ADIPOCYTE APOPTOSIS (KILLING FAT CELLS)
February 23, 2021
HYPOACTIVE SEXUAL DESIRE (WHY PEOPLE HAVE ZERO SEX DRIVE)
February 23, 2021INSULIN PROTECTS CANCER CELLS FROM APOPTOSIS
Insulin can promote the growth and survival of cancer cells. Here’s how:
1. Insulin promotes cell growth and proliferation: Insulin is a hormone that regulates glucose metabolism and promotes the uptake of glucose into cells. Cancer cells have a high demand for glucose to fuel their rapid growth and proliferation. Insulin stimulates the uptake of glucose into cancer cells, providing them with the energy and nutrients they need to grow and divide.
2. Insulin activates signaling pathways: Insulin activates signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, which are involved in cell growth, survival, and metabolism. Dysregulation of these pathways is commonly observed in cancer cells and contributes to their uncontrolled growth. Insulin can enhance the activity of these pathways in cancer cells, promoting their survival and proliferation.
3. Insulin increases insulin-like growth factor (IGF) levels: Insulin can stimulate the production of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), particularly IGF-1. IGFs are growth factors that can bind to receptors on cancer cells and promote their growth and survival. Elevated levels of IGF-1 have been associated with an increased risk of various cancers.
4. Insulin reduces apoptosis: Apoptosis is a programmed cell death process that helps eliminate damaged or abnormal cells, including cancer cells. Insulin can inhibit apoptosis in cancer cells, allowing them to evade cell death and continue to proliferate.
5. Insulin promotes inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of cancer development and progression. Insulin can contribute to inflammation by activating inflammatory signaling pathways and promoting the release of pro-inflammatory molecules. Inflammation creates a favorable environment for cancer growth and can support tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis.
It’s important to note that insulin itself is not the sole factor in cancer development and progression. Other factors, such as genetic mutations, lifestyle factors, and other hormones, also play significant roles. However, the relationship between insulin and cancer highlights the potential impact of metabolic factors on cancer development and suggests that strategies to reduce insulin levels, such as dietary interventions, may have therapeutic benefits in cancer treatment.
If you are serious about beating and preventing cancer then you want to be secreting as little insulin as possible while remaining as insulin sensitive as possible. That means you only want a tiny amount of insulin being utilized to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
How?
Simple! 22/2 daily intermittent fasting with blends and strict non dairy paleo keto LOW INSULIN INDEX diet.
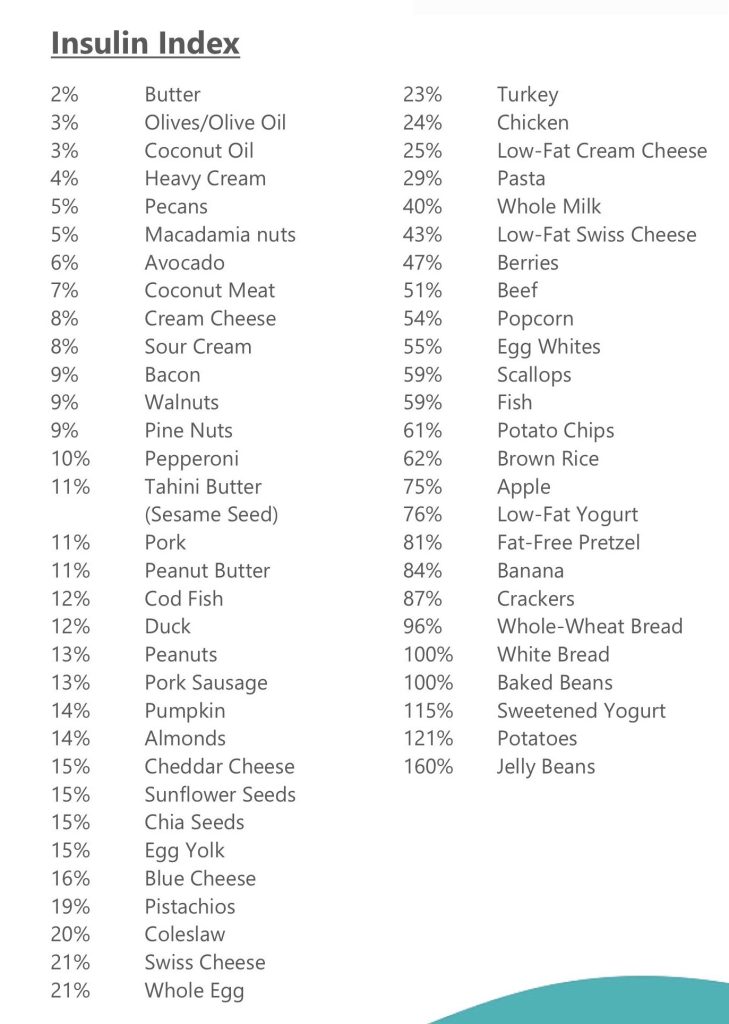
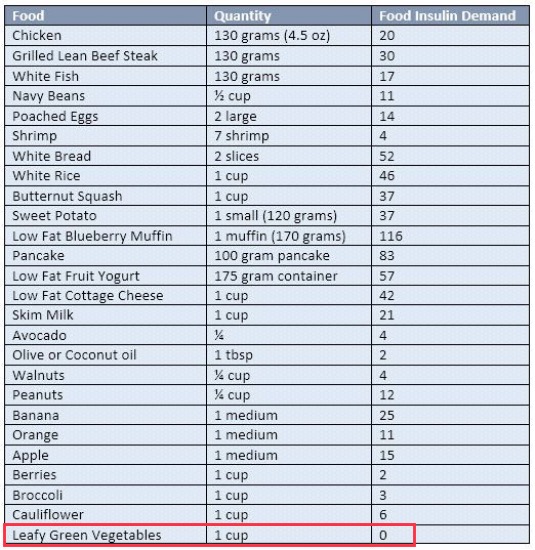
| Low Insulin Foods | Insulin index | Glycemic Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endive | 10 | 10 | 1.25 | 0.2 | 3.35 |
| Sorrel | 10 | 10 | 2 | 0.7 | 3.2 |
| Chives | 10 | 10 | 3.27 | 0.73 | 4.35 |
| Brown champignons | 10 | 15 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 4.3 |
| Champignons | 10 | 15 | 3.09 | 0.34 | 3.26 |
| Champignons (boiled) | 10 | 15 | 2.17 | 0.47 | 5.29 |
| Garlic | 10 | 30 | 6.36 | 0.5 | 33.06 |
| Lemon peel | 10 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 16 |
| Orange peel | 10 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 25 |
| Cauliflower | 10 | 10 | 1.92 | 0.28 | 4.97 |
| Cauliflower (boiled) | 10 | 10 | 1.84 | 0.45 | 4.11 |
| Dill dried | 10 | 10 | 19.96 | 4.36 | 55.82 |
| Dill | 10 | 10 | 3.46 | 1.12 | 7.02 |
| Thyme | 10 | 10 | 5.56 | 1.68 | 24.45 |
| Asparagus | 10 | 15 | 2.2 | 0.12 | 3.88 |
| Asparagus (boiled) | 10 | 15 | 2.4 | 0.22 | 4.11 |
| Celery | 10 | 10 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 2.97 |
| Red lettuce | 10 | 10 | 1.33 | 0.22 | 2.26 |
| Butter lettuce | 10 | 10 | 1.35 | 0.22 | 2.23 |
| Сornsalad | 10 | 10 | 2 | 0.4 | 3.6 |
| Ruccola | 10 | 10 | 2.58 | 0.66 | 3.65 |
| Rosemary | 10 | 10 | 3.31 | 5.86 | 20.7 |
| Radikkyo | 10 | 15 | 1.43 | 0.25 | 4.48 |
| Портулак | 10 | 10 | 2.03 | 0.36 | 3.39 |
| Tomatoes | 10 | 10 | 0.88 | 0.2 | 3.89 |
| Parsley dried | 10 | 10 | 26.63 | 5.48 | 50.64 |
| Parsley | 10 | 10 | 2.97 | 0.79 | 6.33 |
| Chili pepper red hot | 10 | 15 | 1.87 | 0.44 | 8.81 |
| Bulgarian pepper | 10 | 15 | 0.86 | 0.17 | 4.64 |
| Pecan | 10 | 10 | 9.17 | 71.97 | 13.86 |
| Macadamia Nut | 10 | 10 | 7.91 | 75.77 | 13.82 |
| Oregano | 10 | 10 | 9 | 4.28 | 68.92 |
| Opuntia (leaves) | 10 | 10 | 1.32 | 0.09 | 3.33 |
| Peppermint | 10 | 10 | 3.75 | 0.94 | 14.89 |
| Mint fresh | 10 | 10 | 3.29 | 0.73 | 8.41 |
| Marjoram | 10 | 10 | 12.66 | 7.04 | 60.56 |
| Shallot | 10 | 15 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 16.8 |
| Leeks | 10 | 15 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 14.15 |
| Bunching onion | 10 | 10 | 1.9 | 0.4 | 6.5 |
| Red onions (sweet onions) | 10 | 10 | 0.8 | 0.08 | 7.55 |
| Onions | 10 | 10 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 9.34 |
| Green onions | 10 | 10 | 0.97 | 0.47 | 5.74 |
| Chicory leaves | 10 | 10 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 4.7 |
| Pumpkin leaves | 10 | 10 | 3.15 | 0.4 | 2.33 |
| Dandelion leaves | 10 | 10 | 2.7 | 0.7 | 9.2 |
| Amaranth leaves | 10 | 10 | 2.46 | 0.33 | 4.02 |
| Lemongrass | 10 | 10 | 1.82 | 0.49 | 25.31 |
| Saltbush | 10 | 10 | 4.2 | 0.8 | 7.3 |
| Cress Salad | 10 | 15 | 2.6 | 0.7 | 5.5 |
| Cypress | 10 | 10 | 4.71 | 2.75 | 19.22 |
| Cilantro (coriander leaves) | 10 | 10 | 2.13 | 0.52 | 3.67 |
| Savoy cabbage | 10 | 10 | 2 | 0.1 | 6.1 |
| Peking cabbage | 10 | 10 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 2.18 |
| Kale | 10 | 10 | 3.02 | 0.61 | 5.42 |
| Sauerkraut cooked (boiled) | 10 | 10 | 2.71 | 0.72 | 5.65 |
| Curly cabbage raw | 10 | 10 | 4.28 | 0.93 | 8.75 |
| Red cabbage | 10 | 10 | 1.43 | 0.16 | 7.37 |
| Cabbage fresh white | 10 | 15 | 1.28 | 0.1 | 5.8 |
| Cabbage boiled (white cabbage) | 10 | 15 | 1.27 | 0.06 | 5.51 |
| Brussels sprouts (boiled) | 10 | 15 | 2.55 | 0.5 | 7.1 |
| Broccoli (boiled) | 10 | 10 | 2.38 | 0.41 | 7.18 |
| Whitetail (boiled) | 10 | 10 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 2.16 |
| Jerucha | 10 | 10 | 2.3 | 0.1 | 1.29 |
| Enoki mushrooms | 10 | 15 | 2.66 | 0.29 | 7.81 |
| Shiitake mushrooms | 10 | 15 | 2.24 | 0.49 | 6.79 |
| Morels mushrooms | 10 | 15 | 3.12 | 0.57 | 5.1 |
| Portobello mushrooms | 10 | 15 | 2.11 | 0.35 | 3.87 |
| Maitake mushrooms | 10 | 15 | 1.94 | 0.19 | 6.97 |
| Chanterelle mushrooms | 10 | 15 | 1.49 | 0.53 | 6.86 |
| Oyster mushrooms | 10 | 15 | 3.31 | 0.41 | 6.09 |
| Brussels sprouts | 10 | 15 | 3.38 | 0.3 | 8.95 |
| Broccoli raab | 10 | 10 | 3.17 | 0.49 | 2.85 |
| Chinese broccoli | 10 | 10 | 1.2 | 0.76 | 4.67 |
| Broccoli | 10 | 10 | 2.82 | 0.37 | 6.64 |
| Beet | 10 | 10 | 2.2 | 0.13 | 4.33 |
| Turnip tops | 10 | 10 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 7.13 |
| Whitetail | 10 | 10 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 3.61 |
| Eggplant | 10 | 40 | 0.98 | 0.18 | 5.88 |
| Basil | 10 | 10 | 3.15 | 0.64 | 2.65 |
SCIENCE
“We report here that insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) fully protect HT29-D4 colon carcinoma cell”
The role of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) in programmed cell death has been investigated in vivo in a biodiffusion chamber, where the extent of cell death could be determined quantitatively. We found that a decrease in the number of IGF-IRs causes massive apoptosis in vivo in several transplantable tumors, either from humans or rodents. Conversely, an overexpressed IGF-IR protects cells from apoptosis in vivo. We also show that the same conditions that in vitro cause only partial growth arrest with a minimum of cell death, induce in vivo almost complete cell death. We conclude that the IGF-IR activated by its ligands plays a very important protective role in programmed cell death, and that its protective action is even more striking in vivo than in vitro
The Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptor Protects Tumor Cells from Apoptosis in Vivo
Insulin‐like growth factor (IGF)‐I protects many cell types from apoptosis. As a result, it is possible that IGF‐I‐responsive cancer cells may be resistant to apoptosis‐inducing chemotherapies. Therefore, we examined the effects of IGF‐I on paclitaxel and doxorubicin‐induced apoptosis in the IGF‐I‐responsive breast cancer cell line MCF‐7. Both drugs caused DNA laddering in a dose‐dependent fashion, and IGF‐I reduced the formation of ladders. We next examined the effects of IGF‐I and estradiol on cell survival following drug treatment in monolayer culture. IGF‐I, but not estradiol, increased survival of MCF‐7 cells in the presence of either drug. Cell cycle progression and counting of trypan‐blue stained cells showed that IGF‐I was inducing proliferation in paclitaxel‐treated but not doxorubicin‐treated cells. However, IGF‐I decreased the fraction of apoptotic cells in doxorubicin‐ but not paclitaxel‐treated cells. Recent work has shown that mitogen‐activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphotidylinositol‐3 (PI‐3) kinase are activated by IGF‐I in these cells. PI‐3 kinase activation has been linked to anti‐apoptotic functions while MAPK activation is associated with proliferation. We found that IGF‐I rescue of doxorubicin‐induced apoptosis required PI‐3 kinase but not MAPK function, suggesting that IGF‐I inhibited apoptosis. In contrast, IGF‐I rescue of paclitaxel‐induced apoptosis required both PI‐3 kinase and MAPK, suggesting that IGF‐I‐mediated protection was due to enhancement of proliferation. Therefore, IGF‐I attenuated the response of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin and paclitaxel by at least two mechanisms: induction of proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. Thus, inhibition of IGF‐I action could be a useful adjuvant to cytotoxic chemotherapy in breast cancer.
Extracellular matrix (ECM) is known to influence the apoptotic response of cells; therefore, the antiapoptotic effect of IGF-1 on breast cancer cells was examined using different ECMs: laminin, collagen IV, or Matrigel. IGF-1 protected cells from apoptosis induced by methotrexate on all ECMs tested, providing the first evidence that IGF-1 protects against apoptosis in three-dimensional culture systems. These data provide the rationale to search for drugs that lower serum IGF-1 in an effort to improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs for the treatment of breast cancer.
The extent of apoptosis in vivo is correlated to the decrease in IGF-IR levels and, in turn, tumorigenesis in nude mice is correlated to the fraction of surviving cells. In syngeneic rats, a host response leads to complete inhibition of tumorigenesis. These findings establish, for the first time on a quantitative basis, the relationship between IGF-IR levels and the extent of apoptosis, as well as the relationship between the initial apoptotic event and the time of appearance of transplantable tumors.
Correlation between Apoptosis, Tumorigenesis, and Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptors
Ketosis was associated inversely with serum insulin levels (P = 0.03).
Conclusion
Preliminary data demonstrate that an insulin-inhibiting diet is safe and feasible in selected patients with advanced cancer.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899900712001864
As with insulin, inhibition of IGF-1 signaling has anti-cancer effects.
The Links Between Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, and Cancer
The role of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) in programmed cell death has been investigated in vivo in a biodiffusion chamber, where the extent of cell death could be determined quantitatively. We found that a decrease in the number of IGF-IRs causes massive apoptosis in vivo in several transplantable tumors, either from humans or rodents. Conversely, an overexpressed IGF-IR protects cells from apoptosis in vivo. We also show that the same conditions that in vitrocause only partial growth arrest with a minimum of cell death, induce in vivo almost complete cell death. We conclude that the IGF-IR activated by its ligands plays a very important protective role in programmed cell death.
Resistance of cancer cells against apoptosis induced by death factors contributes to the limited efficiency of immune- and drug-induced destruction of tumors. We report here that insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) fully protect HT29-D4 colon carcinoma cells from IFNg/tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF) induced apoptosis. Survival signaling initiated by IGF-I was not dependent on the canonical survival pathway involving phosphatidylinositol 3*-kinase. In addition, neither pp70S6K nor protein kinase C conveyed IGF-I antiapoptotic function. Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) with the MAPK/ERK kinase inhibitor PD098059 and MAPK/p38 with the specific inhibitor SB203580 partially reversed, in a nonadditive manner, the IGF-I survival effect. Inhibition of nuclear factor kB (NF-kB) activity by preventing degradation of the inhibitor of NF-kB (IkB-a) with BAY 11-7082 also blocked in part the IGF-I antiapoptotic effect. However, the complete reversal of the IGF-I effect was obtained only when NF-kB and either MAPK/ERK or MAPK/p38 were inhibited together. Because these pathways are also those used by TNF to signal inflammation and survival, these data point to a cross talk between IGF-Iand TNF-induced signaling. We further report that TNF-induced IL-8 production was indeed strongly enhanced upon IGF-I addition, and this effect was totally abrogated by both MAPK and NF-kB inhibitors. The IGF-I antiapoptotic function was stimulus-dependent because Fas- and IFN/Fas-induced apoptosis was not efficiently inhibited by IGF-I. This was correlated with the weak ability of Fas ligation to enhance IL-8 production in the presence or absence of IGF-I. These findings indicate that the antiapoptotic function of IGF-I in HT29-D4 cells is based on the enhancement of the survival pathways initiated by TNF, but not Fas, and mediated by MAPK/p38, MAPK/ERK, and NF-kB, which act in concert to suppress the proapoptotic signals. In agreement with this model, we show that it was possible to render HT29-D4 cells resistant to Fas-induced apoptosis provided that IGF-I and TNF receptors were activated simultaneously.
- A chimeric humanized single-chain antibody against the type I Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor renders breast cancer cells refractory to the mitogenic effects of …
- A Common Promoter Polymorphism (-23HphI) in Insulin Gene and Susceptibility to Colorectal cancer
- A dominant negative mutant of the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibits the adhesion, invasion, and metastasis of breast cancer
- A dominant negative type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibits metastasis of human cancer cells
- A framework for the in vitro evaluation of cancer-relevant molecular characteristics and mitogenic potency of Insulin analogues
- A higher prediagnostic Insulin level is a prospective risk factor for incident prostate cancer
- A ketogenic diet reduces central obesity and serum Insulin in women with ovarian or endometrial cancer
- A kinome-wide screen identifies the Insulin/IGF-I receptor pathway as a mechanism of escape from hormone dependence in breast cancer
- A longitudinal study of serum Insulin and glucose levels in relation to colorectal cancer risk among postmenopausal women
- A Mechanistic Investigation of Insulin Receptor Substrate 2 Function in Breast cancer Progression
- A mendelian randomization study for the potential causal effect of genetically driven Insulin resistance on invasive breast cancer
- A nested case-control study of stomach cancer and serum Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-2 and IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-3
- A New Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein (mac25) and its Role in Breast cancer and Cell Growth Control
- A New Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein and Its Role in Breast cancer and Cell Growth
- A new single nucleotide polymorphism in the Insulin-like growth factor I regulatory region associates with colorectal cancer risk in Singapore Chinese
- A novel and selective 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 inhibitor, PF-5177624, blocks Insulin-like growth factor-1 induced tumorigenesis in breast cancer cells
- A novel autocrine loop involving IGF-II and the Insulin receptor isoform-A stimulates growth of thyroid cancer
- A novel mechanism underlying prostate cancer progression: an investigation into the impact of Insulin like growth factors (IGFs), PTEN and IGFBP2 on TMPRSS2 …
- A Novel Member of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein Superfamily in Prostate cancer
- A novel role for Insulin resistance in the connection between obesity and postmenopausal breast cancer
- A novel synthetic human Insulin super promoter for targeting PDX-1-expressing pancreatic cancer
- A novel targeted oral Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) inhibitor and its implications for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A phase I clinical …
- A novel unidirectional cross-talk from the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor to leptin receptor in human breast cancer cells
- A phase II study of Insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibition with nordihydroguaiaretic acid in men with non-metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer
- A pilot randomised controlled trial to reduce colorectal cancer risk markers associated with B-vitamin deficiency, Insulin resistance and colonic inflammation
- A pilot safety-feasibility dietary trial targeting Insulin inhibition in ten patients with advanced cancer
- A population-based cohort study in Taiwan––use of Insulin sensitizers can decrease cancer risk in diabetic patients?
- A preliminary study on the relationship of Insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ receptor and the carcinogenesis of gastde cancer
- A prospective evaluation of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor-I as risk factors for endometrial cancer.
- A prospective study of anthropometric and clinical measurements associated with Insulin resistance syndrome and colorectal cancer in male smokers
- A prospective study of C-peptide, Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1, and the risk of colorectal cancer in women
- A prospective study of Insulin‐like growth factor‐I, IGF‐binding proteins‐1,‐2 and‐3 and lung cancer risk in women
- A prospective study of serum Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), IGF-II, IGF-binding protein-3 and breast cancer risk
- A prospective study of the Insulin-like growth factor axis in relation with prostate cancer in the SU. VI. MAX trial
- A protease resistant Insulin like growth factor binding protein 4 as a treatment for prostate cancer
- A review of obesity, Insulin resistance, and the role of exercise in breast cancer patients
- A Salutary Tale—Glargine Insulin and cancer risk
- A sequence repeat in the Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 gene and risk of breast cancer
- A serum-free and Insulin-supplemented cell culture medium ensures fatty acid synthesis gene activation in cancer cells
- A Significance of Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGFs) and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) in Ascites of Ovarian cancer Patients
- A study of prostate cancer and its association with dyslipidemia, elevated Insulin levels in blood, and relative Insulin resistance prevalent in South East Asia
- A study on Insulin receptor on human hepatocellular cancer cell membrane
- A Study on Insulin Resistance and Obesity Among Women at High Risk for Breast cancer Using Cluster Analysis.
- A synergistic combination strategy for optimal inhibition of colon cancer stem cells: Simultaneous inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-AKT-mammalian …
- A tale of two receptors: Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor signaling in cancer
- A twenty-first century cancer epidemic caused by obesity: the involvement of Insulin, diabetes, and Insulin-like growth factors
- A Type I Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor Kinase Inhibitor (PQIP) Enhances the Cytotoxicity of Doxorubicin in Human cancer Cell Lines.
- A63 DEATH TO THE INFIDELS! CELLULAR APOPTOSIS IN LUNG DISEASE: Insulin Receptor Suppresses Apoptosis In H-292 Human Bronchial Epithelial cancer …
- Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous fat increase, Insulin resistance and hyperlipidemia in testicular cancer patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy
- Aberrant cross-talk and expression of β1 integrins and type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor during prostate cancer progression.
- Aberrant neuronal cell cycle re-entry: The pathological confluence of Alzheimer’s disease and brain Insulin resistance, and its relation to cancer
- Abnormality of growth hormone and Insulin-like growth factor I axis in advanced cancer patients
- About the Role of Insulin in the Interaction Between Human Immune and Colon cancer Cells
- Absence of down-regulation of Insulin receptors in human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) cultured in serum-free medium: comparison with epidermal growth factor
- Absence of the common Insulin-like growth factor-1 19-repeat allele is associated with early age at breast cancer diagnosis in multiparous women
- Absence of the full-length breast cancer–associated gene-1 leads to increased expression of Insulin-like growth factor signaling axis members
- Abstract A10: Insulin resistance’s effect on PSA level for prostate cancer screening
- Abstract A33: Utilizing Insulin the treatment of prostate cancer with BKM120 abrogates the therapeutic effect of PI3K pathway inhibition
- Abstract A35: Insulin and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 cooperate to increase the viability of pancreatic cancer cells
- Abstract A43: Basal expression of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor determines intrinsic resistance of cancer cells to a PI3K inhibitor ZSTK474
- Abstract A44: Suppression of Insulin-induced fatty acid synthase gene expression and colon cancer cell proliferation by members of the Krüppel-like family of …
- Abstract A46: Pharmacodynamic biomarkers for OSI‐906, an Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor (IGF‐1R) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in cancer patients with advanced …
- Abstract A58: Role of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein acid labile complex in ER-PR-Her2+ breast cancer in African American women.
- Abstract A61: Smoking modifies the association of Insulin sensitivity biomarkers and pancreatic cancer risk
- Abstract B115: Plasma Insulin‐like growth factor 1, binding protein‐3, and risk of prostate cancer: An update from the Health Professional Follow‐up Study 1993–2004
- Abstract B129: Preclinical assessment of targeting Insulin‐like growth factor‐2 in bone metastasis from prostate cancer by a human neutralizing antibody (m610) and …
- Abstract B22: Modulation of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins expression in human prostate cancer cells in vitro by american cranberry (Vaccinium …
- Abstract B232: Preclinical evaluation of AMG479 a fully human Insulin‐like growth factor receptor‐1 (IGFR1) antibody in ovarian cancer cells
- Abstract B39: Modulation of Insulin receptor alternative splicing to develop cancer therapeutics
- Abstract B51: The tyrphostin, NT157, suppresses Insulin receptor substrates and augments therapeutic response of prostate cancer
- Abstract B59: Race-related differential splicing of the Insulin receptor: A novel target underlying prostate cancer disparities
- Abstract B76: Evidence of a causal association between fasting Insulin concentrations and endometrial cancer: A Mendelian randomization analysis
- Abstract CN13-04: Obesity, Insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and cancer: A novel role for metformin as an anticancer drug
- Abstract D118: Insulin receptor splicing regulation as a potential target for improved prostate cancer disparity outcomes
- Abstract ES9-1: Role for IGF/Insulin signaling in breast cancer
- Abstract KN01: Keynote Lecture: PI 3-kinase links obesity, Insulin resistance, and cancer
- Abstract LB-187: Dietary energy balance modulation of Kras-and Ink4a/Arf+/-driven pancreatic cancer: the role of Insulin-like growth factor-1.
- Abstract LB-28: The IGF/Insulin signaling axis TMPRSS2: ERG and prostate cancer survival.
- Abstract LB-329: Use of Insulin sensitizers is associated with better hormone-receptor pattern and improved breast cancer outcomes
- Abstract NTOC-097: VACCINATION TARGETING Insulin–LIKE GROWTH FACTOR BINDING PROTEIN–2 (IGFBP–2) IN ADVANCED OVARIAN cancer: SAFETY …
- Abstract P1-04-03: Knocking down Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 7 in breast cancer: The role in Insulin-like Growth Factor-I/Phospholipase Cγ-1 signaling
- Abstract P1-07-03: Dual inhibition of IGF1R and Insulin receptor in estrogen receptor positive and triple negative breast cancer and monitoring blockade of metastasis …
- Abstract P1-08-10: Insulin resistance and breast cancer incidence and mortality in postmenopausal women
- Abstract P1-12-12: The Insulin like growth factor axis and development of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
- Abstract P1-21-05: A novel long-acting Insulin for cancer therapy reduces xenograft tumor growth
- Abstract P2-06-03: Insulin receptor isoform signaling in breast cancer
- Abstract P2-07-03: Insulin and breast cancer risk: Novel insights from mammographic density analyses
- Abstract P2-16-18: Does Insulin resistance predict complete response in breast cancer patients who underwent neoadjuvant treatment?
- Abstract P3-05-13: Overexpression of Insulin receptor substrate 4 can mediate acquired resistance to lapatinib-containing regimens in HER2+ breast cancer cells
- Abstract P3-07-03: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor variant associated with decreased breast cancer risk in women with pregnancy-induced hypertension
- Abstract P3-07-54: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor expression and polymorphism are associated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer …
- Abstract P3-10-09: Gene deletion of IRS1 inhibited IGF-I, Insulin and estradiol stimulated MCF-7L breast cancer cell growth
- Abstract P4-04-07: Heterogeneous gene fusions detected by RNASeq show enrichment of Insulin signaling pathway genes in breast cancer
- Abstract P4-06-02: Insulin receptor targeting in breast cancer through yeast surface display
- Abstract P4-06-03: Targeting the Insulin receptor with a small peptide (S961) in cancer
- Abstract P4-11-02: Worse breast cancer prognosis in Insulin treated diabetic patients-A population based registry study in Sweden
- Abstract P4-13-07: Meta-analysis of epidemiological studies of Insulin Glargine and Breast cancer Risk
- Abstract P5-07-05: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 is a key component of the breast cancer cell response to DNA-damaging therapy
- Abstract P6-09-05: Insulin Resistance, Diabetes Mellitus and Breast cancer Risk in Pre-and Postmenopausal Women: Modification Effect by Moderate Physical …
- Abstract P6-12-05: Inducible suppression of Insulin receptor substrate I inhibits IGF-I/Insulin/estradiol dependent cell growth in MCF-7L breast cancer cells
- Abstract P6-15-09: Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor I (IGF1R) Inhibitors May Be Synergistic with Chemotherapy in Basal Breast cancer
- Abstract PD2-07: Insulin receptor substrate (IRS) targeting by the tyrophostin NT157 inhibits breast cancer cell growth
- Abstract PD2-5: Low carbohydrate dietary intervention improves Insulin, hormonal levels and inflammatory markers in early stage, postmenopausal breast cancer …
- Abstract# 34: Colored potato functional compounds suppress Insulin-like growth factor-1-promoted prostate cancer cell proliferation and elevate apoptosis through …
- Abstract# 3421: Her-2 over expression induces metabolic transformation resulting in Insulin-independence in human breast cancer cells
- Abstract# 3900: Resveratrol suppresses Insulin-like growth factor-1 promoted colon cancer cell growth via activation of p53/AMPK/TSC-2 and suppression of IGF-1R …
- Abstract# 4288: Differential Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) expression may impact breast cancer incidence and survival among African-American and Caucasian …
- Abstract# 4404: Possible role of Insulin-like growth factor I in breast cancer proliferation via the CYP1A1 epoxygenase pathway
- Abstract# 4874: Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor-I, and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women
- Abstract# 5048: Deoxycholic acid induces endocytosis of the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in colorectal cancer cells
- Abstract# 793: Elevated epithelial Insulin-like growth factor expression is a risk factor for lung cancer development
- Abstract# 794: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone promotes motility and invasiveness of ovarian cancer cells through transactivation of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 …
- Abstract# 795: The role of tissue expressed Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and the Janus effects of IGFBP-3 in lung cancer development
- Abstract# 827: Antitumor effect of diethylstilbestrol (DES) in combination with an Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) antibody in preclinical prostate cancer.
- Abstract# LB-280: Expression of early placenta Insulin-like growth factor in breast cancer a prerequisite of metastasis forming disseminated tumor cells?
- Acanthosis nigricans and severe Insulin resistance in an adolescent girl with thyroid cancer: clinical response to antineoplastic therapy
- Acquired resistance to tamoxifen is associated with loss of the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor: implications for breast cancer treatment
- Actions of pituitary prolactin and Insulin-like growth factor II in human breast cancer
- Activated Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic target for brain metastasis from lung cancer.
- Activated α2-macroglobulin binding to human prostate cancer cells triggers Insulin-like responses
- Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor/Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor-β-Catenin-CD44 pathway in periampullary cancer
- Activation of Insulin receptors and IGF-1 receptors in COLO-205 colon cancer xenografts by Insulin and Insulin analogue X10 does not enhance growth under …
- Activation of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- Activation of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor regulates the radiation-induced lung cancer cell apoptosis
- Activation of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor confers acquired resistance to osimertinib in non‐small cell lung cancer with EGFR T790M mutation
- Activation of integrin and ceramide signalling pathways can inhibit the mitogenic effect of Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in human breast cancer cell lines
- Activator protein-2 overexpression accounts for increased Insulin receptor expression in human breast cancer
- Adipocyte-released Insulin-like growth factor-1 is regulated by glucose and fatty acids and controls breast cancer cell growth in vitro
- Adipocytokines, obesity, and Insulin resistance during combined androgen blockade for prostate cancer
- Adipokines and Insulin resistance in young adult survivors of childhood cancer
- Adipokines, Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and breast cancer recurrence: a cohort study
- Adiponectin, leptin, and Insulin-pathway receptors as endometrial cancer subtyping markers
- Adiponectin: the “unusual suspect” between Insulin resistance and cancer?
- Adipose Estrogen and Increased Breast cancer Risk in Obesity: Regulation by Leptin and Insulin
- Adiposity and estrogen receptor‐positive, postmenopausal breast cancer risk: Quantification of the mediating effects of fasting Insulin and free estradiol
- Adrenomedullin is up-regulated in patients with pancreatic cancer and causes Insulin resistance in β cells and mice
- Advance on Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 in Lung cancer and Other Solid Tumors
- Advances in Insulin-like growth factor biology and-directed cancer therapeutics
- Advances in targeting Insulin-like growth factor signaling pathway in cancer treatment
- Affinity for the Insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) receptor inhibits autocrine IGF-II activity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
- Age and Insulin levels in breast cancer women and healthy women
- Aging and cancer-related loss of Insulin-like growth factor 2 imprinting in the mouse and human prostate
- AIB1/SRC-3 deficiency affects Insulin-like growth factor I signaling pathway and suppresses v-Ha-ras-induced breast cancer initiation and progression in mice
- Aiming for the Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 system in breast cancer therapeutics
- AKT activation up-regulates Insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression and promotes invasiveness of human pancreatic cancer cells
- Alterations in laminin expression modulate prostate cancer cell behavior through changes in integrin and Insulin-like growth factor receptor actions
- Alterations in promoter usage and expression levels of Insulin-like growth factor-II and H19 genes in cervical and endometrial cancer
- Alterations in Promoter Usage and Expression Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor-II and H19 Genes in Cervical andEndometrial cancer
- Alterations in serum levels of Insulin‐like growth factors and Insulin‐like growth‐factor‐binding proteins in patients with colorectal cancer
- Alterations in the expression of Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in lung cancer
- Alterations in the Insulin-like growth factor system during treatment with diethylstilboestrol in patients with metastatic breast cancer
- Alterations of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor gene copy number and protein expression are common in non-small cell lung cancer
- Altered expression of Insulin receptor isoforms in breast cancer
- Altered expression of Insulin-like growth factor II receptor in human pancreatic cancer.
- Altered glucose metabolism and Insulin resistance in cancer-induced cachexia: a sweet poison
- Altered Insulin response to glucose in weight-losing cancer patients.
- Altered serum levels of Insulin-like growth-factor binding proteins in breast cancer patients
- Alternative splicing of Insulin receptor mRNA in cancer and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review
- Alternative tyrosine phosphorylation of signaling kinases according to hormone receptor status in breast cancer overexpressing the Insulin‐like growth factor receptor …
- An anti-Insulin-like growth factor I receptor antibody that is a potent inhibitor of cancer cell proliferation
- An antibody targeting the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor enhances the castration-induced response in androgen-dependent prostate cancer
- An epidemiologic investigation of the roles of plasma lipids, endogenous Insulin, and CYP17 genotype in breast cancer causation.
- An evaluation of compliance in cancer patients and non-Insulin dependent diabetics.
- An exon variant in Insulin receptor gene is associated with susceptibility to colorectal cancer in women
- An HLA-DR–Degenerate Epitope Pool Detects Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2–Specific Immunity in Patients with cancer
- An Insulin effect on cytoplasmic estrogen receptor in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7.
- An Insulin-like growth factor-II intronic variant affects local DNA conformation and ovarian cancer survival
- An investigation into the role of the transcription factor ERG and its regulation of the members of the Insulin-growth factor signalling pathway in prostate cancer
- An N-terminal fragment of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells in an IGF-independent manner
- Analysis of apoptosis-related gene expression in different serum level of Insulin-like growth factor-1 in mice breast cancer tissue
- Analysis of expression profile of gene encoding proteins of signal cascades activated by Insulin-like growth factors in colorectal cancer
- Analysis of genomic imprinting of Insulin-like growth factor 2 in colorectal cancer
- Analysis of Insulin-like growth factor I gene expression in malignancy: evidence for a paracrine role in human breast cancer
- ANALYSIS OF Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-H IN HUMAN BREAST cancer CELLS
- Analyzing structural differences between Insulin receptor (IR) and IGF1R for designing small molecule allosteric inhibitors of IGF1R as novel anti-cancer agents
- Androgen receptor up-regulates Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) expression in a human prostate cancer xenograft
- Androgens up-regulate the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in prostate cancer cells
- Animal Models of HyperInsulinemia, Insulin Resistance, and cancer
- ANTI-Insulin RESISTANCE TREATMENTS SUPPRESS HER2+ BREAST cancer GROWTH VIA ALTERING METABOLISM
- Anti-Insulin-like growth factor strategies in breast cancer
- Anti‐Insulin‐like growth factor‐I activity of a novel polysulphonated distamycin A derivative in human lung cancer cell lines
- Anticarcinogenic effect of quercetin by inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 signaling in mouse skin cancer
- Antimetastatic activity of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in lung cancer is mediated by Insulin-like growth factor–independent urokinase-type plasminogen …
- Antiproliferative actions of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-3 in human breast cancer cells
- Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of a specific anti-Insulin-like growth factor I receptor single chain antibody on breast cancer cells
- Antiproliferative and proapoptotic effect of ascorbyl stearate in human pancreatic cancer cells: association with decreased expression of Insulin-like growth factor 1 …
- Antiproliferative MCR peptides block physical interaction of Insulin with retinoblastoma protein (RB) in human lung cancer cells
- Antisense oligonucleotide targeting of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor (IGF‐1R) in prostate cancer
- Antisense oligonucleotide to Insulin-like growth factor II induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer AO cell line
- Antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotide down‐regulation of the Insulin‐like growth factor I receptor in ovarian cancer cells
- Antisense RNA to the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor reversed the transformed phenotype of PC-3 human prostate cancer cell line in vitro
- Antisense RNA to the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor suppresses tumor growth and prevents invasion by rat prostate cancer cells in vivo
- Antitumor effects of a soluble Insulin-like growth factor I receptor in human ovarian cancer cells: advantage of recombinant protein administration in vivo
- Antitumor effects of an adenovirus expressing antisense Insulin-like growth factor I receptor on human lung cancer cell lines
- Antitumor effects of dual inhibition of the Src and Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) pathways in prostate cancer (PCa).
- Apigenin attenuates Insulin-like growth factor-I signaling in an autochthonous mouse prostate cancer model
- Apigenin modulates Insulin-like growth factor axis: implications for prevention and therapy of prostate cancer
- Apigenin suppresses Insulin‐like growth factor I receptor signaling in human prostate cancer: An in vitro and in vivo study
- Apigenin: a promising anticancer agent for the modulation of the Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) axis in prostate cancer
- Application of Insulin in external treatment of radioactive dermatitis in nasopharyngeal cancer patients with hyperglycemia
- Applications of Insulin-like growth factor system in the colorectal cancer
- Are dietary influences on the risk of prostate cancer mediated through the Insulin‐like growth factor system?
- Are plasma Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) useful markers of prostate cancer?
- Are racial differences in obesity and Insulin resistance related to aggressive breast cancer?
- Are sulfonylurea and Insulin therapies associated with a larger risk of cancer than metformin therapy? A retrospective database analysis
- Are the Insulin-like growth factors relevant to cancer?
- Are there Relationships between the VDR-FokI Polymorphism and Vitamin D and the Insulin Resistance in Non-melanoma Skin cancer (NMSC) Patients? A Protocol …
- Arthralgia induced by endocrine treatment for breast cancer: a prospective study of serum levels of Insulin like growth factor-I, its binding protein and …
- Aspects of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in cancer
- Aspirin, NSAIDs, and colorectal cancer: possible involvement in an Insulin-related pathway
- Assessing the role of Insulin‐like growth factors and binding proteins in prostate cancer using Mendelian randomization: Genetic variants as instruments for circulating …
- Assessment of Insulin-like growth factors and mutagen sensitivity as predictors of lung cancer risk
- Association between adiponectin, Insulin resistance, and endometrial cancer
- Association between androgen deprivation and serum Insulin levels among Ugandan men with advanced prostate cancer in Mulago Hospital
- Association between cognitive impairment patient with solid cancer and Insulin resistance
- Association between components of the Insulin-like growth factor system and endometrial cancer risk
- Association between components of the Insulin-like growth factor system and epithelial ovarian cancer risk
- Association between expression of Insulin resistance (IR) related genes and breast cancer outcome
- Association between Insulin receptor substrate 1 Gly972Arg polymorphism and cancer risk
- Association between Insulin resistance and breast cancer risk: A Mendelian randomization analysis of data from 228,000 women of European descent
- Association between Insulin resistance and luminal B subtype breast cancer in postmenopausal women
- Association between Insulin therapy and risk of liver cancer among diabetics: a meta-analysis of epidemiological studies
- Association between Insulin-like growth factor 1 gene rs35767 polymorphisms and cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Association between Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 promoter polymorphism of− 1590 C> A and lung cancer susceptibility in a Chinese Han population
- Association between Insulin-like growth factor receptors & cell density in breast cancer cells
- Association between Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) negativity and poor prognosis in a cohort of women with primary breast cancer
- Association between Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 polymorphism-202 A/C and the risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis
- Association between Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 polymorphisms and stomach cancer risk in a Japanese population
- Association between polymorphisms of Insulin-like growth factor receptor gene and susceptibility to non-small-cell lung cancer in Fujian Chinese
- Association between preoperative serum Insulin levels and lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer—a prospective cohort study
- Association Between Serum Insulin and C-Peptide Levels and Breast cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Association between serum Insulin and serum lipid substances and breast cancer
- Association between the Insulin-like growth factor 1 gene rs2195239 and rs2162679 polymorphisms and cancer risk: a meta-analysis
- Association between two functional polymorphisms of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 and colorectal cancer risk in a Chinese population
- Association of abnormal glucose metabolism and Insulin resistance in patients with atypical and typical endometrial cancer
- Association of adipokines and Insulin, which have a role in obesity, with colorectal cancer
- Association of Adipokines and Insulin, Which Have a Role in Obesity, with Colorectal cancer
- Association of angiopoietin-2, C-reactive protein and markers of obesity and Insulin resistance with survival outcome in colorectal cancer
- Association of biomarkers of Insulin resistance and inflammation with PET CT SUV values in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
- Association of biomarkers of Insulin resistance and inflammation with skeletal muscle index (SMI) in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
- Association of circulating Insulin-like growth factor 1 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 with the risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and …
- Association of Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factors and IGF Binding Protein with Early Cases of cancer Cervix.
- Association of dyslipidemia, increased Insulin resistance, and serum CA 15-3 with increased risk of breast cancer in urban areas of North and Central India
- Association of fasting serum Insulin and cancer mortality in a healthy population–28-year follow-up of the French TELECOM Study
- Association of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 G972R Variant with Non-small Cell Lung cancer Risk.
- Association of Insulin-like growth factor-1 polymorphism and risk of esophageal cancer [J]
- Association of Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor polymorphism with colorectal cancer development
- Association of Insulin‐like growth‐factor‐I‐induced DNA synthesis with phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of p53 in human breast cancer MCF‐7 cells
- Association of Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor and Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins with the risk of colorectal cancer
- Association of Insulin, Metformin, and Statin with Mortality in Breast cancer Patients
- Association of markers of Insulin and glucose control with subsequent colorectal cancer risk
- Association of metabolic parameters, lipid and cytokine profiling, androgens and Insulin levels in Precancer and Prostate cancer: A cross-sectional study in …
- Association of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 with age, glucose, BMI, Insulin and other breast cancer biomarkers
- Association of NAFLD and Insulin Resistance with Non Metastatic Bladder cancer Patients: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study
- Association of polymorphisms and haplotypes in the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) gene with breast cancer in Korean women
- Association of polymorphisms and haplotypes in the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) gene with the risk of breast cancer in Korean women
- Association of prognosis with Insulin-like growth factor receptor type I expression in gastric cancer patients: a meta-analysis
- Association of prostate cancer risk with Insulin, glucose, and anthropometry in the Baltimore longitudinal study of aging
- Association of serum hemoglobin A1c, C‑peptide and Insulin‑like growth factor‑1 levels with the occurrence and development of lung cancer
- Association of the Insulin gene polymorphism and colorectal cancer.
- Association of visceral adiposity and Insulin resistance with colorectal adenoma and colorectal cancer
- Associations between circulating Insulin-like growth factor 1 and mortality in women with invasive breast cancer
- Associations between Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins and other prognostic indicators in breast cancer
- Associations between plasma Insulin-like growth factor proteins and C-peptide and quality of life in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
- Associations of adipokines & Insulin resistance with sex steroids in patients with breast cancer.
- Associations of chronic inflammation, Insulin resistance, and severe obesity with mortality, myocardial infarction, cancer, and chronic pulmonary disease
- Associations of hyperglycemia and Insulin usage with the risk of cancer in type 2 diabetes: the Hong Kong diabetes registry
- Associations of Insulin and IGFBP-3 with lung cancer susceptibility in current smokers
- Associations of Insulin resistance and adiponectin with mortality in women with breast cancer
- Associations of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and adiponectin with disease progression and mortality in metastatic colorectal cancer: Results from CALGB …
- Associations of Insulin‐like growth factor and Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3 with mortality in women with breast cancer
- Associations of obesity and circulating Insulin and glucose with breast cancer risk: a Mendelian randomization analysis
- Associations of serum C-peptide and Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins-3 with breast cancer deaths
- Associations of serum isoflavone, adiponectin and Insulin levels with risk for epithelial ovarian cancer: results of a case-control study
- AT1-IR-beta association: A new mechanism for the inhibition of Insulin receptor function in breast cancer
- Augmentation of response to nab-paclitaxel by inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling in preclinical pancreatic cancer models
- Aurora-A down-regulates IkappaBα via Akt activation and interacts with Insulin-like growth factor-1 induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway for cancer …
- Authors’ response: Associations of obesity and circulating Insulin and glucose with breast cancer risk
- Autoantibodies against Insulin-like growth factor‑binding protein-2 as a serological biomarker in the diagnosis of lung cancer
- Autocrine function for Insulin-like growth factor I in human small cell lung cancer cell lines and fresh tumor cells
- Autocrine IGF-I/Insulin receptor axis compensates for inhibition of AKT in ER-positive breast cancer cells with resistance to estrogen deprivation
- Autocrine production of Insulin-like growth factor II using an inducible expression system results in reduced estrogen sensitivity of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.
- Autocrine role of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I in a human thyroid cancer cell line
- Azathioprine desensitizes liver cancer cells to Insulin-like growth factor 1 and causes apoptosis when it is combined with bafilomycin A1
- Basal expression of Insulin‐like growth factor 1 receptor determines intrinsic resistance of cancer cells to a phosphatidylinositol 3‐kinase inhibitor ZSTK474
- Baseline Insulin-like growth factor-I plasma levels, systemic inflammation, weight loss and clinical outcome in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients
- Beta-cell function and Insulin resistance evaluated by HOMA in pancreatic cancer subjects with varying degrees of glucose intolerance
- Bidirectional crosstalk between leptin and Insulin-like growth factor-I signaling promotes invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via transactivation of epidermal …
- Bifurcation analysis of Insulin regulated mTOR signalling pathway in cancer cells
- Binding characteristics of pro-Insulin-like growth factor-II from cancer patients: binary and ternary complex formation with IGF binding proteins-1 to-6
- Bioavailable Insulin-like growth factor-I as mediator of racial disparity in obesity-relevant breast and colorectal cancer risk among postmenopausal women
- Biochemical and Genetic Markers in Aggressiveness and Recurrence of Prostate cancer: Race-Specific Links to Inflammation and Insulin Resistance
- Biochemical characterization of individual human glycosylated pro-Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II and big-IGF-II isoforms associated with cancer
- Biologic roles of estrogen receptor-β and Insulin-like growth factor-2 in triple-negative breast cancer
- Biological activity of rainbow trout Ea4‐peptide of the pro‐Insulin‐like growth factor (pro‐IGF)‐I on promoting attachment of breast cancer cells (MDA‐MB‐231) via α2 …
- Biological effects of Insulin and its analogs on cancer cells with different Insulin family receptor expression
- Biology of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 and its role in cancer
- Biomarkers of Insulin and the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Axis in Relation to Breast cancer Risk in Chinese Women
- Biomarkers of the Insulin-like growth factor pathway predict progression and outcome in lung cancer
- Bisphosphonates inhibit Insulin-like growth factor I-induced HIF-1α protein accumulation and VEGF expression in human beast cancer cells
- Bisphosphonates suppress Insulin‐like growth factor 1‐induced angiogenesis via the HIF‐1α/VEGF signaling pathways in human breast cancer cells
- Blockade of Insulin-like growth factor I receptor function inhibits growth and angiogenesis of colon cancer
- Blockade of Insulin-like growth factor signaling induces apoptosis and reduces tumorigenesis and tumor progression in gastric cancer.
- Blockade of Insulin-like growth factors increases efficacy of paclitaxel in metastatic breast cancer
- Blockade of the Insulin‐like growth‐factor‐I receptor inhibits growth of human colorectal cancer cells: evidence of a functional IGF‐II‐mediated autocrine loop
- Blocking the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a strategy for targeting cancer
- Blood Insulin and Insulin sensitivity in breast cancer patients of various ages: the effect of smoking
- BMAL1 rewires mitochondrial metabolism and promotes tumor progress of triple negative breast cancer during Insulin resistance
- BMS-754807, a small-molecule inhibitor of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor/Insulin receptor, enhances gemcitabine response in pancreatic cancer
- Body composition changes in rats with experimental cancer cachexia: improvement with exogenous Insulin
- Body mass index influences the prognostic impact of combined nuclear Insulin receptor and estrogen receptor expression in primary breast cancer
- Body mass index, type 2 diabetes, and Insulin prescription in adolescents and young adults with cancer
- Body Size, Physical Activity, Early-Life Energy Restriction, and Associations with Methylated Insulin-like Growth Factor–Binding Protein Genes in Colorectal cancer
- Body size, physical activity, genetic variants in the Insulin-like growth factor pathway and colorectal cancer risk
- Bone stromal production of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 promotes growth and survival of prostate cancer
- Bone turnover markers and Insulin-like growth factor components in metastatic breast cancer: results from a randomised trial of exemestane vs megestrol acetate.
- Boostrapping at Several Frequencies Supports Plasma Insulin As a Potential Marker of Breast cancer Risk
- Branched chain amino acid suppressed Insulin-initiated proliferation of human cancer cells through induction of autophagy
- BRCA1 regulates Insulin‑like growth factor 1 receptor levels in ovarian cancer
- Breast cancer Incidence in Diabetes Mellitus Patients on Insulin Glargine Compared with Human Neutral Protamine Hagedorn Insulin Treatment
- Breast cancer is associated to impaired glucose/Insulin homeostasis in premenopausal obese/overweight patients
- Breast cancer Resistance Protein 1 deficient male mice exhibit impaired estrogen action and Insulin resistance
- Breast cancer Risk and Insulin Resistance: Post Genome-Wide Gene–Environment Interaction Study Using a Random Survival Forest
- Breast cancer risk factors in relation to estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, and Ki67 expression in normal breast …
- Breast cancer Risk in Japanese Women with Special Reference to the Growth Hormone-Insulin-Iike Growth Factor Axis
- Breast cancer stem cells cultured without Insulin and effect of estrogen induction
- Breast cancer: Worse Prognosis in Insulin-Treated Diabetic Patients
- Bufalin inhibited cell proliferation and expression of Insulin-like growth factor 2 and type 1 receptor in human colorectal cancer cells
- C-105 Insulin and IGFBP-3 associated with lung cancer susceptibility in current smokers
- c‐Src, Insulin‐like growth factor I receptor, G‐protein‐coupled receptor kinases and focal adhesion kinase are enriched into prostate cancer cell exosomes
- CA repeat polymorphism in the Insulin-like growth factor-I gene is associated with increased risk of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Caffeine and caffeic acid inhibit growth and modify estrogen receptor (ER)-α and Insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) levels in human breast cancer
- Caffeine and caffeic acid inhibit growth and modify estrogen receptor and Insulin-like growth factor I receptor levels in human breast cancer
- Caloric restriction and Insulin-like growth factors in aging and cancer
- Calories and cancer: the role of Insulin-like growth factor-1
- Can the Insulin-like growth factors regulate breast cancer growth?
- cancer and Insulin-like growth factor-I: a potential mechanism linking the environment with cancer risk
- cancer at Insulin injection site
- cancer causes metabolic perturbations associated with reduced Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in peripheral tissues and impaired muscle microvascular …
- cancer causes metabolic perturbations associated with reduced Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in peripheral tissues and impaired muscle microvascular perfusion
- cancer cell-derived clusterin modulates the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase-Akt pathway through attenuation of Insulin-like growth factor 1 during serum deprivation
- cancer incidence among those initiating Insulin therapy with glargine versus human NPH Insulin
- cancer incidence and mortality in patients with Insulin-treated diabetes: a UK cohort study
- cancer incidence and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with human Insulin: a cohort study in Shanghai
- cancer occurrence in Danish diabetic patients: duration and Insulin effects
- cancer risk among Insulin users: comparing analogues with human Insulin in the CARING five-country cohort study
- cancer risk associated with Insulin glargine among adult type 2 diabetes patients–a nationwide cohort study
- cancer risk factors associated with Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3 levels in healthy women: effect modification by menopausal status
- cancer specific mortality in Insulin-treated type 2 diabetes patients
- cancer-drug induced Insulin resistance: innocent bystander or unusual suspect
- cancer: A Paradoxical Form of Adaptation? Insulin-Cortisol Dominance and Epigenetic Aspects
- Carbohydrate restriction, prostate cancer growth, and the Insulin‐like growth factor axis
- Cardiopulmonary fitness, adiponectin, chemerin associated fasting Insulin level in colorectal cancer patients
- Cardiovascular risk and Insulin resistance in childhood cancer survivors
- CARING (cancer Risk and Insulin analoGues): the association of diabetes mellitus and cancer risk with focus on possible determinants-a systematic review and a …
- Case–control study of markers of Insulin resistance and endometrial cancer risk
- Castration aggravates Insulin resistance, reduces immune function and improves quality of life of prostate cancer patients
- Celecoxib inhibits Insulin-like growth factor 1 induced growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer
- Cell-associated Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins inhibit Insulin-like growth factor-I-induced endometrial cancer cell proliferation.
- Cell-Cell Adhesion and Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Receptor in Breast cancer
- Central and Peripheral Effects of Insulin/IGF‐1 Signaling in Aging and cancer: Antidiabetic Drugs as Geroprotectors and Anticarcinogens
- Ceritinib aggravates glycemic control in Insulin-treated patients with diabetes and metastatic ALK-positive lung cancer
- Cervical Epidermal Growth Factor‐Receptor (EGF‐R) and Serum Insulin‐Like Growth Factor II (IGF‐II) Levels are Potential Markers for Cervical cancer 1
- Cetuximab-induced Insulin-like growth factor receptor I activation mediates cetuximab resistance in gastric cancer cells
- Challenges in modulating Insulin receptor signalling as a therapeutic strategy for cancer
- Change of the growth hormone–Insulin-like growth factor-I axis in patients with gastrointestinal cancer: related to tumour type and nutritional status
- Changes in glucose, Insulin, and Insulin resistance from presurgery to post adjuvant treatment for breast cancer.
- Changes in Insulin receptor signaling underlie neoadjuvant metformin administration in breast cancer: a prospective window of opportunity neoadjuvant study
- Changes in metabolic risk, Insulin resistance, leptin and adiponectin following a lifestyle intervention in overweight and obese breast cancer survivors
- Changes of androgen receptor and Insulin-like growth factor-1 in LNCaP prostate cancer cells treated with sex hormones and flutamide.
- Changes of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood and their correlation with Insulin resistance in different stages of prostate cancer
- Characterization of an amino-terminal fragment of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and its effects in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Characterization of Insulin regulation of lipid synthesis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
- Characterization of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors (IGF1-R) in human breast cancer cell lines.
- Characterization of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) binding to human breast cancer cells: kinetics of IGFBP-3 binding and identification of …
- Characterization of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins from human breast cancer cells
- Characterization of Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptors of human breast cancer cells
- Characterization of Insulin-like growth factor I binding sites in human bladder cancer cell lines
- Characterization of Insulin-like growth factor I receptors and growth effects in human lung cancer cell lines
- Characterization of Insulin-like growth factor II receptors in human small cell lung cancer cell lines
- Characterization of the Insulin and Transferrin Receptors of Two cancer Cell Lines.
- Characterization of the Role of Insulin, IGF-1 and their Receptor Signaling in Proliferation and Survival of Non-Small Cell Lung cancer Cells
- Characterization of the Role of Integrins in Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 and 2 (IGF1 and IGF2) Intracellular Signaling In cancer
- Characterizing the role of Insulin signalling in advanced prostate cancer
- Chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer is driven by stroma-derived Insulin-like growth factors
- Chemoresistant colorectal cancer cells, the cancer stem cell phenotype, and increased sensitivity to Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibition
- Chemosensitization of human prostate cancer using antisense agents targeting the type 1 Insulin‐like growth factor receptor
- Cholesterol synthetase DHCR24 induced by Insulin aggravates cancer invasion and progesterone resistance in endometrial carcinoma
- Chronic inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling downregulates Insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 and AKT activation: a crossroad between cancer and …
- Chronic Insulin exposure does not cause Insulin resistance but is associated with chemo-resistance in colon cancer cells
- Chronic Viral Hepatitis Signifies the Association of Premixed Insulin Analogues with Liver cancer Risks: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Chronological Effect on Insulin and Glycemic Status in cancer Pain Patients
- Cigarette smoking exposure, serum Insulin-like growth factors, and cancer risk: A population-based study
- Circ_0000003 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells via miR-338-3p/Insulin receptor substrate 2
- Circadian aspects of growth hormone–Insulin-like growth factor axis function in patients with lung cancer
- Circulating adipokines data associated with Insulin secretagogue use in breast cancer patients
- Circulating concentrations of Insulin-like growth factor I and risk of breast cancer
- Circulating free Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, total IGF-I, and IGF binding protein-3 levels do not predict the future risk to develop prostate cancer: results of a case …
- Circulating growth factors data associated with Insulin secretagogue use in women with incident breast cancer
- Circulating Insulin and c-peptide levels and risk of breast cancer among predominately premenopausal women
- Circulating Insulin-like growth factor axis and the risk of pancreatic cancer in four prospective cohorts
- Circulating Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 and the risk of pancreatic cancer
- Circulating Insulin-like growth factor-1 level and ovarian cancer risk
- Circulating Insulin-like growth factor-I and binding protein-3 and risk of prostate cancer
- Circulating Insulin-like growth factor-I and binding protein-3 and the risk of breast cancer
- Circulating Insulin-like growth factor-I in pregnancy and maternal risk of breast cancer
- Circulating Insulin-like growth factor-I levels regulate colon cancer growth and metastasis
- Circulating Insulin-like growth factors and IGF-binding proteins in PSA-detected prostate cancer: the large case–control study ProtecT
- Circulating Insulin‐like growth factor I in relation to melanoma risk in the European Prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition
- Circulating Insulin‐like growth factor peptides and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta‐analysis
- Circulating Insulin‐like growth factor‐I, total and free testosterone concentrations and prostate cancer risk in 200 000 men in UK Biobank
- Circulating interleukin 6 concentrations and Insulin resistance in patients with cancer
- Circulating Levels of C-Peptide (Pancreatic Marker of Insulin Secretion) in Cervical cancer
- Circulating levels of Insulin-like growth factor 1 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 associate with risk of colorectal cancer based on serologic and …
- Circulating levels of Insulin-like growth factor-II and IGF-binding protein 3 in cervical cancer
- Circulating levels of Insulin-like growth factors, their binding proteins, and breast cancer risk
- Circulating levels of Insulin‐like growth factor I, its binding proteins‐1,‐2,‐3, C‐peptide and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer
- Circulating levels of Insulin‐like growth factor‐I and risk of ovarian cancer
- Circulation Insulin-like growth factor peptides and colorectal cancer risk: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- Classifying the adverse mitogenic mode of action of Insulin analogues using a novel mechanism-based genetically engineered human breast cancer cell panel
- Clinical efficacy of cancer subcutaneous immunotherapy with interleukin-2 in relation to the pretreatment levels of tumor growth factor Insulin-like growth factor-1
- Clinical implications of Insulin-like growth factor 1 system in early-stage cervical cancer
- Clinical implications of Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and II (IGF-II) in stage IIIB cervical cancer.
- Clinical prospects of Insulin-like growth factors and IGF binding proteins study in blood serum of ovarian cancer patients
- Clinical relevance of Insulin regulatory pathways in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression.
- Clinical significance of Insulin like growth factor binding protein 3 in patients with lung cancer
- Clinical significance of Insulin receptor substrate-I down-regulation in non-small cell lung cancer
- Clinical Significance of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 and Insulin Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 3 in Serum of Patients with Lung cancer [J]
- Clinical significance of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) expression in pancreatic cancer
- Clinical significance of Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with advanced gastric cancer
- Clinical significance of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression in stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: immunohistochemical analysis
- Clinical significance of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in platinum-based chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer
- Clinical significance of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 expression in stage I non-small cell lung cancer
- Clinical significance of measurement of serum Insulin-like growth factor Ⅱ levels in patients with cervical cancer [J]
- Clinical significance of serum Insulin like growth factor 1 and Insulin like growth factor binding protein 3 in prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Clinical significance of serum Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and Insulinlike growth binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in patients with gastric cancer
- Clinical significance of serum Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and Insulinlike growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer
- Clinical significance of serum Insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in prostatic cancer
- Clinical value of circulating lipocalins and Insulin-like growth factor axis in pancreatic cancer diagnosis
- Clinical Value of Circulating Lipocalins and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Axis in Pancreatic cancer Diagnosis
- Clinical value of selected markers of angiogenesis, inflammation, Insulin resistance and obesity in type 1 endometrial cancer
- Clinical value of serum level of Insulin-like growth factor-1 diagnosis and treatment for gastric and colorectal cancer
- Clinical, haemodynamic, anthropometric, metabolic and Insulin profile of men with high‐stage and high‐grade clinical prostate cancer
- Clinicopathological implication of Insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA-binding protein 3 (IMP3) expression in gastric cancer
- Clinicopathological significance of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression in breast cancer.
- Cloning of a novel Insulin-regulated ghrelin transcript in prostate cancer
- Co-expression of genes of the Insulin-and estrogen signaling system and correlation with clinical parameters in breast cancer patients
- Co-inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor and Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 enhances radiosensitivity in human breast cancer cells
- Co-operativity between oestrogen and Insulin/IGF-I in the control of breast cancer cell proliferation.
- Co-targeting HER2/ErbB2 and Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors causes synergistic inhibition of growth in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells.
- Co-targeting Insulin-like growth factor I receptor and HER2: dramatic effects of HER2 inhibitors on nonoverexpressing breast cancer
- Co-targeting leptin and Insulin-like growth factor I signaling: dramatic effects of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors on triple negative breast cancer cells.
- Co-targeting the HER and IGF/Insulin receptor axis in breast cancer, with triple targeting with endocrine therapy for hormone-sensitive disease
- Co-targeting the Insulin-like growth factor I receptor enhances growth-inhibitory and pro-apoptotic effects of anti-estrogens in human breast cancer cell lines
- Cohort study of Insulin glargine and risk of breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer among patients with diabetes
- Colon cancer promotion, Insulin resistance and metabolic measures, the role of dietary calcium, vitamin D and fat
- Colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Study of the effect of Insulin therapy
- COLORECTAL cancer AND THE GROWTH HORMONE/Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-I AXIS
- Colorectal cancer mortality and factors related to the Insulin resistance syndrome
- Colorectal cancer: Genomic variations in Insulin-like growth factor-1 and-2
- Combination of Insulin-like growth factor-1, IGF binding protein-3, chromogranin A and prostate specific antigen can improve the detection of prostate cancer
- Combination therapy approaches to target Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in breast cancer
- Combination therapy of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and retinoid X receptor ligands synergize on prostate cancer cell apoptosis in vitro and in vivo
- Combination treatment strategies with a focus on rosiglitazone and adriamycin for Insulin resistant liver cancer
- Combined in vivo effect of A12, a type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor antibody, and docetaxel against prostate cancer tumors
- Combined inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor enhances the effects of gefitinib in a human non-small cell lung cancer resistant cell line
- Combined treatment with GH, Insulin, and indomethacin alleviates cancer cachexia in a mouse model
- Comment on association between Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and bone mineral density: further evidence linking IGF-I to breast cancer risk
- Comment on: Morden et al. Further Exploration of the Relationship Between Insulin Glargine and Incident cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Older Medicare …
- Comment on: Need for Differentiating Diabetes-Specific Mortality from Total Mortality when Comparing Metformin with Insulin Regarding cancer Survival
- Comment on: Yang et al.(2010) Associations of Hyperglycemia and Insulin Usage With the Risk of cancer in Type 2 Diabetes: The Hong Kong Diabetes Registry …
- Comment on: Yang et al.(2010) Associations of hyperglycemia and Insulin usage with the risk of cancer in type 2 diabetes: the Hong Kong Diabetes Registry. Diabetes …
- Commentary on Validation of the type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in renal cancer: Yuen JS, Akkaya E, Wang Y, Takiguchi M, Peak S …
- Comparative Analysis of Insulin-like Growth Factor I and Tumour-associated Antigens in cancer Patients at the Time of Diagnosis
- Comparative gene expression and proteomic analysis of IGF-I and Insulin signaling in a large panel of breast cancer cell lines
- Comparative study of blood Insulin levels in breast and endometrial cancer patients
- Comparative study of Insulin resistance after open and laparoscopic Miles radical resection of rectal cancer
- Comparing pioglitazone to Insulin with respect to cancer, cardiovascular and bone fracture endpoints, using propensity score weights
- Comparison of clinical efficacy between laparotomy and laparoscopic radical surgery for gastric cancer and their effects on CRP, CEA and Insulin resistance.
- Comparison of telomere length and Insulin‐like growth factor‐binding protein 7 promoter methylation between breast cancer tissues and adjacent normal tissues in …
- Comparisons of Endothelial Dysfunction, Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Differentiated Thyroid cancer Patients According to Their Radioactive Iodine …
- Compensatory Insulin receptor (IR) activation on inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R): rationale for cotargeting IGF-1R and IR in cancer
- Compensatory Insulin receptor (IR) activation upon inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R): Rationale for co-targeting IGF-1R and IR in cancer
- Comprehensive analysis of expression patterns of Insulin-like growth factor and Src pathway in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Two large, independent …
- Comprehensive analysis of potential predictive biomarkers for Insulin-like growth factor type-1 receptor (IGF-1R) targeted therapy in pancreatic cancer.
- Concentration of Insulin-like growth factor is linked with breast cancer
- Concordant loss of imprinting of the human Insulin-like growth factor II gene promoters in cancer
- Conditioned media from MCF7 and BT474 breast cancer cells induce Insulin resistance in skeletal muscle myotubes
- Conjugated linoleic acid decreases mcf-7 human breast cancer cell growth and Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor levels
- Conjugated linoleic acid downregulates Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor levels in HT-29 human colon cancer cells
- Connecting Pathway Errors in the Insulin Signaling Cascade: The Molecular Link to Inflammation, Obesity, cancer, and Alzheimer’s Disease
- Constitutive Activation of Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 in Breast cancer: Therapeutic Implication
- Consumption of fresh yellow onion ameliorates hyperglycemia and Insulin resistance in breast cancer patients during doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: a …
- Control of Expression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor II in Stromal Cells of Breast cancer
- Control of luminal type A intrinsic subtype enriched transcription factor network by Insulin: implications of diabetes on breast cancer classification.
- Correction: Hsp27 Promotes Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Survival Signaling in Prostate cancer via p90Rsk-Dependent Phosphorylation and Inactivation of BAD
- Correlation among Insulin binding, degradation, and biological activity in human breast cancer cells in long-term tissue culture
- Correlation between Body Mass Index, Insulin and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in Breast cancer Research [J]
- Correlation between Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 promoter methylation and prognosis of patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer
- Correlation of Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) expression and clinical outcome in K-RAS wild-type colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab-irinotecan
- Correlation of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor Expression With Different Molecular Subtypes of Breast cancer in the UAE
- Correlation of Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) to angiogenesis of breast cancer in IGF-1-deficient mice
- Correlation of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 messenger RNA with protein expression in primary breast cancer tissues: detection of higher levels in tumors …
- Correlation of proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells with both saturation index and cell membrane Insulin receptors
- Correlation of Proliferation of Pancreatic cancer Cells With Both Saturation Index and Cell Membrane Insulin Receptors
- Correlation of Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 with Prostate cancer
- Correlation of the sectetion of Insulin and C-peptide in cancer patients
- Correlations of Insulin-like growth factor I and Insulin-like growth factor I receptor with the clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with colon cancer.
- Correlations of recurrence after radical surgery for esophageal cancer with glucose-lipid metabolism, Insulin resistance, inflammation, stress and serum p53 …
- Corrigendum to” Effects of a home-based exercise program on the Insulin-like growth factor axis in patients operated for colorectal cancer in Sweden: Results from the …
- Could exemestane affect Insulin-like growth factors, interleukin 6 and bone metabolism in postmenopausal advanced breast cancer patients after failure on …
- Critical appraisal of the recent data published on the link between Insulin and cancer
- Cross-talk among estrogen receptor, epidermal growth factor, and Insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer
- Cross-talk between the ErbB/HER family and the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway in breast cancer
- Cross-talk between β1 Integrins and Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptor in Prostate cancer
- Crosstalk between epidermal growth factor receptor-and Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling: implications for cancer therapy
- Crosstalk between Insulin receptor and G protein-coupled receptor signaling systems leads to Ca2+ oscillations in pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells
- Crosstalk between Insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling and the estrogen receptor: Implications for breast cancer cell survival
- Crosstalk between Insulin/IGF-1 and GPCR signaling systems: a novel target for the anti-diabetic drug metformin in pancreatic cancer
- Crosstalk between Runx2 regulatory network and Insulin-like growth factor receptor/Akt signaling pathway in bone metastasis of breast cancer
- Crosstalk between the Insulin-like growth factors and estrogens in breast cancer
- Crosstalk of the Insulin-like growth factor receptor with the Wnt signaling pathway in breast cancer
- Curcumin upregulates Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐5 (IGFBP‐5) and C/EBPα during oral cancer suppression
- Cyclooxygenase-2 modulates the Insulin-like growth factor axis in non–small-cell lung cancer
- Cytotoxic gene therapy for human breast cancer in vitro using thymidine kinase directed by the Insulin promoter
- Data report on inflammatory C–C chemokines among Insulin-using women with diabetes mellitus and breast cancer
- Dataset on granulopoiesis-and lymphopoiesis-stimulating cytokine levels in Insulin secretagogue users with incident breast cancer
- Dataset on growth factor levels and Insulin use in patients with diabetes mellitus and incident breast cancer
- De novo lipogenesis is required for Insulin-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis and contributes to human liver cancer prognosis
- Decline of the red blood cell count in patients receiving androgen deprivation therapy for localized prostate cancer: impact of ADT on Insulin-like growth factor-1 and …
- Decreased expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 and its death receptor in association with poor prognosis of the patients with gastric cancer
- Decreased expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/Insulin-like growth factor-II receptor promotes growth of human breast cancer cells
- Decreased incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using Insulin: a pilot study
- Decreased production of Insulin‐like growth factor‐binding protein (IGFBP)‐6 by transfection of colon cancer cells with an antisense IGFBP‐6 cDNA construct leads to …
- Decreased prostate cancer cell migration by inhibition of the Insulin-like growth factor II/Mannose-6-Phosphate receptor
- Decreased serum levels of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I in patients with lung cancer: temporal relationship with growth hormone (GH) levels.
- Deficiency of proton-sensing ovarian cancer G protein-coupled receptor 1 attenuates glucose-stimulated Insulin secretion
- Defining the Critical role for the Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) axis in prostate cancer using genetically engineered mouse (GEM) models
- Defining the pathway to Insulin-like growth factor system targeting in cancer
- Degradation of Insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor occurs via ubiquitin‐proteasome pathway in human lung cancer cells
- Dehydroepiandrosterone, Insulin-like growth factor-I, and prostate cancer
- Deleterious Effect of Chemotherapy on Measures of Insulin Resistance in Patients with Newly-Diagnosed Invasive Breast cancer.
- Demonstration of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I and-II) receptors and binding protein in human breast cancer cell lines
- Demonstration of receptors for Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 on Hs578T human breast cancer cells.
- Depletion of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor increases radiosensitivity in colorectal cancer
- Detection of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) by ligand blotting in breast cancer tissues
- Determination of the levels of serum leptin and Insulin in patients with primary liver cancer and correlative analysis
- Development and preclinical evaluation of cixutumumab drug conjugates in a model of Insulin growth factor receptor I (IGF-1R) positive cancer
- Development of an insturmal method to evaluate Insulin receptors and Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors homodimers and hybrid receptors in breast cancer
- Development of resistance to Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in transfected T47D breast cancer cells
- Development of the monoclonal antibody figitumumab, targeting the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, for the treatment of patients with non–small-cell lung cancer
- Diabetes and Insulin therapy, but not metformin, are related to hepatocellular cancer risk
- Diabetes but not Insulin increases the risk of lung cancer: a Taiwanese population-based study
- Diabetes but not Insulin is associated with higher colon cancer mortality
- Diabetes may increase risk for oral cancer through the Insulin receptor substrate-1 and focal adhesion kinase pathway
- Diabetes mellitus and increased risk of cancer: focus on metformin and the Insulin analogs
- Diabetes mellitus, genetic variants in the Insulin‐like growth factor pathway and colorectal cancer risk
- Diabetes mellitus, Insulin treatment, diabetes duration, and risk of biliary tract cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma in a European cohort
- Diabetes, body fatness, and Insulin prescription among adolescents and young adults with cancer
- Diabetes, Insulin and cancer risk
- Diabetes, Insulin and cancer risk The molecular role of Insulin signaling and hyperInsulinemia in cancer development and progression in diabetes patients
- Diabetes, Insulin and cancer risk: you and your patient
- Diabetes, Insulin Resistance, and cancer: An Update
- Diabetes, Insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome in women at high risk for breast cancer.
- Diabetes, Insulin therapy, and colorectal cancer
- Diabetes, Insulin treatment, and cancer risk: what is the evidence?
- Diabetes, Insulin use, and cancer risk: are observational studies part of the solution–or part of the problem?
- Diabetes, Insulin use, and gastric cancer: a population-based analysis of the Taiwanese
- Diabetes, Insulin use, smoking, and pancreatic cancer mortality in Taiwan
- Diabetes, Insulin-use and risk of colorectal cancer in a US cohort study
- Diabetes, Insulin, and risk of cancer
- Diabetes, obesity, Insulin resistance: different pathways to cancer?
- Diagnostic accuracy of serum Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 for ovarian cancer
- Diagnostic Value of Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 (IGFBP7) in Colorectal cancer
- Diarylureas are small-molecule inhibitors of Insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling and breast cancer cell growth
- Diazoxide for Lowering Insulin Levels in Breast cancer Patients
- Diet and Endometrial cancer: Insulin related factors
- Diet-induced obesity and Insulin resistance spur tumor growth and cancer cachexia in rats bearing the yoshida sarcoma
- Diet, Insulin-like growth factor-1 and cancer risk
- Dietary and pharmacological modification of the Insulin/IGF-1 system: exploiting the full repertoire against cancer
- Dietary energy balance modulation of Kras-and Ink4a/Arf+/−-driven pancreatic cancer: the role of Insulin-like growth factor-I
- Dietary fiber is associated with serum sex hormones and Insulin-related peptides in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors
- Dietary flaxseed inhibits human breast cancer growth and metastasis and downregulates expression of Insulin-like growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor
- Dietary glycemic and Insulin scores and colorectal cancer survival by tumor molecular biomarkers
- Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load and Insulin index, in relation to risk of prostate cancer
- Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, Insulin index, fiber and whole-grain intake in relation to risk of prostate cancer
- Dietary Insulin index and Insulin load in relation to endometrial cancer risk in the Nurses’ Health Study
- Dietary Insulin load and cancer recurrence and survival in patients with stage III colon cancer: findings from CALGB 89803 (Alliance)
- Dietary Insulin load, dietary Insulin index, and colorectal cancer
- Dietary Insulin load, dietary Insulin index, and risk of pancreatic cancer–
- Different contribution of substrates oxidation to Insulin resistance in malnourished elderly patients with cancer
- Different expression of liver-specific Insulin-like growth factor I gene in breast cancer; expression with mice
- Differential effects of Insulin and IGF1 receptors on ERK and AKT subcellular distribution in breast cancer cells
- Differential effects of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 (IGFBP-6) on migration of two ovarian cancer cell lines
- Differential effects of Insulin-like growth factor-1 CA repeat polymorphism on breast cancer risk along with race: a meta-analysis
- Differential effects of metformin on breast cancer proliferation according to Insulin resistance and tumor subtype in a presurgical trial.
- Differential effects of metformin on breast cancer proliferation according to markers of Insulin resistance and tumor subtype in a randomized presurgical trial
- Differential expression and signaling activation of Insulin receptor isoforms A and B: a link between breast cancer and diabetes
- Differential expression of IGF-I and Insulin receptor isoforms in HPV positive and negative human cervical cancer cell lines
- Differential expression of Insulin receptor isoforms in human lung cancer.
- Differential expression of Insulin-like growth factor 1 in human primary liver cancer.
- Differential expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in high versus low Gleason score prostate cancer
- Differential expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines
- Differential Expression of Insulin‐Like Growth Factor‐1 Receptor in Breast cancer Subtypes: A Marker of Early Metastasis in HER‐2 Subtype
- Differential expression of the Insulin-like growth factor receptor among early breast cancer subtypes
- Differential expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/Insulin-like growth factor-II receptor in human breast cancer cell lines of different invasive potential.
- Differential expression patterns of the Insulin-like growth factor 2 gene in human colorectal cancer
- Differential impacts of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in epithelial IGF-induced lung cancer development
- Differential Insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling and function in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive MCF-7 and ER-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
- Differential Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) expression: A potential role for breast cancer survival disparity
- Differential regulation of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 protease activity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by estrogen and transforming growth factor-β1
- Differential regulation of Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene expression by wild type and mutant androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells
- Differential Roles of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 and-2 (IRS-1, IRS-2) in Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling in Breast cancer Cells
- Diffusion of Insulin-like growth factor 1 in human breast cancer explants
- Direct inhibition of growth and antagonism of Insulin action by glucocorticoids in human breast cancer cells in culture
- Discoidin domain receptor 1 modulates Insulin receptor signaling and biological responses in breast cancer cells
- Disrupting Insulin and IGF Receptor Function in cancer
- Disrupting Insulin-like growth factor signaling as a potential cancer therapy
- Disruption of Insulin receptor function inhibits proliferation in endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells
- Disruption of ligand binding to the Insulin-like growth factor II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor by cancer-associated missense mutations
- Dissecting the cellular and molecular mechanisms of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) action in a cancer cell model
- Distribution of a single nucleotide polymorphism of Insulin-like growth factor-1 in colorectal cancer patients and its association with mucinous adenocarcinoma
- Diverse functions of IGF/Insulin signaling in malignant and noncancerous prostate cells: proliferation in cancer cells and differentiation in noncancerous cells
- Diversity of Insulin and IGF signaling in breast cancer: implications for therapy
- DNA repair, Insulin signaling and sirtuins: at the crossroads between cancer and aging.
- Do Insulin-like growth factor associated proteins qualify as a tumor marker? Results of a prospective study in 163 cancer patients
- Do Insulin-like growth factors mediate the effect of alcohol on breast cancer risk?
- Doctors seek to prevent breast cancer recurrence by lowering Insulin levels
- Does Insulin glargine increase the risk of cancer compared with other basal Insulins?: A French nationwide cohort study based on national administrative databases
- Does Insulin resistance influence breast cancer outcomes?
- Does Insulin-like growth factor moderate the association between height and risk of cancer at 24 sites?
- Does milk intake promote prostate cancer initiation or progression via effects on Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs)? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Does obesity change the effect of aromatase inhibitors (AIs) on estradiol, leptin, Insulin, and IGF-1 serum levels in breast cancer patients?
- Does the negative correlation found in breast cancer patients between plasma melatonin and Insulin-like growth factor-I concentrations imply the existence of an …
- Dominant‐negative effect of truncated mannose 6‐phosphate/Insulin‐like growth factor II receptor species in cancer
- Dopamine, by acting through its D2 receptor, inhibits Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I)-induced gastric cancer cell proliferation via up-regulation of Krüppel …
- Dose–response effects of exercise on Insulin among colon cancer survivors
- Doses of Insulin and its analogues and cancer occurrence in Insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients
- Down-regulation of the Insulin-like growth factor I receptor by antisense RNA can reverse the transformed phenotype of human cervical cancer cell lines
- Down-regulation of type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor increases sensitivity of breast cancer cells to Insulin
- Down‐regulation of Insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor and Insulin receptor substrate‐1 expression in advanced human breast cancer
- Downregulation of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 in cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer
- Downregulation of microRNA‑126 is inversely correlated with Insulin receptor substrate‑1 protein expression in colorectal cancer and is associated with advanced …
- Downregulation of type I IGF receptor increases Insulin sensitivity of breast cancer cells
- DPP4i, thiazolidinediones, or Insulin and risks of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on metformin–sulfonylurea dual therapy with inadequate …
- Drug efflux by breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) is a mechanism of resistance to the Insulin-like growth factor receptor/Insulin receptor inhibitor, BMS-536924.
- Drug efflux by breast cancer resistance protein is a mechanism of resistance to the benzimidazole Insulin-like growth factor receptor/Insulin receptor inhibitor, BMS …
- Drug evaluation: CP-751871, a human antibody against type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor for the potential treatment of cancer.
- Dual blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor and Insulin‐like growth factor receptor–1 signaling in metastatic pancreatic cancer: Phase Ib and randomized …
- Dual role of Insulin-like growth factor-1 in acetyl-CoA carboxylase-alpha activity in human colon cancer cells HCT-8: downregulating its expression and …
- Dual silencing of Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor in colorectal cancer cells is associated with decreased proliferation and …
- Dual silencing of type 1 Insulin-like growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptors to induce apoptosis of nasopharyngeal cancer cells
- Dual targeting of the Insulin-like growth factor and collateral pathways in cancer: combating drug resistance
- Early and progressive Insulin resistance in young, non‐obese cancer survivors treated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Early Breast cancer Agressiveness does not Differ Between Insulin-Sensitive and Insulin-Resistant Postmenopausal Non-Diabetic Women
- Early changes of muscle Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 and myostatin gene expression in gastric cancer patients
- Early diet and later cancer risk: prospective associations of dietary patterns during critical periods of childhood with the GH-IGF axis, Insulin resistance and body …
- Early placenta Insulin-like growth factor (EPIL) indicates highly motile breast cancer cells and poor prognostic breast cancer subgroups
- Editor’s Note: Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins Inhibit the Growth of Human Non-small Cell Lung cancer Xenografts by Targeting Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding …
- Effect of 12 weeks of selected Pilates exercise training on serum adiponectin level and Insulin resistance in female survivors of breast cancer and its role in prevention …
- Effect of 12-week home-based exercise program on fasting Insulin in stage II-III colorectal cancer survivors: A randomized controlled trial.
- Effect of aerobic exercise intervention on markers of Insulin resistance in breast cancer women
- Effect of AMPK/mTOR/S6K1 pathways and the Insulin-sensitizing effect for adiponectin in endometrial cancer cells
- Effect of Androgen Deprivation Therapy on Indices of Glycaemia and Insulin Resistance in Native African Prostate cancer Patients
- Effect of chemotherapy and aromatase inhibitors in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer on glucose and Insulin metabolism—A systematic review
- Effect of cholecystokinin and secretin on Insulin binding to rat pancreatic acini and pancreatic cancer cell line AR42J cells
- Effect of diallyl disulfide on Insulin-like growth factor signaling molecules involved in cell survival and proliferation of human prostate cancer cells in vitro and in silico …
- Effect of different doses of metformin on serum testosterone and Insulin in non-diabetic women with breast cancer: a randomized study
- Effect of dual inhibition of the Src and Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) pathways on antitumor effects in prostate cancer (PCa).
- Effect of elevated basal Insulin on cancer incidence and mortality in cancer incident patients: the Israel GOH 29-year follow-up study
- Effect of endocrine therapy on growth of T61 human breast cancer xenografts is directly correlated to a specific down-regulation of Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II)
- Effect of Fast Track Surgery on Insulin Resistance Indexes and Inflammatory Reaction in Colorectal cancer Patients with Laparoscopic Surgery
- Effect of fast track surgery on Insulin resistance indexes of esophageal cancer patients
- Effect of fenretinide and low-dose tamoxifen on Insulin sensitivity in premenopausal women at high risk for breast cancer
- Effect of FTS on TRB3 Expression of Insulin Signaling Pathway in Patients with Colorectal cancer.
- Effect of glargine on Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients with esophageal cancer during perioperative period [J]
- Effect of home-based exercise intervention on fasting Insulin and adipocytokines in colorectal cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial
- Effect of human Insulin on breast cancer risk in Taiwanese women with type 2 diabetes.
- Effect of inhibition of Src and Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IR/IGF-1R) on tumor activity and bone turnover in prostate cancer (PCa) models in vivo …
- Effect of Insulin at dilution endpoint concentrations on macromolecular synthesis in normal mouse mammary and human breast cancer epithelial cells
- Effect of Insulin glargine and human Insulin on proliferation of a human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231
- Effect of Insulin like growth factor binding protein 3 on non-small cell lung cancer
- Effect of Insulin on cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: direct and potentiating influence
- Effect of Insulin on functional status of cord blood-derived dendritic cells and on dendritic cell-induced CTL cytotoxicity against pancreatic cancer cell lines.
- Effect of Insulin on the proliferation of human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-543 growth
- Effect of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor on sensitization of head and neck cancer cells to cetuximab and methotrexate
- Effect of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 on integrin signalling and the induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
- Effect of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) on colon cancer epithelial cells growth and apoptosis
- Effect of Insulin-like growth factor gene polymorphisms alone or in interaction with diabetes on the risk of pancreatic cancer
- Effect of Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on apoptosis of colon cancer cell and its mechanism
- Effect of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I on Apoptosis of Colon cancer Cell Through Signaling Pathway of PI-3K/Akt
- Effect of intensive Insulin therapy on glutathione synthesis rate in cancer patients with stress hyperglycemia after major surgery.
- Effect of intensive Insulin therapy on the clinical results of postoperative patients with gastric cancer
- Effect of intraoperative glucose and Insulin infusion on the metabolism in patients undergoing esophageal cancer surgery under combined general anesthesia with …
- Effect of isocaloric low-fat diet on human LAPC-4 prostate cancer xenografts in severe combined immunodeficient mice and the Insulin-like growth factor axis
- Effect of isoliquiritigenin (ISL) on Insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor and ErbB3 signaling in prostate cancer cells
- Effect of kaempferol on Insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor and ErbB3 signaling in HT‐29 human colon cancer cells
- Effect of L-arginine supplementation on Insulin resistance and adipocitokines levels in head and neck cancer non diabetic patients after surgery
- Effect of long-acting Insulin analogs on the risk of cancer: a systematic review of observational studies
- Effect of lycopene on Insulin-like growth factor-I, IGF binding protein-3 and IGF type-I receptor in prostate cancer cells
- Effect of lycopene on the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling pathway in human colon cancer HT-29 cells
- Effect of metformin and Insulin-/IGF1-receptor inhibitor combination drug therapy in triple negative breast cancer
- Effect of metformin on Insulin binding to receptors in cultured human lymphocytes and cancer cells
- Effect of obesity on plasma Insulin-like growth factor-I in cancer patients.
- Effect of systemic Insulin on protein kinetics in postoperative cancer patients
- Effect of tamoxifen on plasma Insulin-like growth factor I in patients with breast cancer
- Effect of transforming growth factor-β 1, Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin-like growth factor-II on cell growth and oestrogen metabolism in human breast cancer …
- Effect of Twelve Weeks Concurrent Yoga and Pilates Training on Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Resistance in Breast cancer Survivors: A Clinical Trial Study
- Effect of two 4-hydroxyandrostenedione doses on serum Insulin-like growth factor I levels in advanced breast cancer
- Effect of type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor targeted therapy on chemotherapy in human cancer and the mechanisms involved
- Effect of zinc on regulation of Insulin-like growth factor signaling in human androgen-independent prostate cancer cells
- Effects of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on Insulin-induced responses in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
- Effects of a 12-week home-based exercise program on the level of physical activity, Insulin, and cytokines in colorectal cancer survivors: a pilot study
- Effects of a home-based exercise program on the Insulin-like growth factor axis in patients operated for colorectal cancer in Sweden: results from the randomised …
- Effects of alcohol consumption on Insulin sensitivity and breast cancer development.
- Effects of anti-Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) antibodies with or without the ER-retention signal KDEL on cancer cell growth
- Effects of aromatase complex selective inhibition on Insulin-like growth factor 1 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 circulating levels in breast cancer
- Effects of bisphosphonates and Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) on prostate cancer cells in vitro
- Effects of Carbohydrate-electrolyte Solution on Serum Glucose and Peptide C and Insulin Levels and Its Safety in Postoperative Patients with Lung cancer
- Effects of different n-6/n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid ratio on Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 expression in human breast cancer cells
- Effects of endogenous Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 on cell cycle regulation in breast cancer cells
- Effects of exercise on Insulin, IGF axis, adipocytokines, and inflammatory markers in breast cancer survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of exogenous growth hormone on Growth Hormone-Insulin-Like growth factor axis of human gastric cancer cell
- Effects of genetic blockade of the Insulin-like growth factor receptor in human colon cancer cell lines
- Effects of Hormones on Tumor Growth and Immunoreactive Insulin–like Growth Factor–1 of Estrogen Receptor–positive Human Breast cancer (MCF‐7) Transplanted …
- Effects of Insulin analogs and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on proliferation and cellular energy metabolism in papillary thyroid cancer
- Effects of Insulin and somatostatin on the growth and the colony formation of two human pancreatic cancer cell lines
- Effects of Insulin Degrading Enzyme (IDE)-activity on the liver cancer cell transcriptome
- Effects of Insulin on human pancreatic cancer progression modeled in vitro
- Effects of Insulin on proliferation and invasion of human pancreatic cancer PANC1 cells
- Effects of Insulin-1ike growth factor 1 and its receptor on proliferation of ovarian cancer cells [J]
- Effects of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) on endometrial cancer (HHUA) cell apoptosis and EGF stimulated cell proliferation in vitro
- Effects of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and its inhibitor AG1024 on the progress of lung cancer
- Effects of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 gene on the biological characteristics of colorectal cancer
- Effects of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 on cell cycle and proliferation of gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo
- Effects of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and farnesyltransferase inhibitor SCH66336 on Akt expression and apoptosis in non–small-cell lung cancer cells
- Effects of Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF receptor antibodies on the proliferation of human breast cancer cells
- Effects of Insulin-like growth factors I and II on oestrone sulphatase activity in human breast cancer cell lines.
- Effects of isoflavones and lycopene on the Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system in men and women at increased colorectal cancer risk; randomized cross-over trials.
- Effects of isoflavones on the Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system: A randomized trial in women with high colorectal cancer risk.
- Effects of Long-acting Insulin Analogues on Breast and Colon cancer Promotion
- Effects of lycopene on the Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system in premenopausal breast cancer survivors and women at high familial breast cancer risk
- Effects of metformin on markers of Insulin resistance and on breast cancer proliferation: the putative role of IGFBP-1 as a predictive biomarker
- Effects of monoclonal antibodies, MLS128 against Tn-antigen and 1H7 against Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor, on colon cancer cell growth
- Effects of octreotide and Insulin on colon cancer cellular proliferation and correlation with hTERT activity
- Effects of quercetin on Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and their binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) secretion and induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer …
- Effects of serum and Insulin on the sensitivity of the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 to estrogen and antiestrogens
- Effects of Tai Chi Chuan on Insulin and cytokine levels in a randomized controlled pilot study on breast cancer survivors
- Effects of tamoxifen on Insulin-like growth factors, IGF binding proteins and IGFBP-3 proteolysis in breast cancer patients.
- Effects of tumor removal and body weight loss on Insulin resistance in patients with cancer.
- Effects of two monoclonal antibodies, MLS128 against Tn-antigen and 1H7 against Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor, on the growth of colon cancer cells
- EGCG inhibits activation of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in human colon cancer cells
- Eighteen Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) pathway genes, circulating levels of IGF-1 and its binding protein (IGFBP-3), and risk of prostate and breast cancer
- Eighteen Insulin-like growth factor pathway genes, circulating levels of IGF-I and its binding protein, and risk of prostate and breast cancer
- Electronic medical record cancer incidence over six years comparing new users of glargine with new users of NPH Insulin
- Elevated epithelial Insulin-like growth factor expression is a risk factor for lung cancer development
- Elevated Gluconeogenesis in Aging and Lung cancer is Related to Inflammation and Blunted Insulin‐Induced Protein Anabolism
- Elevated Insulin and Insulin resistance are associated with the advanced pathological stage of prostate cancer in Korean population
- Elevated Insulin receptor content in human breast cancer.
- Elevated Insulin-like growth factor I receptor autophosphorylation and kinase activity in human breast cancer
- Elevated Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐1 (IGFBP‐1) in men with metastatic prostate cancer starting androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is associated with …
- Elevated levels of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 in the serum of prostate cancer patients
- Elevated serum Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II and IGF binding protein-2 in patients with colorectal cancer
- Elevated serum Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 as a prognostic marker in patients with ovarian cancer
- Elevated serum Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) and decreased IGFBP-3 in epithelial ovarian cancer: correlation with cancer antigen 125 and …
- Emodin increases expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 through activation of MEK/ERK/AMPKα and interaction of PPARγ and Sp1 in lung cancer
- Employing Quantitative Systems Pharmacology to Characterize Differences in IGF1 and Insulin Signaling Pathways in Breast cancer
- Endogenous hyperInsulinaemia and exogenous Insulin: A common theme between atherosclerosis, increased cancer risk and other morbidities
- Endogenous Insulin contributes to pancreatic cancer development
- Endometrial cancer Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) expression increases with body mass index and is associated with pathologic extent and prognosis
- Endometrial expression of hormonal and Insulin/IGF receptors in relation to cancer risk factors
- Endurance training improves Insulin sensitivity and body composition in prostate cancer patients treated with androgen deprivation therapy
- Energy balance and cancer: the role of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor-I
- Energy balance, Insulin resistance biomarkers, and breast cancer risk
- Energy balance, Insulin‐related genes and risk of colon and rectal cancer
- Energy imbalance, fat, fiber, and pancreatic cancer: Role of Insulin resistance
- Energy restriction at young age, genetic variants in the Insulin‐like growth factor pathway and colorectal cancer risk in the Netherlands Cohort Study
- Engineered ubiquitin ligase PTB-U-box targets Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor receptor for degradation and coordinately inhibits cancer malignancy
- Enhanced expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 sensitizes the growth inhibitory effect of anticancer drugs in gastric cancer cells
- Enhanced expression of Rab27A gene by breast cancer cells promoting invasiveness and the metastasis potential by secretion of Insulin-like growth factor-II
- Enhanced expression of the Insulin receptor substrate-2 docking protein in human pancreatic cancer
- Enhanced function of TRPV1 via up‐regulation by Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 in a rat model of bone cancer pain
- Enhanced Insulin signaling via Shc in human breast cancer
- Enhancement of 5-Flurouracil Uptake by Insulin in Human Colonic cancer
- Enhancement of doxorubicin cytotoxicity of human cancer cells by tyrosine kinase inhibition of Insulin receptor and type I IGF receptor
- Enhancement of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling in Human Breast cancer: Estrogen Regulation of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 Expression in Vitro and in Vivo
- Enhancement of tumor necrosis factor-α-induced growth inhibition by Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5), but not IGFBP-3 in human breast cancer …
- Enhancing the apoptotic potential of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in prostate cancer by modulation of CK2 phosphorylation
- Epidemiology and biology of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) as an anti-cancer molecule
- Epidermal growth factor induces Insulin receptor substrate-2 in breast cancer cells via c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase/activator protein-1 signaling to regulate cell …
- Epidermal growth factor receptor and K‐Ras mutations and resistance of lung cancer to Insulin‐like growth factor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- Epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2/Insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling and oestrogen receptor activity in clinical breast cancer
- Epidermal growth factor, Insulin-like growth factor-1 and basic fibroblast growth factor modulate the cytostatic effect of tumour necrosis factor-α on the breast cancer …
- Epigenetic inhibition of miR-663b by long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation via up-regulation of Insulin-like growth factor …
- Epigenetic regulation of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in cancer
- Epithelial Insulin receptor expression–prognostic relevance in colorectal cancer
- epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer: a role for Insulin-like growth factor i and Insulin-like growth factor–binding protein 3?
- Epsilon-aminocaproic acid prevents high glucose and Insulin induced-invasiveness in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, modulating the plasminogen activator system
- Equol, adiponectin, Insulin levels and risk of breast cancer
- erbB3 recruitment of Insulin receptor substrate 1 modulates Insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling in oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell lines
- Erratum to: Non-metabolisable Insulin glargine does not promote breast cancer growth in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes
- Essential considerations in the investigation of associations between Insulin and cancer risk using prescription databases
- Essential fatty acids, Insulin resistance, and breast cancer risk
- Establishment and characterization of MCF-7 human breast cancer cell clones expressing an intracellular form of Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II)
- Estradiol and antiestrogens regulate a growth inhibitory Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 autocrine loop in human breast cancer cells
- Estradiol and Insulin cross-talk in breast cancer.
- Estradiol down-regulates the mannose-6-phosphate/Insulin-like growth factor-II receptor gene and induces cathepsin-D in breast cancer cells: a receptor saturation …
- Estradiol increases IRS-1 gene expression and Insulin signaling in breast cancer cells
- Estrogen and Insulin crosstalk: breast cancer risk implications
- Estrogen and Insulin modulation of intracellular Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in human breast cancer cells: possible involvement in lysosomal hydrolases …
- Estrogen and Insulin synergistically promote endometrial cancer progression via crosstalk between their receptor signaling pathways
- Estrogen and Insulin synergistically promote type 1 endometrial cancer progression
- Estrogen and Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) independently down-regulate critical repressors of breast cancer growth
- Estrogen and Insulin/IGF-1 cooperatively stimulate cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells through differential regulation of c-Myc and cyclin D1
- Estrogen and progesterone regulate secretion of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins by human breast cancer cells
- Estrogen receptor-α regulates the degradation of Insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 in breast cancer cells
- Estrogen receptor-β and the Insulin-like growth factor axis as potential therapeutic targets for triple-negative breast cancer
- Ethnic Differences in Insulin Resistance as a Mediator of cancer Disparities
- Ethyl Acetate Fraction of Helianthus tuberosus L. Induces Anti-Diabetic, and Wound-Healing Activities in Insulin-Resistant Human Liver cancer and Mouse Fibroblast …
- Evaluating associations of diabetes, Insulin use, and BMI with efficacy in patients with resected pancreatic cancer: An ancillary analysis of NRG Oncology/RTOG 9704.
- Evaluating serum Insulin-like growth factor 1 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 as markers in prostate cancer diagnosis
- Evaluation of breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 & T47D): influence of Insulin and metformin on growth parameters
- Evaluation of continuous infusion suramin in metastatic breast cancer: impact on plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF-binding proteins.
- Evaluation of drug resistance to doxorubicin in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line as a result of Insulin treatment
- Evaluation of Insulin like growth facror-1 genetic polymorphism with gastric cancer susceptibility and clinicopathological features
- Evaluation of Insulin resistance among endometrial cancer patients.
- Evaluation of Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor 1 Inhibition as a Treatment for Prostate cancer: Preclinical Efficacy and Resistance
- Evaluation of Insulin-like growth factor-I in postmenopausal women with breast cancer treated with raloxifene
- Evaluation of the Insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway in patients with advanced breast cancer treated with trastuzumab
- Evaluation of the Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) IGF-I and IGF binding protein 3 in patients at high risk for breast cancer
- Evidence for autocrine mitogenic stimulation by somatomedin-C/Insulin-like growth factor I on an established human lung cancer cell line
- Evidence of direct mitogenic activity of Insulin and the Insulin receptor in prostate cancer cell lines
- Exercise intervention lowers aberrant serum WISP-1 levels with Insulin resistance in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial
- Exosomal miR‑130a‑3p promotes the progression of differentiated thyroid cancer by targeting Insulin‑like growth factor 1
- Exosomes derived from pancreatic cancer cells induce Insulin resistance in C2C12 myotube cells through the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway
- Exploitation of the Ligand-Binding Properties of the Mannose 6-Phosphate/Insulin-Like Growth Factor II (IGF-II) Receptor to Inhibit IGF-II-Dependent Growth of cancer …
- Expression and Activity of Both IGF and Insulin Signaling Pathways in a Large Panel of Breast cancer Cell Lines.
- Expression and clinical significance of Insulin-like growth factor 1 in lung cancer tissues and perioperative circulation from patients with non-small-cell lung cancer
- Expression and Clinical Significance of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Ⅰand Insulin-like Growth Factor-Ⅱ in Gastric cancer [J]
- Expression and clinical significance of sushi domain-containing protein 3 (SUSD3) and Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) in breast cancer
- Expression and function of the Insulin receptor substrate proteins in cancer
- Expression and function of the Insulin‐like growth factor I system in human non‐small‐cell lung cancer and normal lung cell lines
- Expression and prognostic analyses of the Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein family in human pancreatic cancer
- Expression and prognostic significance of Insulin-like growth factor 1 in non-small-cell lung cancer [J]
- Expression characteristics of proteins of the Insulin-like growth factor axis in non-small cell lung cancer patients with preexisting type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Expression level of Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein 5 mRNA is a prognostic factor for breast cancer
- Expression levels of Insulin-like growth factor-1 and multidrug resistance-associated protein-1 indicate poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer
- Expression of a protease-resistant Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-4 inhibits tumour growth in a murine model of breast cancer
- Expression of early placenta Insulin-like growth factor (EPIL) in breast cancer cells provides an autocrine loop with enhancement of predominantly HER-2-related …
- Expression of early placenta Insulin-like growth factor in breast cancer cells provides an autocrine loop that predominantly enhances invasiveness and motility
- Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), platelet growth factor receptor (PGFR) and Insulin growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) on lung cancer cell
- Expression of estrogen receptors in non-malignant mammary tissue modifies the association between Insulin-like growth factor 1 and breast cancer risk
- Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α and Insulin in pancreatic cancer and their correlation
- Expression of IGF/Insulin receptor in prostate cancer tissue and progression to lethal disease
- EXPRESSION OF IGFBP-6 IN COLORECTAL cancer: THE RELATION WITH Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR RECEPTOR, ADIPONECTIN LEVEL AND ITS …
- EXPRESSION OF Insulin LIKE GROWTH FACTOR Ⅱ RECEPTOR IN PANCREATIC cancer
- Expression of Insulin receptor and c-MET is associated with clinicopathologic characteristics and molecular subtypes in premenopausal breast cancer patients
- Expression of Insulin receptor substrate 1 in primary breast cancer and lymph node metastases
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor 1 and its receptors in colorectal cancer and their significances
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in primary breast cancer: immunohistochemical analysis
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA in human gastric cancer.
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 by MCF-7 breast cancer cells is regulated through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mammalian target of …
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) is down regulated in breast cancer compared to normal breast tissue
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 before and after neoadjuvant hormonal therapy in human prostate cancer tissues: correlation with …
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) in human thyroid papillary cancer tissues
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins by T-47D human breast cancer cells: regulation by progestins and antiestrogens
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in female breast cancer as related to established prognostic factors and long-term prognosis
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor I receptor as a biomarker for predicting prognosis in biliary tract cancer patients
- Expression of Insulin-like Growth Factor Ⅰ Receptor in the Gastric cancer and its Significance
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor I, its binding proteins, and its receptor in ovarian cancer
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) in human primary liver cancer: mRNA and protein analysis
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor II in female breast cancer as related to established prognostic factors and long-term prognosis.
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 in breast cancer and its clinical significance [J]
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 correlate with lymphatic metastases in human gastric cancer
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor receptors I and II in normal human lung and in lung cancer
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 in breast cancer tissues
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in human colorectal cancer
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in local and metastatic prostate cancer
- Expression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor mRNA in Human Breast cancer Tissues and Its Clinical Significance
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor-2 can predict the prognosis of human colorectal cancer patients: correlation with tumor progression, proliferative activity and …
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor-2, c-MET, matrix metalloproteinase-7 and MUC-1 in primary lesions and lymph node metastatic lesions of gastric cancer.
- Expression of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Ⅰ Receptor (IGF-ⅠR) in Breast cancer and Its Significance [J]
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor, estrogen receptor α, Bcl-2 and Bax proteins in human breast cancer
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factor-related genes in breast cancer cell cultures and tissues
- Expression of Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in the estrogen responsive Ishikawa human endometrial cancer cell line
- Expression of Insulin‐like growth factor binding proteins in human breast cancer correlates with estrogen receptor status
- Expression of Insulin‐like growth factor II, α‐fetoprotein and hepatitis B virus transcripts in human primary liver cancer
- Expression of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor in circulating tumor cells of patients with breast cancer is associated with patient outcomes
- Expression of Insulin‐Like Growth Factor‐I Receptor and Transferrin Receptor By Breast cancer Cells In Pleural Effusion Smears
- Expression of messenger RNA for Insulin-like growth factors and Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins by experimental breast cancer and normal breast tissue in …
- Expression of metalloprotease Insulin-degrading enzyme (insulysin) in breast and ovarian cancer tissues
- Expression of nuclear Insulin receptor substrate 1 in breast cancer
- Expression of the Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 in primary tumors and lymph node metastases in breast cancer: correlations with Bcl-xL and Bax proteins.
- Expression of the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) in breast cancer cells: evidence for a regulatory role of dolichyl phosphate in the transition from an …
- Expression of the Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) in Colon cancer.
- Expression of the Insulin-like growth factor I receptor and urokinase plasminogen activator in breast cancer is associated with poor survival: potential for intervention …
- Expression of the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in primary breast cancer and lymph node metastases: correlations with estrogen receptors α and β
- Expression of the Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor in Primary Breast cancer and Lymph Node Metastases: Correlations with Estrogen Receptors α and β
- Expression of the Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGFs) and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) in Bladder cancer Tissue
- Expression of the Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and the IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs) in human gastric cancer cells
- Expression of the Insulin‐like growth factor system and cancer progression in hormone‐treated prostate cancer patients
- Expression of the Insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor and proapoptotic Bax and Bak proteins in human colorectal cancer
- Expression of the type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor is up-regulated in primary prostate cancer and commonly persists in metastatic disease
- Expression of tumor-associated vascular Insulin receptor in colorectal cancer and its relationship with tumor pathological features
- Expression of two Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in a human endometrial cancer cell line: structural, immunological, and genetic characterization
- Expression of various Insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA isoforms in colorectal cancer
- Expression patterns of Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-I) and its receptor in mammary tissues and their associations with breast cancer survival
- Expression profile, clinical significance, and biological function of Insulin-like growth factor 2 messenger RNA-binding proteins in non–small cell lung cancer
- Expressions of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 in human gastric cancer cell lines and methylation regulation [J]
- Expressions of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor-1 and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 3 in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung cancer
- Expressions ofCLDN1and Insulin-like growth factor 2 are associated with poor prognosis in stage N2 non-small cell lung cancer
- Extinction of Insulin-like growth factor-I mitogenic signaling by antiestrogen-stimulated Fas-associated protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 in human breast cancer cells
- factor-i/Insulin receptor is present in all breast cancer subtypes and is related to poor survival
- Factors associated with circulating levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in 740 women at risk for breast cancer
- Factors associated with circulating levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in women at risk for breast cancer
- Family-based genetic association study of Insulin-like growth factor I microsatellite markers and premenopausal breast cancer risk
- Fast-track surgery improves postoperative clinical recovery and reduces postoperative Insulin resistance after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer
- Fasting Insulin and outcome in early-stage breast cancer: results of a prospective cohort study
- Fasting Insulin and risk of cancer related mortality in non-diabetic adults: A dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies
- Fasting serum Insulin concentration and risk of prostate cancer.
- Fatty acid synthase: association with Insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cancer
- Fatty acid uptake by breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231): Effects of Insulin, leptin, adiponectin, and TNFα
- Fatty acid uptake by MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells: Effects of Insulin, TNFalpha, adiponectin and leptin
- Fenretinide, a synthetic retinoid, improves Insulin sensitivity in premenopausal women at increased risk for breast cancer
- Fibronectin confers survival against chemotherapeutic agents but not against radiotherapy in DU145 prostate cancer cells: involvement of the Insulin like growth factor …
- Five genes influenced by obesity may contribute to the development of thyroid cancer through the regulation of Insulin levels
- Flavonoids from Enicostema littorale blume enhances glucose uptake of cells in Insulin resistant human liver cancer (HepG2) cell line via IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway
- Fluorescent-antibody targeting of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor visualizes metastatic human colon cancer in orthotopic mouse models
- FOXA1 Promotes Tumor Progression in Prostate cancer via the Insulin-Like Growth
- FOXA1 promotes tumor progression in prostate cancer via the Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 pathway
- Free Insulin‐like growth factor‐I and breast cancer risk
- Freedom from Disease: The Breakthrough Approach to Preventing cancer, Heart Disease, Alzheimer’s, and Depression by Controlling Insulin
- Frequency and circadian timing of eating may influence biomarkers of inflammation and Insulin resistance associated with breast cancer risk
- Frequency of cancer among Insulin-treated diabetic patients in Denmark
- Frequency of Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGFR-1) expression and correlation with clinical and selected molecular parameters in advanced non-small cell lung cancer …
- Frequent deletion of chromosome 19 and a rare rearrangement of 19p13. 3 involving the Insulin receptor gene in human ovarian cancer.
- Fucoidan downregulates Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor levels in HT-29 human colon cancer cells
- Function of Insulin‑like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer resistance to chemotherapy
- Functional imaging markers for blockade of breast cancer metastasis by IGF1R and Insulin receptor targeted drugs using novel MRI and targeted iron oxide …
- Further exploration of the relationship between Insulin glargine and incident cancer: a retrospective cohort study of older Medicare patients
- Fusion of gelonin and anti-Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) affibody for enhanced brain cancer therapy
- GAIP-interacting protein, C-terminus is involved in the induction of zinc-finger protein 143 in response to Insulin-like growth factor-1 in colon cancer cells
- Gastric cancer containing Insulin and associated with hypoglycemia
- Gastric cancer: the role of Insulin‐like growth factor 2 (IGF 2) and its receptors (IGF 1R and M6‐P/IGF 2R)
- Gene expression and prognosis of Insulin‑like growth factor‑binding protein family members in non‑small cell lung cancer
- Gene Expression Profiling And Insights Into The Involvement Of The Insulin Signaling Pathway In Oral cancer
- Gene polymorphisms related to Insulin resistance and gene–environment interaction in colorectal cancer risk
- Gene Targets of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Receptor (IGF-IR) Signaling and Their Potential Role in Breast cancer.
- Gene therapy for colorectal cancer by an oncolytic adenovirus that targets loss of the Insulin-like growth factor 2 imprinting system
- Gene therapy for human colorectal cancer cell lines with recombinant adenovirus 5 based on loss of the Insulin-like growth factor 2 imprinting
- Generation of engineered small protein scaffolds and Insulin receptor targeting in human breast cancer
- Genetic and plasma variation of Insulin‐like growth factor binding proteins in relation to prostate cancer incidence and survival
- Genetic blockade of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor via recombinant adenovirus in lung cancer can be enhanced by the histone deacetylase inhibitor, vorinostat
- Genetic blockade of the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor: a promising strategy for human pancreatic cancer
- Genetic factors related to racial variation in plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor-1: implications for premenopausal breast cancer risk
- Genetic screen identifies Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 as a modulator of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
- Genetic variants and traits related to Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin resistance and their interaction with lifestyles on postmenopausal colorectal cancer …
- Genetic variants in Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 are associated with prostate cancer susceptibility in Eastern Chinese Han men
- Genetic variants in the Insulin-like growth factor pathway and colorectal cancer risk in the Netherlands cohort study
- Genetic variants, prediagnostic circulating levels of Insulin-like growth factors, Insulin, and glucose and the risk of colorectal cancer: the Multiethnic Cohort study
- Genetic Variation at the Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Gene and Association with Breast cancer, Breast Density and Anthropometric Measures
- Genetic variation in Insulin-like growth factor 2 may play a role in ovarian cancer risk
- Genetic variation in Insulin-like growth factor signaling genes and breast cancer risk among BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers
- Genetic variation in Insulin-like growth factor-1 influences risk of colorectal cancer.
- Genetic variation in the Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor, growth hormone, and leptin pathways in relation to breast cancer in African-American women: the …
- Genetic variation in the SST gene and its receptors in relation to circulating levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I, IGFBP3, and prostate cancer risk
- Genistein enhances Insulin-like growth factor signaling pathway in human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells
- Genistein inhibits Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in HT-29 human colon cancer cells: a possible mechanism of the growth inhibitory effect of Genistein
- Genome-wide gene-environmental interaction and random survival forest analyses: Insulin resistance and breast cancer risk
- Genome-Wide Meta-analysis of Gene–Environmental Interaction for Insulin Resistance Phenotypes and Breast cancer Risk in Postmenopausal Women
- Genome-wide profiling of congenital Insulin-like growth factor-1 deficient patients: translational implications in cancer prevention and metabolism
- Genomic copy number of a carcinogenic single nucleotide polymorphism at 8q24 in non‐risk allele colorectal cancer associated with Insulin growth factor 2 receptor …
- Genomic imprinting of Insulin-like growth factor II in prostate cancer and its clinical significance
- Genomic imprinting of Insulin-like growth factorⅡ in colorectal cancer and its relationship with the presence of metastasis
- German agency suspects that Insulin analogue glargine increases risk of cancer
- GIPC mediates the generation of reactive oxygen species and the regulation of cancer cell proliferation by Insulin-like growth factor-1/IGF-1R signaling
- Glucagon/Insulin ratio as a potential biomarker for pancreatic cancer in patients with new-onset diabetes mellitus
- Glucagon/Insulin ratio in preoperative screening before pancreatic surgery: correlation with hemoglobin A 1C in subjects with and without pancreatic cancer
- Glucose impairments and Insulin resistance in prostate cancer: The role of obesity, nutrition and exercise
- Glucose lowering therapies and cancer specific mortality in adult Insulin-treated diabetes
- Glucose tolerance and Insulin secretion in experimental pancreatic cancer in the Syrian hamster
- Glucose tolerance and Insulin secretion in pancreatic cancer.
- Glucose uptake in the human gastric cancer cell line, MKN28, is increased by Insulin stimulation
- Glucose‐lowering with exogenous Insulin monotherapy in type 2 diabetes: dose association with all‐cause mortality, cardiovascular events and cancer
- Glutathione S-transferase M1 gene but not Insulin-like growth factor-2 gene or epidermal growth factor gene is associated with prostate cancer☆
- Gly972Arg variant of Insulin receptor substrate 1 gene and colorectal cancer risk in overweight/obese subjects
- Glycans as regulatory elements of the Insulin/IGF system: impact in cancer progression
- Glycemic Status, Insulin Resistance, and Risk of Pancreatic cancer Mortality in Individuals With and Without Diabetes
- GPER1 is regulated by Insulin in cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts
- Grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit the growth of human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts by targeting Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, tumor cell …
- Grb10, a negative regulator of Insulin signaling, is a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer.
- GREEN TEA SUPPLEMENTATION LOWERS Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR I IN MEN AT HIGH RISK FOR PROSTATE cancer
- Growth Factors and cancer—The Role of Insulin-Like Growth Factors
- Growth hormone and Insulin like growth factor-1 in relation to prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Growth hormone and Insulin reverse net whole body and skeletal muscle protein catabolism in cancer patients.
- Growth hormone, alone and in combination with Insulin, increases whole body and skeletal muscle protein kinetics in cancer patients after surgery.
- Growth Hormone, Insulin-like Growth Factor I and Insulin: their Relationship to Aging and cancer
- Growth hormone, Insulin, and somatostatin therapy of cancer cachexia
- Growth hormone, the Insulin-like growth factor axis, Insulin and cancer risk
- Growth inhibition and increase of Insulin receptors in antiestrogen-resistant T47DCO human breast cancer cells by progestins: implications for endocrine therapies
- Growth inhibition by Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in T47D breast cancer cells requires transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and the type II TGF-β …
- Growth inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor I receptor monoclonal antibody to human colorectal cancer cells
- Growth inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cells by stable expression of an Insulin-like growth factor I receptor antisense ribonucleic acid
- Growth inhibition of pancreatic cancer by antisense oligonucleotide against the Insulin like growth factor Ⅰ receptor
- Growth regulation and co-stimulation of human colorectal cancer cell lines by Insulin-like growth factor I, II and transforming growth factor α
- Growth regulation by Insulin-like growth factors in lung cancer
- Growth regulation of human breast cancer by Insulin-like growth factors
- Growth-promoting effect, biological activity, and binding of Insulin in human intestinal cancer cells in culture
- Guidelines for investigation of associations between Insulin and cancer risk using prescription databases.
- Hammerhead Ribozyme-Mediated Cleavage of the Human Insulin-Like Growth Factor-II Ribonucleic Acid in Vitro and in Prostate cancer Cells
- Haplotype variation in Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and prostate cancer risk: the multiethnic cohort
- Hepatic steatosis and cancer development: role of Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein p62/IGF2BP2/IMP2-2 and fatty acid elongase ELOVL6
- Heterodimerization of glycosylated Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors and Insulin receptors in cancer cells sensitive to anti-IGF1R antibody
- Heterotrimerization of the growth factor receptors erbB2, erbB3, and Insulin-like growth factor-i receptor in breast cancer cells resistant to herceptin
- Heterozygous knockdown Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor (IGF‐1R) regulates mitochondrial functions and prevents colitis and colorectal cancer
- Heterozygous knockout Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) regulates mitochondrial functions and prevents colitis and colorectal cancer
- High dose human Insulin and Insulin glargine promote T24 bladder cancer cell proliferation via PI3K-independent activation of Akt
- High expression of Insulin receptor on tumour‐associated blood vessels in invasive bladder cancer predicts poor overall and progression‐free survival
- High glucose and Insulin enhance uPA expression, ROS formation and invasiveness in breast cancer-derived cells
- High Insulin levels in newly diagnosed breast cancer patients reflect underlying Insulin resistance and are associated with components of the Insulin resistance …
- High Insulin levels linked to deaths from breast cancer
- High Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) expression is associated with poor survival in surgically treated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (pts)
- High Insulin-like growth factor-2 (IGF-2) gene expression is an independent predictor of poor survival for patients with advanced stage serous epithelial ovarian cancer
- High Insulin‐like growth factor mRNA‐binding protein 3 (IMP3) protein expression is associated with poor survival in muscle‐invasive bladder cancer
- High levels of circulating Insulin-like growth factor-I increase prostate cancer risk: a prospective study in a population-based nonscreened cohort
- High prevalence of papillary thyroid cancer in Korean women with Insulin resistance
- High-affinity Insulin binding to an atypical Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in human breast cancer cells.
- Higher Concentrations of Glucose or Insulin Increase the Risk of Various Types of cancer in Obesity or Type 2 Diabetes by Decreasing the Expression of …
- Higher doses of Insulin glargine linked to cancer
- Higher glucose and Insulin levels are associated with risk of liver cancer and chronic liver disease mortality among men without a history of diabetes
- Higher Insulin resistance and adiposity in postmenopausal women with breast cancer treated with aromatase inhibitors
- Highly specific role of the Insulin receptor in breast cancer progression
- HMGA1 controls transcription of Insulin receptor to regulate cyclin D1 translation in pancreatic cancer cells
- Hormonal and metabolic strategies to overcome Insulin resistance and prevent endometrial cancer
- Hormonal regulation of Insulin-like growth factor II and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein expression by breast cancer cells in vivo: evidence for stromal …
- Hormone responsive human breast cancer in long-term tissue culture: effect of Insulin
- Hospicells promote upregulation of the ATP-binding cassette genes by Insulin-like growth factor-I via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in an ovarian cancer …
- Host genetic variants in the Insulin Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 impact on servival of patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with palliative chemotharapy
- How the association between obesity and inflammation may lead to Insulin resistance and cancer
- Hsp27 promotes Insulin-like growth factor-I survival signaling in prostate cancer via p90Rsk-dependent phosphorylation and inactivation of BAD
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) inhibits cisplatin‐induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells: Possible role of up‐regulation of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 by …
- Human colon cancer stem cells are enriched by Insulin-like growth factor-1 and are sensitive to figitumumab
- Human Insulin does not increase bladder cancer risk
- Human Insulin does not increase prostate cancer risk in Taiwanese
- Human Insulin therapy is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer: A population-based retrospective cohort study
- Human Insulin to increase breast cancer risk in Taiwanese women with type 2 diabetes.
- Human monoclonal antibodies targeting nonoverlapping epitopes on Insulin-like growth factor II as a novel type of candidate cancer therapeutics
- Human Prostate cancer Expresses the Low Affinity Insulin-like
- Human prostate cancer expresses the low affinity Insulin-like growth factor binding protein IGFBP-rP1
- Humoral autoimmune responses to Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding proteins IMP1 and p62/IMP2 in ovarian cancer
- Hyperactivation of the Insulin-like growth factor receptor I signaling pathway is an essential event for cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells
- hyperglycemia Promotes TMPrss2-erg gene Fusion in Prostate cancer cells via Upregulating Insulin-like growth Factor-Binding Protein-2
- Hyperglycemia, Insulin Resistance, and the Risk of Pancreatic cancer
- Hyperglycemia, Insulin resistance, impaired pancreatic β-cell function, and risk of pancreatic cancer
- HyperInsulinemia, Insulin resistance, vitamin D, and colorectal cancer among whites and African Americans
- Hypermethylation of let-7a-3 in epithelial ovarian cancer is associated with low Insulin-like growth factor-II expression and favorable prognosis
- Hypoglyceamia due to Paranoeplastic Secretion of Insulin in a Patient with Metastasizing Colon cancer
- Hypoglycemia caused by co-secretion of Insulin from lung tumor and cardia cancer: First case report
- Hypogonadism might cause Insulin resistance in prostate cancer
- Hypoleptinemia in gastric cancer patients: relation to body fat mass, Insulin, and growth hormone
- Hypomethylation of 5’CpG island of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 is associated with its overexpression in colorectal cancer
- Hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid axis disruption in rats with breast cancer is related to an altered endogenous oxytocin/Insulin-regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP) …
- Hypoxia increases gefitinib-resistant lung cancer stem cells through the activation of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- Hypoxia inducible factor-1 mediates effects of Insulin on pancreatic cancer cells and disturbs host energy homeostasis
- Hypoxia negates hyperglycaemia-induced chemo-resistance in breast cancer cells: the role of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2
- Hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1α (HIF‐1α) gene polymorphisms, circulating Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)‐3 levels and prostate cancer
- ID: 43: Insulin RESISTANCE AND ENDOMETRIAL cancer RISK: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS
- Identification and regulation of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins produced by hormone-dependent and-independent human breast cancer cell lines
- Identification and validation of the potential biomarker Insulin-like growth factor binding protein acid-labile subunit for breast cancer in African American women
- Identification of a Prognostic Signature Based on the Expression of Genes Related to the Insulin Pathway in Early Breast cancer
- Identification of a Prognostic Signature Based on the Expression of Insulin-Related Genes in Early Breast cancer.
- Identification of BRCA1 as a potential biomarker for Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor targeted therapy in breast cancer
- Identification of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF I) receptors in ovarian cancer tissue
- Identification of Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRna-binding protein 3 as a radioresistance factor in squamous esophageal cancer cells
- Identification of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in breast cancer cells
- Identification of Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) gene promoter-binding proteins in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive and ER-depleted breast cancer cells
- Identification of microRNAs involved in gefitinib resistance of non‑small‑cell lung cancer through the Insulin‑like growth factor receptor 1 signaling pathway
- Identification of p122RhoGAP (deleted in liver cancer-1) Serine 322 as a substrate for protein kinase B and ribosomal S6 kinase in Insulin-stimulated cells
- Identification of the Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 5 and 6 (IGFBP-5 and 6) in human breast cancer cells
- IFN-β is a potent inhibitor of Insulin and Insulin like growth factor stimulated proliferation and migration in human pancreatic cancer cells
- IGF and Insulin receptor signaling in breast cancer
- IGF-I and Insulin Receptor Families in cancer
- IGF-I and Insulin signaling enhances levels of choline kinase in breast cancer cells: Implications for developing noninvasive magnetic resonance spectroscopy of …
- IL‐17 and Insulin/IGF1 enhance adhesion of prostate cancer cells to vascular endothelial cells through CD44‐VCAM‐1 interaction
- Immunization with breast cancer cells treated with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (AS [S] ODN) to type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) induced an …
- Immunization with murine breast cancer cells treated with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor induced an antitumoral effect …
- Immunochemical demonstration of immunoreactive Insulin in human breast cancer.
- Immunohistochemical evaluation of Insulin-like growth factor I receptor status in cervical cancer specimens
- Immunohistochemical expression of Insulin-like growth factor 1-receptor in invasive breast cancer from women of African ancestry.
- Immunohistochemical Modifications of “B Cells” in Experimentally-induced Pancreatic cancer—Correlation with Serum Insulin Values
- Immunohistochemical Staining of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in Human Lung cancer cells of NSCLC and SCLC.
- ImmunoPET imaging of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) in pancreatic cancer
- ImmunoPET imaging of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in a subcutaneous mouse model of pancreatic cancer
- Impact of a behaviorally-based weight loss intervention on parameters of Insulin resistance in breast cancer survivors
- Impact of a mixed strength and endurance exercise intervention on Insulin levels in breast cancer survivors
- Impact of diabetes and Insulin use on prognosis in patients with resected pancreatic cancer: an ancillary analysis of NRG Oncology RTOG 9704
- Impact of diabetes mellitus and Insulin use on survival after colorectal cancer diagnosis: the cancer Prevention Study-II Nutrition Cohort
- Impact of diabetes, Insulin, and metformin use on the outcome of patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive primary breast cancer …
- IMPACT OF ESTROGEN, IGF-I AND Insulin SIGNALING ON BREAST cancer SPHEROIDS.
- Impact of Insulin resistance (IR) on the prognosis of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients treated with first-line chemotherapy (CT).
- Impact of Insulin-like growth factor (igf) kinetics on the development of prostate cancer: age-adjusted and baseline Psa-adjusted case control study
- Impact of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) and amphiregulin (AREG) expressions on survival in patients with stage II/III gastric cancer enrolled in the …
- Impact of Insulin-like growth factor gene polymorphisms on survival of patients with colorectal cancer.
- Impact of Insulin-like growth factor receptor-I function on angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis of colon cancer
- Impact of Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor, epidermal growth factor receptor, and HER2 expressions on outcomes of patients with gastric cancer
- Impact of Insulin-sensitizing agents on risk for liver cancer and liver-related death in diabetic patients with compensated hepatitis C cirrhosis
- Impact of Intensive Insulin Therapy on C-Reactive Protein in Gastric cancer Patients with Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Impact of intravenous Insulin on 18F-FDG PET in diabetic cancer patients
- Impact of metabolic disorders on prostate cancer growth: Androgen and Insulin resistance perspectives
- Impact of obesity on MMTV-Wnt-1 mammary cancer: role of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)/Akt/mTOR pathway
- Impact of Obesity on MMTV-Wnt-1 Mammary cancer: Role of The Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1)/Akt/mTOR Pathway
- Impact of phosphorylated Insulin‑like growth factor‑1 receptor on the outcome of breast cancer patients and the prognostic value of its alteration during …
- Impact of physical activity on Insulin levels in breast cancer survivors
- Impact of prediagnosis smoking, alcohol, obesity, and Insulin resistance on survival in male cancer patients: National Health Insurance Corporation Study
- Impact of preoperative oral liquid carbohydrate on postoperative Insulin resistance in gastric cancer patients and its associated study
- Impact of systemic inflammation on the relationship between Insulin resistance and all-cause and cancer-related mortality
- Impact of treatment exposures on cardiovascular risk and Insulin resistance in childhood cancer survivors
- Impaired binding of Insulin to erythrocyte membrane receptor and the activation of nitric oxide synthase by the hormone in human breast cancer
- Impaired Insulin action on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and glucose transport in skeletal muscle of pancreatic cancer patients
- Impaired Insulin Signaling Is Associated with Decreased Incidence of Experimental Skin cancer.
- Impairment of stimulation by estrogen of Insulin‐activated nitric oxide synthase in human breast cancer
- Implication of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)/IGF binding protein-3 and alpha-tocopherol in the chemopreventive activity of 9-cis retinoic acid in lung cancer
- Implication of milk and dairy products consumption through Insulin-like growth factor-I in induction of breast cancer risk factors in women
- Implication of the Insulin-like growth factor-IR pathway in the resistance of non–small cell lung cancer cells to treatment with gefitinib
- Implications for Prostate cancer of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) Genetic Variation and Circulating IGF-I Levels
- Implications of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor activation in lung cancer
- Implications of Insulin‐like growth factor‐I for prostate cancer therapies
- Importance of the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor in HER2, FGFR2 and MET-unamplified gastric cancer with and without Ras pathway activation
- In a randomized trial in prostate cancer patients, dietary protein restriction modifies markers of leptin and Insulin signaling in plasma extracellular vesicles
- in basal and estradiol-stimulated Insulin-like growth factor I secretion and action in breast cancer cells in culture
- In prostate cancer, low adiponectin levels are not associated with Insulin resistance
- In vitro downregulation of growth factors by Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in cervical cancer☆
- In vitro enhancement of response to radiation of human lung cancer cells following Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inactivation
- In vitro immune response of Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope from lung cancer immunotherapy target
- In Vivo Activity of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 in Prevention of Prostate cancer Progression
- In vivo progression of LAPC-9 and LNCaP prostate cancer models to androgen independence is associated with increased expression of Insulin-like growth factor I …
- In vivo suppression of hormone-refractory prostate cancer growth by inositol hexaphosphate: induction of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and inhibition of …
- In-utero exposures and breast cancer risk: joint effect of estrogens and Insulin-like growth factor?
- Inactivation of Rac1 reduces Trastuzumab resistance in PTEN deficient and Insulin-like growth factor I receptor overexpressing human breast cancer SKBR3 cells
- Incidence of Pancreatic cancer Associated Insulin Dependent Diabetes at an Inner City Hospital
- Increased Activity of Insulin‐like Growth Factor‐binding Protein in Human Thyroid Papillary cancer Tissue
- Increased apoptosis and decreased proliferation of colorectal cancer cells using Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐4 gene delivered locally by gene transfer
- Increased autocrine production of Insulin‐like growth factor II (IGF‐II) alters serum sensitivity of MCF‐7 human breast cancer cell proliferation
- Increased blood glucose and Insulin, body size, and incident colorectal cancer
- Increased cancer mortality in diabetic people treated with Insulin: a register-based follow-up study
- Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or Insulin
- Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or Insulin: Response to Bowker et Al.
- Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or Insulin: Response to Farooki and Schneider
- Increased expression of Insulin receptor substrate-1 in human pancreatic cancer
- Increased Expression of Insulin-like Growth Factor-II Messenger RNA–Binding Protein 1 Is Associated with Tumor Progression in Patients with Lung cancer
- Increased expression of the mannose 6‐phosphate/Insulin‐like growth factor‐II receptor in breast cancer cells alters tumorigenic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Increased Insulin-like growth factor 1 production by polyploid adipose stem cells promotes growth of breast cancer cells
- Increased Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor protein expression and gene copy number in small cell lung cancer
- Increased Insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression and signaling are components of androgen-independent progression in a lineage-derived prostate cancer …
- Increased levels of mannose-6-phosphate/Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (M6P/IGF2-R) found in serum of patients with breast cancer
- Increased life-time risk for colorectal cancer among patients with loss of genomic imprinting of Insulin-like growth factor 2: A survival analysis
- Increased plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor 2 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 are associated with endometrial cancer risk
- Increased plasma transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFβ1) level in lung cancer patients may be due to the loss of mannose 6-phosphate/Insulin like growth factor 2 …
- Increased serum Insulin associated with increased risk of prostate cancer recurrence
- Increased serum Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 levels are associated with prolonged response to dasatinib‐based regimens in metastatic prostate cancer
- Individual Insulin use and the risk of breast cancer: An international clinical epidemiology study.
- Inducible expression of dominant negative Insulin-like growth factor I receptor in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Inducible knockdown of Insulin receptor substrate I desensitizes ER alpha response to both agonist (estradiol) and antagonist (fulvestrant) in MCF-7L breast cancer …
- Induction of anterior gradient 2 (AGR2) plays a key role in Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)-induced breast cancer cell proliferation and migration
- Induction of Apoptosis in Human cancer Cells by Human Eb-or Rainbow Trout Ea4-Peptide of Pro-Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I (Pro-IGF-I)
- Induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells by Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 does not require binding to retinoid X receptor-α
- Induction of fascin spikes in breast cancer cells by activation of the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor
- Induction of Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein expression by ICI 182,780 in a tamoxifen‐resistant human breast cancer cell line
- Induction of interleukin-6 by adjuvant breast cancer treatment in mice promotes loss of lean body mass via down-regulation of Insulin-like growth factor I: the role of …
- Induction of myasthenia gravis, myositis, and Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus by high-dose interleukin-2 in a patient with renal cell cancer
- Induction of steroid sulfatase expression in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells by Insulin-like growth factor II
- Inflammatory, Insulin resistance metabolic markers and pancreatic cancer: quo vadis?
- Influence of bicalutamide with or without tamoxifen or anastrozole on Insulin-like growth factor 1 and binding proteins in prostate cancer patients
- Influence of dietary Insulin scores on survival in colorectal cancer patients
- Influence of early enteral nutrition (EEN) on Insulin resistance in gastric cancer patients after surgery
- Influence of hormones on tumor growth, cell kinetics, estrogen receptor and Insulin-like growth factor-I-related protein of human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells …
- Influence of Inflammation, Insulin Resistance and Excess Body Size on Breast cancer Risk: A Nested Case-Control Study
- INFLUENCE OF Insulin AND METFORMIN ON PROSTATE cancer
- Influence of Insulin resistance on adiponectin receptor expression in breast cancer
- Influence of Insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus on cancer incidence.
- Influence of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Gene Expression in Women with Breast cancer: A Systematic Review
- Influence of pituitary stalk section on growth hormone, Insulin and TSH secretion in women with metastatic breast cancer
- Influence of remifentanil combined with propofol on sober and Insulin resistance in patients after esophageal cancer radical surgery
- Influence of tamoxifen on plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor I and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein I in breast cancer patients
- Influences of Maixiansan on Insulin-like growth factor hinding protein7 and apoptosis in rats with ulcerative colitis-related colorectal cancer
- Infusion therapy in sessions of general artificial hyperthermia using large doses of Insulin in cancer patients
- Inhibition of apoptosis by amphiregulin via an Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-dependent pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines
- Inhibition of Apoptosis by Amphiregulin via an Insulin‐like Growth Factor‐1 Receptor—Dependent Pathway in Non‐Small Cell Lung cancer Cell Lines
- Inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by Insulin receptor downregulation
- Inhibition of colon cancer cell growth by dietary components: role of the Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system.
- Inhibition of growth and increased expression of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and-6 in prostate cancer cells stably transfected with antisense …
- Inhibition of growth of prostatic cancer cell lines by peptide analogues of Insulin-like growth factor 1
- Inhibition of growth, production of Insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II), and expression of IGF-II mRNA of human cancer cell lines by antagonistic analogs of growth …
- Inhibition of human MCF-7 breast cancer cells and HT-29 colon cancer cells by rice-produced recombinant human Insulin-like growth binding protein-3 …
- Inhibition of in vivo breast cancer growth by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to type I Insulin like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) mRNA acting through a specific …
- Inhibition of in vivo breast cancer growth by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor mRNA involves inactivation of ErbBs …
- Inhibition of Insulin receptor isoform-A signalling restores sensitivity to gefitinib in previously de novo resistant colon cancer cells
- Inhibition of Insulin-and Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated growth of human breast cancer cells by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and the vitamin D3 analogue EB1089
- Inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor by CP-751,871 radiosensitizes non–small cell lung cancer cells
- Inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling by the vitamin D analogue EB1089 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: A role for Insulin-like growth factor binding …
- Inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor receptor/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin axis targets colorectal cancer stem cells by attenuating mevalonate …
- Inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling enhances growth-inhibitory and proapoptotic effects of gefitinib (Iressa) in human breast cancer …
- Inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling impairs proliferation of head and neck, lung, prostate and breast cancer cells
- Inhibition of Insulin-like growth factor-I-mediated cell signaling by the von Hippel-Lindau gene product in renal cancer
- Inhibition of Insulin-like Growth Factor–Binding Protein-3 Signaling through Sphingosine Kinase-1 Sensitizes Triple-Negative Breast cancer Cells to EGF Receptor …
- Inhibition of Insulin‑like growth factor 1 signaling synergistically enhances the tumor suppressive role of triptolide in triple‑negative breast cancer cells
- Inhibition of mitochondria ATP synthase suppresses prostate cancer growth through reduced Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 secretion by prostate stromal cells
- Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase selectively inhibits cell proliferation in human breast cancer cells displaying enhanced Insulin-like growth factor I …
- Inhibition of mTOR and targeting Insulin-like growth factor I synergistically enhance taxol-induced cytotoxicity in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer cells.
- Inhibition of Src and Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IR/IGF-1R) on tumors and bone turnover in prostate cancer (PCa) models in vivo compared with …
- Inhibition of T47D human breast cancer cell growth by the synthetic progestin R5020: effects of serum, estradiol, Insulin, and EGF
- Inhibition of the biologic response to Insulin-like growth factor I in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by a new monoclonal antibody to the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor …
- Inhibition of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) tyrosine kinase as a novel cancer therapy approach
- Inhibition of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor enhances effects of simvastatin on prostate cancer cells in co-culture with bone
- Inhibition of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor potentiates acute effects of castration in a rat model for prostate cancer growth in bone
- Inhibition of tumor cell kinetics and serum Insulin growth factor I levels by octreotide in colorectal cancer patients
- Inhibition of type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling attenuates the development of breast cancer brain metastasis
- Inhibitors of Insulin-like growth factor signaling: a therapeutic approach for breast cancer
- Inhibitors of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor tyrosine kinase are preferentially cytotoxic to nutrient-deprived pancreatic cancer cells
- Inhibitory effect of exogenous Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 on proliferation of human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-453 and its mechanism
- Inhibitory effect of small interfering RNA targeting Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in ovarian cancer OVCAR3 cells
- Insight into the growth hormone–Insulin-like growth factor-I axis in cancer cachexia
- Insights into Insulin resistance, lifestyle, and anthropometric measures of patients with prior colorectal cancer compared to controls: a National Health and Nutrition …
- Insights into the pharmacologic inhibition of Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase in cancer: avoiding severe metabolic toxicity
- Insulin action and metabolism in patients with head and neck cancer
- Insulin action on glucose and branched-chain amino acid metabolism in cancer cachexia: differential effects of Insulin.
- Insulin allergy and immunologic Insulin resistance caused by interleukin-6 in a patient with lung cancer
- Insulin analog linked to breast cancer risk
- Insulin analogs and cancer
- Insulin analogs and cancer: a note of caution
- Insulin analogues and cancer risk: cause for concern or cause célèbre?
- Insulin analogues and cancer risk: the emergence of second-generation studies
- Insulin analogues display IGF‐I‐like mitogenic and anti‐apoptotic activities in cultured cancer cells
- Insulin analogues to stimulate cell growth in human cancer initiating cells (CICs).
- Insulin and Breast cancer Risk
- Insulin and C-peptide response to oral glucose in patients with breast cancer
- Insulin and cancer
- Insulin and cancer: Should one worry?
- Insulin and colon cancer
- Insulin and Diazoxide for treatment of cancer
- Insulin and endometrial cancer
- Insulin and estrogen receptor ligand influence the FGF-2 activities in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Insulin and glucose homeostasis in childhood cancer survivors treated with abdominal radiation: A pilot study.
- Insulin and hybrid Insulin/IGF receptors are major regulators of breast cancer cells
- Insulin and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 cooperate in pancreatic cancer cells to increase cell viability
- Insulin and IGF-1 in Breast cancer Patients are Associated with Tumor Cell Proliferation (Ki67) in their Breast Tumors
- Insulin and IGF-I as determinants of low ‘Western’cancer rates in the rural third world
- Insulin and IGFs in obesity-related breast cancer
- Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor signaling are defective in the MDA MB-468 human breast cancer cell line
- Insulin and Insulin-like growth factors act as renal cell cancer intratumoral regulators
- Insulin and leptin levels in obese patients with and without breast cancer
- Insulin and Metformin Control Cell Proliferation by Regulating TDG-Mediated DNA Demethylation in Liver and Breast cancer Cells
- Insulin and Metformin Control Cell Proliferation by Regulating Thymine DNA Glycosylase-Mediated DNA Demethylation in Liver and Breast cancer Cells
- Insulin and NADPH-generating enzymes as molecular targets to repress colon cancer cell proliferation
- Insulin and related factors in breast-cancer mortality
- Insulin and related factors in premenopausal breast cancer risk
- Insulin and risk of pancreatic cancer
- Insulin binding by a cell line (HT 29) derived from human colonic cancer
- Insulin breast cancer connection: confirmatory data set the stage for better care
- Insulin caused drug resistance to oxaliplatin in colon cancer cell line HT29
- Insulin clearance in normal and cancer involved human kidneys
- Insulin controls key steps of carbohydrate metabolism in cultured HT29 colon cancer cells
- Insulin decreases therapeutic efficacy in colon cancer cell line HT29 via the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway
- Insulin effects on methotrexate polyglutamate synthesis and enzyme binding in cultured human breast cancer cells
- Insulin enhancement of the antitumor activity of chemotherapeutic agents in colorectal cancer is linked with downregulating PIK3CA and GRB2
- Insulin enhances metabolic capacities of cancer cells by dual regulation of glycolytic enzyme pyruvate kinase M2
- Insulin enhances migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells by up-regulation of FOXC2
- Insulin exacerbated high glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostatic epithelial cells BPH-1 and prostate cancer cells PC-3 via MEK/ERK signaling …
- Insulin gene enhancer protein 1 mediates glycolysis and tumorigenesis of gastric cancer through regulating glucose transporter 4
- Insulin glargine (Lantus) and cancer risk
- Insulin glargine and cancer
- Insulin glargine and cancer risk in patients with diabetes: a meta-analysis
- Insulin glargine and cancer risk: an opinion statement of the Endocrine and Metabolism Practice and Research Network of the American College of Clinical Pharmacy
- Insulin glargine and cancer–Authors’ reply
- Insulin glargine and cancer—an unsubstantiated allegation
- Insulin glargine and cancer: a storm in a glass of water?
- Insulin glargine and cancer: another side to the story?
- Insulin Glargine and Incidence of cancer—An Ongoing Debate
- Insulin glargine and risk of cancer: a cohort study in the French National Healthcare Insurance Database
- Insulin glargine and risk of cancer: a meta-analysis
- Insulin glargine and the risk of cancer
- Insulin glargine use and breast cancer risk: associations with cumulative exposure
- Insulin glargine use and breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
- Insulin glargine use and short-term incidence of breast cancer—a four-year population-based observation
- Insulin growth factor (IGF) 1, IGF-binding proteins and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Insulin growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7)-related cancer and IGFBP3 and IGFBP7 crosstalk
- Insulin growth factor enhances colon cancer risk
- Insulin Growth Factor Receptor as a Prognostic Marker in Operable Squamous-Cell Laryngeal cancer
- Insulin growth factor receptor‐1 expression and loss of PTEN protein predict early recurrence in triple‐negative breast cancer
- Insulin growth factor signaling is regulated by microRNA-486, an underexpressed microRNA in lung cancer
- Insulin growth factor-1 pathway in cervical carcinoma cancer stem cells
- Insulin growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) expression as a prognostic indicator of local recurrence in conservatively treated breast cancer: a case-control study
- Insulin growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) expression in small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
- Insulin growth factor-binding protein 2 is a candidate biomarker for PTEN status and PI3K/Akt pathway activation in glioblastoma and prostate cancer
- Insulin in aging and cancer: antidiabetic drug Diabenol as geroprotector and anticarcinogen
- Insulin in combination with cisplatin induces the apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells via p53 and JNK activation
- Insulin in the adjuvant breast cancer setting: a novel therapeutic target for lifestyle and pharmacologic interventions?
- Insulin increases apoptotic resistance in prostate cancer cells, but are sensitised by metformin
- Insulin increases de novo steroidogenesis in prostate cancer cells
- Insulin induces anticancer cytotoxicity of 5-Fu to two human colon cancer cell lines
- Insulin induction instigates cell proliferation and metastasis in human colorectal cancer cells
- Insulin is an important risk factor of endometrial cancer among premenopausal women: a case-control study in China
- Insulin levels and Body Mass Index in non-diabetic pre-and post-menopausal women with breast cancer
- Insulin like growth factor (IGF) and IGF binding proteins in growth hormone dysregulation and abnormal glucose tolerance in small cell lung cancer patients
- Insulin like growth factor 2 regulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Insulin like growth factor and its association with lung, breast, and prostate cancer: a brief review
- Insulin like growth factor binding protein-7 reduces growth of human breast cancer cells and xenografted tumors
- Insulin like growth factor I is an autocrine regulator of human colon cancer cell differentiation and growth
- Insulin Like Growth Factor I Receptor Function in Estrogen Receptor Negative Breast cancer
- Insulin Like Growth Factor I Receptor Function in Estrogen Receptor Negative Breast cancer. Addendum
- Insulin like growth factor in breast cancer subtypes.
- Insulin mediates hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human pancreatic cancer ASPC-1 cells
- Insulin pathway related genes and risk of colorectal cancer: INSR promoter polymorphism shows a protective effect
- Insulin prevents leptin inhibition of RM1 prostate cancer cell growth
- Insulin priming effect on estradiol-induced breast cancer metabolism and growth
- Insulin promotes pancreatic cancer: evidence for endocrine influence on exocrine pancreatic tumors
- Insulin promotes progression of colon cancer by upregulation of ACAT1
- Insulin promotes proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through the extracellular regulated kinase pathway
- Insulin promotes proliferative vitality and invasive capability of pancreatic cancer cells via hypoxia-inducible factor 1α pathway
- Insulin Promotes Proliferative Vitality and Invasive Capability of Pancreatic cancer Cells via Hypoxia-inducible Factor 1α Pathway
- Insulin protects against hepatic bioenergetic deterioration induced by cancer cachexia: an in vivo 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy study
- Insulin receptor (IR) and Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF-1R) signaling systems: novel treatment strategies for cancer
- Insulin receptor alternative splicing during development and cancer
- Insulin receptor and cancer
- Insulin receptor and GPCR crosstalk stimulates YAP via PI3K and PKD in pancreatic cancer cells
- Insulin receptor compensates for IGF1R inhibition and directly induces mitogenic activity in prostate cancer cells
- Insulin receptor compensates for IGF1R inhibition and induces mitogenic activity in prostate cancer cell lines
- Insulin receptor expression and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer.
- Insulin receptor expression and function in human breast cancer cell lines
- Insulin receptor expression and survival of patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- Insulin receptor H1085H C> T and Insulin receptor substrate 1 G972R polymorphisms and prostate cancer risk: a pilot study
- Insulin receptor is an independent predictor of a favorable outcome in early stage breast cancer
- Insulin receptor isoform A modulates metabolic reprogramming of breast cancer cells in response to IGF2 and Insulin stimulation
- Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity Insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells
- Insulin receptor isoform B is downregulated in intestinal stem cells and tumors, limits colon cancer cell growth, and promotes differentiation
- Insulin receptor isoform expression in ovarian cancer in African American women
- Insulin receptor isoform variations in prostate cancer cells
- Insulin receptor isoforms A and B as well as Insulin receptor substrates-1 and-2 are differentially expressed in prostate cancer
- Insulin receptor isoforms and Insulin-like growth factor receptor in human follicular cell precursors from papillary thyroid cancer and normal thyroid
- Insulin receptor isoforms in cancer
- Insulin receptor kinase inhibition is better tolerated than hypoInsulinemia and more effective than metformin in treating breast cancer
- Insulin receptor signaling activated by penta-O-galloyl-α-D-glucopyranose induces p53 and apoptosis in cancer cells
- Insulin receptor substrate 1 is a target for the pure antiestrogen ICI 182,780 in breast cancer cells
- Insulin receptor substrate 1 may play divergent roles in human colorectal cancer development and progression
- Insulin receptor substrate 1 modulates the transcriptional activity and the stability of androgen receptor in breast cancer cells
- Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 modulates the transcriptional activity and turnover of Androgen Receptor in breast cancer cells.
- Insulin receptor substrate 1, a novel oncogene target in breast cancer
- Insulin receptor substrate adaptor proteins mediate prognostic gene expression profiles in breast cancer
- Insulin receptor substrate is a mediator of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation in quiescent pancreatic cancer cells
- Insulin receptor substrate suppression by the tyrphostin NT157 inhibits responses to Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin in breast cancer cells
- Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) and IRS-2 expression levels are associated with prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) mediates progesterone receptor-driven stemness and endocrine resistance in oestrogen receptor+ breast cancer
- Insulin receptor substrate-1 expression is regulated by estrogen in the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line
- Insulin receptor substrate-1 is an important mediator of ovarian cancer cell growth suppression by all-trans retinoic acid
- Insulin receptor substrate-1 regulates the transformed phenotype of BT-20 human mammary cancer cells
- Insulin Receptor Substrate-2 (IRS-2): A Novel Hypoxia-Responsive Gene in Breast cancer: A Dissertation
- Insulin receptor substrate-2 gene polymorphism: is it associated with endometrial cancer?
- Insulin receptor substrate-4 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and promotes retinoblastoma–cyclin-dependent kinase activation
- Insulin Receptor Substrate-4 Regulates HepG2 cancer Cells Motility Stimulated by EGF in A FAK/AKT-dependent Mechanism
- Insulin receptor substrates mediate distinct biological responses to Insulin-like growth factor receptor activation in breast cancer cells
- Insulin Receptor Substrates-1 And-2 Regulate cancer Cell Proliferation
- Insulin receptor targeting in breast cancer through yeast surface display
- Insulin receptor: what role in breast cancer?
- Insulin receptors in breast cancer
- Insulin receptors in breast cancer: biological and clinical role
- Insulin receptors in human cancer.
- Insulin resistance (IR) and prognosis of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients
- Insulin Resistance and Abnormal Glucose Tolerance After Paediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Blood cancer Survivors
- Insulin resistance and body composition in cancer patients
- Insulin Resistance and Breast cancer in Postmenopausal Women
- Insulin resistance and breast cancer incidence and mortality in postmenopausal women in the Women’s Health Initiative
- Insulin resistance and breast‐cancer risk
- Insulin resistance and cachexia development in patients with metastatic upper gastrointestinal cancer
- Insulin resistance and cancer risk: an overview of the pathogenetic mechanisms
- Insulin resistance and cancer-specific and all-cause mortality in postmenopausal women: the Women’s Health Initiative
- Insulin resistance and cancer: epidemiological evidence
- Insulin Resistance and cancer: Epidemiology, Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications
- Insulin resistance and cancer: the role of Insulin and IGFs
- Insulin resistance and cancer.
- Insulin resistance and colon cancer in African Americans and Caucasians
- Insulin resistance and colon cancer promotion in rats on diets differing in fat, energy, and starch
- Insulin resistance and colorectal cancer risk: the role of elevated plasma resistin levels
- Insulin resistance and endometrial cancer (GI, G2) in postmenopausal women
- Insulin resistance and endometrial cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Insulin Resistance and Endometrial cancer: Emerging Role for microRNA
- Insulin resistance and familial history of breast cancer
- Insulin resistance and hyperInsulinaemia in the development and progression of cancer
- Insulin resistance and hyperInsulinemia correlate with colorectal cancer promotion
- Insulin resistance and inflammation in black women with and without breast cancer: Cause for concern
- Insulin Resistance and Insulin Receptor Isoform A in cancer [J]
- Insulin resistance and long-term cancer-specific and all-cause mortality: The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI)
- Insulin resistance and prostate cancer risk
- Insulin resistance and risk of renal cell cancer: a case-control study
- Insulin Resistance and Thyroid cancer
- Insulin resistance as a predictor of venous thromboembolism in breast cancer
- Insulin resistance contributes to racial disparities in breast cancer prognosis in US women
- Insulin resistance in breast cancer: relevance and clinical implications
- Insulin resistance in cancer cachexia and metabolic syndrome
- Insulin resistance in cancer patients is associated with enhanced tumor necrosis factor-α expression in skeletal muscle
- Insulin resistance in pancreatic cancer
- Insulin resistance in patients with advanced prostate cancer undergoing intermittent or continuous androgen blockade.
- Insulin resistance in patients with advanced prostate cancer who received surgical castration
- Insulin resistance in patients with cancer
- Insulin resistance in patients with cancer: relationships with tumor site, tumor stage, body-weight loss, acute-phase response, and energy expenditure
- Insulin resistance in patients with colorectal cancer
- Insulin resistance in prostate cancer patients and predisposing them to acute ischemic heart disease
- Insulin Resistance Is a Common Core Tethered to Diabetes and Pancreatic cancer Risk
- Insulin resistance is another factor that increases the risk of recurrence in patients with thyroid cancer
- Insulin resistance is associated with early gastric cancer: a prospective multicenter case control study
- Insulin resistance is associated with elevated circulating androgens in postmenopausal women: A potential pathway for breast cancer etiology
- Insulin resistance is inversely related to prostate cancer: a prospective study in Northern Sweden
- Insulin resistance was connected with the alterations of substrate utilization in patients with cancer
- Insulin resistance-related biomarker clustering and subclinical inflammation as predictors of cancer mortality during 21.5 years of follow-up
- Insulin Resistance–Related Gene Polymorphisms and Risk of Prostate cancer
- Insulin resistance, growth factors and cytokine levels in overweight women with breast cancer before and after chemotherapy
- Insulin Resistance, IGFs and Energy Balance on the Risk of Breast cancer
- Insulin resistance, Insulin‐like growth factor I and breast cancer: a hypothesis
- Insulin resistance, its consequences for the clinical course of the disease, and possibilities of correction in endometrial cancer
- Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes in Women at High Risk for Breast cancer
- Insulin resistance, obesity and breast cancer risk
- Insulin resistance, obesity, and liver cancer
- Insulin Resistance: A Hidden Risk Factor for Gastric cancer?
- Insulin resistance: a significant risk factor of endometrial cancer
- Insulin resistance: an independent risk factor for lung cancer?
- Insulin resistance: any role in the changing epidemiology of thyroid cancer?
- Insulin Resistance: Clinical Implications for cancer Treatment and Prevention
- Insulin resistance: Influence on cancer risk and cancer prognosis
- Insulin resistance/hyperInsulinemia and cancer mortality: the Cremona study at the 15th year of follow-up
- Insulin reversal of cancer cachexia in rats
- Insulin reverses ammonia‐induced anorexia and experimental cancer anorexia
- Insulin secretagogue use and circulating inflammatory C–C chemokine levels in breast cancer patients
- Insulin secretion and action in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Insulin secretion as a determinant of pancreatic cancer risk
- Insulin secretion, glucose production, and Insulin sensitivity in underweight and normal-weight volunteers, and in underweight and normal-weight cancer patients: a …
- Insulin sensitivity during combined androgen blockade for prostate cancer
- Insulin Sensitivity in Septic cancer‐Bearing Patients
- Insulin Signaling & Hypoxic Response in Brain cancer
- Insulin signaling in Insulin resistance states and cancer: a modeling analysis
- Insulin signaling network in cancer
- Insulin stimulated MCF7 breast cancer cells: Proteome dataset
- Insulin Stimulation of Fatty Acid Synthesis in Human Breast cancer Cells: Brief Communication
- Insulin stimulation of fatty acid synthesis in human breast cancer in long term tissue culture
- Insulin supplementation attenuates cancer-induced cardiomyopathy and slows tumor disease progression
- Insulin suppresses the expression and function of breast cancer resistance protein in primary cultures of rat brain microvessel endothelial cells
- Insulin Therapy and Breast cancer Risk
- Insulin therapy and cancer
- Insulin therapy and cancer in type 2 diabetes
- Insulin therapy and cancer risk in diabetes mellitus
- Insulin therapy and colorectal cancer risk among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
- Insulin therapy and colorectal cancer risk among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a systemic review and meta-analysis
- Insulin therapy and risk of colorectal cancer: an updated meta-analysis of epidemiological studies
- Insulin therapy and risk of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- Insulin therapy and the risk of colorectal cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta‐analysis of observational studies
- Insulin therapy contributes to the increased risk of colorectal cancer in diabetes patients: a meta-analysis
- Insulin therapy in diabetes and cancer risk: current understanding and implications for future study
- Insulin therapy, duration of diabetes linked to cancer risk
- Insulin treatment and breast cancer risk; A systematic review of in vitro, animal and epidemiological evidence
- Insulin treatment in cancer cachexia: effects on survival, metabolism, and physical functioning
- Insulin use and cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- Insulin use and cancer risk: the effect of choices in study design on risk estimates
- Insulin use and smoking jointly increase the risk of bladder cancer mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Insulin use is not significantly predictive for prostate cancer mortality in diabetic patients: a 12‐year follow‐up study
- Insulin use, adipokine profiles and breast cancer prognosis
- Insulin use, hormone receptor status and hematopoietic cytokines׳ circulation in women with diabetes mellitus and breast cancer
- Insulin-and obesity-related variables in early-stage breast cancer: correlations and time course of prognostic associations
- Insulin–cancer relationships: possible dietary implication
- Insulin-dependent leptin expression in breast cancer cells
- Insulin-increasing diabetes therapies raise risk of death from cancer
- Insulin-induced enhancement of antitumoral response to methotrexate in breast cancer patients
- Insulin-induced enhancement of MCF-7 breast cancer cell response to 5-fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide
- Insulin-induced gene 2 expression is associated with breast cancer metastasis
- Insulin-induced GPX4 Expression in Breast cancer Cells
- Insulin-like factor binding protein-3 promotes the G1 cell cycle arrest in several cancer cell lines
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) and the clinical course of prostate cancer, benign hyperplasia and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and IGF binding proteins in growth hormone dysregulation and abnormal glucose tolerance in small cell lung cancer patients
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) family and prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I down-regulates type 1 IGF receptor (IGF 1R) and reduces the IGF I response in A549 non-small-cell lung cancer and Saos-2/B-10 …
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) pathway targeting in cancer: role of the IGF axis and opportunities for future combination studies
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling in tumorigenesis and the development of cancer drug resistance
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-binding protein-3, and pancreatic cancer in male smokers
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 mutants that do not bind IGF-I or IGF-II stimulate apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-4 inhibits colony formation of colorectal cancer cells by IGF-independent mechanisms
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-6 inhibits IGF-II-induced but not basal proliferation and adhesion of LIM 1215 colon cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-II serum concentrations in patients with benign and malignant breast lesions: free IGF-II is correlated with breast cancer size
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and breast cancer risk: eight years on
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis
- Insulin-like growth factor (IgF)-I, IgF binding protein-3, and prostate cancer: correlation with gleason score
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-3 and breast cancer (BC) risk: A synthetic case-control study
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-II and IGF type I receptor (IGFR-I) expression in prostatic cancer.
- Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-I, IGF-II, IGF Binding Protein-3, and Risk of Colorectal cancer: a Nested Case-control Study in the JACC Study
- Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-I, IGF-II, IGF Binding Protein-3, and Risk of Colorectal cancer: A Nested Casecontrol Study in the JACC Study
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-independent action of IGF-binding protein-3 in Hs578T human breast cancer cells. Cell surface binding and growth inhibition
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-system mRNA quantities in normal and tumor breast tissue of women with sporadic and familial breast cancer risk
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) alters drug sensitivity of HBL100 human breast cancer cells by inhibition of apoptosis induced by diverse anticancer drugs
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and its receptor mRNA levels in breast cancer and adjacent non-neoplastic tissue
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) pathway targeting in the treat-ment of cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), IGF-1 density, and IGF-1/PSA ratio for prostate cancer detection
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), and breast cancer risk: pooled individual data analysis of 17 prospective studies
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 activates methionine adenosyltransferase 2A transcription by multiple pathways in human colon cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 and musculoskeletal pain among breast cancer patients on aromatase inhibitor therapy and women without a history of cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 and oestradiol promote cell proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells: new insights into their synergistic effects
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 and prostate cancer risk: a population-based, case-control study
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 and protein kinase B signalling in prostate cancer progression.
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 attenuates antiestrogen-and antiprogestin-induced apoptosis in ER+ breast cancer cells by MEK1 regulation of the BH3-only pro …
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 differentially regulates estrogen receptor-dependent transcription at estrogen response element and AP-1 sites in breast cancer …
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 effects on mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy in cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 gene polymorphism and breast cancer risk
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 gene polymorphism and breast cancer risk among arab omani women: a case-control study
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 gene polymorphism in women with breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 genotype, phenotype and breast cancer risk, by racial/ethnic group.
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 in relation to prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 in relation to prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia-reply to the letter from Cohen, Peehl and Rosenfeld
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 in relation to prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 is a potent stimulator of cervical cancer cell invasiveness and proliferation that is modulated by α v β 3 integrin …
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 pathway mutations and protein expression in resected non–small cell lung cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 polymorphism and breast cancer risk in Jewish women
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 promotes cancer cell growth via RAC1 activation in ovarian epithelial cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 promotes cancer progression via GTPase RAC activation in epithelial ovarian cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) as a target of MiR-497 and plasma IGF-1R levels associated with TNM stage of pancreatic cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) expression and survival in operable squamous-cell laryngeal cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor activates c-SRC and modifies transformation and motility of colon cancer in vitro.
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor affects the survival of primary prostate cancer patients depending on TMPRSS2-ERG status
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor enhances invasion and induces resistance to apoptosis of colon cancer cells through the Akt/Bcl-xL pathway
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor expression in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and its impact on overall survival
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor promotes the growth and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor targeted therapeutics: novel compounds and novel treatment strategies for cancer medicine
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in human breast cancer and their relation to estradiol and progesterone receptors
- Insulin-Like growth factor 1 related pathways and high-fat diet promotion of transgenic adenocarcinoma mouse prostate (TRAMP) cancer progression
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling is essential for mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy in cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 stimulates KCl cotransport, which is necessary for invasion and proliferation of cervical cancer and ovarian cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor 1-induced enolase 2 deacetylation by HDAC3 promotes metastasis of pancreatic cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 1, chromogranin A and prostate specific antigen serum levels in prostate cancer patients and controls
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 (IGF2) Signaling in Colorectal cancer—From Basic Research to Potential Clinical Applications
- Insulin-like growth factor 2 expression modulates Taxol resistance and is a candidate biomarker for reduced disease-free survival in ovarian cancer
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 in Physiology, cancer, and cancer Treatment
- Insulin-like growth factor 2 messenger RNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) is a marker of unfavourable prognosis in colorectal cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) in cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): post-transcriptional drivers of cancer progression?
- Insulin-like growth factor 2 promotes ovarian cancer growth and resistance to traditional chemotherapy.
- Insulin-like growth factor 2 silencing restores taxol sensitivity in drug resistant ovarian cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor and breast cancer risk: evidence from observational studies
- Insulin-like growth factor and epidermal growth factor signaling in breast cancer cell growth: focus on endocrine resistant disease
- Insulin-like growth factor and lung cancer
- Insulin-like Growth Factor Axis Elements in Breast cancer Progression
- Insulin-like growth factor axis gene polymorphisms and clinical outcomes in pancreatic cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor axis gene polymorphisms modify risk of pancreatic cancer
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein (IGFBP) 3 Suppresses HIF1a Expression in cancer Cells through Reactivating mTOR/Tln Pathway
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-3 levels in conditioned media of Hs578T human breast cancer cells are post-transcriptionally regulated.
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-3 protease activity secreted by MCF-7 breast cancer cells: inhibition by IGFs does not require IGF-IGFBP interaction
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 expression inhibits Insulin-like growth factor I action in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP2) expression is associated with radiation resistance and worse prognosis in rectal cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 is a marker for antiestrogen resistant human breast cancer cell lines but is not a major growth regulator
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 promotes ovarian cancer cell invasion
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2: an androgen-dependent predictor of prostate cancer survival
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGF-BP3) inhibits estrogen-stimulated breast cancer cell proliferation
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 mediates retinoic acid-and transforming growth factor β2-induced growth inhibition in human breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein expression in human small cell lung cancer cell lines
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) inhibits breast cancer cell motility
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) targets both the Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and integrin pathways for the inhibition of breast cancer cell …
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) upregulated by Helicobacter pylori and is associated with gastric cancer cells migration
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 inhibits cancer cell invasion and is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-1 Interacts with Integrins to Inhibit Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Induced Breast cancer Growth and Migration
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) as a novel biomarker in lung cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP2), CEA and Ca19-9 in monitoring colon cancer patients
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 alters the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to chemotherapy
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 expression by ER+ ve breast cancer cells is regulated by PI-3 kinase pathway signaling
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 is a novel therapeutic target associated with breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 level is increased in blood of lung cancer patients and associated with poor survival
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) facilitates the response to DNA-damaging chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer cells.
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) plays a role in the anti-tumorigenic effects of 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine (AZA) in breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) proteolysis in patients with colorectal cancer: A possible early prognostic factor of metastatic progression
- Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 (IGFBP-3) regulates mitochondrial dynamics, EMT and angiogenesis in progression of prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and Insulin receptor substrate-1 in breast cancer: correlation with clinical parameters and disease-free survival.
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 enhances etoposide-induced cell growth inhibition by suppressing the NF-κB activity in gastric cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 expression is associated with growth stimulation of T47D human breast cancer cells: the role of altered epidermal growth …
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 induces apoptosis in MCF7 breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 induces G1 cell cycle arrest with inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and 4 in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 inhibits migration of endometrial cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 inhibits the growth of non-small cell lung cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 is secreted as a phosphoprotein by human breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 links obesity and breast cancer progression
- Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR BINDING PROTEIN-3 MEDIATES 1α,25-DIHYDROXYVITAMIN D3 GROWTH INHIBITION IN THE LNCaP PROSTATE cancer …
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 mediates interleukin-24-induced apoptosis through inhibition of the mTOR pathway in prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 prevents retinoid receptor heterodimerization: implications for retinoic acid-sensitivity in human breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 Suppresses VEGF Expression and Inhibits Head and Neck Squamous cancer Cell Angiogenesis
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, induced by hypoxia inducible factor-1α, determines esophageal cancer cell adaptation to the microenvironment
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 (IGFBP-4) tumor and serum levels are increased across all stages of epithelial ovarian cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 and-5 modulate ligand-dependent estrogen receptor-α activation in breast cancer cells in an IGF-independent manner
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 gene therapy increases apoptosis by altering Bcl-2 and Bax proteins and decreases angiogenesis in colorectal cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 influences pancreatic cancer cell growth
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 activates programmed cell death in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) has a tumor-suppressive activity in human lung cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) is a potential tumor suppressor protein for prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 and cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 inhibits proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells via a senescence-like mechanism
- Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) in breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 1 and 3 and breast cancer outcomes
- Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and angiogenesis: from cancer to cardiovascular disease
- Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins as mediators of IGF-I effects on colon cancer cell proliferation
- Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins IGFBP3, IGFBP4, and IGFBP5 predict endocrine responsiveness in patients with ovarian cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in human breast cancer tissue
- Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins related to progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) …
- Insulin-like growth factor expression in breast cancer epithelium and stroma
- Insulin-like growth factor expression in human cancer cell lines
- Insulin-like growth factor gene polymorphisms and risk of pancreatic cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor genetic variation, colorectal cancer and diabetes
- Insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) gene polymorphism in patients with non-metastatic breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-3 in benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-binding proteins, and breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor I activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor I and prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor I and risk of epithelial invasive ovarian cancer by tumour characteristics: results from the EPIC cohort
- Insulin-like growth factor I and transforming growth factor α as autocrine growth factors in human pancreatic cancer cell growth
- Insulin-like growth factor I differentially regulates the expression of HIRF1/hCAF1 and BTG1 genes in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor I in pregnancy and maternal risk of breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor I induces tumor hexokinase RNA expression in cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor I is not a useful marker of prostate cancer in men with elevated levels of prostate-specific antigen
- Insulin-like growth factor I overexpression in human pancreatic cancer: evidence for autocrine and paracrine roles
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Polymorphisms in Breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor I preserves host lean tissue mass in cancer cachexia
- Insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) inhibition enhances response to trastuzumab in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) inhibition in trastuzumab (T) resistant HER2+ breast cancer (BrCa) cells
- Insulin-like growth factor I receptor antagonism augments response to chemoradiation therapy in colon cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor I receptor blockade enhances chemotherapy and radiation responses and inhibits tumour growth in human gastric cancer xenografts
- Insulin-like growth factor I regulates the expression of isoforms of Wilms’ tumor 1 gene in breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor I secreted from prostate stromal cells mediates tumor-stromal cell interactions of prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates telomerase activity in prostate cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor I suppresses bone morphogenetic protein signaling in prostate cancer cells by activating mTOR signaling
- Insulin-like growth factor I triggers nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1 in MCF-7S breast cancer cells
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor I, IGF-Binding Protein 3, and Lung cancer Risk in a Prospective Study of Men in
- Insulin-like growth factor I, IGF-binding protein 3, and lung cancer risk in a prospective study of men in China
- Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) immunohistochemistry in breast cancer: relationship with the most important morphological and biochemical prognostic parameters
- Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) regulates differential expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-XL and Survivin in African-American (AA) and Caucasian breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor II activates mitogenic signaling in pancreatic cancer cells via IRS-1
- Insulin-like growth factor II and colorectal cancer risk in women
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor II as a Prognostic Indicator in Breast cancer.
- Insulin-like growth factor II differential activation of the IGF-1 and Insulin receptors in African-American and Caucasian breast cancer tissues
- Insulin-like growth factor II mediates epidermal growth factor-induced mitogenesis in cervical cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor II mediates resveratrol stimulatory effect on cathepsin D in breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor II modulates the routing of cathepsin D in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA binding protein 3 (IMP3) is overexpressed in prostate cancer and correlates with higher Gleason scores
- Insulin-like growth factor Ⅱ mRNA binding protein 3 expression in the non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and its relationships with the prognosis
- Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA binding protein 3 regulates proliferation, invasion and migration of neuroendocrine cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA expression in human breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor II-messenger RNA-binding protein-3 and lung cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor II-producing metastatic colon cancer with recurrent hypoglycemia
- Insulin-like growth factor levels in cord blood, birth weight and breast cancer risk
- Insulin-like growth factor mediated stromal-epithelial interactions in human breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor pathway aberrations and gastric cancer; evaluation of prognostic significance and assessment of therapeutic potentials
- Insulin-like growth factor pathway genetic polymorphisms, circulating IGF1 and IGFBP3, and prostate cancer survival
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor Pathway–Targeted Therapy in Breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor pathway: a link between androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), Insulin resistance, and disease progression in patients with prostate cancer?
- Insulin-like growth factor physiology and cancer risk
- Insulin-like growth factor polymorphisms and colorectal cancer risk
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) in breast cancer subtypes
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) expression and survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients: a meta-analysis
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) expression and survival in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) gene copy number is associated with survival in operable non–small-cell lung cancer: a comparison between …
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) protein expression, mRNA expression and gene copy number in operable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR-1) and outcome measures in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with gefitinib
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR-1) is significantly associated with longer survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 as a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 mRNA expression as a prognostic marker in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 pathway signature correlates with adverse clinical outcome in ovarian cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor activity in cancer biology & therapy responses
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor and sphingosine kinase are prognostic and therapeutic targets in breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor and sphingosine kinase co-expression has prognostic and therapeutic potential in breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor expression and function in human breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor I signaling in a breast cancer cell line
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor I targeting in epithelial ovarian cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor levels are regulated by cell density and by long term estrogen deprivation in MCF7 human breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor polymorphism defines clinical outcome in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in tumorigenesis and drug resistance: a challenge for cancer therapy
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathways and resistance to tarceva (erlotinib) in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor type I as a target for cancer therapy
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor type I as a target for cancer therapy
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-IR) as a target for prostate cancer therapy
- Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 as an anti-cancer target: blocking transformation and inducing apoptosis
- Insulin-like growth factor receptors in colorectal cancer.
- Insulin-like growth factor signaling as a therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor signaling in normal mammary gland development and breast cancer progression
- Insulin-like growth factor signalling in oestrogen nonresponsive breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor system gene expression in cervical scrapes from women with squamous intraepithelial lesions and cervical cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor system gene expression in women with type 2 diabetes and breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor system in cancer: novel targeted therapies
- Insulin-like growth factor type I and Insulin-like growth factor type II stimulate oestradiol-17β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (reductive) activity in breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor type I receptor: a new target in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer patients
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor-induced resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin) in breast cancer (BC) xenografts in athymic mice can be measured using …
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and breast cancer risk: observational and Mendelian randomization analyses
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 alters apoptotic signalling in prostate cancer.
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 and 17β-estradiol down-regulate prostate apoptosis response-4 expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-1 AND BREAST cancer RISK IN KURDISH WOMEN
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal African-American women.
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 and childhood cancer risk
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 for prostate cancer detection in patients undergoing prostate biopsy
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 and risk of breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 attenuates cisplatin-induced γH2AX formation and DNA double-strand breaks repair pathway in non-small cell lung cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 enhances mortality risk in women with breast cancer through epithelial-mesenchymal transition initiation
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 genotypes and haplotypes influence the survival of prostate cancer patients with bone metastasis at initial diagnosis
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces lymphangiogenesis and facilitates lymphatic metastasis in colorectal cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 inscribes a gene expression profile for angiogenic factors and cancer progression in breast epithelial cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 is essential to the increased mortality caused by excess growth hormone: a case of thyroid cancer and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in a …
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 modulates polycomb Cbx8 expression and inhibits colon cancer cell apoptosis
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 promoter polymorphisms and colorectal cancer: a functional genomics approach
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) as a biomarker for resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) expression on circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and metastatic breast cancer outcome: results from the TransMYME trial
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy: advances and perspectives
- Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor as a Prognostic Factor for Breast cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor gene expression is associated with survival in breast cancer: a comprehensive analysis of gene copy number, mRNA and protein …
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor induces immunosuppression in lung cancer by upregulating B7–H4 expression through the MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Inhibitors: A Potential cancer Treatment: Patent Highlight
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling increases the invasive potential of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells via Src-FAK and FoxM1
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Signaling Increases the Invasive Potential of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Overexpressing Breast cancer Cells …
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signalling and acquired resistance to gefitinib (ZD1839; IRESSA™) in DU 145 human prostate cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: a mini review
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors in head and neck cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 regulates oestrogen production in breast cancer tissue.
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling promotes mitochondrial turnover and protection in cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling regulates miRNA expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human ovarian cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-1, IGF binding protein-3, and the risk of esophageal cancer in a nested case-control study
- Insulin-like growth factor-1, IGF-binding protein-3, C-peptide and colorectal cancer: a case-control study
- Insulin-like growth factor-1, Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3, and breast cancer risk: observational and Mendelian randomization analyses with∼ …
- Insulin-like growth factor-1, metabolic abnormalities, and pathological complete remission rate in HER2-positive breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant …
- Insulin-like growth factor-2 (IGF-2) activates estrogen receptor-α and-β via the IGF-1 and the Insulin receptors in breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like Growth Factor-2 (IGF-2) Activates Estrogen Receptor-α and-β via the IGF-1 and the Insulin Receptors in Breast cancer Cells.
- Insulin-like growth factor-2 is induced following 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy in SW620 human colon cancer cell line
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP-3) predisposes breast cancer cells to
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 and 5 are differentially regulated in ovarian cancer of different histologic types
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 induces caspase-dependent apoptosis through a death receptor-mediated pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 and prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 promotes prostate cancer cell growth via IGF-dependent or-independent mechanisms and reduces the efficacy of …
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 gene-202 A/C polymorphism is correlated with advanced disease status in prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in breast cancer: analysis with tissue microarray
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 inhibition of prostate cancer growth involves suppression of angiogenesis
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 is partially responsible for high-serum-induced apoptosis in PC-3 prostate cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 production by MCF-7 breast cancer cells: stimulation by retinoic acid and cyclic adenosine monophosphate and differential …
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 (IGFBP5) supports prostate cancer cell proliferation
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 inhibits the growth of human breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-6 and cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-6 produced by human PC-3 prostate cancer cells: isolation, characterization and its biological action
- Insulin-like growth factor-dependent proliferation and survival of triple-negative breast cancer cells: implications for therapy
- Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-1), IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), and outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC): Results from Intergroup Trial N9741
- Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and all-cancer mortality in older men: The Rancho Bernardo study
- Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and chosen parameters of hormonal condition in women with breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein-3 as predictors of advanced-stage prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-2 are increased in cyst fluids of epithelial ovarian cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding proteins blood serum levels in women with early-and late-stage breast cancer: mutual relationship and possible …
- Insulin-like growth factor-I activates gene transcription programs strongly associated with poor breast cancer prognosis
- Insulin-like growth factor-I activates NFκB and NLRP3 inflammatory signalling via ROS in cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and binding protein-3 and risk of cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and breast cancer therapy
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and breast cancer: epidemiological and clinical data
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and C-reactive protein during pregnancy and maternal risk of non-epithelial ovarian cancer: a nested case–control study
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and cancer mortality in older men
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and cancer risk
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and estrogen interactions in breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and its autocrine role in growth of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in culture
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and new opportunities for cancer prevention
- Insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer: a meta-analysis
- Insulin-like growth factor-i and risk of differentiated thyroid carcinoma in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition
- Insulin-like growth factor-I antagonizes the antiproliferative effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I as a risk factor for breast cancer among Ugandan women in Mulago National Referral Hospital
- Insulin-like growth factor-I axis as a pathway for cancer chemoprevention
- Insulin-like growth factor-I can mediate autocrine proliferation of human small cell lung cancer cell lines in vitro.
- Insulin-like growth factor-I concentration and risk of prostate cancer: results from the European Prospective Investigation into cancer and Nutrition
- Insulin-like growth factor-I dependent up-regulation of ZEB1 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human prostate cancer cells: Tisheeka R. Graham, Haiyen …
- Insulin-like growth factor-I induces chemoresistence to docetaxel by inhibiting miR-143 in human prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I induces CLU expression through Twist1 to promote prostate cancer growth
- Insulin-like growth factor-I induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression via PI3K, MAPK and PKC signaling pathways in human ovarian cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition via GSK-3β and ZEB2 in the BGC-823 gastric cancer cell line
- Insulin-like growth factor-I induces MAPK and JAK/STAT signaling and protects breast cancer cells from hormonally-induced cytostasis and cell death
- Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits cell growth in the a549 non-small lung cancer cell line
- Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits progesterone receptor expression in breast cancer cells via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin …
- Insulin-like growth factor-I promotes migration in human androgen-independent prostate cancer cells via the αvβ3 integrin and PI3-K/Akt signaling
- Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Protects Colon cancer Cells from
- Insulin-like growth factor-I protects colon cancer cells from death factor-induced apoptosis by potentiating tumor necrosis factor α-induced mitogen-activated protein …
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) dowregulation in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) targeting with monoclonal antibody cixutumumab (IMC-A12) inhibits IGF-I action in endometrial cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) translocates to nucleus and autoregulates IGF-IR gene expression in breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor antagonism results in increased cytotoxicity of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin and taxol
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in human oral cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in proliferation and motility of pancreatic cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibition by specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor NVP-AEW541 in endometrioid and serous papillary endometrial cancer cell lines
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor is a candidate molecular target for human esophageal squamous cell cancer.
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor NVP-AEW541 is active in breast cancer cells and enhances growth inhibition by herceptin through an increase in …
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor overexpression mediates cellular radioresistance and local breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling and resistance in breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: a supporting role to the epidermal growth factor receptor
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signalling and acquired resistance to gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) in human breast and prostate cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 heterodimerization contributes to trastuzumab resistance of breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I receptors are overexpressed and predict a low risk in human breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-I regulates GPER expression and function in cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-i signalling in tamoxifen sensitive and tamoxifen resistant breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I–dependent up-regulation of ZEB1 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human prostate cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor-I, IGF binding protein-3, and breast cancer in young women: a comparison of risk estimates using different peptide assays
- Insulin-like growth factor-I, interleukin-1 α and β in pancreatic cancer: role in tumor invasiveness and associated diabetes
- Insulin-like growth factor-I, its binding proteins (IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-3), and growth hormone and breast cancer risk in The Nurses Health Study II
- Insulin-like growth factor-I, soy protein intake, and breast cancer risk
- Insulin-like growth factor-I: a key regulator of human cancer risk?
- Insulin-like growth factor-II bound to vitronectin enhances MCF-7 breast cancer cell migration
- Insulin-like growth factor-II imprinting in cancer.
- Insulin-like growth factor-II methylation status in lymphocyte DNA and colon cancer risk in the Northern Sweden Health and Disease cohort
- Insulin-like growth factor-II participates in the biphasic effect of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist on ovarian cancer cell growth
- Insulin-like growth factor-II renders LIM 2405 human colon cancer cells resistant to butyrate-induced apoptosis: a potential mechanism for colon cancer cell survival in …
- Insulin-like growth factor-l and risk of breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factor-ll (IGF-II): a potential autocrine/paracrine growth factor for human breast cancer acting via the IGF-I receptor
- Insulin-like growth factor-related components and the risk of liver cancer in a nested case-control study
- Insulin-like growth factor-related signaling and cancer development
- Insulin-like Growth Factor–Binding Protein-2 Is a Target for the Immunomodulation of Breast cancer
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor–Binding Protein-3, Breast cancer Risk, and Different Serum Assays
- Insulin-like growth factor–type 1 receptor inhibitor NVP-AEW541 enhances radiosensitivity of PTEN wild-type but not PTEN-deficient human prostate cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factor: current concepts and new developments in cancer therapy
- Insulin-like growth factorⅠregulates the type IGF receptor in A549 non-small cell lung cancer and Lymphocytic cells
- Insulin-like growth factors (IGF), IGF-binding proteins (IGFBP), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in blood serum of patients with colorectal cancer
- Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF-binding proteins in active monitoring of localized prostate cancer: a population-based observational study
- Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) stimulate the release of alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and soluble IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor from MCF7 breast cancer cells
- Insulin-like growth factors and breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factors and breast cancer risk in Chinese women
- Insulin-like growth factors and breast cancer therapy
- Insulin-like growth factors and cancer
- Insulin-like growth factors and cancer: from basic biology to therapeutics.
- Insulin-like growth factors and cancer: no role in screening. Evidence from the BUPA study and meta-analysis of prospective epidemiological studies
- Insulin-like growth factors and cancer.
- Insulin-like growth factors and cytokines in pediatric cancer
- Insulin-like growth factors and Insulin control a multifunctional signalling network of significant importance in cancer
- Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Insulin-Like Growth Factor–Binding Proteins and Prostate cancer Risk: Results from the Prostate cancer Prevention Trial
- Insulin-like growth factors and its binding proteins in serum in colon cancer
- Insulin-like growth factors and kidney cancer risk in men
- Insulin-like growth factors and liver cancer risk in male smokers
- Insulin-like growth factors and ovarian cancer risk: a nested case-control study in three cohorts
- Insulin-like growth factors and prostate cancer
- Insulin-like growth factors and prostate cancer: a population-based case-control study in China
- Insulin-like growth factors and risk of kidney cancer in men
- Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in prostate cancer: Cause or consequence?☆
- Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in tumors and ascites of ovarian cancer patients: association with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- Insulin-like growth factors are essential to prevent anoikis in oestrogen-responsive breast cancer cells: importance of the type I IGF receptor and PI3-kinase …
- Insulin-like growth factors as targets for cancer treatment
- Insulin-like growth factors I and II receptors in the breast cancer survival disparity among African–American women
- Insulin-like growth factors in breast and prostatic cancer
- Insulin-like growth factors in breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factors in human breast cancer
- Insulin-like growth factors in lung cancer cell lines
- Insulin-like growth factors stimulate the release of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and degradation of IGFBP-4 in nonsmall cell lung cancer cell …
- Insulin-like growth factors, Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women: results from a US case-control study
- Insulin-like growth factors, Insulin, and growth hormone signaling in breast cancer: implications for targeted therapy
- Insulin-like growth factors, sex hormones, C-reactive protein, and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer.
- Insulin-like growth factors, their binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: analysis of individual patient data from 12 prospective studies
- Insulin-like-growth factor-binding-protein 7: an antagonist to breast cancer
- Insulin-lowering effects of metformin in women with early breast cancer
- Insulin-mediated acceleration of breast cancer development and progression in a nonobese model of type 2 diabetes
- Insulin-RB heterodimer: potential involvement in the linkage between aging and cancer
- Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase in Women with Breast cancer: A Role beyond the Regulation of Oxytocin and Vasopressin
- Insulin-regulated aminopeptidase/placental leucil Aminopeptidase (IRAP/P-lAP) and angiotensin IV-forming activities are modified in serum of rats with breast cancer …
- Insulin-resistant MDA-MB231 human breast cancer cells contain a tyrosine kinase inhibiting activity.
- Insulin-sensitizers, polycystic ovary syndrome and gynaecological cancer risk
- Insulin‐induced gene 2 expression correlates with colorectal cancer metastasis and disease outcome
- Insulin‐induced proliferation of bladder cancer cells is mediated through activation of the epidermal growth factor system
- Insulin‐like factor 3, luteinizing hormone and testosterone in testicular cancer patients: effects of β‐hCG and cancer treatment
- Insulin‐like growth factor (IGF) system components in human prostatic cancer cell‐lines: LNCaP, DU145, and PC‐3 cells
- Insulin‐like growth factor (IGF)‐I and IGF‐binding protein 3 and the risk of premenopausal breast cancer: a meta‐analysis of literature
- Insulin‐like growth factor (IGF)‐I rescues breast cancer cells from chemotherapy‐induced cell death–proliferative and anti‐apoptotic effects
- Insulin‐like growth factor (IGF)–binding protein‐3 (IGFBP‐3) proteolysis in patients with colorectal cancer: possible association with the metastatic potential of the …
- Insulin‐like growth factor 1 expression correlates with clinical outcome in K‐RAS wild type colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab and irinotecan
- Insulin‐like growth factor 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic liver cancer in men
- Insulin‐like growth factor 1 promotes proliferation and invasion of papillary thyroid cancer through the STAT3 pathway
- Insulin‑like growth factor 1 receptor expression in breast cancer tissue and mammographic density
- Insulin‐like growth factor 2 expression in prostate cancer is regulated by promoter‐specific methylation
- Insulin‐like growth factor 2 hypomethylation of blood leukocyte DNA is associated with gastric cancer risk
- Insulin‐like growth factor axis targeting in cancer and tumour angiogenesis–the missing link
- Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3 (IGFBP‐3) in the prostate and in prostate cancer: Local production, distribution and secretion pattern indicate a role in …
- Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3 (IGFBP‐3) potentiates paclitaxel‐induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
- Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3 induces early apoptosis in malignant prostate cancer cells and inhibits tumor formation in vivo
- Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐4 inhibits cell growth, migration and invasion, and downregulates COX‐2 expression in A549 lung cancer cells
- Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐related protein 1 (IGFBP‐rP1) has potential tumour‐suppressive activity in human lung cancer
- Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐related protein 1 (IGFBP‐rP1/mac 25) is reduced in human prostate cancer and is inversely related to tumor volume and …
- Insulin‐like growth factor I and risk of breast cancer by age and hormone receptor status—A prospective study within the EPIC cohort
- Insulin‐like growth factor I and risk of incident cancer in elderly men–results from MrOS (Osteoporotic Fractures in Men) in Sweden
- Insulin‐like growth factor I: Action and receptor characterization in human prostate cancer cell lines
- Insulin‐like growth factor ligands, receptors, and binding proteins in cancer
- Insulin‐like growth factor pathway genes and blood concentrations, dietary protein and risk of prostate cancer in the NCI Breast and Prostate cancer Cohort …
- Insulin‐like growth factor stimulation increases radiosensitivity of a pancreatic cancer cell line through endoplasmic reticulum stress under hypoxic conditions
- Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptors and Insulin‐like growth factor‐1‐like activity in human primary breast cancer
- Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 signaling is responsible for cathepsin G‐induced aggregation of breast cancer MCF‐7 cells
- Insulin‐like growth factor‐2 (IGF2) loss of imprinting marks a field defect within human prostates containing cancer
- Insulin‐like growth factor‐I gene polymorphism and breast cancer risk in Chinese women
- Insulin‐like growth factor‐I promotes multidrug resistance in MCLM colon cancer cells
- Insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor blockade reduces tumor angiogenesis and enhances the effects of bevacizumab for a human gastric cancer cell line, MKN45
- Insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor correlates with connexin 26 and Bcl‐xL expression in human colorectal cancer
- Insulin‐like growth factor‐I, Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3 and risk of benign prostate hyperplasia in the prostate cancer prevention trial
- Insulin‐like growth factor–binding protein‐3 and breast cancer survival
- Insulin‐like growth factors induce apoptosis as well as proliferation in LIM 1215 colon cancer cells
- Insulin‐like growth factors modulate the growth inhibitory effects of retinoic acid on MCF‐7 breast cancer cells
- Insulin‐like growth‐factor‐binding protein 3 is decreased in early‐stage operable pre‐menopausal breast cancer
- Insulin‐sensitising drugs versus the combined oral contraceptive pill for hirsutism, acne and risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and endometrial cancer in …
- Insulin–PI3K signalling: an evolutionarily insulated metabolic driver of cancer
- Insulin—carcinogen or mitogen? Preclinical and clinical evidence from prostate, breast, pancreatic, and colorectal cancer research
- Insulin, carbohydrate restriction, metabolic syndrome and cancer
- Insulin, CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins and lactate regulate the human 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 gene expression in colon cancer cell …
- Insulin, chemotherapy, and the mechanisms of malignancy: the design and the demise of cancer
- Insulin, estradiol levels and body mass index in pre-and post-menopausal women with breast cancer
- Insulin, glucose and the increased risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Insulin, glucose, Insulin resistance, and incident colorectal cancer in male smokers
- Insulin, glucose, Insulin resistance, and pancreatic cancer in male smokers
- Insulin, growth factors, and cancer cell energy metabolism: an hypothesis on oncogene action
- Insulin, IGFs, and energy balance: Relevance to cancer risk.
- Insulin, Insulin receptors, and cancer
- Insulin, Insulin resistance, and cancer associations
- Insulin, Insulin resistance, obesity, and cancer
- Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), IGF binding proteins, their biologic interactions, and colorectal cancer
- Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor-I and breast cancer risk in Japanese women
- Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor-I, and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women
- Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor-I, endogenous estradiol and risk of colorectal cancer in postmenopausal women
- Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor-I, endogenous estradiol, and risk of colorectal cancer in postmenopausal women
- Insulin, Insulin-like growth factors and colon cancer: a review of the evidence
- Insulin, leptin, and tumoral adipocytes promote murine pancreatic cancer growth
- Insulin, macronutrient intake, and physical activity: are potential indicators of Insulin resistance associated with mortality from breast cancer?
- Insulin, physical activity, and caloric intake in postmenopausal women: breast cancer implications
- Insulin, the Insulin-like growth factor axis, and mortality in patients with nonmetastatic colorectal cancer
- Insulin: a novel agent in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer
- Insulin/IGF and sex hormone axes in human endometrium and associations with endometrial cancer risk factors
- Insulin/IGF Axis in Breast cancer: Clinical Evidence and Translational Insights
- Insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway driving aging and cancer as a target for pharmacological intervention
- Insulin/IGF-driven cancer cell-stroma crosstalk as a novel therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer
- Insulin/IGF-I hybrid receptors play a major role in IGF-I signaling in thyroid cancer
- Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor-I and estrogen cooperate to stimulate cyclin E-Cdk2 activation and cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells …
- Insulin/Insulin-like growth factors in cancer: new roles for the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, tumor resistance mechanisms, and new blocking strategies
- Insulin/PI3K signalling pathway regulates the expression of survivin in liver cancer HepG2 cells
- Intact and total Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) levels in relation to breast cancer risk factors: a cross-sectional study
- Integrating Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) score into Barcelona Clinic Liver cancer (BCLC) and cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) scores.
- Integration of downstream signals of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor by endoplasmic reticulum stress for estrogen-induced growth or apoptosis in breast cancer …
- Intensive versus conventional Insulin therapy in nondiabetic patients receiving parenteral nutrition after D2 gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a randomized controlled …
- Intensive versus conventional Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes patients undergoing D2 gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a randomized controlled trial
- Interaction between cyclooxygenase-2 and Insulin-like growth factor in breast cancer: A new field for prevention and treatment
- Interaction between estrogen receptor alpha and Insulin/IGF signaling in breast cancer.
- Interaction between nuclear Insulin receptor substrate-2 and NF-κB in IGF-1 induces response in breast cancer cells
- Interaction of breast cancer and Insulin resistance on PD1 and TIM3 expression in peripheral blood CD8 T cells
- Interaction of Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin resistance-related genetic variants with lifestyle factors on postmenopausal breast cancer risk
- Interaction of Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin resistance-related genetic variants with obesity and lifestyle factors on postmenopausal breast cancer risk
- Interactions between Insulin-like growth factor-I, estrogen receptor-α (ERα) and ERβ in regulating growth/apoptosis of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
- Interactions between plasma levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D, Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 and C-peptide with risk of colorectal cancer
- Interactions of the Insulin-like growth factor axis and vitamin D in prostate cancer risk in the prostate cancer prevention trial
- Interleukin-1 blocks Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor-stimulated growth in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by inhibiting receptor tyrosine kinase activity
- Interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) and IL-6 modulate Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) secretion in colon cancer epithelial (Caco-2) cells
- Interrelationships between plasma testosterone, SHBG, IGF-I, Insulin and leptin in prostate cancer cases and controls
- Interventions to improve Insulin resistance for the prevention of endometrial cancer
- Intestinal Insulin/IGF1 signalling through FoxO1 regulates epithelial integrity and susceptibility to colon cancer
- Intra-Pancreatic Insulin Nourishes cancer Cells: Do Insulin-Receptor Antagonists such as PGG and EGCG Play a Role?
- Intracellular presence of Insulin and its phosphorylated receptor in non‐small cell lung cancer
- Introduction of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 gene into human bladder cancer cells enhances their metastatic potential
- Inverse relation between prostate-specific antigen and Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 in bone metastases and serum of patients with prostate cancer
- Investigating the Insulin-like growth factor axis in head and neck cancer
- Investigation of Insulin resistance gene polymorphisms in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
- Investigation of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1), P53, and Wilms’ Tumor 1 (WT1) Expression Levels in the Colon Polyp Subtypes in Colon cancer
- Involvement of alternative splicing of the Insulin and androgen receptors in prostate cancer: role of the Insulin like growth factor axis
- Involvement of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated inhibition of breast cancer cell growth
- Involvement of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 in Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-B Ligand-Targeted Therapy in Mouse Model of Lung cancer Bone …
- Involvement of p53 in Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 regulation in the breast cancer cell response to DNA damage
- Involvement of the Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the cancer cell response to DNA damage
- IRS-1 and SOCS2 are key regulators of Insulin-like growth factor signaling in intestinal cancer
- Is elevated serum Insulin a marker of increased risk of colorectal cancer?
- Is Insulin resistance a predictor for complete response in breast cancer patients who underwent neoadjuvant treatment?
- Is Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 associated with metastasis in lung cancer?
- Is maternal variability in the Insulin-like growth factor I pathway associated with testicular cancer risk? A case-parent triad study.
- Is profound peripheral Insulin resistance in patients with pancreatic cancer caused by a tumor-associated factor?
- Is the mannose-6-phosphate/Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor coded by a breast cancer suppressor gene?
- Is the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor a therapeutic target in endometrial cancer?
- Is there an association between variants in candidate Insulin pathway genes IGF-I, IGFBP-3, INSR, and IRS2 and risk of colorectal cancer in the Iranian population?
- Is there any association between Insulin resistance and thyroid cancer?: a case control study
- Isoflavone effects on Insulin like growth factors and breast cancer.
- Isolated isoflavones do not affect the circulating Insulin-like growth factor system in men at increased colorectal cancer risk
- Isolation of a cDNA for a Growth Factor of Vascular Endothelial Cells from Human Lung cancer Cells: Its Identity with Insulin‐like Growth Factor II
- James Forsythe, MD, HMD: The Success of Integrative cancer Therapy Based on Chemosensitivity Testing and Insulin Potentiation Therapy
- Joint effect of Insulin-like growth factors and mutagen sensitivity in lung cancer risk
- Joint effect of Insulin-like growth factors and sex steroids on breast cancer risk
- Judicious toggling of mTOR activity to combat Insulin resistance and cancer: current evidence and perspectives
- Kaempferol downregulates Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and ErbB3 signaling in HT-29 human colon cancer cells
- Kallikrein 11 expressed in human breast cancer cells releases Insulin-like growth factor through degradation of IGFBP-3
- Kernel density estimation as a measure of environmental exposure related to Insulin resistance in breast cancer survivors
- Key protein expressions in the Insulin-like growth factor-1 signal pathway involved in the resistance of ovarian cancer to cisplatin
- Klotho expression in epithelial ovarian cancer and its association with Insulin-like growth factors and disease progression
- Knockdown of Insulin-like growth factor I receptor inhibits the growth and enhances chemo-sensitivity of liver cancer cells
- Knockdown of type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibits human colorectal cancer cell growth and downstream PI3K/Akt, WNT/β-catenin signal pathways
- Knotwood extract from Norway spruce (Picea abies) as treatment for androgen-independent prostate cancer: In vitro study of Insulin signaling and proliferation in PC-3 …
- Lack of any prognostic role of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in non-small cell lung cancer
- Lack of association between Insulin receptor substrate2 rs1805097 polymorphism and the risk of colorectal and breast cancer: a meta-analysis
- Lack of Association between Risk of Biliary Tract cancer and Circulating IGF (Insulin-like Growth Factor)-I, IGF-II or IGFBP-3 (IGF-binding Protein 3): A Nested …
- Lack of interaction between ErbB2 and Insulin receptor substrate signaling in breast cancer
- Lack of prognostic value of Insulin-like growth factor-1 in patients with breast cancer: analysis with tissue microarray
- Laminin-5 and Insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA binding protein-3 (IMP3) expression in preoperative biopsy specimens from oral cancer patients: Their role in neural …
- Laparoscopic surgery improves blood glucose homeostasis and Insulin resistance following distal gastrectomy for cancer
- Lapatinib induces apoptosis in trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer cells: effects on Insulin-like growth factor I signaling
- Lead identification to generate isoquinolinedione inhibitors of Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) for potential use in cancer treatment
- Lean mass is inversely associated with breast cancer, while abdominal adiposity and Insulin resistance increases the chances of developing the cancer
- Leptin and Insulin growth factor I in relation to breast cancer (Greece)
- Leptin and Insulin up-regulate miR-4443 to suppress NCOA1 and TRAF4, and decrease the invasiveness of human colon cancer cells
- Leptin in Breast cancer: Its Relationship with Insulin, Estrogens and Oxidative Stress
- Leptin, Insulin and body composition changes during adjuvant taxane based chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer, preliminary study
- let-7a and its target, Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, are differentially expressed in recurrent prostate cancer
- Let-7a regulation of Insulin-like growth factors in breast cancer
- Let‐7e enhances the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by directly targeting Insulin‐like growth factor 1 receptor
- Letter regarding article,“Associations of obesity and circulating Insulin and glucose with breast cancer risk: a Mendelian randomization analysis”
- Leucinostatin A inhibits prostate cancer growth through reduction of Insulin‐like growth factor‐I expression in prostate stromal cells
- Levels of Insulin-like growth factor during pregnancy and maternal cancer risk: a nested case–control study
- Levels of Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF binding proteins 2 and 3 in serial postoperative serum samples and risk of prostate cancer recurrence
- Lin28b promotes head and neck cancer progression via modulation of the Insulin-like growth factor survival pathway
- Link between Insulin and metabolic disorders in cancer: does leptin play a key role?
- Linoleic acid induces an increased response to Insulin in MDA‐MB‐231 breast cancer cells
- Lipolysis in lipid turnover, cancer cachexia, and obesity-induced Insulin resistance
- Lipopolysaccharide, TNFα, IL-6, dexamethasone, and Insulin increase the expression of GPR54 in the MCF7 breasr cancer cell line
- Liposomal Insulin promoter–thymidine kinase gene therapy followed by ganciclovir effectively ablates human pancreatic cancer in mice
- Local expression of Insulin-like growth factor-I affects angiogenesis in colorectal cancer
- Local expression of Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor, and estrogen receptor alpha in ovarian cancer
- Localization of Insulin Receptor Substrate-2 in Breast cancer: A Dissertation
- Long-acting Insulin analogs and cancer
- Long-acting Insulin analogs exposure and cancer specific mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus
- Long-Acting Insulin Analogues and Risk of Breast cancer—Meta-analysis
- Long-term effects of fenretinide, a retinoic acid derivative, on the Insulin-like growth factor system in women with early breast cancer
- Long-term effects of Insulin glargine on the risk of breast cancer
- Long-term metformin use reduces gastric cancer risk in type 2 diabetics without Insulin treatment: a nationwide cohort study
- Long-term use of basal Insulin and the risk of breast cancer
- Long-term use of Insulin glargine might increase the risk of breast cancer
- Long-term use of long-acting Insulin analogs and breast cancer incidence in women with type 2 diabetes
- Long‐term metformin use reduces gastric cancer risk in type 2 diabetics without Insulin treatment: a nationwide cohort study
- Longitudinal associations of blood biomarkers of Insulin and glucose metabolism and colorectal cancer risk in the Framingham Heart Study Offspring population (1971 …
- Longitudinal associations of blood markers of Insulin and glucose concentrations and cancer mortality in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination …
- Longitudinal associations of blood markers of Insulin and glucose metabolism and cancer mortality in the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Loss of imprinting and abnormal expression of Insulin-like growth factor II in gastric cancer
- Loss of imprinting and abnormal expression of the Insulin‐like growth factor 2 gene in gastric cancer
- Loss of imprinting of Insulin-like growth factor 2 is associated with increased risk of lymph node metastasis and gastric corpus cancer
- Loss of imprinting of Insulin-like growth factor 2 is associated with increased risk of primary lung cancer in the central China region
- Loss of imprinting of Insulin-like growth factor II is associated with increased risk of proximal colon cancer
- Loss of imprinting of the Insulin-like growth factor 2 gene and risk of colorectal cancer
- Loss of imprinting of the Insulin-like growth factor II gene occurs by biallelic methylation in a core region of H19-associated CTCF-binding sites in colorectal cancer
- Loss of Insulin Receptor Substrates 1 and 2 Suppresses Kras-Driven Non-Small Cell Lung cancer
- Loss of Insulin-like growth factor II imprinting is a hallmark associated with enhanced chemo/radiotherapy resistance in cancer stem cells
- Loss of Insulin-like growth factor II receptor expression promotes growth in cancer by increasing intracellular signaling from both IGF-I and Insulin receptors
- Low levels of Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor expression at cancer cell membrane predict liver metastasis in Dukes’ C human colorectal cancers
- Low serum Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1): a significant association with prostate cancer.
- Low-dose chemotherapy with Insulin (Insulin potentiation therapy) in combination with hormone therapy for treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer
- LOW-PENETRANCE SUSCEPTIBILITY GENES FOR COLORECTAL cancer IN THE Insulin/Insulin GROWTH FACTOR 1 AXIS
- Lower Concentrations of Glucose or Insulin Decrease the Risk of Various Types of cancer in the Long-Lived Ames Dwarf Mouse by Increasing the Expression …
- Lung cancer–Related Mortality With Inhaled Insulin or a Comparator: Follow-Up Study of patients previously enrolled in Exubera Controlled Clinical Trials (FUSE) …
- Lupeol, a novel diet-based triterpene modulates Insulin growth factor receptor 1 and β-catenin signaling in human prostate cancer cells
- Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists interfere with the mitogenic activity of the Insulin-like growth factor system in androgen-independent prostate cancer …
- Luteolin decreases IGF-II production and downregulates Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in HT-29 human colon cancer cells
- Luteolin inhibits Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells
- Lycopene enhances docetaxel’s effect in castration-resistant prostate cancer associated with Insulin-like growth factor I receptor levels
- Lycopene interferes with cell cycle progression and Insulin-like growth factor I signaling in mammary cancer cells
- Lycopene supplementation elevates circulating Insulin-like growth factor–binding protein-1 and-2 concentrations in persons at greater risk of colorectal cancer
- Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and impairs Insulin secretion function of β-cell
- Mammary cancer in transgenic mice expressing Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II)
- Marginal effects of glucose, Insulin and Insulin‑like growth factor on chemotherapy response in endothelial and colorectal cancer cells
- Markers of Insulin resistance and colorectal cancer mortality
- Markers of Insulin resistance and sex steroid hormone activity in relation to breast cancer risk: a prospective analysis of abdominal adiposity, sebum production, and …
- Material-induced Senescence (MIS): Fluidity induces senescent type cell death of lung cancer cells via Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5
- Matrix metalloproteinase 9 promotes breast cancer through regulation of Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins
- Measurement of Insulin-like growth factor axis does not enhance specificity of PSA-based prostate cancer screening
- Mechanism involved in genistein activation of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor expression in human breast cancer cells
- Mechanism of protein kinase B activation by Insulin IGF1 revealed by specific inhibitors of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Significance for diabetes and cancer
- Mechanisms linking diet and colorectal cancer: the possible role of Insulin resistance
- Mechanisms of acquired resistance to Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line
- Mechanisms of antibody-mediated Insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) down-regulation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
- Mechanisms of disease: signaling of the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor pathway—therapeutic perspectives in cancer
- Mechanisms of Insulin resistance in cancer associated malnutrition
- Mechanisms of regulation of cell adhesion and motility by Insulin receptor substrate-1 in prostate cancer cells
- Mechanisms underlying lack of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Mechanistic links between obesity, Insulin, and cancer
- Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR): a point of convergence in the action of Insulin/IGF-1 and G protein-coupled receptor agonists in pancreatic cancer …
- Medically managed hypercholesterolemia and Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus preoperatively predicts poor survival after surgery for pancreatic cancer
- Meeting Report: 3 rd International Workshop on Insulin & cancer Heidelberg, Germany, October 30-31, 2010
- Megestrol acetate may stimulate the production of Insulin-like growth factor 1 in breast tissues of women with breast cancer
- MEK1 and MEK2 differentially regulate human Insulin-and Insulin glargine-induced human bladder cancer T24 cell proliferation
- Membrane localization of Insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) is associated with decreased overall survival in breast cancer
- Mendelian Randomization Analysis Identifies Body Mass Index and Fasting Insulin as Potential Causal Risk Factors for Pancreatic cancer Risk
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among users of Insulin glargine.
- Meta-analysis of Insulin glargine and cancer risk.
- Meta-analysis of the association between Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 genetic polymorphisms and colorectal cancer susceptibility
- Metabolic disturbance and Insulin resistance in patients with colorectal cancer
- Metabolic health, Insulin, and breast cancer: Why oncologists should care about Insulin
- Metabolic modification by Insulin enhances methotrexate cytotoxicity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
- Metabolic syndrome and colon cancer: Is hyperInsulinemia/Insulin receptor-mediated angiogenesis a critical process?
- Metabolic syndrome and colorectal cancer: is hyperInsulinemia/Insulin receptor-mediated angiogenesis a critical process?
- Metabolic syndrome and Insulin resistance in patients with prostate cancer treated with androgen deprivation hormone
- Metabolic syndrome and Insulin resistance in relation to biliary tract cancer and stone risks: a population-based study in Shanghai, China
- Metabolic syndrome, central obesity and Insulin resistance are associated with adverse pathological features in postmenopausal breast cancer
- Metabolic syndrome, Insulin resistance, and inflammation in breast cancer: impact on prognosis and adjuvant interventions
- METABOLIC SYNDROME, Insulin RESISTANCE, AND SEDENTARY BEHAVIOR AMONG OVERWEIGHT AND OBESE BREAST cancer SURVIVORS
- Metastasis-associated protein 1 is an upstream regulator of DNMT3a and stimulator of Insulin-growth factor binding protein-3 in breast cancer
- Metformin affects breast cancer cell growth and disturbs an IGF1/Insulin related gene network that correlates with breast cancer progression
- Metformin and an Insulin/IGF-1 receptor inhibitor are synergistic in blocking growth of triple-negative breast cancer
- Metformin and cancer occurrence in Insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients
- Metformin and energy metabolism in breast cancer: from Insulin physiology to tumour-initiating stem cells
- Metformin disrupts crosstalk between G protein–coupled receptor and Insulin receptor signaling systems and inhibits pancreatic cancer growth
- Metformin inhibits the androgen mediated up-regulation of Insulin Growth Factor-I Receptor in prostate cancer cells
- Metformin inhibits the proliferation of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells via the downregulation of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- Metformin revert Insulin‐induced oxaliplatin resistance by activating mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in human colon cancer HCT116 cells
- Metformin, Insulin, breast cancer and more…
- Methylation of the Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 gene and prognosis of epithelial ovarian cancer
- Methylation status of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 concurs with the malignance of oral tongue cancer
- Methylation status of Insulin‐like growth factor‐binding protein‐3 promoter in prostate cancer tissues
- MHC-restricted phosphopeptides from Insulin receptor substrate-2 and CDC25b offer broad-based immunotherapeutic agents for cancer
- Micro RNA 145 targets the Insulin receptor substrate-1 and inhibits the growth of colon cancer cells
- Microarray Identifies Cyclo-oxygenase-2–Dependent Modulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 in Non-small Cell Lung cancer Cells
- MicroRNA-10b inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion in cervical cancer cells via direct targeting of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
- MicroRNA-126 inhibits the migration and invasion of endometrial cancer cells by targeting Insulin receptor substrate 1
- MicroRNA-139-5p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in human non-small cell lung cancer
- MicroRNA-140-5p targets Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) to suppress cervical cancer growth and metastasis
- microRNA-141 inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth and metastasis by targeting Insulin receptor substrate 2
- MicroRNA-145 directly targets the Insulin-like growth factor receptor I in human bladder cancer cells
- MicroRNA-146a inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting Insulin receptor substrate 2
- MicroRNA-30a inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis through down-regulation of type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor
- MicroRNA-497 is a potential prognostic marker in human cervical cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- MicroRNA-497 targets Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and has a tumour suppressive role in human colorectal cancer
- MicroRNA-503 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells via targeting Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- MicroRNA-664 targets Insulin receptor substrate 1 to suppress cell proliferation and invasion in breast cancer
- MicroRNA-7 functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA in gastric cancer by targeting Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
- MicroRNA-7 functions as antimetastic microRNA in gastric cancer by targeting Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- MicroRNA‑30a‑5p inhibits the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting Insulin‑like growth factor 1 receptor
- MicroRNA‑320a is downregulated in non‑small cell lung cancer and suppresses tumor cell growth and invasion by directly targeting Insulin‑like growth factor …
- MicroRNA‑320a suppresses tumor cell growth and invasion of human breast cancer by targeting Insulin‑like growth factor 1 receptor
- MicroRNA‑454‑3p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in esophageal cancer by targeting Insulin‑like growth factor 2 mRNA‑binding protein 1
- MicroRNA‑455 is downregulated in gastric cancer and inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion via targeting Insulin‑like growth factor 1 receptor
- MicroRNA‑497 inhibits tumor growth through targeting Insulin receptor substrate 1 in colorectal cancer
- MicroRNA‑766 inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression by directly targeting Insulin receptor substrate 2 and regulating the PI3K/Akt pathway
- Milk intake, circulating levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I, and risk of colorectal cancer in men
- Minireview: IGF, Insulin, and cancer
- miR-133a suppresses ovarian cancer cell proliferation by directly targeting Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- MiR-139 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor
- miR-140 suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- MiR-205 serves as a prognostic factor and suppresses proliferation and invasion by targeting Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 in human cervical cancer
- miR-223 enhances the sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells to erlotinib by targeting the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
- miR-29a regulated ER-positive breast cancer cell growth and invasion and is involved in the Insulin signaling pathway
- miR-497 may enhance the sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells to gefitinib through targeting the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
- MiR-99a suppress proliferation, migration and invasion through regulating Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in breast cancer
- miR‑197 promotes the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer by targeting Insulin‑like growth factor‑binding protein 3
- miRNAs in Insulin resistance and diabetes-associated pancreatic cancer: the ‘minute and miracle’molecule moving as a monitor in the ‘genomic galaxy’
- Mitogenic and anti-apoptotic effects of Insulin in endometrial cancer are phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt dependent
- Mitogenic signaling of Insulin-like growth factor I in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and is independent of mitogen …
- Mitogenic stimulation of human breast cancer cells in a growth factor‐defined medium: synergistic action of Insulin and estrogen
- Modulation of both Insulin resistance and cancer growth by inositol
- Modulation of Insulin degrading enzyme activity: A link between T2DM and liver cancer?
- Modulation of Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptors and membrane-associated IGF-binding proteins in endometrial cancer cells by estradiol
- Modulation of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and its signaling network for the treatment of cancer: current status and future perspectives
- Modulation of Insulin-like growth factors (IGF I-II) and IGF binding-protein 3 (IGFBP-3) through exercise training in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and …
- Modulation of Insulin-like growth factors following exercise in breast cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
- Modulation of response to radiation of human lung cancer cells following Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inactivation
- Modulation of the growth-inhibitory effects of progestins and the antiestrogen hydroxyclomiphene on human breast cancer cells by epidermal growth factor and Insulin
- Modulation of the Insulin-like growth factor-I system by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-retinamide in human breast cancer cell lines
- Molecular analysis of non–small cell lung cancer identifies subsets with different sensitivity to Insulin-like growth factor I receptor inhibition
- Molecular and circulatory expression of Insulin growth factors in Indian females with advanced cervical cancer
- Molecular aspects of the link between obesity, Insulin resistance and breast cancer.
- Molecular forms of the Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 in patients with colorectal cancer
- Molecular imaging of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer
- Molecular Interactions Between Insulin-like Growth Factor Signal Transduction and Retinoids in Breast cancer Cells
- Molecular links between energy balance and colorectal cancer risk: A key role for methylation of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein genes.
- Molecular pathology of lung cancer and Insulin-like growth factors
- Molecular predictors of response to a humanized anti–Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor monoclonal antibody in breast and colorectal cancer
- Molecular Profiling of Breast cancer Susceptibility of Obese or Insulin-Resistant and Pre-Diabetic Patients Using ITLN1 and CD295 SNPs
- Monoallelic expression of the Insulin-like growth factor-2 gene in ovarian cancer.
- More about: prospective study of colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3
- Mouse Models Used to Study the Effects of Diabetes, Insulin, and IGFs on cancer
- MP37-12 Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-I INDUCES CLU EXPRESSION THROUGH TWIST1 TO PROMOTE PROSTATE cancer GROWTH
- MP39-10 SERUM Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-1 (IGF-1) WAS A VALUABLE BIOMARKER TO PREDICT THE HIGH GRADE PROSTATE cancer IN FINAL …
- MP46-08 THE TYRPHOSTIN, NT157, SUPPRESSES Insulin RECEPTOR SUBSTRATES AND AUGMENTS THERAPEUTIC RESPONSE OF PROSTATE cancer
- MP46-10 UTILIZING Insulin IN THE TREATMENT OF PROSTATE cancer WITH BKM120 ABROGATES THE THERAPEUTIC EFFECT OF PI3K PATHWAY …
- MP68-09 Insulin RECEPTOR IS OVEREXPRESSED IN TUMOR BLOOD VESSELS AND PREDICTS WORSE OUTCOME IN BLADDER cancer
- mRNA expression of components of the Insulin-like growth factor system in breast cancer cell lines, tissues, and metastatic breast cancer cells.
- Multifunctional roles of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 in breast cancer
- Multihormonal regulation of Insulin-like growth factor-I-related protein in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
- Multihormonal regulation of the progesterone receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: interrelationships among Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor-I, serum, and …
- Multiple roles for the mannose-6-phosphate/Insulin-like growth factor II receptor in prostate cancer growth.
- Multiple signaling pathways are activated during Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) stimulated breast cancer cell migration
- Mutational analysis of the Insulin‑like growth factor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase domain in non-small cell lung cancer patients
- Myotubularin-related protein 7 inhibits Insulin signaling in colorectal cancer
- Nanog regulates self‐renewal of cancer stem cells through the Insulin‐like growth factor pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma
- Naproxen, clenbuterol and Insulin administration ameliorates cancer cachexia and reduce tumor growth in Walker 256 tumor-bearing rats
- Neuroendocrine cancer-specific up-regulating mechanism of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 in small cell lung cancer
- New advances on the functional cross-talk between Insulin-like growth factor-I and estrogen signaling in cancer
- New doctorial cancer research: novel animal models to study the role of the growth hormone Insulin-like growth factor I axis in prostate cancer
- New metformin derivative HL 156A prevents oral cancer progression by inhibiting the Insulin‐like growth factor/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathways
- New players for advanced prostate cancer and the rationalisation of Insulin-sensitising medication
- Newly diagnosed Insulin resistance in patients with esophageal cancer
- Nitric oxide inhibits the proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through degradation of Insulin receptor substrate-1 protein
- No association between genetic polymorphisms in Insulin and Insulin receptor substrate-1 and prostate cancer
- No association between serum Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-binding protein-3, and lung cancer risk
- No association of Insulin-like growth factor gene polymorphisms with survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- No effect of red clover–derived isoflavone intervention on the Insulin-like growth factor system in women at increased risk of colorectal cancer
- No Increased Risk of Breast cancer in Patients Exposed to Insulin Glargine Compared with Human NPH Insulin
- Non-metabolisable Insulin glargine does not promote breast cancer growth in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes
- Non-receptor mediated, post-transcriptional regulation of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-3 in Hs578T human breast cancer cells
- Non-small cell lung cancer cell survival crucially depends on functional Insulin receptors
- Nonsecreted Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) can induce apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells by IGF-independent mechanisms …
- Nordihydroguaiaretic acid, a cytotoxic Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor/HER2 inhibitor in trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer
- Normal protein anabolic response to hyperaminoacidemia in Insulin-resistant patients with lung cancer cachexia
- Normal protein anabolic response to hyperaminoacidemia in Insulin‐resistant patients with lung cancer cachexia
- Novel aspects concerning the functional cross-talk between the Insulin/IGF-I system and estrogen signaling in cancer cells
- Novel Insulin receptor substrate 1 and 2 variants in breast and colorectal cancer
- Novel multiplex method to assess Insulin, leptin and adiponectin regulation of inflammatory cytokines associated with colon cancer
- Novel stimulatory role for Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐2 in prostate cancer cells
- Novel Targets for the Treatment of Pancreatic cancer I: Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor
- Novel therapeutic targets in advanced gastric cancer: $$ b the Insulin-like growth factor signal transduction pathway
- NR2F2 plays a major role in Insulin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells
- Nuclear expression of Insulin receptor (InsR) adds prognostic information in primary breast cancer patients with high BMI
- Nuclear Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 as a biomarker in triple-negative breast cancer xenograft tumors: effect of targeted therapy and comparison …
- Nuclear localization of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in a lung cancer cell line
- Null association between Insulin-like growth factors, Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and prostate cancer in a prospective study
- Nutrition and breast cancer risk: can an effect via Insulin resistance be demonstrated?
- Nutrition, energy balance and colon cancer risk: the role of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor-I.
- Nutrition, hormones, and breast cancer: is Insulin the missing link?
- Nutrition, Insulin, IGF-1 metabolism and cancer risk: a summary of epidemiological evidence
- Nutrition, Insulin, Insulin-like growth factors and cancer
- Nutrition, physical activity and cancer risks: the role of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor-1
- Nutritional predictors of Insulin-like growth factor I and their relationships to cancer in men
- O4-4.3 cancer incidence and Insulin therapy in a cohort of diabetic patients
- Obesity and cancer risk: the role of the Insulin–IGF axis
- Obesity and cancer, a case for Insulin signaling
- Obesity and Insulin resistance in breast cancer–chemoprevention strategies with a focus on metformin
- Obesity, adipocytokines, and Insulin resistance in breast cancer
- Obesity, Dyslipidemia and Insulin Resistance in Survivors of Childhood cancer
- OBESITY, HYPERInsulinEMIA, THE Insulin AND Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR 1 RECEPTORS, AND RISK OF COLORECTAL cancer
- Obesity, Insulin and chemoresistance in colon cancer
- Obesity, Insulin resistance and breast cancer outcomes
- Obesity, Insulin resistance and cancer risk
- Obesity, Insulin Resistance and cancer: The PI3K connection
- Obesity, Insulin resistance and endometrial cancer risk
- Obesity, Insulin resistance and lifestyle factors: implications for prostate cancer screening
- Obesity, Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: risk factors for breast cancer
- Obesity, Insulin Resistance Pathway Factors, and Colon cancer
- Obesity, Insulin resistance, adipocytokines and breast cancer: New biomarkers and attractive therapeutic targets
- Obesity, Insulin resistance, and cancer prognosis: implications for practice for providing care among cancer survivors
- Obesity, Insulin resistance, and colorectal cancer: could miRNA dysregulation play a role?
- Obesity, Insulin, and colon cancer.
- Obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cancer: the Insulin and IGF connection
- Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and cancer: The Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Connection.
- Obesity, weight change, fasting Insulin, proInsulin, C-peptide, and Insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in women with and without breast cancer: the Rancho Bernardo …
- Observation of application mode of Insulin in perioperative colon cancer patients with diabetes mellitus
- Observation of different infusion methods of Insulin in TPN in gastric cancer patients with diabetes after operation
- Observations on the effects of suppressor of cytokine signaling 7 (SOCS7) knockdown in breast cancer cells: their in vitro response to Insulin like growth factor I (IGF-I)
- Oestrogen/Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor interaction in early breast cancer: clinical implications
- Omega-3 free fatty acids attenuate Insulin-promoted breast cancer cell proliferation
- On the status of β-cell dysfunction and Insulin resistance of breast cancer patient without history of diabetes after systemic treatment
- Oncogene activation induces metabolic transformation resulting in Insulin-independence in human breast cancer cells
- Oncogenes and Human cancer Blood Groups in cancer Copper and Inflammation Human Insulin
- Oncogenic function of the homeobox A13-long noncoding RNA HOTTIP-Insulin growth factor-binding protein 3 axis in human gastric cancer
- Oncogenic function of the homeobox A13-long noncoding RNA HOTTIP-Insulin growth factor-binding protein 3 axis in human gastric cancer.
- Oncogenic ras causes resistance to the growth inhibitor Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in breast cancer cells
- Oral consumption of green tea polyphenols inhibits Insulin-like growth factor-I–induced signaling in an autochthonous mouse model of prostate cancer
- Oral Insulin Secretagogues and cancer Risk in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Review
- Oral Insulin secretagogues, Insulin, and cancer risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Osthole inhibits Insulin-like growth factor-1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition via the inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in human brain cancer cells
- Over-expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein-1 (IGFBP-rP1/mac25) in the M12 prostate cancer cell line alters tumor growth by a …
- Overexpression of Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 induces loss of estrogen requirements for growth and transformation …
- Overexpression of Insulin receptor substrate-4 is correlated with clinical staging in colorectal cancer patients
- Overexpression of Insulin-like growth factor II alters serum sensitivity of breast cancer cells
- Overexpression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor is associated with penile cancer progression
- Overexpression of Insulin‐like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 (IGFBP1) Generates Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast cancer Cells
- Overexpression of Insulin‐like growth factor II (IGFII) in ZR‐75‐1 human breast cancer cells: higher threshold levels of receptor (IGFIR) are required for a proliferative …
- Overexpression of mature Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II leads to growth arrest in Caco-2 human colon cancer cells
- Overexpression of membrane glycoprotein PC-1 in MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells is associated with inhibition of Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity.
- Overexpression of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and autocrine stimulation in human cervical cancer cells
- Overlaps Between the Insulin and IGF-I Receptor and cancer
- P-10 Mitogenic activity and signaling pathways elicited by long-acting Insulin analogues Glargine and Detemir in colon cancer derived cell lines
- P-cadherin cooperates with Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor to promote metastatic signaling of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in ovarian cancer via …
- P10 Circulating Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) concentrations and incidence of cancer at 26 sites: prospective analyses in UK Biobank
- P3-016: In vitro activity of picropodophyllin in lung cancer cell lines and association to the Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 receptor
- P4-02-09: Estrogen-Related Receptor a Mediates Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Dependent Migration in Breast cancer Cells.
- P4-02-11: Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Promotes Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast cancer Cell Proliferation, in Part, through CYP1A1 Signaling.
- P4-07-15: Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor I (IGFIR) Expression in Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) of Patients with Early and Metastatic Breast cancer (BC).
- P5-06-04: Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor Inhibitor in MCF-7 Breast cancer Cell Line.
- Paclitaxel and trastuzumab treatment affects Insulin growth factor I expression in breast cancer cell lines
- Pamidronate and Clodronate Inhibit Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-I)-Induced HIF-1α Protein Accumulation and VEGF Expression in Human Breast cancer Cells
- Pancreatic cancer and factors associated with the Insulin resistance syndrome in the Korean cancer prevention study
- Pancreatic cancer cells activate CCL5 expression in mesenchymal stromal cells through the Insulin-like growth factor-I pathway
- Pancreatic Insulin secretion in exocrine pancreatic cancer
- Paracrine/autocrine regulation of breast cancer by the Insulin-like growth factors
- Paradoxical effects of overexpression of the type I Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor on the responsiveness of human breast cancer cells to IGFs and estradiol
- Patient concerns about Insulin and cancer
- Patients with both cognitive impairment and solid cancer present increased Insulin resistance
- Patterns of Intravenous Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Response Before and After Treatment with Streptozotocin (NSC-85998) in Patients with cancer 1, 2, 3
- PD33-04 INVERSE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN Insulin RECEPTOR EXPRESSION AND cancer PROGRESSION IN RENAL CELL CARCINOMA: CLINICAL AND …
- Peptide as potential imaging agent of breast cancer by phage display for Insulin receptor
- Permissive role of polyamines in the cooperative action of estrogens and Insulin or Insulin-like growth factor I on human breast cancer cell growth
- Perturbation by Insulin of human breast cancer cell cycle kinetics
- Pharmacological Strategies for Insulin Sensitivity in Obesity and cancer: Thiazolidinediones and Metformin
- Phenformin increases Insulin binding to human cultured breast cancer cells
- Phenotypes and genotypes of Insulin-like growth factor 1, IGF-binding protein-3 and cancer risk: evidence from 96 studies
- Phloroglucinol induces apoptosis through the regulation of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling pathways in human colon cancer HT-29 cells
- Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling regulates Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 expression in endometrial cancer cell lines
- Phosphorylated Insulin like growth factor-I receptor expression and its clinico-pathological significance in histologic subtypes of human thyroid cancer
- Phosphorylated Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor is implicated in resistance to the cytostatic effect of gefitinib in colorectal cancer cells
- Phosphorylated Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression predicts poor prognosis of Chinese patients with gastric cancer
- Phosphorylation of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein-3 by breast cancer cell membranes enhances IGF-I binding
- Physical activity and breast cancer: Quantitative risk assessment and investigation of Insulin-like growth factor proteins as a potential molecular pathway
- Physical activity, Insulin-like growth factor 1, Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3, and survival from colorectal cancer
- Physiological concentrations of Insulin augment pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and glucose utilization by activating MAP kinase, PI3 kinase and enhancing GLUT …
- Plasma and tissue Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) as a prognostic marker for prostate cancer and anti-IGF-IR agents as novel therapeutic strategy for …
- Plasma C‐peptide, Insulin‐like growth factor‐I, Insulin‐like growth factor binding proteins and risk of colorectal cancer in a nested case‐control study: The Japan …
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor 1, Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3, and risk of colorectal cancer: a prospective study in northern Sweden
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 proteolysis is increased in primary breast cancer
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor in primary breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentrations in human breast cancer
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), IGF-binding protein-3, and the risk of prostate cancer: a Matched Case-Control Study in a Korean population
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor-1 and binding protein-3 and subsequent risk of prostate cancer in the PSA era
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 levels as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of colorectal cancer
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor-I and serum IGF-binding protein 3 can be associated with the progression of breast cancer, and predict the risk of recurrence and the …
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study
- Plasma Insulin-like growth factors, Insulin-like binding protein-3, and outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from intergroup trial N9741
- Plasma Insulin‐like growth factor 1 is positively associated with low‐grade prostate cancer in the Health Professionals Follow‐up Study 1993–2004
- Plasma Insulin‐like growth factor I and its binding proteins 1 and 3 in postmenopausal patients with breast cancer receiving long term tamoxifen
- Plasma Insulin, C‐peptide and blood glucose and the risk of gastric cancer: The J apan P ublic H ealth C enter‐based prospective study
- Plasma Insulin, IGF-I and breast cancer
- Plasma Insulin, IGF‐binding proteins‐1 and‐2 and risk of colorectal cancer: a prospective study in northern Sweden
- Plasma levels of acid-labile subunit, free Insulin-like growth factor-I, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study
- Plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor-1 and binding protein-3, and their association with bladder cancer risk
- Plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I and lung cancer risk: a case-control analysis
- Polyethylene glycol conjugated Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) inhibits growth of breast cancer in athymic mice
- Polymorphic CA repeat length in Insulin-like growth factor 1 and risk of breast cancer in Iranian women
- Polymorphic markers associated with genes responsible for lipid and carbohydrate metabolism disorders and Insulin resistance in cancer patients
- Polymorphism of genes related to Insulin sensitivity and the risk of biliary tract cancer and biliary stone: a population-based case–control study in Shanghai, China
- Polymorphism of gnes rlated to Insulin sensitivity and the risk or biliary tract cancer and biliary stones: a population-based case-control study in Shanghai, China
- Polymorphism of the Insulin gene is associated with increased prostate cancer risk
- Polymorphism-23HPhI in the promoter of Insulin gene and pancreatic cancer: a pilot study
- Polymorphisms and circulating levels in the Insulin-like growth factor system and risk of breast cancer: a systematic review
- Polymorphisms in Insulin-related genes predispose to specific KRAS2 and TP53 mutations in colon cancer
- Polymorphisms in the Insulin like growth factor 1 and IGF binding protein 3 genes and risk of colorectal cancer
- Polymorphisms in the Insulin-like growth factor axis are associated with gastrointestinal cancer
- Polymorphisms of Insulin-like growth factor 1 pathway genes and breast cancer risk
- Positive expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor is associated with a positive hormone receptor status and a favorable prognosis in breast cancer
- Positive expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor is associated with a positive hormone receptor status in ovarian cancer
- Possible Involvement of Insulin Resistance in the Progression of cancer Cachexia in Mice.
- Possible roles of Insulin, IGF-1 and IGFBPs in initiation and progression of colorectal cancer
- Post genome-wide gene-environment interaction study: The effect of genetically driven Insulin resistance on breast cancer risk using Mendelian …
- Post Genome-Wide Gene–Environment Interaction Study Using Random Survival Forest: Insulin Resistance, Lifestyle Factors, and Colorectal cancer Risk
- Post-diagnosis serum Insulin-like growth factors in relation to dietary and lifestyle changes in the Prostate testing for cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) trial
- Post‐hypophysectomy Insulin response in patients with advanced breast cancer
- Postdiagnostic Dietary Glycemic Index, Glycemic Load, Dietary Insulin Index, and Insulin Load and Breast cancer Survival
- Postsynthetic regulation of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 by MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in culture
- Potential crosstalk between Insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 and epidermal growth factor receptor in progression and metastasis of pancreatic cancer
- Potential impact on breast cancer risk of circulating Insulin–like growth factor I modifications induced by oral HRT in menopause
- Potential Mechanisms Linking Insulin to cancer
- Potential molecular mechanisms of Insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)/Insulin like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) interaction in prostate cancer invasion
- Potential therapeutic strategies to interrupt Insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer
- Potential use of serum Insulin‐like growth factor 1 and E‐cadherin as biomarkers of colorectal cancer
- PPAR γ and colon and rectal cancer: associations with specific tumor mutations, aspirin, ibuprofen and Insulin-related genes (United States)
- PPARγ induces growth inhibition and apoptosis through upregulation of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in gastric cancer cells
- PRAS40 as a mediator of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-induced resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in head and neck cancer
- Pre-diagnosis Insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of epithelial invasive ovarian cancer by histological subtypes: a collaborative re-analysis from the Ovarian cancer …
- Pre‐diagnostic circulating Insulin‐like growth factor‐I and bladder cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into cancer and Nutrition
- Preclinical evaluation of a small molecule inhibitor of the IGF-1/Insulin receptor kinases in prostate cancer
- Preclinical evidence supporting cotargeting Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) and Src in non-small cell lung cancer.
- Prediagnosis circulating Insulin-like growth factors and pancreatic cancer survival
- Prediagnosis smoking, obesity, Insulin resistance, and second primary cancer risk in male cancer survivors: National Health Insurance Corporation Study
- Prediction the Risk of Breast cancer from Body Mass Index (BMI), Glucose and Insulin
- Predictors of fasting serum Insulin and glucose and the risk of pancreatic cancer in smokers
- Premenopausal breast cancer and the association between estrogen receptor status, Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 …
- Premenopausal Levels of Circulating Insulin-Like Growth Factor I and the Risk of Post-Menopausal Breast cancer: A Population-Based, Nested Case-Control Study
- Premenopausal levels of circulating Insulin-like growth factor I and the risk of postmenopausal breast cancer: A population-based, nested case-control study.
- Premenopausal levels of circulating Insulin‐like growth factor I and the risk of postmenopausal breast cancer
- Preoperative serum levels of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 predict prognosis of gastric cancer patients
- Prepubertal exposure to cow’s milk reduces expression of Insulin like growth factor-1 in the rat mammary gland and susceptibility to breast cancer
- Presence of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins correlates with tumor-promoting effects of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in breast cancer
- Present research on the status and the prospect of Insulin-like growth factor-I in head and neck cancer
- Pretreatment Insulin levels as a prognostic factor for breast cancer progression
- Pretreatment with Insulin enhances anticancer functions of 5‐fluorou‐racil in human esophageal and colonic cancer cells
- Prevalence of diagnosed cancer according to duration of diagnosed diabetes and current Insulin use among US adults with diagnosed diabetes: findings from the …
- Prevalence of Obesity, Dyslipidemia, and Insulin Resistance in Childhood cancer Survivors
- Preventive effect of 8 weeks moderate training on susceptible colon cancer factor (Insulin Growth Factor I and Insulin Growth Factor Binding Protein 3 in rats)
- Primary and Permissive Actions of Insulin in Breast cancer
- Processing of Insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) by human breast cancer cells
- Production of immunoreactive Insulin-like growth factor I and response to exogenous IGF-I in small cell lung cancer cell lines
- Production of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins by small-cell lung cancer cell lines
- Profiling the Roles of Insulin Receptor Substrate Isoforms 1 and 2 in Breast cancer
- Progesterone crosstalks with Insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer cells via induction of Insulin receptor substrate-2
- Progesterone receptor-B regulation of Insulin-like growth factor–stimulated cell migration in breast cancer cells via Insulin receptor substrate-2
- Progesterone Regulation of Insulin Receptor Substrates Mediates Focal Adhesion Formation in Breast cancer Cells
- Progesterone-induced secretion of growth hormone, Insulin-like growth factor I and prolactin by human breast cancer explants
- Progestin inhibition of estrogen-dependent proliferation in ZR-75-1 human breast cancer cells: antagonism by Insulin
- Progestin regulation of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor I receptors in cultured human breast cancer cells
- Progestins induce down-regulation of Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptors in human breast cancer cells: potential autocrine role of IGF-II
- Prognostic impact of Insulin receptor expression on survival of patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer
- Prognostic Implications of Tumoral Expression of Insulin Like Growth Factors 1 and 2 in Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung cancer
- Prognostic role of Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGFR-1) and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) expression in small cell lung cancer
- Prognostic role of Insulin‐like growth factor receptor‐1 expression in small cell lung cancer
- Prognostic role of plasma Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and IGF-binding protein 3 in metastatic colorectal cancer
- Prognostic significance of Insulin growth factor-I receptor and Insulin growth factor binding protein-3 expression in primary breast cancer
- Prognostic significance of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in human breast cancer
- Prognostic Significance of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein (IGFBP)-4 and IGFBP-5 Expression in Breast cancer
- Prognostic significance of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein expression in axillary lymph node-negative breast cancer
- Prognostic Significance of Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 in Hepatocellular cancer Patients: A Validation Study
- Prognostic significance of serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and Insulin-like growth factor-1 in advanced gastric cancer patients treated with FOLFOX …
- Prognostic value of Insulin-like growth factor 1 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 blood levels in breast cancer
- Prognostic value of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors in patients with colon/rectal cancer: correlation with plasma prolactin
- Prognostic value of receptors for Insulin-like growth factor 1, somatostatin, and epidermal growth factor in human breast cancer
- Prognostic value of vitamin D receptor and Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer
- Progress in the Research of Insulin-like Growth Factor Family in Gastric cancer
- Progress in the research of Insulin-like growth factor family in lung cancer
- Progress in the Research of Insulin-Like Growth Factor in Non-Small Cell Lung cancer [J]
- Progress of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in Colorectal cancer
- Prolactin does not require Insulin-like growth factor intermediates but synergizes with Insulin-like growth factor I in human breast cancer cells
- Proliferation of cultured human prostate cancer cells is inhibited by Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein-1: evidence for an IGF-II autocrine growth loop
- Proliferation of DU145 prostate cancer cells is inhibited by suppressing Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐2
- Proliferative and signaling activities of Insulin analogues in endometrial cancer cells
- Prolonged use of human Insulin increases breast cancer risk in Taiwanese women with type 2 diabetes
- Promoter-202 A/C polymorphism of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 gene and non-small cell lung cancer risk
- Promoter-specific transcription of Insulin-like growth factor-II in epithelial ovarian cancer
- Promoter− 202 A/C polymorphism of Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3 gene and non‐small cell lung cancer risk
- Promotion of cancer cell migration: an Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-independent action of IGF-binding protein-6
- Prospective evaluation of abnormal glucose metabolism and Insulin resistance in patients with atypical endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer
- Prospective Evaluation of Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Resistance Among Patients with Endometrial cancer and Atypical Endometrial Hyperplasia
- Prospective evaluation of Insulin resistance among endometrial cancer patients
- Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3
- Prospective study of prostate cancer in relation to serum concentrations of Insulin-like growth factor-1 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3.
- Prospective study reveals associations between colorectal cancer and type 2 diabetes mellitus or Insulin use in men
- PROSTATE cancer AND DIABETES LINK: ROLE OF Insulin AND Insulin LIKE GROWTH FACTORS
- Prostate cancer patients with unmanaged diabetes or on Insulin have worse outcomes and toxicities after treatment with radiation therapy
- Prostate cancer patients with unmanaged diabetes or receiving Insulin experience inferior outcomes and toxicities after treatment with radiation therapy
- Prostate cancer risk and serum levels of Insulin and leptin: a population-based study
- Prostate cancer risk in relation to a single nucleotide polymorphism in the Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP3) gene: a meta-analysis
- Prostate cancer risk in relation to Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3: A Nested Case-Control Study in Large Scale Cohort Study in …
- Prostate cancer Risk in Relation to Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-I and IGF-Binding Protein-3: A Nested Case-Control Study in Large Scale Cohort Study in …
- Prostate cancer risk in relation to Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3: a prospective multiethnic study
- Prostate cancer Risk is associated with Polymorphism of Insulin gene
- Prostate cancer, Insulin, and androgen deprivation therapy
- Prostate cancer: another aspect of the Insulin‐resistance syndrome?
- Prostate-specific antigen and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in nipple aspirate fluid are associated with breast cancer
- Prostatic cancer, hypogonadism, and Insulin resistance: A case report
- Prostatic fluid‐free Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 in relation to prostate cancer
- Protein anabolism is resistant to Insulin action in lung cancer cachexia
- Protein expression of PTEN, Insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR), and lethal prostate cancer: a prospective study
- Protein of type 1 binding Insulin-like growth factors in blood serum in cancer and prostatic adenoma
- Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B antagonized signaling by Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and kinase BRK/PTK6 in ovarian cancer cells
- Proteomic profiling of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) altered metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) after protein kinase B (Akt) inhibition: Insulin like growth factor …
- Proteomics demonstration that normal breast epithelial cells can induce apoptosis of breast cancer cells through Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 …
- PS 1587; Lung cancer: MicroRNA-146a Inhibits Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Non Small Cell Lung cancer by Targeting Insulin Receptor Substrate 2
- PTEN inhibits Insulin-stimulated MEK/MAPK activation and cell growth by blocking IRS-1 phosphorylation and IRS-1/Grb-2/Sos complex formation in a breast cancer …
- PTEN, Insulin resistance and cancer
- Purification of a colon cancer cell growth inhibitor and its identification as an Insulin-like growth factor binding protein
- Putative role of serum Insulin-like growth factor–1 (IGF-1) and IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) levels in the development of prostate cancer in Arab men
- PYCR1 interference inhibits cell growth and survival via c-Jun N-terminal kinase/Insulin receptor substrate 1 (JNK/IRS1) pathway in hepatocellular cancer
- Quality and quantity of visceral fat tissue are associated with Insulin resistance and survival outcomes after chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer
- Quantification of Insulin receptor mRNA splice variants as a diagnostic tumor marker in breast cancer
- Quantifying mediating effects of endogenous estrogen and Insulin in the relation between obesity, alcohol consumption, and breast cancer
- Quantitative determination of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor mRNA in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues of invasive breast cancer
- Rab GTPases Accelerates GLUT4 Translocation in Colorectal cancer Progression by Insulin/IGF System
- Racial differences in Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in men at increased risk of prostate cancer
- Randomized controlled trial of aerobic exercise on Insulin and Insulin-like growth factors in breast cancer survivors: the Yale Exercise and Survivorship study
- Re: Insulin resistance and prostate cancer risk
- Re: Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor-I, and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women
- Re: plasma Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study
- Re: Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3
- Re: Re: Role of the Insulin-like growth factors in cancer development and progression
- RE:“SERUM Insulin AND GLUCOSE LEVELS AND BREAST cancer INCIDENCE: THE ATHEROSCLEROSIS RISK IN COMMUNITIES STUDY”
- Reactive oxygen species regulate Insulin-induced VEGF and HIF-1α expression through the activation of p70S6K1 in human prostate cancer cells
- Realationship of Insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ and breast cancer
- Recent advances in the research on the relationship between Insulin resistance and endometrial cancer
- Recent advances on the role of microRNAs in both Insulin resistance and cancer
- Receptor binding and growth-promoting activity of Insulin-like growth factors in human breast cancer cells (T-47D) in culture
- Receptors for epidermal growth factor and Insulin-like growth factor I and their relation to steroid receptors in human breast cancer
- Receptors for Insulin-like growth factor-2 and androgens as therapeutic targets in triple-negative breast cancer
- Recombinant adenoviruses expressing dominant negative Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor demonstrate antitumor effects on lung cancer
- Recombinant human Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 inhibits tumor growth and targets the Akt pathway in lung and colon cancer models
- Recombinant Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐1 inhibits IGF‐I, serum, and estrogen‐dependent growth of MCF‐7 human breast cancer cells
- Recombinant PAPP-A resistant Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 4 (dBP4) inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis in a murine model of breast cancer
- Recruitment of Insulin receptor substrate-1 by erbB3 impacts on IGF-IR signalling in oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells
- Reduced expression of Insulin-like growth factor I receptors in MCF-7 breast cancer cells leads to a more metastatic phenotype
- Reduced Insulin sensitivity in differentiated thyroid cancer patients with suppressed TSH
- Reduction of the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor expression in DU145 human prostate cancer cell line by antisense RNA
- Regarding the article’Does the negative correlation found in breast cancer patients between plasma melatonin and Insulin-like growth factor-1 concentrations imply …
- Regulation of breast cancer cell motility by Insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) in metastatic variants of human breast cancer cell lines
- Regulation of breast cancer growth by Insulin-like growth factors
- Regulation of DUI45 human prostate cancer cell proliferation by Insulin‐like growth factors and its interaction with the epidermal growth factor autocrine loop
- Regulation of endometrial cancer cell growth by Insulin-like growth factors and the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone antagonist SB-75
- Regulation of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) II and IGF binding protein 3 autocrine loop in human PC-3 prostate cancer cells by vitamin D metabolite 1, 25 (OH) 2D3 …
- Regulation of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 in Ah responsive and Ah nonresponsive human breast cancer cells by 17 B-estradiol and 2, 3, 7, 8 …
- Regulation of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in ovarian cancer cells by oestrogen
- Regulation of Insulin-like growth factor receptor activity and its therapeutic targeting in cancer
- Regulation of Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor expression in A549 non-small cell lung cancer and Saos-2/B-10 osteoblastic osteosarcoma cells and its …
- Regulation of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein (IGFBP) Expression by Breast cancer Cells: Use of IGFBP-1 as as Inhibitor of Insulin-like Growth Factor …
- Regulation of Insulin-like growth factors and NF-kappaB by proteasome system in endometrial cancer
- Regulation of Insulin-like growth NF-κB proteasome system in endometrial cancer
- Regulation of Insulin‑like growth factor signaling by metformin in endometrial cancer cells
- Regulation of interleukin-8 expression in human prostate cancer cells by Insulin-like growth factor-I and inflammatory cytokines
- Regulation of the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene by oncogenes and antioncogenes: implications in human cancer
- Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human colon cancer by Insulin-like growth factor-I
- Regulatory Mechanism of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 in Non-Small Cell Lung cancer
- Relation between duration of androgen deprivation therapy and degree of Insulin resistance in men with prostate cancer
- Relation between Insulin resistance and breast cancer among Chilean women
- Relation between Insulin resistance and serum concentrations of IL-6 and TNF-α in overweight or obese women with early stage breast cancer
- Relation of blood lipids and Insulin to body fat content, body surface area and state of the subcutaneous fatty tissue in patients with breast and lung cancer
- Relation of serum Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein-3 to risk of prostate cancer (United States)
- Relations of Insulin Resistance and Serum Concentrations of Estradiol and Sex Hormone‐binding Globulin to Potential Breast cancer Risk Factors
- Relationship Between ABO Blood Groups and Insulin Resistance in Patients with Colon and Gastric cancer
- Relationship between aerobic capacity of African American males, serum concentration of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 and growth of prostate cancer cells
- Relationship between exogenous Insulin therapy and colorectal cancer in diabetic patients: a meta-analysis
- Relationship between Insulin Receptor (INSR rs 1799817) and Colorectal cancer (CRC)
- Relationship between Insulin resistance related factors and colon cancer stem cells
- Relationship between Insulin-like growth factor axis gene polymorphisms and clinical outcome in advanced gastric cancer patients treated with FOLFOX
- Relationship between Insulin-like growth factor II and prognosis of colorectal cancer
- Relationship between Insulin-like growth factor-1 and human testicular cancer
- Relationship between Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor and human papillomavirus in patients with oropharyngeal cancer
- Relationship between Prostate Sspecific Antigen and Testosterone, Insulin, Adeponectin on Prostate cancer Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
- Relationship between serum levels of Insulin-like growth factors and subsequent risk of cancer mortality: Findings from a nested case–control study within the Japan …
- Relationship of dyslipidemia, Insulin resistance, and prostate‑specific antigen with prostate cancer
- Relationship of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor expression to clinical outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer
- Relationship of obesity and physical activity with C-peptide, leptin, and Insulin-like growth factors in breast cancer survivors
- Relationship of Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor I and Parameters in Patients with Prostate cancer
- Relationship of serum isoflavone, Insulin and adiponectin levels with breast cancer risk
- Relationships between critical period of estrogen exposure and circulating levels of Insulin‐like growth factor‐I (IGF‐I) in breast cancer: evidence from a case‐control …
- Relationships between Insulin-like growth factor i and selected clinico-morphological parameters in colorectal cancer patients.
- Relationships between plasma Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and second breast cancer risk in a prevention trial of …
- Relationships of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor expression to clinical outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer
- Relaxation of imprinting of the Insulin-like growth factor II gene in colorectal cancer
- Relaxation of Insulin-Like Growth Factor II Imprinting in Prostate cancer Development
- Relaxation of Insulin‐like growth factor 2 gene imprinting in esophageal cancer
- Relevance of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor gene expression as a prognostic factor in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Repeat dose study of the cancer chemopreventive agent resveratrol in healthy volunteers: safety, pharmacokinetics, and effect on the Insulin-like growth factor axis
- Repeated measures of serum glucose and Insulin in relation to postmenopausal breast cancer
- Reply: Prostate cancer, Insulin and androgen deprivation therapy
- Repression of the Insulin receptor promoter by the tumor suppressor gene product p53: a possible mechanism for receptor overexpression in breast cancer
- Research advances in Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and its pathway in diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer
- Research advances in Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in pancreatic cancer
- Research Article Adipokines and Insulin Resistance in Young Adult Survivors of Childhood cancer
- Research progress in the relationship between Insulin like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) and lung cancer
- Resistance exercise reduces body fat and Insulin during androgen-deprivation therapy for prostate cancer
- Response of extensive breast cancer skin metastases to rechallenge with trastuzumab together with low-dose chemotherapy and Insulin
- Response of the Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system to IGF-IR inhibition and androgen deprivation in a neoadjuvant prostate cancer trial: effects of obesity and …
- Response to Comment on: Morden et al. Further Exploration of the Relationship Between Insulin Glargine and Incident cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Older …
- Response: More About: Prospective Study of Colorectal cancer Risk in Men and Plasma Levels of Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF)-I and IGF- Binding Protein-3
- Response: re: plasma Insulin-like growth factor-i, Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study
- Responses of human pancreatic cancer cells to treatment with Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor NVP-AEW541 alone and in …
- Restoration of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 has a tumor-suppressive activity through induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer
- Resveratrol attenuates prostate cancer growth by inhibiting Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling.
- Resveratrol inhibits Insulin-like growth factor-1 mediated migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells
- Resveratrol Phenocopies the Suppressive Effects of Insulin‐like Growth Factor Receptor‐1 siRNA on IGF‐1 Promoted Colon cancer Cell Proliferation
- Resveratrol regulates Insulin-like growth factor-II in breast cancer cells
- Rethinking the Relationship between Insulin and cancer
- Retinoic acid stimulation of the sodium/iodide symporter in MCF-7 breast cancer cells is meditated by the Insulin growth factor-I/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and p38 …
- Retinoic acid suppresses Insulin-induced cell growth and cyclin D1 gene expression in human breast cancer cells.
- Retnoic Acid-Induced Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF)-I and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 Secretion in Breast cancer Cell Involves in Selective …
- RETRACTED ARTICLE: Insulin-like growth factor 1 promotes growth of gastric cancer by inhibiting foxo1 nuclear retention
- RETRACTED: Quercetin suppresses Insulin receptor signaling through inhibition of the Insulin ligand-receptor binding and therefore impairs cancer cell proliferation.
- Retraction Notice to: The cancer-Associated FGFR4-G388R Polymorphism Enhances Pancreatic Insulin Secretion and Modifies the Risk of Diabetes
- Retraction: Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Suppresses Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling in Prostate cancer Cells by Activating mTOR Signaling
- RETRACTION: Quercetin suppresses Insulin receptor signaling through inhibition of the Insulin ligand–receptor binding and therefore impairs cancer cell proliferation
- Retraction: Targeting 3-Phosphoinoside-Dependent Kinase-1 to Inhibit Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Induced AKT and p70 S6 Kinase Activation in Breast cancer Cells
- Retrospective evaluation of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) and type II non-Insulin-dependent diabetes (NIDDM).
- Reversal of cathepsin D routing modulation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells expressing antisense Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II)
- Reversal of enhanced pancreatic cancer growth in diabetes by Insulin
- Review of: Inhibition of in vivo breast cancer growth by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor mRNA involves inactivation of …
- Review: Milk and milk products, Insulin-like growth factor-1 and cancer
- Ripk2 dictates blood Insulin and glucose responses to cancer drug and microbial xenobiotics
- Rising thyroid cancer incidence in the world might be related to Insulin resistance
- Risk factors for breast cancer and expression of Insulin-like growth factor-2 (IGF-2) in women with breast cancer in Wuhan City, China
- Risk of breast cancer by individual Insulin use: an international multicenter study
- Risk of breast cancer in patients exposed to Insulin glargine compared to human NPH Insulin.
- Risk of breast cancer in patients on long-acting Insulin analogues in comparison with those on human Insulin
- Risk of cancer in patients on Insulin glargine and other Insulin analogues in comparison with those on human Insulin: results from a large population-based …
- Risk of cancer in patients receiving Insulin glargine
- Risk of ovarian cancer in relation to prediagnostic levels of C-peptide, Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins-1 and-2 (USA, Sweden, Italy)
- RNAi‐mediated silencing of Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS‐1) enhances tamoxifen‐induced cell death in MCF‐7 breast cancer cells
- RNAi‐mediated silencing of Insulin receptor substrate‐4 enhances actinomycin D‐and tumor necrosis factor‐α‐induced cell death in hepatocarcinoma cancer cell …
- Role of cyclic AMP response element–binding protein in Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor up-regulation by sex steroids in prostate cancer cells
- Role of estrogen receptor (ER) α in Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I-induced responses in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Role of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I-induced responses in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Role of estrogen-induced Insulin-like growth factors in the proliferation of human breast cancer cells
- Role of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mouse Models of Breast cancer
- Role of Insulin and IGF-1 receptors in bronchial epithelial cancer cells
- Role of Insulin dysregulation in the development of yoshida sarcoma-induced cancer cachexia
- Role of Insulin in development of cancer cachexia in nongrowing sarcoma-bearing mice: special reference to muscle wasting.
- Role of Insulin like growth factor binding proteins and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer epithelial cells
- Role of Insulin receptor isoform A in breast cancer
- Role of Insulin receptor substrates and protein kinase C-ζ in vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor expression in pancreatic cancer …
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis in the development of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer epithelial cells
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in pancreatic cancer pathogenesis
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signalling in cancer
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signalling in cancer.
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin-D3-induced breast cancer cell apoptosis
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 in prevention of colon cancer
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 in pancreatic cancer cell survival
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) in breast cancer proliferation and metastasis
- Role of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptors in cancer Signaling
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling pathway in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor-2 in colorectal cancer.
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor-type 1 receptor (IGF-IR) signalling in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer
- Role of Insulin-like growth factor, Insulin-like growth factor receptors, and Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in ovarian cancer
- Role of Insulin-like growth factors and the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor in the estrogen-stimulated proliferation of human breast cancer cells.
- Role Of Insulin-Like Growth Factors Binding Protien 2 (IGFBP2) In Breast cancer
- Role of Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3 in breast cancer cell growth
- Role of Insulin‐like growth factor binding proteins in 1α,25‐dihydroxyvitamin D3‐induced growth inhibition of human prostate cancer cells
- Role of Insulin like growth factors family in endometrial cancer
- Role of IRS-1 signaling in Insulin-induced modulation of estrogen receptors in breast cancer cells
- Role of PRAS40 in mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) modulation in cancer and Insulin resistance
- Role of testosterone, estradiol, and Insulin in diet-and exercise-induced reductions in serum-stimulated prostate cancer cell growth in vitro
- Role of the Insulin-like growth factor family in cancer development and progression
- Role of the Insulin-like growth factor signaling system on post-confluent growth by MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Role of the Insulin-like growth factor system on an estrogen-dependent cancer phenotype in the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line
- Role of tumor necrosis factor system in pregnancy induced Insulin resistance and in the pathogenesis of cancer of the uterine cervix
- Roles of the Insulin-like growth factor system and nutrition in cancer
- Roles of transforming growth factor-beta, Insulin-like growth factors and proteases in human breast cancer
- Rye whole grain and bran intake compared with refined wheat decreases urinary C-peptide, plasma Insulin, and prostate specific antigen in men with prostate cancer
- S961, a biosynthetic Insulin receptor antagonist, downregulates Insulin receptor expression & suppresses the growth of breast cancer cells
- Sa1444 Does Insulin Influence the Risk of Colon Adenomas and Colorectal cancer? a Multicenter Look At a Minority Population
- Safety and efficacy of weight training in recent breast cancer survivors to alter body composition, Insulin, and Insulin-like growth factor axis proteins
- Sam68 mediates the activation of Insulin and leptin signalling in breast cancer cells
- Saturated free fatty acids activate a c-Src-JNK1 axis within lipid rafts: Implications for the development of Insulin resistance, obesity, and obesity-associated cancer
- Screen‐detected prostate cancer and the Insulin‐like growth factor axis: results of a population‐based case‐control study
- Search for breast cancer susceptibility genes in the growth hormone/Insulin-like growth factor-1 axis
- Secretion of an Insulin-like growth factor-I-related protein by human breast cancer cells
- Selective Effects of Glucose, Insulin and Leptin by Molecular Breast cancer Subtype.
- Selective tyrosine kinase inhibition of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor inhibits human and mouse breast cancer–induced bone cell activity, bone remodeling, and …
- Self reported non-Insulin dependent diabetes, family history, and risk of prevalent colorectal cancer: population based, cross sectional study
- Sensitivity of breast cancer cell lines to the novel Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) inhibitor NVP-AEW541 is dependent on the level of IRS-1 expression
- Sequencing of type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibition with chemotherapy in breast cancer cells.
- Serum adiponectin and Insulin-like growth factor 1 in predominantly female patients with thyroid cancer: association with the histologic characteristics of the tumor
- Serum and Insulin inhibit cell death induced by cycloheximide in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7
- Serum and tissue level of Insulin‐like growth factor‐I (IGF‐I) and IGF‐I binding proteins as an index of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer
- Serum and tissue levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I in women with dysplasia and HPV-positive cervical cancer
- Serum C-peptide, Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-binding proteins, and colorectal cancer risk in women
- Serum changes of adiponectin, Insulin resistance and their correlation in endometrial cancer patients
- Serum concentration of Insulin, C-peptide and Insulin-like growth factor I in patients with colon adenomas and colorectal cancer
- Serum concentrations of Insulin, Insulin-like growth factor I, vascular endothelial growth factor and gastrin in patients with colon adenomas and colorectal cancer
- SERUM GROWTH HORMONE IN PATIENTS WITH BREAST cancer AND Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-I LEVELS AND THEIR CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE [J]
- Serum human glandular kallikrein (hK2) and Insulin‐like growth factor 1 (IGF‐1) improve the discrimination between prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia …
- Serum Insulin and C-peptide concentration and breast cancer: a meta-analysis
- Serum Insulin and fructosamine levels and pancreatic cancer risk: A nested case-control study in Japan
- Serum Insulin and glucose levels and breast cancer incidence: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study
- Serum Insulin level, disease stage, prostate specific antigen (PSA) and Gleason score in prostate cancer
- Serum Insulin level, HOMA-IR and prostate cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Serum Insulin levels in patients with colorectal cancer
- Serum Insulin to predict time to castration-resistant progression and overall survival in metastatic androgen-dependent prostate cancer (mADPCa).
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and IGF-binding protein levels and risk of lung cancer: a case-control study nested in the β-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy Trial …
- Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) and IGF-binding Protein Levels and Risk of Lung cancer: A Case-Control Study Nested in the-Carotene and Retinol …
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 and IGF binding protein-3 in relation to breast cancer among Hispanic and white, non-Hispanic women in the US Southwest
- Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-l and in Lung cancer Patients
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-I) and prostatic cancer risk a retrospective study
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor 1 correlates with the risk of nodal metastasis in endocrine-positive breast cancer
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor axis and the risk of pancreatic cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor I and subsequent risk of colorectal cancer among Japanese-American men
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor I: tumor marker or etiologic factor? A prospective study of prostate cancer among Finnish men
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor-1 is not a useful marker of prostate cancer.
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in response to dasatinib-based regimens in bone-metastatic prostate cancer.
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) is increased and IGFBP-3 is decreased in patients with prostate cancer: correlation with serum prostate …
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in localized, metastasized prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor-I and platelet-derived growth factor as biomarkers of breast cancer prognosis
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor-I and tumor size in patients with metastatic liver cancer
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor-I is positively associated with serum prostate-specific antigen in middle-aged men without evidence of prostate cancer
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor-I levels and prostate cancer risk—interpreting the evidence
- Serum Insulin-like growth factor-I levels and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a clue to the relationship between IGF-I physiology and prostate cancer risk
- Serum Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF binding protein (IGFBP)-3 in patients with gastric cancer: IGFBP-3 protease activity induced by surgery
- Serum Insulin-like growth factors and mortality in localised and advanced clinically detected prostate cancer
- Serum Insulin-like Growth Factors I and II, Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 and Risk of Breast cancer in the JACC Study
- Serum Insulin-like growth factors, Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women
- Serum Insulin‐like growth factor (IGF)‐1 and IGF‐binding protein‐3 do not correlate with Gleason score or quantity of prostate cancer in biopsy samples
- Serum Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3/prostate‐specific antigen ratio is a useful predictive marker in patients with advanced prostate cancer
- Serum Insulin‐like growth factor I/free prostate specific antigen (IGF‐I/fPSA) ratio enhances prostate cancer detection in men with total PSA 4.0–10.0 ng/ml
- Serum Insulin‐like growth factor‐I and breast cancer
- Serum Insulin‐like growth factor‐I, Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3, and the risk of pancreatic cancer death
- Serum Insulin‐like Growth Factors, Insulin‐like Growth Factor‐binding Protein‐3, and Risk of Lung cancer Death: A Case‐control Study Nested in the Japan …
- Serum Insulin‐like, growth factor binding protein‐related protein 1 (IGFBP‐rP1) and endometrial cancer risk in Chinese women
- Serum Insulin, glucose, indices of Insulin resistance, and risk of lung cancer
- Serum Insulin, glucose, indices of Insulin resistance, and risk of prostate cancer
- Serum interleukin-8 and Insulin like growth factor-1 in Egyptian bladder cancer patients
- Serum leptin levels in gastric cancer patients and the relationship with Insulin resistance
- Serum Levels of Gastrin, and Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF-1) in Patients with Gastro-Esophageal cancer
- Serum levels of Insulin growth factor (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein predict risk of second primary tumors in patients with head and neck cancer
- Serum levels of Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-II, IGF-binding protein-3, and prostate-specific antigen as predictors of clinical prostate cancer
- Serum levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I in operable breast cancer in relation to the main prognostic variables and their perioperative changes in relation to those of …
- Serum levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I, IGF-binding protein 1 and 3, and Insulin and endometrial cancer risk
- Serum levels of Insulin-like growth factors (IGF-I and IGF-II) and their binding protein (IGFBP-3) are not elevated in pancreatic cancer
- Serum levels of Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and their binding proteins (IGFBPs),-1,-2,-3, in oral cancer
- SERUM LEVELS OF Insulin, IGF-1 AND PSA IN PROSTATE cancer PATIENTS IN LOCAL POPULATION
- Serum levels of leptin, Insulin, and lipids in relation to breast cancer in china
- Serum prolactin contributes to enhancing prolactin receptor and pJAK2 in type I endometrial cancer cells in young women without Insulin resistance
- Serum tumour necrosis factor alpha and Insulin resistance in gastrointestinal cancer
- Serum vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) as a specific biomarker for advanced cervical cancer: Relationship to Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II), IGF …
- Session 4: CVD, diabetes and cancer Diet, Insulin resistance and diabetes: the right (pro) portions: Symposium on ‘Dietary management of disease’
- Severe hypoglycaemia caused by raised Insulin-like growth factor II in disseminated breast cancer.
- Sex hormone, Insulin, and Insulin-like growth factor signaling in recurrence of high stage endometrial cancer: Results from the NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology …
- Short chain fatty acids in the colon and peripheral tissues: a focus on butyrate, colon cancer, obesity and Insulin resistance
- Short-term effects of anastrozole treatment on Insulin-like growth factor system in postmenopausal advanced breast cancer patients
- Signal relay by retinoic acid receptors α and β in the retinoic acid-induced expression of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in breast cancer cells
- Signaling through the Smad Pathway by Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein-3 in Breast cancer Cells: RELATIONSHIP TO TRANSFORMING GROWTH …
- Significance and expression of Insulin-like growth factor 1 and IGF binding protein 3 in serum of patients with lung cancer
- Significance and expression of serum Insulin-like growth factor-Ⅱ levels in prostatic cancer [J]
- Significance of determination of serum Insulin-like growth factor-1 in prostate cancer and benign prostate hypertrophy [J]
- Significance of Determination of Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) in Prostate cancer and Benign Prostate Hypertrophy [J]
- Significance of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) in the Ascites of the Ovaran cancer
- Significance of serum c-erbB-2 oncoprotein, Insulin-like growth factor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor levels in ovarian cancer.
- Significance of serum vascular endothelial growth factor, Insulin-like growth factor-I levels and nitric oxide activity in breast cancer patients
- Silencing Insulin‑like growth factor‑1 receptor expression inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion
- Silibinin up-regulates Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 expression and inhibits proliferation of androgen-independent prostate cancer cells
- Simultaneous blockade of both the epidermal growth factor receptor and the Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathways in cancer cells with a fully …
- SIMULTANEOUS OVEREXPRESSION OF Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR Ⅱ (IGF-Ⅱ) AND IGF Ⅱ RECEPTOR GENES IN HUMAN PRIMARY HEPATIC cancer
- Simvastatin induces apoptosis and suppresses Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in bile duct cancer cells
- Simvastatin inhibits the proliferation of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells via down-regulation of the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- siRNA mediated the type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor silencing induces chemosensitization of liver cancer cells
- siRNA‐mediated type 1 Insulin‐like growth factor receptor silencing induces chemosensitization of a human liver cancer cell line with mutant P53
- Small is beautiful: Insulin-like growth factors and their role in growth, development, and cancer
- Smoking-associated lung cancer prevention by blockade of the beta-adrenergic receptor-mediated Insulin-like growth factor receptor activation
- Smoking, green tea consumption, genetic polymorphisms in the Insulin-like growth factors and lung cancer risk
- SNPs in the Insulin-like growth factor gene and obesity impact on colorectal cancer in Egyptians
- Somatic mutations in the Insulin-like growth factor-1 and Insulin receptors found in cancer genomes result in constitutive activation of the receptor kinases
- Somatomedin-C/Insulin-like growth factor-I is a mitogen for human small cell lung cancer.
- Somatuline (BIM 23014) and tamoxifen treatment of postmenopausal breast cancer patients: clinical activity and effect on Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) levels.
- Specific binding and growth-promoting activity of Insulin in endometrial cancer cells in culture
- Specific binding sites for Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor I in human endometrial cancer
- Specific gene expression and therapy for pancreatic cancer using the cytosine deaminase gene directed by the rat Insulin promoter
- Specific targeting of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling in human estrogen dependent breast cancer cell by a novel tyrosine-based benzoxazepine …
- Sporadic amplification of the Insulin receptor gene in human breast cancer
- Statin induces apoptosis of human colon cancer cells and downregulation of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor via proapoptotic ERK activation
- Stimulation of endometrial cancer cell growth by tamoxifen is associated with increased Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I induced tyrosine phosphorylation and …
- Stimulation of TPA-responsive element activity by a cooperative action of Insulin and estrogen in human breast cancer cells
- Stop the Insulin Hazardous Abbreviation for “Intranasal” cancer Patients Deserve the Safest Practices Regardless of Where They are Treated
- Stromal cells promote anti-estrogen resistance of breast cancer cells through an Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (IGFBP5)/B-cell leukemia …
- Structural and functional studies of Insulin receptors in human breast cancer
- Structural commonality of C1q TNF‐related proteins and their potential to activate relaxin/Insulin‐like family peptide receptor 1 signalling pathways in cancer cells
- Study of Effect of Dyslipidemia And Insulin Resistance on Colorectal cancer risk patients in A Teaching Hospital of India
- Study of Insulin resistance and antioxidant vitamin status in prostate cancer patients
- Study of serum IGF-1, IGFBP-3 and Insulin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and their relationship with colorectal cancer
- Study on the correlation between expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and loco-regional recurrence of breast cancer after postoperative irradiation
- Study on the relations between serum Insulin-like growth factor-1, Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis
- Study on the relationship between Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 and anti-proliferating effect of tetrandrine on human colon cancer cells
- Study on the relationship between Insulin-like growth factor I receptor and the cisplatin resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer
- Study Protocol: Insulin and its role in cancer
- Substrate contribution to endogenous glucose production, Insulin resistance and protein metablism in non-small cell lung cancer cachexia
- Sugar pills for pancreatic cancer: The benefits of becoming (Insulin) sensitive
- Summary Insulin-Like Activity of the Blood Serum in Breast cancer and in Specific Age-Related Pathology
- SUN-131 The Roles of Two Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Triple Negative Breast cancer Growth
- Suppressed expression of Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐1 mRNA in the endometrium: A molecular mechanism associating endometrial cancer with its risk …
- Suppressing Insulin feedback to improve efficacy of cancer therapeutics
- Suppression of homologous recombination by Insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to PARP inhibitors
- Suppression of serum Insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in breast cancer patients during adjuvant tamoxifen therapy
- Suppression of Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor Expression by Small Interfering RNA Inhibits A549 Human Lung cancer Cell Invasion in vitro and …
- Suppressor of cytokine signaling-2 (SOCS2) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) modulate Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) signaling in intestinal cancer
- Suramin and serum Insulin-like growth factor levels in metastatic cancer patients.
- Suramin interferes with auto/paracrine Insulin-like growth factor I-controlled proliferative loop on human lung cancer cell lines
- Survival time in pancreatic cancer patients with metabolic syndrome varies by use of Insulin and statins
- Survivin associates with cell proliferation in renal cancer cells: regulation of survivin expression by Insulin-like growth factor-1, interferon-γ and a novel NF-κB inhibitor
- Synthesis of novel inhibitors that target the Insulin growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R):(potential anti-breast cancer compounds)
- Systematic review and meta-analysis of Insulin therapy and risk of cancer
- SYSTEMIC RISK FACTORS FOR FACTORS FOR ORAL cancer: ESTROGEN DEFICIENCY AND Insulin RESISTANCE
- Systems analysis of Insulin and IGF1 receptors networks in breast cancer cells identifies commonalities and divergences in expression patterns
- T-helper I immunity, specific for the breast cancer antigen Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR), is associated with increased adiposity
- Tamoxifen alters levels of serum Insulin-like growth factors and binding proteins in postmenopausal breast cancer patients: a prospective paired cohort study
- Tamoxifen interferes with the Insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) signaling pathway in breast cancer cells
- Targeted therapy of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in cancer
- Targeting 3-phosphoinoside-dependent kinase-1 to inhibit Insulin-like growth factor-I induced AKT and p70 S6 kinase activation in breast cancer cells
- Targeting AMP-activated protein kinase in adipocytes to modulate obesity-related adipokine production associated with Insulin resistance and breast cancer …
- Targeting colorectal cancer via its microenvironment by inhibiting IGF-1 receptor-Insulin receptor substrate and STAT3 signaling
- Targeting Downstream Effectors of IGF/Insulin Signaling System in Human Breast cancer
- Targeting Heat Shock Protein 90 in Pancreatic cancer Impairs Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor Signaling, Disrupts an Interleukin-6/Signal-Transducer and …
- Targeting heat shock protein 90 in pancreatic cancer impairs Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling, disrupts an interleukin-6/signal-transducer and activator of …
- Targeting Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor pathways in epithelial ovarian cancer
- Targeting Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer
- Targeting Insulin inhibition as a metabolic therapy in advanced cancer: a pilot safety and feasibility dietary trial in 10 patients
- Targeting Insulin receptor in breast cancer using small engineered protein scaffolds
- Targeting Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis
- Targeting Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 signaling in triple-negative breast cancer
- Targeting Insulin-like growth factor in breast cancer therapeutics
- Targeting Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor 1 (IGF-1R) and Insulin Receptor Signaling by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in cancer
- Targeting Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor in cancer therapy
- Targeting Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in cancer
- TARGETING Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-1 RECEPTOR WITH ANTISENSE OLIGONUCLEOTIDES IN PROSTATE cancer
- Targeting Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 by microRNA-125b promotes tumor invasion and poor outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Targeting Insulin-like growth factors in the treatment of cancer
- Targeting IRS‐1/mPGES‐1/NOX2 to inhibit the inflammatory response caused by Insulin‐like growth factor‐I‐induced activation of NF‐κB and NLRP3 in cancer cells
- Targeting non-small cell lung cancer cells by dual inhibition of the Insulin receptor and the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
- Targeting of bone-derived Insulin-like growth factor-II by a human neutralizing antibody suppresses the growth of prostate cancer cells in a human bone environment
- Targeting STAT1 in both cancer and Insulin resistance diseases
- Targeting the Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) and the Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor 1 (IGF1R) in crizotinib resistant lung cancer cells
- Targeting the Insulin growth factor and the vascular endothelial growth factor pathways in ovarian cancer
- Targeting the Insulin growth factor-1 receptor with fluorescent antibodies enables high resolution imaging of human pancreatic cancer in orthotopic mouse …
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) signaling pathway for cancer therapy
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor axis as a cancer therapy
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor I receptor inhibits proliferation and VEGF production of non-small cell lung cancer cells and enhances paclitaxel-mediated anti …
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor network in cancer therapy
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor receptor and Src signaling network for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway in lung cancer: problems and pitfalls
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1R pathway for cancer therapy
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor receptor/Insulin receptor and Src signaling network for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in human cancer
- Targeting the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in cancer therapy
- Targeting the Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor by picropodophyllin for lung cancer chemoprevention
- Targeting the type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor as a treatment for cancer
- Targeting the type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor as anti-cancer treatment
- Targeting the type I Insulin-like growth factor system for breast cancer therapy
- Telephone-based nutrition coaching decreases Insulin resistance in patients undergoing breast cancer treatment.
- TET1-GPER-PI3K/AKT pathway is involved in Insulin-driven endometrial cancer cell proliferation
- TGFβ activates Insulin‐like growth factor 1‐mediated signaling pathway in human liver cancer cells (144.9)
- TH1 and TH2 cytokine data in Insulin secretagogues users newly diagnosed with breast cancer
- TH1 and TH2 cytokines dataset in Insulin users with diabetes mellitus and newly diagnosed breast cancer
- The “Cross Talk” between the receptors of Insulin, estrogen and progesterone in neutrophils in the synthesis of maspin through nitric oxide in breast cancer
- The “Cross Talk” between the Receptors of Insulin, Estrogen and Progesterone in Neutrophils in the Synthesis of Maspin through Nitric Oxide in Breast cancer
- The “Cross Talk” between the receptors of Insulin, estrogen and progesterone in neutrophils in the synthesis of maspin through nitric oxide in breast cancer
- The “Cross Talk” between the Receptors of Insulin, Estrogen and Progesterone in Neutrophils in the Synthesis of Maspin through Nitric Oxide in Breast cancer
- The A− 336C Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 Promoter Polymorphism Is Not a Modulator of Breast cancer Risk in Caucasian Women
- The activation of ERK1/2 and JNK MAPK signaling by Insulin/IGF-1 is responsible for the development of colon cancer with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The aging suppressor klotho interacts with the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, inhibits it activation and reduces growth of breast cancer cells.
- The apoptotic effect of HIF-1α inhibition combined with glucose plus Insulin treatment on gastric cancer under hypoxic conditions
- The aromatase inhibitor letrozole in advanced breast cancer: effects on serum Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3 levels
- The association between bladder cancer and a single nucleotide polymorphism (rs2854744) in the Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) gene
- The association between diabetes, Insulin use, and colorectal cancer among Whites and African Americans
- The association between plasma Insulin-like-growth factor (IGF)-I and colorectal cancer is modified by BMI or C-peptide.
- The association between polymorphismsin Insulin and obesity related genesand risk of colorectal cancer
- The association between thyroid cancer and Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and its components: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- The association of hyperInsulinemia with cardiovascular risk and cancer poses new challenges in the treatment of the Insulin resistance type 2 diabetes patient
- The association of serum ghrelin, GIP, Insulin, and leptin levels with sleep quality and cancer-related fatigue in cancer survivors.
- The association of serum Insulin-like growth factor-I with mortality, cardiovascular disease, and cancer in the elderly: a population-based study
- The association of tissue and serum adiponectin levels with the parameters of Insulin-resistance in breast cancer patients
- The biological and clinical roles of increased Insulin receptors in human breast cancer
- The cancer-associated FGFR4-G388R polymorphism enhances pancreatic Insulin secretion and modifies the risk of diabetes
- The cellular and molecular mechanisms by which Insulin influences breast cancer risk and progression
- The Change of Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 3 (IGFBP-3) in the Diagnosis and Management of Prostate cancer
- The Clinical Application of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor (IGF-IR) and Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 (IRS-1) Expression in Breast cancer
- The Clinical Research on the Dynamic Change of Insulin Resistance during the Therapy of Prostate cancer
- The clinical significance of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor polymorphism in non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation
- The colonic protein fermentation and Insulin resistance hypotheses for colon cancer etiology: experimental tests using precursor lesions
- The combination of everolimus and terameprocol exerts synergistic antiproliferative effects in endometrial cancer: molecular role of Insulin-like growth factor binding …
- The combination treatment with inhibitors targeting the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor and the epidermal growth factor receptor in human colon cancer.
- The consequences of Insulin-like growth factors/receptors dysfunction in lung cancer
- The Correlation between Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factor-Ⅰ in Blood and Clinicopathological Parameters in Non-Small Cell Lung cancer
- The correlation between zinc and Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), its binding protein (IGFBP-3) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in prostate cancer
- The development of the metabolic syndrome and Insulin resistance after adjuvant treatment for breast cancer
- The dichotomy of the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor: RTK and GPCR: friend or foe for cancer treatment?
- The dietary glycemic index and its implications in cancer risk, Insulin-like growth factors and oxidative stress
- The dog as a naturally-occurring model for Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor-overexpressing breast cancer: an observational cohort study
- The Effect and Mechanism of Action of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 in Human Breast cancer; A Systematic Review.
- The effect of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the Insulin-like growth factor I regulatory region on breast cancer risk is modified by body mass index
- The effect of droloxifene on the Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated growth of breast cancer cells.
- THE EFFECT OF EIGHT WEEKS AEROBIC ACTIVITY ON CA15-3 MARKER, GROWTH HORMONE AND Insulin OF WOMEN WITH BREAST cancer
- The effect of exercise intensity on Insulin levels in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors
- The effect of graded doses of Insulin on peripheral glucose uptake and lactate release in cancer cachexia.
- The effect of green tea extract compounds on regulation of glucose homoeostasis in Insulin-sensitive and breast cancer cells
- The effect of Insulin analogues only or combined with metformin on the prolifeation of breast cancer cell line (MCF-7)
- The effect of Insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells
- The effect of Insulin on glucose and protein metabolism in the forearm of cancer patients
- The effect of Insulin on human breast cancer cell line in vitro [J]
- The effect of Insulin on INSR receptor and Bax and Bcl-2 protein expression in drug resistance situation on MCF-7 breast cancer cells line
- The effect of Insulin resistance on breast cancer risk in Latinas of Mexican origin
- The effect of serum Insulin like factor Ⅰ on mouse cancer
- The effect of the preoperative oral carbohydrate treatment on immediate postoperative Insulin resistance in patients after colorectal cancer resection
- The Effects of Ellagic Acid on Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 in Human Prostate cancer Cells
- The effects of exercise on Insulin, glucose, IGF‐axis and CRP in cancer survivors: Meta‐analysis and meta‐regression of randomised controlled trials
- The Effects of Exercise Training on Insulin Supply and Demand in Breast cancer Survivors
- The Effects of Fructose Injection on the Levels of Blood Glucose, Insulin in cancer by Chemotherapy [J]
- The effects of genetic variants related to Insulin metabolism pathways and the interactions with lifestyles on colorectal cancer risk
- The effects of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factors on tumor vascularization: new insights of Insulin-like growth factor family in cancer
- The effects of Insulin receptor substrate-1 regulation on cell cycle progression in non-small cell lung cancer
- The effects of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) on T47D breast cancer cells enriched for IGFBP-3 binding sites
- The Effects of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) in Mouse Lung cancer Cells
- The effects of pioglitazone treatment on pancreatic cancer-related Insulin resistance.
- The Effects of Recombinant Synucleins and Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 on cancer Cell Migration
- The emerging role of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor signaling in cancer stem cells
- The emerging role of Insulin receptor isoforms in thyroid cancer: clinical implications and new perspectives
- The emerging role of the Insulin‐like growth factor pathway as a therapeutic target in cancer
- The estrogen receptor α: Insulin receptor substrate 1 complex in breast cancer: structure–function relationships
- The expression and imprinting status of Insulin-like growth factor 2 gene in colorectal cancer
- The expression and significance of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and its pathway on breast cancer stem/progenitors
- The expression of ADAM-9 and-10 in prostate cancer and their regulation by dihydrotestosterone, Insulin-like growth factor-1 and epidermal growth factor
- The expression of Insulin receptor substrate 1 and estrogen receptor as prognostic factor on breast cancer patient
- The expression of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF), IGF-binding protein (IGFBP) and the role of IGFBP-3 in the Korean gastric cancer cell lines
- The Expression of Insulin-like Growth Factor I and its Receptor in Colorectal Polypus and Colorectal cancer [J]
- The expression of Insulin-like growth factor Ⅱ (IGF-Ⅱ) in serum and tissues of patients with breast cancer
- The Expression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor (IGF-1R) in Early Breast cancer.
- The expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor on breast cancer and normal breast tissue
- The expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor on LN (-) breast cancer, LN (+) breast cancer and normal breast tissue
- The expression of Insulin‐like growth factor and its binding protein mRNA in the endometrium of postmenopausal patients with breast cancer receiving tamoxifen
- The expression of the Insulin receptor in gastric cancer correlates with the HER2 status and may have putative therapeutic implications
- The expression of VEGF in colon cancer tissue was affected by the serum levels of Insulin–like Growth Factor I
- The glucose tolerance test and Insulin secretion test as risk factors in liver cancer surgery
- The growth hormone-Insulin-like growth factor axis and colorectal cancer
- The growth hormone–Insulin-like growth factor-I axis and colorectal cancer
- The growth hormone/Insulin-like growth factor axis and breast cancer risk
- The human Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 4 gene maps to chromosome region 17q12-q21. 1 and is close to the gene for hereditary breast-ovarian cancer
- The IGF-II–Insulin Receptor Isoform-A Autocrine Signal in cancer: Actionable Perspectives
- The Impact of Insulin Exposure on Colorectal cancer Metabolism
- The impact of Insulin on chemotherapeutic sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in gastric cancer cell lines SGC7901, MKN45 and MKN28
- The impact of obesity and Insulin resistance on thyroid cancer: a systematic review
- The importance of serum Insulin-like growth factor-I level determination in the follow-up of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.
- The Importance of the Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Lung cancer and the Potential of its Components as Therapeutic Targets
- The influence of exercise intensity on Insulin sensitivity and the Insulin-like growth factor axis in colorectal cancer survivors
- The influence of oral administration of glucose before surgery on Insulin resistance and oxidative stress in castric cancer patients undergoing surgery
- The influence of overweight and Insulin resistance on breast cancer risk and tumour stage at diagnosis: a prospective study
- The influence of overweight and Insulin resistance on localised and advanced breast cancer risk: A prospective study
- The inhibition of Insulin‐like growth factor 1 receptor pathway targets putative cancer stem cells in human malignant mesothelioma
- The Insulin like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) as a drug target: novel approaches to cancer therapy
- The Insulin receptor isoform exon 11-(IR-A) in cancer and other diseases: a review
- The Insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins: at the intersection of metabolism and cancer
- The Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) in intestinal epithelial differentiation and in colorectal cancer
- The Insulin receptor substrate-1: a biomarker for cancer?
- The Insulin receptor: a new target for cancer therapy
- The Insulin resistance Grb14 adaptor protein promotes thyroid cancer ret signaling and progression
- The Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis as an anticancer target in prostate cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis is involved in normal prostate differentiation and downregulated in local prostate cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) family and breast cancer
- The Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Signaling Pathway: Strategies for Successful Therapeutic Tasks in cancer Treatment
- The Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) is differentially expressed in metastatic breast cancer, both in metastases to the brain and to the lymph nodes.
- The Insulin-like growth factor 1 axis in prognosis and treatment of breast cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer: old focus, new future
- The Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein IMP2/IGF2BP2 is overexpressed and correlates with poor survival in pancreatic cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor axis and prostate cancer: lessons from the transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate (TRAMP) model
- The Insulin-like growth factor axis, adipokines, physical activity, and obesity in relation to breast cancer incidence and recurrence
- The Insulin-like growth factor axis: A biological mechanism linking physical activity to colorectal cancer survival
- The Insulin-like growth factor axis: a potential link between glycemic index and cancer,
- The Insulin-like growth factor binding protein BP-25 is expressed by human breast cancer cells
- The Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) in human breast cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 3 and 7 are associated with colorectal cancer and liver metastasis
- The Insulin-like growth factor family and breast cancer prognosis: a prospective cohort study among postmenopausal women in Denmark
- The Insulin-like growth factor II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor: implications for IGF action in breast cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor network and breast cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor pathway as a target for cancer therapy
- The Insulin-like growth factor pathway in lung cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor receptor I promotes motility and invasion of bladder cancer cells through Akt-and MAPK-dependent activation of paxillin
- The Insulin-like growth factor receptor I promotes motility and invasion of bladder cancer cells through Akt-and mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent …
- The Insulin-like growth factor receptor is a promising target for innovative treatment approaches of hepatocellular cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor system and cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor system and cancer: what are the implications?
- The Insulin-like growth factor system and colorectal cancer: clinical and experimental evidence
- The Insulin-like growth factor system as a target in breast cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor system as a therapeutic target in colorectal cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor system as a treatment target in breast cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor system in advanced breast cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor system in cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor system in cancer prevention: potential of dietary intervention strategies
- The Insulin-like growth factor system is modulated by exercise in breast cancer survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- The Insulin-like growth factor-1 ligand in breast cancer management
- The Insulin-like growth factor-1 pathway mediator genes: SHC1 Met300Val shows a protective effect in breast cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factor-2 (IGF-2): A potential therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer metastasis
- The Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) in breast cancer: biology and treatment strategies
- The Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a target for cancer therapy
- The Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor, NVP-ADW742, sensitizes small cell lung cancer cell lines to the effects of chemotherapy
- The Insulin-like growth factor/Insulin system in epithelial ovarian cancer
- The Insulin-like growth factors and breast cancer—revisited
- The Insulin-like growth factors and Insulin-signalling systems: an appealing target for breast cancer therapy?
- The Insulin-like growth factors, their receptors, and their binding proteins in human breast cancer
- The Insulin‐like growth factor 1 receptor causes acquired resistance to erlotinib in lung cancer cells with the wild‐type epidermal growth factor receptor
- The Insulin‐like growth factor I receptor gene is the target for the 15q26 amplicon in breast cancer
- The Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 elevates urokinase‐type plasminogen activator‐1 in human breast cancer cells: A new avenue for breast cancer therapy
- The Insulin/IGF system in colorectal cancer development and resistance to therapy
- The integrative role of leptin, oestrogen and the Insulin family in obesity‐associated breast cancer: potential effects of exercise
- The interactions between Insulin and androgens in progression to castrate-resistant prostate cancer
- The interactions of obesity, inflammation and Insulin resistance in breast cancer
- The international study of Insulin and cancer
- The International Study of Insulin and cancer
- The intracellular mechanism of Insulin resistance in pancreatic cancer patients
- The involvement of Insulin-like growth factor 2 binding protein 3 (IMP3) in pancreatic cancer cell migration, invasion, and adhesion
- The involvement of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 in promoting prostate cancer progression and metastasis
- The involvement of survivin in Insulin-like growth factor 1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer
- The key role of growth hormone–Insulin–IGF-1 signaling in aging and cancer
- The kinetics of methotrexate polyglutamate formation and efflux in a human breast cancer cell line (MDA. MB. 436): the effect of Insulin
- The lack of an effect by Insulin or Insulin-like growth factor-1 in attenuating colon-26-mediated cancer cachexia
- The level of Insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ in blood circulation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer after surgery and its clinical significance [J]
- The Limited Screening Value of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I in 610 Very Long Term Adult Survivors of Leukemia and Other Types of Childhood cancer
- The limited screening value of Insulin‐like growth factor‐i as a marker for alterations in body composition in very long‐term adult survivors of childhood cancer
- The links between Insulin resistance, diabetes, and cancer
- The matrix metalloproteinase and Insulin-like growth factor system in oral cancer–a prospective clinical study
- The Mechanisms and Impact of Obesity and Insulin Resistance on Breast cancer Incidence
- The miRNA let-7a1 inhibits the expression of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) in prostate cancer PC-3 cells
- The need for differentiating diabetes-specific mortality from total mortality when comparing metformin with Insulin regarding cancer survival
- The neglected Insulin: IGF-II, a metabolic regulator with implications for diabetes, obesity, and cancer
- The nuclear receptor coactivator AIB1 mediates Insulin-like growth factor I-induced phenotypic changes in human breast cancer cells
- The nuclear translocation of Insulin‐like growth factor receptor and its significance in cancer cell survival
- The p53-family members p63 and p73 inhibit Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene expression in colon cancer cells
- The PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway mediates Insulin-like growth factor 1-induced E-cadherin down-regulation and cell proliferation in ovarian cancer cells
- The possible role of Insulin-like growth factors and matrix metalloproteinases as a diagnostic of colorectal cancer.
- The potential clinical applications of Insulin-like growth factor-1 ligand in human breast cancer
- The potential role of Insulin (and stress response) pathway components in breast cancer development and progression
- The potential role of Insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibitors in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- The potentiation of estrogen on Insulin-like growth factor I action in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells includes cell cycle components
- The predictive value of Insulin-like growth factor 1 in irradiation-dependent growth hormone deficiency in childhood cancer survivors
- THE PRICE OF MEDICINE FOR cancer, Insulin, AND ADDICTION RELATED DRUGS: A CASE OF PERFECT INELASTICITY OF DEMAND
- The prognostic significance of the expression of Insulin-like growth factor receptor-I in prostate cancer
- The prognostic significance of the Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 ligand and receptor expression in breast cancer tissue
- The prognostic value of Insulin-like growth factor-I in breast cancer patients. Results of a follow-up study on 126 patients
- The prognostic value of polymorphisms in the Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGFR) pathway in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC)
- The prognostic values of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein in breast cancer
- The Prognostic Values of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein Family in Ovarian cancer
- The proliferating role of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factors in cancer
- The proliferative role of Insulin and the mechanism underlying this action in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7
- The prospective estimation of blood serum free IGF-1, Insulin concentration, and body mass index as a prognostic factor for breast cancer patients.
- The Prospective Estimation of Body Mass Index, Blood Serum Free Igf-1, Insulin Concentration as Prognostic Factor for Colorectal cancer Patients
- The Protective Effect of Lycopene on Prostate Growth Inhibitory Efficacy by Decreasing Insulin Growth Factor-1 in Indonesian Human Prostate cancer Cells
- The R-Ras GTPase mediates cross talk between estrogen and Insulin signaling in breast cancer cells
- The regulation of expression of the Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF2) gene in breast cancer.
- The regulation of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 production and secretion by ovarian hormones in human breast cancer cells
- The Relation of Cytokines, Serum Insulin and Insulin Resistance with the Progression Free Survival and Overall Survival of Metastatic Breast cancer Patients
- The relation of Insulin and IGF-II in human colorectal cancer and its biological significance [J]
- The relationship between HPV infection and the expression of Insulin-like growth factor Ⅱ in lung cancer and its clinical significance [J]
- The relationship between HPV infection and the expression of Insulin-like growth factor II in lung cancer and its clinical significance.
- The Relationship between Insulin PSTI Polymorphism and Prostate cancer in Turkish Population
- The relationship between Insulin resistance and colon cancer
- The Relationship Between Insulin Resistance and HyperInsulinemia on Mammary cancer Growth and Development
- The relationship between serum levels of erythropoietin (EPO) and Insulin-like growth factor-1 (ILGF-1) and hematocrit (HCT) in breast cancer patients receiving non …
- The relationship between the exposure time of Insulin glargine and risk of breast and prostate cancer: an observational study of the time-dependent effects of …
- The Relationship Between the Insulin Resistance and cancer [J]
- The relationship between the Insulin-like growth factor-1 system and the oestrogen metabolising enzymes in breast cancer tissue and its adjacent non-cancerous …
- The relationship of circulating Insulin‐like growth factor 1, its binding protein‐3, prostate‐specific antigen and C‐reactive protein with disease stage in prostate cancer
- The relationship of Insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome with known breast cancer prognostic factors in postmenopausal breast cancer patients
- The Relationship of Type 2 Diabetes, Oral Diabetes Medications, and Insulin Therapy to Risk for Breast cancer
- The role of activation of Insulin-like growth factors in colorectal cancer
- The Role of Adiponectin, Leptin, Soluble Leptin Receptor and Insulin-like Growth Factor in A Sample of Breast cancer Iraqi woman
- The role of early placenta Insulin like growth factor in invasion and metastasis of HER2 positive breast cancer cells in vivo
- The role of early placenta Insulin-like growth factor (EPIL) as a potential regulator of cancer progenitor cells
- The role of endocrine Insulin-like growth factor-I and Insulin in breast cancer
- The role of genetic variation in Insulin-like growth factors in prostate cancer risk: The multiethnic cohort
- The role of growth factors in pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer. Part III: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs)
- The Role of Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 in Human Breast cancer Growth in a Mouse Xenograft Model
- The role of Insulin and IGF system in pancreatic cancer
- The role of Insulin and IGF2 signalling on metabolic pathways in prostate cancer progression
- The role of Insulin and Insulin-like growth factors in the increased risk of cancer in diabetes
- The role of Insulin dependent NO synthesis in the impaired production of maspin in human breast cancer
- The role of Insulin in advanced prostate cancer
- The role of Insulin in cancer malnutrition.
- The role of Insulin Receptor in cancer
- The role of Insulin receptor isoforms and hybrid Insulin/IGF-I receptors in human cancer
- The role of Insulin receptors and IGF-I receptors in cancer and other diseases
- The role of Insulin resistance and hyperInsulinemia in cancer causation
- The role of Insulin resistance in the development of muscle wasting during cancer cachexia
- The Role of Insulin Signaling on c-Myc Expression in Breast cancer Cells
- The role of Insulin-like amyloid polypeptide in pancreatic cancer
- The role of Insulin-like growth factor 1 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in human esophageal cancer
- The role of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in the breast cancer cell response to DNA-damaging agents
- The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I), and IGF Binding Protein (IGFBP) in Mouse Lung cancer Cells.
- The role of Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptor (IGF-IR) in Trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer cells
- The Role of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling in Prostate cancer Development and Progression
- The role of Insulin-like growth factor-1 and Insulin like growth factor-1 receptor in obesity and oesophageal cancer
- The role of Insulin-like growth factor-1 in the pathogenesis of cancer and inflammatory skin diseases.
- The role of Insulin-like growth factor-II in cancer growth and progression evidenced by the use of ribozymes and prostate cancer progression models
- The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factors in cancer Therapy
- The role of Insulin-like growth factors in the development of prostate cancer
- The role of Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3 in the growth inhibitory actions of androgens in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells
- The Role of Insulin, IGF-1 and PRAS40 in the Processes of Oncogenesis in Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Endometrial cancer
- The Role of Legumes in Weight Management, Insulin Resistance and Colon cancer Prevention
- The role of Notch signaling pathway in Insulin regulation of endometrial cancer cell growth and apoptosis
- The role of somatostatin analog octreotide on gastrointestinal cancer and its influence on the serum level of Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)
- The role of some ADAM-proteins and activation of the Insulin growth factor-related pathway in colorectal cancer
- The role of the Insulin-like growth factor signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer and other solid tumors
- The role of the Insulin-like growth factor system in colorectal cancer: review of current knowledge
- The role of the Insulin-like growth factor system in human cancer
- The Role of the Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor (IGF-1R), Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN), c-Met, and the PI3-Kinase Pathway in Colorectal cancer
- The role of the Insulin-like growth factor-1 system in breast cancer
- The role of the Insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor in cancer
- The role of the Insulin/IGF system in cancer: lessons learned from clinical trials and the energy balance-cancer link
- The Role of Type I Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Breast cancer Brain Metastasis
- The roles of Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 in cancer and cancer stem cells
- The roles of integrins and extracellular matrix proteins in the Insulin-like growth factor I-stimulated chemotaxis of human breast cancer cells
- The significance of serum levels of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 in patients with prostate cancer
- The synthetic retinoid fenretinide lowers plasma Insulin-like growth factor I levels in breast cancer patients
- The Therapeutic and Preventive Effect of RRR-A-Vitamin E Succinate on Prostate cancer via Induction of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3
- The therapeutic and preventive effect of RRR-α-vitamin E succinate on prostate cancer via induction of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3
- The type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling system and targeted tyrosine kinase inhibition in cancer
- The type 1 Insulin‐like growth factor receptor is over‐expressed in bladder cancer
- The type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway: a key player in cancer therapeutic resistance
- The type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor regulates cancer metastasis independently of primary tumor growth by promoting invasion and survival
- The type-1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and breast cancer: biology and therapeutic relevance
- The tyrphostin NT157 suppresses Insulin receptor substrates and augments therapeutic response of prostate cancer
- The use of Insulin and the effect on survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients
- The Use of Long-Acting Insulin Analogs and the Risk of Colorectal cancer Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Cohort Study
- The value of Insulin-like growth factor in the evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in gastric cancer [J]
- The Yin and Yang function of microRNAs in Insulin signalling and cancer
- Thematic Poster: TP-47; MicroRNA-146a Inhibits Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Non Small Cell Lung cancer by Targeting Insulin Receptor Substrate 2
- Therapeutic Destruction of Insulin Receptor Substrates for cancer
- Therapeutic destruction of Insulin receptor substrates for cancer treatment
- Therapeutic Potential of Insulin-sensitizing Drugs in the Treatment of Prostate cancer with Coexisting Obesity
- Therapeutic targeting of the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) plus oxaliplatin decreases hepatic growth of human colon cancer
- Therapy of Prostate cancer Using a Human Antibody Targeting the Type 1 Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor (IGF-IR)
- Thyroid cancer and Insulin resistance: is it important?
- Time course of fenretinide‐induced modulation of circulating Insulin‐like growth factor (IGF)‐i, IGF‐II and IGFBP‐3 in a bladder cancer chemoprevention trial
- Tissue distribution and cancer growth inhibition of magnetic lipoplex-delivered type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor shRNA in nude mice
- Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator Is Upregulated in Metastatic Breast cancer Cells Exposed to Insulin-Like Growth Factor—I
- Tissue‐Specificity and Ethnic Diversity in Obesity‐Related Risk of cancer May Be Explained by Variability in Insulin Response and Insulin Signaling Pathways
- TMPRSS2-ERG fusion protein regulates Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) gene expression in prostate cancer: involvement of transcription factor …
- To Study the Dose and Time Dependent Effect of Human Insulin and Metformin on the Growth of Breast cancer Cells
- To study the effect of Insulin on advanced androgen-indpendent prostate cancer (pc-3) cells
- Tomato and soy polyphenols reduce Insulin-like growth factor-I–stimulated rat prostate cancer cell proliferation and apoptotic resistance in vitro via inhibition of …
- Tomato lycopene extract supplementation decreases Insulin-like growth factor-I levels in colon cancer patients
- Total Insulin-like activity of blood serum in patients with mammary gland cancer and in specific age-associated pathology
- trans-10, cis-12 Conjugated Linoleic Acid Reduces Insulin-Like Growth Factor-II Secretion in HT-29 Human Colon cancer Cells
- trans-10,cis-12 Conjugated Linoleic Acid Inhibits Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Receptor Signaling in TSU-Pr1 Human Bladder cancer Cells
- Transactivation of CXCR4 by the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer epithelial cells
- Transcriptional activation of the porcine P450 11A Insulin-like growth factor response element in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Transcriptional regulation of Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene expression in prostate cancer cells
- Transcriptional regulation of the Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene in breast cancer
- Transcriptome analysis of a human colorectal cancer cell line shows molecular targets of Insulin‐like growth factor‐binding protein‐4 overexpression
- Transfection of antisense oligonucleotide against the Insulin like growth factor# IOTA# on proliferactio and apoptosis of liver cancer cell
- Transfection of human Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 gene inhibits cell growth and tumorigenicity: a cell culture model for lung cancer
- Transforming growth factor-α and Insulin-like growth factor-I, but not epidermal growth factor, elicit autocrine stimulation of mitogenesis in endometrial cancer cell lines
- Transforming growth factor-β-induced cell growth inhibition in human breast cancer cells is mediated through Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 …
- Transforming growth factor-β1 modulates tumor-stromal cell interactions of prostate cancer through Insulin-like growth factor-I
- Transforming growth factor‑β, Insulin‑like growth factor I/Insulin‑like growth factor I receptor and vascular endothelial growth factor‑A: Prognostic and predictive …
- Treatment of human breast cancer cells with antisense RNA to the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibits cell growth, suppresses tumorigenesis, alters the …
- Treatment of murine breast cancer cells with antisense RNA to the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor decreases the level of plasminogen activator …
- Treatment with growth hormone, somatostatin, and Insulin in combination with hypocaloric parenteral nutrition in gastrointestinal cancer patients after surgery
- Treatment with human Insulin does not increase thyroid cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Treatment with Insulin (analogues) and breast cancer risk in diabetics; a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro, animal and human evidence
- Treatment with Insulin (analogues) and breast cancer risk in women with diabetes; a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro, animal and human …
- Treatment with Insulin analog X10 and IGF-1 increases growth of colon cancer allografts
- Treatment with Insulin glargine (Lantus®) increases the proliferative potency of the serum of patients with type-1 diabetes: a pilot study on MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Treatment with Insulin secretagogues and cancer-related mortality in type 2 diabetic patients a retrospective cohort study
- Treatment with Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor reverses hypoxia-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer
- Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) as a new potential therapeutic target for Insulin resistance and cancer
- Troglitazone: from an Insulin sensitizer to a novel class of anti-cancer agent
- TTP inhibits Insulin receptor signals in cancer cell
- Tumor expression of the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor is an independent prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer
- Tumor Suppressor BRCA1 Is Expressed in Prostate cancer and Controls Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptor (IGF-IR) Gene Transcription in an Androgen Receptor …
- Tumor suppressor gene Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) induces senescence-like growth arrest in colorectal cancer cells
- Tumor suppressors govern Insulin-like growth factor signaling pathways: implications in metabolism and cancer
- Tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and fasting serum Insulin correlate with clinical outcome in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy
- Type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibition as treatment for urological cancer
- Type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody (HX-1162) treatment for liver cancer
- Type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor targeted therapies in pediatric cancer
- Type 2 diabetes and cancer: Should we prefer antihyperglycaemic treatments without unnecessarily increasing Insulin levels?
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin Resistance, Obesity, there is Any Association with Liver cancer?
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus, Insulin‐use and risk of bladder cancer in a large cohort study
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oral diabetic medications, Insulin therapy, and overall breast cancer risk
- Type 2 diabetes, but not Insulin (analog) treatment, is associated with more advanced stages of breast cancer: a national linkage of cancer and pharmacy registries
- Type 2 diabetes, Insulin treatment and prognosis of breast cancer
- Type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor antisense strategies in experimental breast cancer
- Type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in cancer
- Type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor function in breast cancer
- Type I Insulin-like growth factor receptors in human colorectal cancer
- Type-I Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor (IGF1R)-Estrogen Receptor (ER) Crosstalk Contributes to Antiestrogen Therapy Resistance in Breast cancer Cells
- Tyrosine kinase of Insulin-like growth factor receptor as target for novel treatment and prevention strategies of colorectal cancer
- Tyrosine kinase signalling in breast cancer: Insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in breast cancer
- Tyrosine kinases expressed in vivo by human prostate cancer bone marrow metastases and loss of the type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor
- Unbalanced cancer Status May Undermine Results on Insulin and Insulin-like Growth Factor
- Understanding the Contribution of Insulin Resistance to the Risk of Pancreatic cancer.
- Unravelling the link between diabetes, Insulin treatment and breast cancer
- UP-01.024 The Association Between Bladder cancer and a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (Rs2854744) in the Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Binding Protein-3 …
- UP-02.208 Insulin and Insulin Resistance Are Associated with the Advanced Pathological Stage of Prostate cancer in the Korean Population
- UP-02.50: A study of the role of Insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF1) and rapamycin sensitive signaling in an androgen independent prostate cancer cell line
- UP-1.089: Prostate cancer Risk in Relation to Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF)-I and IGF-Binding Protein-3: A Nested Case-Control Study in Japan
- Up-regulation of Insulin-like growth factor axis components in human primary prostate cancer correlates with tumor grade
- Up-regulation of intracellular signalling pathways may play a central pathogenic role in hypertension, atherogenesis, Insulin resistance, and cancer program-the ‘PKC …
- Upper abdominal obesity, Insulin resistance and breast cancer risk
- Upregulated Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate promotes the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells via the bFGF/AKT signaling pathway
- Urinary 2/16 alpha-hydroxyestrone ratio: correlation with serum Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and a potential biomarker of breast cancer risk.
- Urinary bladder cancer risk in relation to a single nucleotide polymorphism (rs2854744) in the Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP3) gene
- Use of an Insulin Pump in the Elderly Surgical Patient: Tolerance of Total Pancreatectomy After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Multifocal Pancreatic cancer
- Use of elevated Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) to predict outcomes in men with metastatic prostate cancer treated with androgen-deprivation …
- Use of Insulin and Insulin analogs and risk of cancer—systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- Use of Insulin and mortality from breast cancer among Taiwanese women with diabetes
- Use of Insulin and Risk of cancer among Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Nonconcurrent Prospective Study
- Use of Insulin glargine and cancer incidence in Scotland: a study from the Scottish Diabetes Research Network Epidemiology Group
- Use of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) pathway polymorphism IGF1R_rs2016347 to predict tumor recurrence in estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer patients.
- Use of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Gene Expression to Distinguish Between Breast and Ovarian cancer
- Use of statins offsets Insulin‐related cancer risk
- Usefullness of serum Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) for colorectal cancer diagnosis
- Usefulness of the Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins for the assessment of the treatment results in patients with colorectal cancer
- Utility of Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 expression in gefitinib-treated patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- Vaccination Targeting Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 (IGFBP-2) in Advanced Ovarian cancer: Safety, Immunogenicity, and Surveillance …
- Validation of the type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in renal cancer
- Value of circulating Insulin-like growth factor–associated proteins for the detection of stage I non–small cell lung cancer
- Vascular endothelial growth factor and Insulin-like-growth factors in prostate cancer.
- Virtual screening of specific Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) inhibitors from the National cancer Institute (NCI) molecular database
- Visceral adiposity, Insulin resistance and cancer risk
- Visceral obesity, metabolic syndrome, Insulin resistance and cancer
- Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms, dietary promotion of Insulin resistance, and colon and rectal cancer
- Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms, Insulin-like growth factors, and prostate cancer risk: a population-based case-control study in China
- Vitamin D status and its relation with Insulin resistance and VDR-FokI polymorphism in Iranian non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) patients: a case-control …
- Vitamin D status and its relation with Insulin resistance and VDR-FokI polymorphism in Iranian non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) patients: a case-control study
- Vitamin D–Binding Protein Enhances Epithelial Ovarian cancer Progression by Regulating the Insulin-like Growth Factor-1/Akt Pathway and Vitamin D Receptor …
- Vitamin D3 levels and Insulin resistance in papillary thyroid cancer patients
- Weight control and cancer preventive mechanisms: role of Insulin growth factor-1-mediated signaling pathways
- Western nutrition and the Insulin resistance syndrome: a link to breast cancer
- What is the role of the Insulin‐like growth factor system in the pathophysiology of cancer cachexia, and how is it regulated?
- When “flawed” translates into “flood”: The unproven association between cancer incidence and glargine Insulin therapy
- Which hormones promote breast cancer in postmenopause: estrogens, progestins, Insulin and/or adipocytokines?
- Whole‐body protein metabolism in cancer‐bearing patients. Effect of total parenteral nutrition and associated serum Insulin response
- Window opportunity studies in head and neck cancer to target the Insulin growth factor-1 and the epidermal growth factor receptors: from bed to bench
- WITHDRAWN: Significance of serum vascular endothelial growth factor, Insulin-like growth factor-I levels and nitric oxide activity in breast cancer patients
- Worse breast cancer prognosis in Insulin treated diabetic patients-A population based registry study in Sweden
- WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (WWP1) expression in breast cancer and its correlation with estrogen receptor (ER) and Insulin-like growth factor …
- YAP/TAZ regulates the Insulin signaling via IRS1/2 in endometrial cancer
- … -01-12: Prevalence of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) expression in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) of patients with early breast cancer and its association …
- … -02.092 Relationship of Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Binding Protein-3 (IGFBP-3) Gene Polymorphism with the Susceptibility to Development of Prostate cancer …
- … -04: Interactions between plasma levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-binding proteins and C-peptide with risk of colorectal cancer
- … -0646 (MK), Insulin growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) antibody combined with pemetrexed (P) and cisplatin (C) in stage IIIb or IV metastatic nonsquamous lung cancer …
- … -1 is the predominant signaling molecule activated by Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin, and interleukin-4 in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer …
- … -1 receptor (IGF-1R) expression does not predict for resistance to trastuzumab-based treatment in patients with Her-2/neu overexpressing metastatic breast cancer
- … -10, in prostate cancer and its regulation by dihydrotestosterone, Insulin-like growth factor I, and epidermal growth factor in the prostate cancer cell model LNCaP
- … -20: Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R) expression is highly correlated with HER2 amplification on circulating epithelial tumor cells (CETCs) in breast cancer …
- … -536924 is better tolerated than alloxan-induced hypoInsulinemia and more effective than metformin in the treatment of experimental Insulin-responsive breast cancer.
- … -7 (MMP7) and phosphorylated Insulin growth factor receptor I (pIGF-IR) as predictors of resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in advanced colorectal cancer (ACRC): A …
- … -binding protein 3 by 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) leads to the potent anti-proliferative effect of androgen deprivation therapy combined with 5-FU in human prostate cancer …
- … -delivery of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor specific siRNA and doxorubicin using chitosan-based nanoparticles enhanced anticancer efficacy in A549 lung cancer …
- … -II (IGF II) and IGF-II receptor (IGF-II R) genes in human primary cancer-implication of autocrine and paracrine mechanism in autonomous growth of hepatic cancer
- … -Ⅱ R) GENES IN HUMAN PRIMARY cancer-IMPLICATION OF AUTOCRINE AND PARACRINE MECHANISM IN AUTONOMOUS GROWTH OF HEPATIC cancer
- … -induced Insulin growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) activation determines response to combined EM164/chemotherapy treatment in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) …
- … -induced upregulation of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 potentiates IGF-1 and accelerates androgen-independent progression in prostate cancer.
- … –Insulin-growth factor receptor-1 [pIGF-IR] and matrilysin [MMP7]) expression as a predictive marker of resistance in previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer …
- … –Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor monoclonal antibody, in combination with cetuximab and irinotecan in Japanese patients with advanced colorectal cancer
- … -like growth factor 1/mammalian target of rapamycin and AMP-activated protein kinase signaling involved in the effects of metformin in the human endometrial cancer
- … -like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 promotes cell proliferation via activation of AKT and is directly targeted by microRNA-494 in pancreatic cancer
- … -like growth factor family as serum biomarkers for response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- … -Like Growth Factor I (IGF) Induced Metastasis Signature Correlates with Poor Prognosis and Decreased Distant Metastasis-Free Survival in Human Breast cancer.
- … -like growth factor I receptor, matrix metalloproteinases, and epidermal growth factor receptor to activate mitogen-activated protein kinase in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- … -like growth factor system in human intestinal epithelial cells. Unique apical sorting of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 in differentiated human colon cancer …
- … -like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) expression and the efficacy of trastuzumab (T) monotherapy for hormone-resistant HER2-postitive metastatic breast cancer …
- … -like growth factor-1 receptor inhibitor IMC-A12, with or without cetuximab, in patients with cetuximab-or panitumumab-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer
- … -like growth factor-binding protein-3 inhibits Insulin-like growth factor-I-induced Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in ishikawa endometrial cancer …
- … -like growth factor-I-induced hypoxia inducible factor 1α protein accumulation and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human breast cancer cells
- … -mediated induction of Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (Her2) expression in gastrointestinal cancer …
- … -Mediated Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 (IGF2) Signal Pathway on Immune Function and Invasion and Migration of cancer Cells in Rats with Ovarian cancer
- … -regulation of Insulin receptor by antibodies against the type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor: implications for anti–Insulin-like growth factor therapy in breast cancer
- … ‐LIKE GROWTH FACTOR‐I AND Insulin‐LIKE GROWTH FACTOR BINDING PROTEIN‐3 FOLLOWING CHEMOTHERAPY FOR ADVANCED BREAST cancer
- … ‐Molecule Dual Insulin‐Like Growth Factor‐1 Receptor/Insulin Receptor Kinase Inhibitor, in Combination with Irinotecan in Patients with Advanced cancer
- … , 4‐hydroxyandrostenedione or tamoxifen on plasma concentrations of Insulin‐like growth factor (IGF)‐I, IGF‐II and IGFBP‐1 in women with advanced breast cancer
- … , adipocyte hormones, and nutrient-sensing pathways in regulating fuel metabolism and energy homeostasis: a nutritional perspective of diabetes, obesity, and cancer
- … , an inhibitor of the Insulin-like growth factor I receptor and Insulin receptor, inhibits proliferation and induces mitochondrial pathway-mediated apoptosis in cancer cell …
- … , an Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor/Insulin receptor inhibitor, induces apoptosis and reduces viability of docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer cells both in …
- … , an open access journal ISSN: 1948-593X 12. Mu N, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Zhang H, Xue F (2012) Insulin resistance: A significan t risk factor of endometrial cancer
- … , dual IGF‐1R/Insulin receptor (IR) inhibitor: Early pharmacodynamic (PD) and positron emission tomography (PET) imaging results from a daily‐dose study in cancer …
- … , estimated by serum C-peptide level, is associated with reduced event-free survival for postmenopausal women in NCIC CTG MA. 14 adjuvant breast cancer trial
- … , human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, and Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and adjuvant tamoxifen resistance in postmenopausal breast cancer …
- … , or formestane on Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I and II, IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs), and IGFBP-3 protease status in patients with advanced breast cancer
- … : Association of Polymorphisms and Haplotypes in the Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) Gene with the Risk of Breast cancer in Korean Women
- … : Dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor for focal adhesion kinase and Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (TAE226) leads to apoptosis in esophageal cancer by inhibiting AKT …
- … : Emodin increases expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 through activation of MEK/ERK/AMPKα and interaction of PPARγ and Sp1 in lung cancer
- … : Hydroxyzine-Hydroxyurea Mix-up: Concomitant Use of Entresto and ACE Inhibitors can Lead to Serious Outcomes: More Outpatient Oral cancer Drugs should be in …
- … : MK-0646 (Dalotuzumab), Insulin growth factor 1 receptor antibody combined with pemetrexed and cisplatin in stage IV metastatic non-squamous lung cancer
- … . Identification of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Receptor (IGF-IR) Gene Promoter-Binding Proteins in Estrogen Receptor (ER)-Positive and ER-Depleted Breast cancer …
- … (IGF-1R) monoclonal antibody cixutumumab (cix) plus mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus (tem) in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC): Results of a …
- … (IGF-1R) predicts poor responses to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring activating …
- … (IGF-IR) monoclonal antibody cixutumumab plus mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor temsirolimus in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer …
- … (IGF1R) expression in small cell lung cancer and the effect of inhibition of IGF1R expression by RNAi on growth of human small cell lung cancer NCI-H446 cell
- … (IGFI), Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) and transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) in patients with locally-advanced and metastatic cancer …
- … (Ir) and Pathologic Complete Response (Pcr) to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (Nac) Among No Diabetic Women with Localized Infiltrating Breast cancer (Libc …
- … (MAb), against the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-IR), as monotherapy in patients with metastastic, asymptomatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC …
- … ) supplementation on antioxidant capacity, DNA single‐strand breaks and levels of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1/IGF‐binding protein 3 in the ferret model of lung cancer
- … 1 receptor antibody CP-751,871 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in previously untreated, locally advanced, or metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer
- … 1 receptor expression and IGF1R 3129G> T polymorphism are associated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients: results from …
- … 1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression, which is dependent on MAP kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in colon cancer …
- … 1855: The novel Hsp90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 reduces Insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 expression and lowers migration rate in triple-negative breast cancer …
- … abrogates the stimulatory effects of 17β-estradiol and Insulin-like growth factor-1 on proliferation of epithelial and granulosa ovarian cancer cell lines via …
- … ACCELERATION OF PROSTATE cancer INHIBITED BY A SMALL MOLECULE INHIBITOR OF Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR 1 RECEPTOR/Insulin …
- … activity and stabilization of IGF-1R mRNA and contributes to growth factor independence and increased survival of the pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2
- … activity of BMS-754807, a small molecule inhibitor of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor/Insulin receptor, in combination with gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer
- … Adipose Tissue Distribution, and Insulin-like Growth Factor-I and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 in Men and Women. cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev …
- … agent N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) decreases Insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) levels on colorectal cancer cell …
- … amino‐acid sequence of the Mannose‐6‐phosphate/Insulin‐like growth‐factor‐II receptor in ovarian carcinomas with loss of heterozygosity and in breast‐cancer cell …
- … amphiregulin and Insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibits Bax-and Bad-mediated apoptosis via a protein kinase C-dependent pathway in non-small cell lung cancer …
- … analog octreotide acetate on circulating Insulin-like growth factor-1 and related peptides in patients with non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: results of a …
- … analysis of serum and tumor vascular endothelial growth factor, Insulin-like growth factor 1, matrix metalloproteinase 7 levels in patients with ovarian cancer
- … and antiestrogen modulation of MCF7 human breast cancer cell proliferation is associated with specific alterations in accumulation of Insulin-like growth factor …
- … and differentiation of a human colon cancer cell line (CaCo2) is associated with significant changes in the expression and secretion of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) …
- … and hormonal regulation of radioimmunoassayable IGF-I (Insulin-like growth factor I) like activity and IGF-binding proteins secreted by human breast cancer cells.
- … and Insulin have identical effects on proliferation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signalling in rat thyrocytes and human follicular thyroid cancer cells
- … and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 (IGFBP-1) Are Key Components of Tamoxifen Action and the Development of Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast cancer …
- … and Insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibits Bax-and Bad-mediated apoptosis via a protein kinase C-dependent pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- … and is associated with circulating Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 levels: implications for risk of early‐onset breast cancer in young women from hereditary breast cancer …
- … and non-secreted forms of intact Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and its 1-97 N-terminal fragment in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells
- … AND NOVEL TARGETS: Microrna-146a Inhibits Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition In Non-Small Cell Lung cancer By Targeting Insulin Receptor Substrate 2
- … and patterns of phospho Insulin growth factor receptor-1 (pIGF-1R) and matrilysin (MMP7) expression in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), and correlation with …
- … AND PHYSIOLOGICAL MATURITY ALONGSIDE Insulin-LIKE ANDROGENIC GLAND (IAG) EXPRESSION AND SIZE IN MALE JONAH CRAB, cancer BOREALIS …
- … and predictive significance of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and HER2 in metastatic colorectal cancer
- … and Survival Data in Non-Metastatic Breast cancer Patients in Correlation with Tumour Infiltrating Lymphocytes, Androgen Receptor and Insulin-Like Growth Factor …
- … antibody (Ab), combined with exemestane and everolimus in hormone receptor-positive (HR+) locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer (LA/mBC): Randomized …
- … antibody, combined with exemestane (Ex) and everolimus (Ev) in hormone receptor-positive (HR+) locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer (BC): primary phase …
- … Antigen (CCA-CA) and Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) in Blood Serum and Bile in Patients with Extrahepatic Bile Duct cancer and Obstructive Jaundice
- … antitumor activity of deguelin targeting the Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor pathway via up-regulation of IGF-binding protein-3 expression in breast cancer
- … are less potent local human growth hormone and Insulin-like growth factor I secretion stimulators than progesterone in human breast cancer explants expressing the …
- … as a survival mechanism of prostate cancer cells in osteoblastic metastases: development of anti-survival factor therapy for hormone-refractory prostate cancer
- … B LYMPHOMAS2 ROLE OF MACROPHAGES IN HUMAN B LYMPHOMA PROGRESSION3 INTERACTION OF BREAST cancer WITH FOLLICULAR DENDRITIC …
- … between carbohydrate metabolism and serum Insulin-like growth factor system in postmenopausal women: comparison of endometrial cancer patients with healthy …
- … between Insulin resistance and frailty with body composition and testosterone in men undergoing androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer
- … between sex hormones, sex hormone binding globulin, Insulin‐like growth factor‐I and Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐I in post‐menopausal breast cancer …
- … BINDING PROTEIN-2 (IGFBP-2) ALTERS PTEN ACTIVITY AND REDUCES THE EFFICACY OF DOCETAXEL IN THE TREATMENT OF PROSTATE cancer (PCA)
- … blockade inhibits the action of EGF, Insulin-like growth factor I, and a protein kinase A activator on the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in prostate cancer cell …
- … blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R) signaling in metastatic pancreatic cancer: Phase I/randomized …
- … both epidermal growth factor receptor and Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor showing enhanced antitumor efficacy against non-small cell lung cancer
- … by 17β-estradiol or bisphenol A via down-regulation of the cross-talk between estrogen receptor α and Insulin growth factor-1 receptor in BG-1 ovarian cancer cells
- … cancer risk in relation to selected genetic polymorphisms in Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, and Insulin-like growth factor-I …
- … cancer Society, and Eli Lilly & Company. An assessment of the efficacy and safety of orlistat for the long-term management of obesity-Molecular regulation of Insulin …
- … carcinogenesis in the Noble rat: The role of Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 (IGF‐1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the development of prostate cancer
- … cell growth of BG-1 ovarian cancer cells induced by 17-estradiol or bisphenol A through down-regulating cross-talk of estrogen receptor and Insulin-like growth factor …
- … cells, of CP-751,871 (C), a monoclonal antibody against the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R), with docetaxel (D) in patients (p) with advanced cancer
- … charantia) extract suppresses adrenocortical cancer cell proliferation through modulation of the apoptotic pathway, steroidogenesis, and Insulin-like growth factor type …
- … Circulating Sex Hormones and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Axis Proteins in a Randomized Controlled Trial of Postmenopausal Women at High Risk of Breast cancer
- … concentrations of androgens up-regulate Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 expression via an androgen response element in LNCaP human prostate cancer …
- … contraception and is associated with circulating IGF-1 levels: implications for risk of early-onset breast cancer in young women from hereditary breast cancer …
- … cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21CIP/WAF is a positive regulator of Insulin-like growth factor I-induced cell proliferation in MCF-7 human breast cancer …
- … diabetes mellitus induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in an Insulinoma-associated antigen-2 autoantibody-positive patient with advanced gastric cancer
- … disruption of Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) signaling via phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 prevents the protective effect of IGF-1 on human cancer …
- … effects of calorie restriction and Insulin-like growth factor-1 treatment on body composition and bone mineral density of C57BL/6 mice: implications for cancer …
- … enhances Insulin-like growth factor I receptor phosphorylation by decreasing its association with the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in MCF-7 breast cancer …
- … epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) heterodimerization and resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer
- … epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number in the prediction of clinical outcome for K-RAS wild-type colorectal cancer patients receiving irinotecan …
- … erlotinib in combination with placebo or R1507, a monoclonal antibody to Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R), for advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer …
- … erlotinib in combination with placebo or R1507, a monoclonal antibody to Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, for advanced-stage non–small-cell lung cancer
- … estrogen receptor-alpha dependent expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and Insulin receptor substrate-1 and proliferation of human breast cancer cells
- … et al., A Prospective Study of Plasma Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and Binding Protein-3 and Risk of Colorectal Neoplasia in Women. cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev …
- … et al.: decline of the red cell blood count in patients receiving androgen deprivation therapy for localized prostate cancer: impact of ADT on Insulin-like growth factor 1 …
- … expression of Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor, Insulin receptor and phospho-Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor/Insulin receptor in primary breast cancer …
- … expression of phospho-Insulin growth factor receptor-1 and matrilysin in KRAS (exon 2) wild-type (WT) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients treated with …
- … factor binding protein-6 inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation: implication for anticancer effect of diethylstilbestrol in hormone refractory prostate cancer
- … factor receptor (IGF1R) pathway driven metastasis signature correlates with poor prognosis and decreased distant metastasis-free survival in human breast cancer
- … factor receptor I (IGF-IR) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) are expressed on the circulating epithelial tumor cells of breast cancer …
- … factor receptor-1 (IGFR-1) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is associated with shorter disease-free survival in resected non-small-cell lung cancer …
- … FACTOR-1 RECEPTOR (IGF-1R) SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS WITH INHIBITORS OF IGF-1R, EGFR, PI3K, MEK, AND MTOR IN BREAST cancer …
- … factor-I in the monitoring of growth hormone treatment with respect to efficacy of treatment and side effects: should potential risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer …
- … factor-I receptor expression and binding protein secretion associated with tamoxifen resistance and estrogen independence in human breast cancer cells in vitro
- … factor-Ⅱ, carbohydrate antigen 19-9 and alpha fetoprotein levels after intervention and percutaneons ethanol injection therapy in patients with primary hepatic cancer
- … factor‑induced mesenchymal‑epithelial transition factor activation leads to Insulin‑like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor unresponsiveness in gastric cancer …
- … farnesyl transferase inhibitor SCH66336-induced negative regulator of angiogenesis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (Clinical cancer Research (2006) 12 …
- … FERMENTED SOYBEAN DREGS ENHANCES GLUCOSE UPTAKE AND MITIGATES Insulin RESISTANCE IN HUMAN LIVER cancer CELL (HEPG2) MODEL …
- … Following Intravenous Alimentation-II. Insulin-and growth hormone responses following oral or intravenous alimentation in patient with far advanced gastric cancer
- … food frequency questionnaire compared to 24 h recalls and biochemical measurements: pilot phase of Golestan cohort study of esophageal cancer. Eur J Clin …
- … for epidermal growth factor and Insulin-like growth factor I by ZR-75-1 human breast cancer cell variants is inversely related: the effect of steroid hormones on Insulin …
- … for the selenium and vitamin E cancer prevention trial: effects of delayed processing on carotenoids, tocopherols, Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin-like growth factor …
- … FOR: Science Writers and Editors on the Journal Press List: Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptors May Be Involved in Development of Resistance to the Breast cancer …
- … from hen’s‐egg yolks against human mannose‐6‐phosphate/Insulin‐like growth‐factor‐II receptor (M6P/IGFII‐R): Characterization and potential use in clinical cancer …
- … from human Insulin‐like growth factor‐II mRNA binding protein 3 can induce human leukocyte antigen‐A2‐restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes reactive to cancer cells
- … from Ruiter et al regarding ‘Risk of cancer in patients on Insulin glargine and other Insulin analogues in comparison with those on human Insulin: results from a large …
- … fusion protein targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor shows potent antitumor efficacy against esophageal cancer
- … genetic variation in 61 genes related to steroid hormone and Insulin-like growth factor-I metabolism and breast cancer risk in the NCI breast and prostate cancer …
- … growth factor (EGF), Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), cortisol, and melatonin in women with breast cancer
- … growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein-1 modulate prostate cancer cell growth and apoptosis: possible mediators for the effects of diet and exercise on cancer …
- … growth factor I receptor/Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor PQIP exhibits enhanced antitumor effects in combination with chemotherapy against colorectal cancer …
- … growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene copy number (GCN) in the prediction of clinical outcome for K-RAS wild type colorectal cancer patients receiving irinotecan …
- … growth factor receptor (EGFR) or Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) contributes to adaptive resistance to NVP-BKM120 in non-small cell lung cancer …
- … growth factor receptor and Insulin‐like growth factor receptor in the expression of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans and cell motility in breast cancer cells
- … growth factor receptor type 1 antibody (h7C10) enhances the antitumor activity of Navelbine® and anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy against human cancer …
- … growth factor receptor type I antibody (h7C10) enhances the antitumor activity of vinorelbine and anti‐epidermal growth factor receptor therapy against human cancer …
- … growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) correlates with a poor patient prognosis in resected non-small cell lung cancer …
- … growth factor-binding protein-3 modulates expression of Bax and Bcl-2 and potentiates p53-independent radiation-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer …
- … Growth Factor-β–Stimulated Clone-22 Is an Androgen-Regulated Gene That Enhances Apoptosis in Prostate cancer following Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Receptor …
- … growth of ovarian cancer cells was reversed by a phytoestrogen, genistein, by inhibition of a crosstalk between estrogen receptor and Insulin-like growth factor 1 …
- … hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-3 with gefitinib resistance in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- … hormone-releasing hormone antagonists interfere with autocrine and paracrine growth stimulation of MCF-7 mammary cancer cells by Insulin-like growth factors
- … human monoclonal antibody to Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor, combined with gemcitabine as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer …
- … hyperlipidemia in patients with advanced cancer receiving combination treatment with the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor temsirolimus and Insulin …
- … hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, vascular endothelial growth factor, and angiogenesis by an Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor autocrine loop in human pancreatic cancer
- … I obliterates the pregnancy-associated protection against mammary carcinogenesis in rats: evidence that IGF-I enhances cancer progression through estrogen …
- … I trial of a DNA plasmid-based vaccine targeting Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) in patients with advanced ovarian cancer: Preliminary safety and …
- … IGF1 receptor/Insulin receptor dual kinase inhibitor BMS-754807 targets the cancer stem cell population in addition to its synergism with Lapatinib in colorectal cancer …
- … II comparative study of metformin plus first-line chemotherapy (CT) versus CT alone in HER2-negative, Insulin-resistant (IR), nondiabetic metastatic breast cancer …
- … II study of the anti‐Insulin‐like growth factor receptor type 1 (IGF‐1R) monoclonal antibody robatumumab (SCH 717454) in patients with advanced colorectal cancer
- … importance of Cannabis sativa L. in regulation of Insulin and IL-6R/MAO-A in cancer cell progression and migration of breast cancer patients with diabetes
- … in a cellular model of prostate cancer is associated with methylation of the androgen receptor gene and transcriptional suppression of the Insulin-like growth factor-I …
- … in androgens and upregulation of Insulin-like growth factor-1 are involved in high bone turnover in men receiving androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer
- … in Human MCF7 ER+ Breast cancer Cells by Nuclease-Resistant IRS1 siRNA Conjugated To a Disulfide-Bridged d-Peptide Analogue of Insulin-Like Growth Factor …
- … inactivation implies independent functions for Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-related protein 1 and the related IGFBPL1 in inhibiting breast cancer …
- … increased Insulin-like growth factor-1 concentrations, in healthy nulligravid women aged 19-25 years who were first and/or second degree relatives to breast cancer …
- … induced by combination of farnesyl transferase inhibitor SCH66336 and Insulin like-growth factor binding protein-3 in apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cell …
- … induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation through the AMP-activated protein kinase and Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor pathways in the bile duct cancer …
- … inhibition of synergistically Insulin-like growth factor-1-and bisphenol A-induced poliferation of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha)-positive human breast cancer MCF …
- … inhibitor for focal adhesion klinase (FAK) and Insulin like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR), exhibits antiproliferative effect in Barrett’s esophageal cancer in vitro and in …
- … inhibitor letrozole and inhibitors of Insulin-like growth factor I receptor synergistically induce apoptosis in in vitro models of estrogen-dependent breast cancer
- … Insulin growth factor/Insulin growth factor receptor1 (IGF-I, IGF-I-1R) and VEGF-A as prognostic factors and surrogate biomarkers in triple negative breast cancer …
- … Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding protein (IGFBP)-3 levels and postmenopausal breast cancer risk in the prostate, lung, colorectal, and ovarian cancer …
- … Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3 concentrations and prostate cancer risk: results from the European Prospective Investigation into cancer …
- … Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and estrogen receptor with pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-negative breast cancer
- … Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 in the prognosis of breast cancer and promotion of accelerated growth and chemo-resistance in MDAMB-231 breast cancer …
- … Insulin-Like Growth Factor I (IGF-I)-Induced Gene, Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11 (SLC7A11)/xCT, Mediates IGF-I-Induced Biological Behaviors in Breast cancer …
- … Insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene silencing inhibits cell proliferation, induces cell apoptosis, and suppresses tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer: in vitro …
- … Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) with Platinum-based Chemotherapy Outcomes in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung cancer.
- … Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 inhibitor) in patients with asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic (non-opioid requiring) metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer …
- … Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) expression in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) with E-cadherin (E-CAD) expression and improved survival in breast cancer …
- … Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor kinase inhibitor NVP-ADW742, in combination with STI571, delineates a spectrum of dependence of small cell lung cancer …
- … Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, and breast cancer risk: results from the European prospective investigation into cancer and …
- … Insulin-like growth factor-II (proIGF-II) and mature IGF-II differentially mediate resveratrol-induced downregulation of survivin and apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer …
- … Insulin-using diabetes mellitus patients, non-Insulin-using diabetes mellitus patients and patients without diabetes mellitus after partial gastrectomy for gastric cancer
- … Insulin‐like growth factor (IGF)‐independent interactions of IGF binding protein‐3 and IGF binding protein‐5 on apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Involvement of …
- … Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors and G protein-coupled receptor signaling systems: a novel target for the antidiabetic drug metformin in pancreatic cancer
- … interfering RNAs targeting Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and inslin-like growth factor 1 receptor potentiate the cytotoxic effect of chemotherapy in ovarian cancer …
- … is better tolerated than alloxan-1 induced hypoInsulinemia and more effective than metformin in the treatment of 2 experimental Insulin responsive breast cancer …
- … is expressed in normal canine mammary gland and benign adenomas but decreased in metastatic canine mammary carcinomas similar to human breast cancer
- … kinase and Insulin growth factor 1 signaling pathways were inhibited by small interfering RNA against AT‑rich interactive domain 1A in endometrial cancer
- … LB-391: Combination of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor/Insulin receptor (IGF1R/IR) antagonist with anti-PD-L1 antibody blocks triple-negative breast cancer …
- … level of Insulin growth factor-1 receptor expression is directly correlated with the tumor uptake of 111In-IGF-1 (E3R) in vivo and the clonogenic survival of breast cancer …
- … Levels and Secretion of Insulin‐Like‐Growth‐Factor‐Binding Proteins in MCF‐7/6, MCF‐7/AZ and MDA‐MB‐231 Breast cancer Cells: Differential Modulation by …
- … levels of circulating Insulin-like growth factor-I, IGF-binding globulin-3 and testosterone predict hormone-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal women: a case …
- … levels of Insulin-like growth factor I, II, and binding protein 3, transforming growth factor β-1, soluble Fas ligand and superoxide dismutase activity in stomach cancer …
- … levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I and decreased circulating levels of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 in postmenopausal women with endometrial cancer
- … levels of Insulin-like growth factor-I and-II and Insulinlike growth factor binding protein 3 in women with squamous intraepithelial lesions and cervical cancer
- … like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) antibody CP-751871 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer …
- … Lindera obtusiloba extract suppresses growth and attenuates Insulin like growth factor-1 receptor signaling and NF-kappaB activity in human liver cancer cell …
- … low-affinity Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein, LIBC (lost in inflammatory breast cancer), and RhoC GTPase correlate with the inflammatory breast cancer …
- … measurements of testosterone, Insulin‐like growth factor 1, and Insulin‐like growth factor binding protein‐3 in the diagnosis of prostate cancer among Korean men
- … metabolic disorder in patients with prostate cancer receiving androgen deprivation therapy (ADT): impact of ADT on the growth hormone/Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 …
- … METABOLISM IS INFLUENCED DIFFERENTLY BY THE Insulin-LIKE-GROWTH-FACTOR (IGF)/Insulin AXIS IN PROSTATE cancer & BENIGN PROSTATE …
- … model assessment to detect Insulin resistance and identify patients at high risk of breast cancer development: National cancer Institute of Naples experience
- … module associated with Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF1) pathway activation predicts poor response to tamoxifen in women with ER+/HER2-early breast cancer (BC) …
- … monoclonal antibody against Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor (IGF-1R) as second-line therapy in patients with recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer.
- … mutations in the cancer gene Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), at a locus previously associated with metformin response, cause dysglycaemia and Insulin …
- … of a legume-enriched, low-glycemic index diet is associated with biomarkers of Insulin resistance and inflammation among men at risk for colorectal cancer
- … OF BG-1 OVARIAN cancer CELLS INDUCED BY 17β-ESTRADIOL OR BISPHENOL A THROUGH DOWNREGULATING ESTROGEN RECEPTOR α AND Insulin …
- … of Blood Hemoglobin Concentration in Patients Receiving Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) for Prostate cancer: Impact of ADT on Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 …
- … of both MCF-7 and Hs578T human breast cancer cell lines by vitamin D analogues is associated with increased expression of Insulin-like growth factor binding …
- … of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Insulin-Like Growth Factor: A Potential New Therapeutic Strategy To Reduce Bone Pain in Bone Metastases of Breast cancer …
- … of droloxifene on plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, pro-IGF-IIE, Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-1 and IGFBP-3 in breast cancer …
- … of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and Insulin-like growth factor 1 and its binding protein 3 in advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer
- … of estrogen receptor and Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling pathways is involved in the anticancer effect of genistein on ovarian cancer growth induced by …
- … of excess body weight in postmenopausal breast cancer patients, in relation to expression of Insulin‐like growth factor I receptor and Insulin‐like growth factor II genes
- … of exercise training on fasting Insulin, Insulin resistance, Insulin-like growth factors, and Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in postmenopausal breast cancer …
- … of genes coding for Insulin-like growth factor 1 and its major binding proteins, circulating levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and breast cancer risk: results from the …
- … of genes involved in the Insulin signalling pathway (IGF1, PTEN and IGFBP1) in the endometrium may link polycystic ovarian syndrome and endometrial cancer
- … of genistein on BG-1 ovarian cancer growth induced by 17 β-estradiol or bisphenol A via the suppression of the crosstalk between estrogen receptor alpha and Insulin …
- … of growth and migration of MDA-MB-468 breast cancer and SW480 colon cancer cells when cultured with diabetogenic levels of glucose and Insulin
- … of Insulin like growth factor 1 and Insulin like growth factor binding protein 3 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and serum of patients with lung cancer
- … of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) gene polymorphism with the susceptibility to development of prostate cancer and influence on serum …
- … of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-3, and C-peptide predict long-term prostate cancer survival in men without apparent prostate cancer at …
- … of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling enhanced silibinin-induced activation of death receptor and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in human breast cancer …
- … of Insulin-like growth factor 1, sex hormones, and binding proteins in relation to prostate cancer risk in the National cancer Institute Breast and Prostate cancer …
- … of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 4 (IGFBP-4) in MCF-7 breast cancer cells is associated with reduced responsiveness to Insulin-like growth factors in vitro …
- … of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 potentiates Insulin-like growth factor-I activity and accelerates progression to androgen independence in prostate cancer …
- … of Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins-2 and-4 associated with the development of tamoxifen resistance and estrogen independence in human breast cancer …
- … of Insulin-like growth factor I receptor is associated with increased expression of transcription factor Sp1 and regional lymph node metastasis of human gastric cancer
- … of Insulin-like growth factor II and stimulate production of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-6 in conjunction with growth suppression of HT-29 colon cancer …
- … of Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor-A by heat shock protein 90 inhibition effect in triple negative breast cancer
- … of Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor humanized monoclonal antibody MK-0646 and small molecule kinase inhibitor OSI-906 in colorectal cancer
- … of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor/Insulin receptor (IGF1R/IR) and androgen receptor (AR) antagonists with metformins inhibits triple-negative breast cancer …
- … of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1-Receptor expression and endocrine treatment on clinical outcome of postmenopausal hormone receptor positive breast cancer …
- … of Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) using NVP-AEW541, a small molecule kinase inhibitor, reduces orthotopic pancreatic cancer growth and angiogenesis
- … of Insulin-like growth factor-II, Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, and estrogen receptor-alpha expression to disease progression in epithelial ovarian cancer.
- … of matrix metalloproteinase-7, Insulin-like growth factor-1, Insulin-like growth factor-2 and Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in patients with colorectal cancer: Insulin …
- … of PKB/Akt Kinase Activity by the Vacuolar-ATPase in the Canonical Insulin Signaling Pathway: Implications for the Targeted Pharmacotherapy of cancer
- … of polymorphic variants in steroid hormone and Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 metabolism and risk of in situ breast cancer: Results from the Breast and Prostate cancer …
- … of polymorphisms in genes of Insulin receptor substrate-1 and enzymes involved in estrogen biosynthesis and metabolism among breast cancer patients with BRCA1 …
- … of preoperative plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor I and Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins-2 and-3 with prostate cancer invasion, progression, and …
- … of protein kinase B activation by Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor-1 revealed by specific inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase—significance for diabetes and cancer
- … of protumorigenic pathways by Insulin like growth factor binding protein2 and its association along with β-catenin in breast cancer lymph node metastasis
- … of radiation and docetaxel on anti-tumor effects of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) in hormone-refractory human prostate cancer …
- … of radioimmuno and carbon nanotube field-effect transistor assays for measuring Insulin-like growth factor-1 in a preclinical model of human breast cancer
- … of raloxifene on Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, and leptin in premenopausal women at high risk for developing breast cancer
- … of sense and antisense Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-4 complementary DNA alters the mitogenic response of a human colon cancer cell line (HT-29) …
- … OF SERUM Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR IS INDEPENDENTLY ASSOCIATED WITH INCREASED RISK OF HIGH GRADE PROSTATE cancer
- … of serum Insulin, osteopontin, and hepatocyte growth factor predicts time to castration-resistant progression in androgen dependent metastatic prostate cancer …
- … of short-acting intravenous Insulin therapy in preparation of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography computed tomography scan in cancer …
- … of the luteinizing hormone production in men receiving androgen deprivation therapy with gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues for localized prostate cancer
- … of the role of Insulin-like and vascular endothelial growth factors in development, prognosis and targeted therapy in patients with ovarian cancer
- … of type I Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) in tamoxifen-resistant cells: Implications for cotargeting of IGF1R and estrogen receptor (ER) in breast cancer.
- … of vitamin D deficiency, part 2: deficiency and its association with autoimmune disease, cancer, infection, asthma, dermopathies, Insulin resistance, and type 2 …
- … of α-interferon on Insulin-like growth factor-I, Insulin-like growth factor-II and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 secretion by a human lung cancer cell line in …
- … oil slows prostate cancer xenograft growth relative to other dietary fats and is associated with decreased mitochondrial and Insulin pathway gene expression
- … oligonucleotide targeting Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) enhances paclitaxel sensitivity in a castrate-resistant and paclitaxel-resistant prostate cancer …
- … on circulating free prostate-specific antigen, Insulin-like growth factor-I, and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 levels in men with superficial bladder cancer
- … on PI3K/Akt/mTOR rather than MAPK pathways in upregulation of basal growth following long-term oestrogen deprivation in three human breast cancer cell …
- … on the downregulation of MYC, Insulin and IGF-1 receptors: a possible mechanism underlying the anti-growth and anti-migration in chemoresistant colorectal cancer …
- … P2-05-05: Canine invasive mammary carcinoma as a spontaneous model for Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-overexpressing triple negative breast cancer
- … pathway calcium ATPase 1 (SPCA1) is a key regulator of Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) processing in the basal-like breast cancer cell line MDA …
- … pathway modulator AXL1717 in combination with gemcitabine HCl and carboplatin in previously untreated, locally advanced, or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
- … patterns of AKT/protein kinase B, Insulin-like growth factor-1, Insulin-like growth factor-2 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in human prostate cancer
- … PD01-06: Activation of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Pathway Distinguishes African American from European American Patients with Triple-Negative Breast cancer …
- … phosphorylation correlates with Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-induced resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in head and neck cancer cells
- … plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-binding protein 3 and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer …
- … polymorphisms of Insulin-like growth factor 1 and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3, xenoestrogen, phytoestrogen, and premenopausal breast cancer
- … Profiling of Phenotypically-Defined Hormone-Receptor Positive Breast cancer: Evidence for Increased Transcriptional Activity of the Insulin Growth Factor Receptor …
- … prostate cancer cells in human adult bone implanted into nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient mice by a ligand-specific antibody to human Insulin …
- … protein and receptors for epidermal growth factor (EGF-R), Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1-R) and somatostatin (SS-R) in patients with breast and ovarian cancer
- … protein-2 stimulates proliferation and activates multiple cascades of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in NIH-OVCAR3 human epithelial ovarian cancer …
- … quality and quantity of visceral fat tissue are associated with Insulin resistance and survival outcome after chemotherapy for patients with early-stage breast cancer
- … re: Chokkalingam A. et al., Insulin-like Growth Factors and Prostate cancer: A Population-based Case-Control Study in China. cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev., 10 …
- … receptor and amphiregulin expression on survival in patients with stage II/III gastric cancer enrolled in the Adjuvant Chemotherapy Trial of S-1 for Gastric cancer
- … receptor gene expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: a comparison of the effects of cyclic adenosine 3′, 5′-monophosphate, estradiol, Insulin-like growth factor-I …
- … receptor sites for Insulin. Insulin brings glucose into the cells…. and cancer cells feed on the glucose. if the cancer cell is not exposed to glucose or Insulin, it is …
- … Receptor Substrate 1 (IRS1) in tumor samples of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Implications for aberrant Insulin signaling in development of cancer
- … receptor-A with a dual IGF-1R/IR inhibitor: Overcoming a potential escape mechanism from IGF-1R-specific signaling inhibition in Insulin receptor-A transfected cancer …
- … receptor–positive locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer: randomized phase 2 results. Paper presented at: 41th Annual San Antonio Breast cancer …
- … receptor, mesenchymal–epithelial transition factor, and Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 expression on survival of patients with oral and oropharyngeal cancer
- … regulates Insulin like growth factor signaling and induces intrinsic and extrinsic pathway mediated apoptosis in androgen independent prostate cancer cells (PC-3)
- … relationship between the Insulin-like growth factor-1 axis, weight loss, an inflammation-based score and survival in patients with inoperable non-small cell lung cancer
- … RESPONSE AFTER VACCINATION TARGETING Insulin GROWTH FACTOR BINDING PROTEIN 2 IN A SYNGENEIC MOUSE MODEL OF OVARIAN cancer …
- … role of Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in estrogen receptor signaling pathway and possible therapeutic target for hormone therapy-resistant breast cancer
- … roles for the Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II and mannose 6-phosphate (Man-6-P) binding activities of the IGF-II/Man-6-P receptor in the growth of prostate cancer …
- … scrapes levels of Insulin-like growth factor-II and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in women with squamous intraepithelial lesions and cervical cancer
- … sensitivity and Insulin-like growth factors in predicting the risk of developing secondary primary tumors and tumor recurrence in patients with head and neck cancer
- … sensory neuropeptides, epidermal growth factor, Insulin, and somatostatin on the non-transformed intestinal epithelial cell line IEC-6 and the colon cancer cell line HT …
- … signaling cascade in the mononuclear cells of peripheral blood: association with Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor levels in the blood of patients with cancer and …
- … significance of combined determination of serum levels of free prostate specific antigen (fPSA) and Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) in patients with prostatic cancer
- … significance of immunohistochemical expression of Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and matrix metalloproteinase-7 in resected non-small cell lung cancer
- … significance of Insulin-like growth factor 1 and Insulin like growth factor binding protein 3 in serum and bronchoalveolar lavagae fluids of patients with lung cancer
- … significance of pretreatment plasma levels of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-2, and IGF binding protein-3 in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- … Stem Cell Plasticity Through Modulation of Epidermal Growth Factor and Insulin‐Like Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell cancer
- … study of the association of circulating levels of serum Insulin-like growth factor I and Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 with breast cancer in young women in …
- … STUDY ON EXPRESSION OF Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR 1 RECEPTOR (IGF-1R) IN CHINESE PROSTATE cancer AND BENIGN PROS TATIC …
- … subcellular and extracellular localisations of proteins required for Insulin-like growth factor-and extracellular matrix-induced signalling events in breast cancer …
- … Suppresses the Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) Ablating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor Resistance in Adult High Grade Gliomas.”[cancer …
- … tamoxifen-sensitive and resistant human breast cancer cell lines in relation to expression of receptors for epidermal growth factor and Insulin-like growth factor …
- … target of metformin indirectly is mammalian target of rapamycin, then the Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor axis will audit the efficacy of metformin in cancer clinical …
- … targeting the Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R), in combination with cetuximab, can reverse acquired resistance to cetuximab in pancreatic and colon cancer …
- … Tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 engages ErbB3 and Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling to promote antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer
- … the effects of alcohol, Insulin, glucose analogues, hypoglycaemic agents, 434 MHz and ionizing electromagnetic radiation and other agents upon normal and cancer …
- … the Expression Reduction of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein (IGFBP)-3 and PTEN and the Clinicopathological Parameters in Breast cancer
- … the Insulin/Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Receptor Pathway as a Mechanism of Escape from Hormone Dependence in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast cancer
- … the mitogenicity of Insulin analogues relative to human Insulin—response to: Weinstein D, Simon M, Yehezkel E, Laron Z, Werner H. Insulin analogues display IGF‐I …
- … the somatostatin analog lanreotide on the circulating levels of chromogranin‐A, prostate‐specific antigen, and Insulin‐like growth factor‐1 in advanced prostate cancer …
- … the World cancer Research Fund/American Institute for cancer Research cancer prevention recommendations and biomarkers of inflammation, hormonal, and Insulin …
- … to the Editor‐responses to Weisntein D, Simon M, Yehezkel E, Laron Z, Werner H. Insulin analogues display IGF‐I‐like mitogenic and antiactivity in cultured cancer …
- … to the role of fatty acid binding protein-7, Insulin like growth factor binding protein-2 and phosphatase and tensin homolog in triple negative breast cancer, in vitro and …
- … transition and γ‐radiation‐resistant subtypes by focal adhesion kinase‐associated Insulin‐like growth factor 1 receptor activation in non‐small‐cell lung cancer cells
- … value of Insulin‑like growth factor 2 mRNA‑binding protein 3 and vascular endothelial growth factor‑A in patients with primary non‑small‑cell lung cancer
- … variation at the ‐202 locus in IGFBP3: Influence on serum levels of Insulin‐like growth factors, interaction with plasma retinol and vitamin D and breast cancer risk
- … via the PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway and of the anit-apoptotic translationally controlled tumour protein TCTP in the development of drug resistance in colon cancer …
- … with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and 5‐fluorouracil on plasma Insulin‐like growth factor‐I and chosen hormones in breast cancer pre‐menopausal patients
- … with the anti-Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor monoclonal antibody IMC-A12 (cixutumumab) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- * Association of the Insulin-like growth factor 1 microsatellite with predisposition to colorectal cancer
- 1323 FOXA1 PROMOTES TUMOR PROGRESSION VIA Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR BINDING PROTEIN 3 PATHWAY IN PROSTATE cancer
- Physical activity and Insulin-like growth factors in breast cancer survivors: A metaanalysis
- 15-Lipoxygenase-1 expression upregulates and activates Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in prostate cancer cells
- 1668: Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 is an Independant Predictor of Prostate cancer Survival
- 17β-estradiol levels during an entire menstrual cycle in response to adult stature and Insulin, of possible importance for breast cancer risk. The EBBA-I study.
- 17β-Estradiol up-regulates the Insulin-like growth factor receptor through a nongenotropic pathway in prostate cancer cells
- 184: Targeting the type 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) in renal cancer.
- 1P280 Possible involvement of glucose metabolism regulation in Insulin-mediated modulation of radiosensitivity in human breast cancer cells.(Radiobiology & Active …
- 2-Deoxyglucose Reverses the Promoting Effect of Insulin on Colorectal cancer Cells In Vitro
- 2052 Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-I (IGF-I) POLYMORPHISMS PREDICT THE SURVIVAL OF PROSTATE cancer PATIENTS WITH BONE METASTASIS AT …
- 239: Silencing of the Type 1 Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor (IGF1R) Gene Enhances Sensitivity of Prostate cancer to Dna Damaging Agents Through Impaired …
- 316 DECREASED MITOCHONDRIAL AND Insulin PATHWAY GENE EXPRESSION SIGNAL IN PROSTATE cancer XENOGRAFT MOUSE MODEL WITH …
- 40 YEARS OF IGF1: Anti-Insulin-like growth factor therapy in breast cancer
- 409: High Levels of Circulating Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Increase Prostate cancer Risk. A Prospective Study
- 412 Insulin resistance in amino acid transport system A in head and neck cancer patients studied by positron emission tomography (PET) and carbon-11-methionine
- 461: Insulin Resistance is Inversely Related to Prostate cancer; A Prospective Study in Northern Sweden
- 54 Diagnostic accuracy of serum Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 for ovarian cancer
- 643 Insulin-like growth faCtors (igfs) and igf binding Proteins in Psa-deteCted Prostate cancer: Control study (ProteCt)
- 725: Overexpression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 in Human Bladder cancer Cells Enhances their Metastatic Potential
- 726 Insulin-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-2 (IGF2) LOSS OF IMPRINTING MARKS A FIELD DEFECT WITHIN HUMAN PROSTATES CONTAINING cancer
- 735 THE IMPACT OF Insulin AND ITS RECEPTORS ON IGF TARGETING THERAPIES IN PROSTATE cancer
- 736: The Type-1 Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor is Overexpressed in Bladder cancer, and Targeting by RNA Interference Reduces in Vitro Survival
- 9 The Insulin-Like Growth Factor A Target for cancer Treatment