a PKCδ-independent fashion
- Rottlerin is a mitochondrial uncoupler that decreases cellular ATP
- Rottlerin is a mitochondrial uncoupler that decreases cellular ATP levels and indirectly blocks protein kinase Cδ tyrosine phosphorylation
- Rottlerin is a pan phosphodiesterase inhibitor and can induce neurodifferentiation in IMR-32 human neuroblastoma cells
- Rottlerin Mediated Modulation of Tonicity-Responsive Enhancer Binding Protein (TonEBP) In Wistar Rats
- Rottlerin potentiates camptothecin-induced cytotoxicity in human hormone refractory prostate cancers through increased formation and stabilization of topoisomerase I …
- Rottlerin promotes apoptosis and autophagy in pancreatic stellate cells via AMPK activation
- Rottlerin promotes autophagy and apoptosis in gastric cancer cell lines
- Rottlerin protected dopaminergic cell line from cytotoxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine by inhibiting PKCδ phosphorylation
- Rottlerin Reduces cAMP/CREB-Mediated Melanogenesis via Regulation of Autophagy
- Rottlerin sensitizes colon carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis via uncoupling of the mitochondria …
- Rottlerin sensitizes glioma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by inhibition of Cdc2 and the subsequent downregulation of survivin and XIAP
- Rottlerin stimulates apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Rottlerin stimulates apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through interactions with proteins of the Bcl-2 family
- Rottlerin stimulates apoptosis in pancreatic cancer through inhibition of Bcl-xL
- Rottlerin stimulates metallothionein gene expression but inhibits metal transport in Chinese hamster ovary cells
- Rottlerin Suppresses Airway Hyperreactivity And Inflammation In Mouse Models Of Experimental Asthma
- Rottlerin suppresses growth of human pancreatic tumors in nude mice, and pancreatic cancer cells isolated from KrasG12D mice
- Rottlerin synergistically enhances imatinib-induced apoptosis of BCR/ABL-expressing cells through its mitochondrial uncoupling effect independent of protein …
- Rottlerin upregulates DDX3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Rottlerin-independent attenuation of pervanadate-induced tyrosine phosphorylation events by protein kinase C-δ in hemopoietic cells
- Rottlerin-induced autophagy leads to apoptosis in bladder cancer cells
- Rottlerin-induced autophagy leads to the apoptosis in breast cancer stem cells: molecular mechanisms
- Rottlerin-induced BKCa channel activation impairs specific contractile responses and promotes vasodilation
- Rottlerin-mediated inhibition of Chlamydia trachomatis growth and uptake of sphingolipids is independent of p38-regulated/activated protein kinase (PRAK)
- Rottlerin-mediated inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii growth in BeWo trophoblast-like cells
- Rottlerin, a novel protein kinase inhibitor
- Rottlerin, a PKC isozyme‐selective inhibitor, affects signaling events and cytokine production in human monocytes
- Rottlerin, a PKC-delta Inhibitor, Strongly Suppresses Cell Cycle Progression in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Through AMPK Activation.
- Rottlerin, a polyphenolic compound from the fruits of Mallotus phillipensis (Lam.) Müll. Arg., impedes oxalate/calcium oxalate induced pathways of oxidative stress in …
- Rottlerin, a specific inhibitor of protein kinase C-delta, impedes barrier repair response by increasing intracellular free calcium
- Rottlerin, an inhibitor of protein kinase Cδ (PKCδ), inhibits astrocytic glutamate transport activity and reduces GLAST immunoreactivity by a mechanism that appears to …
- Rottlerin: a multifaced regulator of keratinocyte cell cycle
- Rottlerin: An antibacterial agent and inhibitor of plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance transfer
- Rottlerin: an inappropriate and ineffective inhibitor of PKCδ
- Rottlerin: bases for a possible usage in psoriasis
- SALUBRIOUS EFFECT OF Rottlerin ON HYPEROXALURIA INDUCED OXIDATIVE DAMAGE IN RATS
- Selective inhibition by Rottlerin of macropinocytosis in monocyte‐derived dendritic cells
- Semisynthesis of mallotus B from rottlerin: evaluation of cytotoxicity and apoptosis-inducing activity
- Sorafenib in combination with Rottlerin show an additive effects in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells.
- Statin and Rottlerin small-molecule inhibitors restrict colon cancer progression and metastasis via MACC1
- Stimulation of suicidal erythrocyte death by Rottlerin
- Sustained Release of Rottlerin Encapsulated within Poly (D, L-Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles Inhibits Migration and Clonogenicity in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
- Synergism between PKCδ regulators hypericin and Rottlerin enhances apoptosis in U87 MG glioma cells after light stimulation
- The effect of PKC-delta inhibitor Rottlerin on human colon cancer cell line SW1116 and its mechanism
- The effect of Rottlerin in calcium regulation in HMC‐1560 cells is mediated by a PKC‐δ independent effect
- The Group I Pak inhibitor Frax-1036 sensitizes 11q13-amplified ovarian cancer cells to the cytotoxic effects of Rottlerin
- The Link between rottlerin, Na+, K+-ATPase activity and Na+-dependent glutamate transport
- The mechanisms of proapoptotic effects of Rottlerin in pancreatic cancer cells involve interaction with Bcl-2 protein
- The mosaic of rottlerin
- The Mosaic of Rottlerin: The Sequel
- The natural plant product Rottlerin activates Kv7. 1/KCNE1 channels
- The PKC delta inhibitor, rottlerin, induces apoptosis of haematopoietic cell lines through mitochondrial membrane depolarization and caspases’ cascade
- The PKC delta inhibitor; rottlerin; induces apoptosis of haematopoietic cell lines through mitochondrial membrane depolarization and caspases’ cascade
- The protein kinase C delta inhibitor Rottlerin greatly stimulates apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells
- Therapeutic potential of Rottlerin for skin hyperpigmentary disorders by inhibiting the transcriptional activity of CREB-regulated transcription coactivators
- Tumor suppressive role of Rottlerin in cancer therapy
- Use of Rottlerin and its derivatives as activators of BK channel for therapy of hypertension and related disorders