
VICTORIOUS : Science Based Anti Viral Formula 200:1
July 12, 2020
PARASLAYER : Anthelmintic 200:1
November 6, 2020AUTONOMOUS : Nootropic Tour De Force 200:1
$275.00
200:1 concentration
300 1/8 tsp servings per 100g.
Featuring: Abelmoschus Esculents • Acorus Calamus • Adhatoda Vasica Nees • Aegle Marmelos • Ajuga Bracteosa Wall • Alangium Salvifolium • Albizzia Lebbeck Bark • Alpha-Gpc • Alpha-Lipoic Acid • Amycenone (Hericium Erinaceum) • Andrographolide (Andrographis Paniculata) • Aniracetam • Arabica Coffee Pulp • Argyreia Speciosa • Artemisia Absinthium • Withanolides (Ashwagandha • Bacopa Monnieri • Bauhinia Variegata • Benincasa Hispida • Berberine (Coptis Chinensis Franch.) • Brassica Oleraceae • Carica Papaya Seeds • Carissa Carandus • Carnosine • Carum Carvi • Cdp-Choline • Celastrus Paniculatus • Centella Asiatica • Citicoline • Clitoria Ternatea • Convolvulus Pluricaulis • Cordycepin ( Cordyceps Sinensis) • Cornus Officinalis • Crataeva Nurvala • Cressa Cretica • Dangsheng Polysaccharide (Radix Codonopsis) • Dichrocephala Integrifolia • Docosahexaenoic Acid (Marine Microalgae) • Eclipta Alba • Eclipta Prostrata • Embelin • Epicatechin • Etiracetam • Evolvulus Alsinoides • Fasoracetam • Ficus Religiosa • Filipendula Vulgaris • Foeniculum Vulgare • Galantamine • Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (Gaba) • Ginkgo Biloba Extract • Hibiscus Sabdariffa • Hovenia Dulcis • Huperzine A (Lycopodium Serratum Thunb) • Hypericin (Hypericum Perforatum) • Idebenone • Ipomoea Aquatic Forsk • Juniperus Recurva • Leontopodium Alpinum • Leuzea Carthamoides • Marsilea Minuta • Meclofenoxat • Mimosa Pudica • Moringa Oleifera Leaves • Murraya Koenigii • Nardostachys Jatamansi • Nefiracetam • Nigella Sativa • Noopept • Nyctanthes • Ocimum Sanctum Leaf • Gallic Acid (Olive Olea Europaea L. Fruit) • Oxiracetam • Panax Ginseng Ginsenoside • Passiflora Actinia • Phenlypiracetam • Phloretin (Apple Peel) • Phosphatidylserine (Soybean) • Phyllanthus Reticulatus Poir • Piper Longum L • Pramiracetam • Prunus Amygdalus • Ptychopetalum Olacoides • Pueraria Tuberosa • Pyritinol • Pyroglutamate • Radix Polygalae • Red Ginseng Ginsenoside Rg1 Rb1 • Reishi Mushroom Polysaccharid • Resveratrol (Polygonum Cuspidatum) • Rice Bran Oil • Rubia Cordifolia Linn. • Sarsasapogenin-Aa13 • Salidroside (Rhodiola Rosea) • Shankhpushpi • Sida Cordifolia Alkaloids • Slimaluma • Sulbutiamine • Sunifiram • Tabernaemontana • Taxillus Tomentosus • Thespesia Populnea • Tiliacora Racemosa Colebr • Tinospora Cordifolia • Trapa Bispinosa • Unifiram • Vateria Indica Vitis Vinifera L. • Vigna Mungo • Vinpocetine (Cavinton) • Vitis Vinifera • Yashtimadhu Choorna • Zingiber Officinale
SCIENCE & ingredients:
Abelmoschus Esculentus
Abelmoschus esculentus L. (ladies finger, okra) is a well-known tropical vegetable, widely planted from Africa to Asia and from South Europe to America. In the present study, we investigated the in vitro Antioxidant capacity and in vivo protective effect of the aqueous and methanolic seed extracts of Abelmoschus esculentus against scopolamine-induced Cognitive impairment using passive avoidance task and acute restraining stress-induced behavioural and biochemical changes using elevated plus maze (EPM) and forced swimming test (FST) in mice. Our results demonstrated that the pretreatment of mice with aqueous and methanolic seed extracts of Abelmoschus esculentus (200 mg/kg, p.o.) for seven days significantly (P < 0.01) attenuated scopolamine-induced Cognitive impairment in the passive avoidance test.
In addition, these extracts significantly reduced the blood glucose, corticosterone, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels elevated by acute restraint stress and also significantly increased the time spent in open arm in EPM and decreased the immobility time in FST. It has also been revealed that these extracts showed a significant Antioxidant activity and no signs of toxicity or death up to a dose of 2000 mg/kg, p.o. These results suggest that the seed extracts of Abelmoschus esculentus L. possess Antioxidant, antistress, and Nootropic activities which promisingly support the medicinal values of ladies finger as a vegetable.
Acorus Calamus
Nootropic herbs (Medhya Rasayana) in Ayurveda
Nootropic agents used as a memory enhancer can improve thinking, memor y, and alertness in people with Alzheimer’s disease andother disease that affect the mind. memory is perhaps the most vital of all aspects that differentiates human beings from other animals. However, memory can become faulty due to several reasons, and in that case the person is not able to make full use of his or her potentials. Since ages, agents and natural remedies have been prescribed to enhance memories in people. 4 million people are thought to be suffering from age related memory and increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Although several Nootropic agents are available to treat memory problems. In recent years research on medicinal plants have been studied for Nootropic activity. Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi), Evolvulus alsinoides (Shankhpushpi),Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha), Acorus calamus(Bach)etc.,are used as a memory enhancer agents. The abstract refers to several plants with their activity. The main aim of this article isto give up the data reviews on plants with nootropic properties.
Adhatoda Vasica Nees
Objectives: The Present study was planned to evaluate the Nootropic activity of ehanolic extract of Adhatoda vasica nees (EERAV) and aqueous extract of A. vasica (AQERAV) in experimentally induced amnesic models in mice and rats.
Methods: AERAV and AQERAV were prepared successively with roots of A. vasica using soxhlet apparatus. LD50 studies for these two extracts were carried out in albino mice up to the dose level of 2000 mg/kg as per guidelines No. 425 of CPCSEA. EERAV and AQERAV were studied for their Nootropic effect evaluated in five different experimental models like Active (Rats) and Passive avoidance, Diazepam, Scopolamine, Sodium nitrite induced amnesia and Sodium nitrite induced hypoxia models all in mice. The parameters studied in Nootropic activity are Step Down Latency (SDL), Step Down Error (SDE), Time spent in Shock Zone (TSZ), Number of shocks, Transfer Latency (TL) and Time for cessation of respiration.
Results: No mortality observed even at the highest dose tested (2000 mg/kg) and did not produce any significant effect on locomotor activity in mice. experimental studies have shown that EERAV and AQERAV have exhibited a dose dependent Nootropic activity. A Significant Nootropic activity was recorded with both the extracts in Active and Passive avoidance, Scopolamine, Diazepam and Sodium nitrite induced amnesia models. AQERAV exhibited a significant Nootropic effect with medium and high doses only in Active and Passive avoidance models, scopolamine and Diazepam induced amnesia models.
Conclusion: The present study suggests that both extracts possessed a significant Nootropic activity in mice and rats.
n the present study A. marmelos selected for evaluation of its anti-amnesic activity and also to study its influence on cholinergic system of the Brain of rats, because there were no reporters on its anti-amnesic activity being evaluated pharmacologically. The electroshock (MES) induced amnesia model and scopolamine a well known anticholinergic agent was another model also used to produce loss of memory. Chronic exposure to MES for 7 days produced a significant decrease in latency to expose to electroshock grid in step down latency and increased the time of transfer latency in elevated plus maze. The same effect was also seen in scopolamine exposed animals, we foundthat there was a significant increase in acetylcholine sterase enzyme activity in MES exposed and also in Scopolamine exposed rats.
Whereas, administration of ethanol extracts of leaf of A. marmelos simultaneously with MES and scopolamine exposure for 7 days prevented the impairment of memory consolidation and also reduced the Acetyl cholinesterase enzyme activity in all parts of the brain. Daily administration of extracts significantly attenuated the amnesic effect of both MES and scopolamine, which was also observed in performance of learned tasks in elevated plus maze and step-down apparatus.
Objective: Nootropic activity of Ajuga bracteosa herb was investigated using scopolamine induced amnesia (memory deficits), elevated plus-maze (EPM) and Morris water maze (MWM) experimental models in Swiss albino mice.
Materials and Methods: Successive maceration of the plant was made using n-hexane followed by methanol solvent to extract out active principles according to their solubility. Methanolic herbal extract of Ajuga bracteosa (ABE) was prepared using maceration. neuroprotective effect of ABE in Swiss albino mouse was recorded in transfer latency time (TLT) as inflation-ratio in EPM, escape latency time (ELT) and time spent in target quadrant (TSTQ) in MWM model using scopolamine induced amnesia. agent induced lipid per-oxidation was measured by estimation of the content of acetyl cholinesterase (AChE), glutathione (GSH), malondialdehyde (MDA) and total protein in Brain blood sample of the mouse.
Results: ABE (500 and 750 mg/kg, p.o.) increased the TLT, ELT and TSTQ. Scopolamine markedly decreased the TLT over 3 minutes, ELT, TSTQ over 90 sec and consecutively impaired Learning and memory . Higher levels of Brain AChE and MDA but lower levels of Brain GSH and total protein were significantly attenuated by chronic administration of ABE herb in scopolamine treated mice at higher doses. The herb improves Learning and memory of scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice.
Conclusion: Reversal of scopolamine induced amnesia by ABE may be mediated through the inhibition of oxidative stress and due to presence of withanolides containing anti-cholinesterase activity. ABE may be beneficial in management of memory deficits with normal life and clinical dementia associated with ageing and neurodegenerative states.
Background: Alangium salvifolium possesses completely different medicine activities such as Antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, bactericide, antifungal, and antifertility. It is also employed in the treatment of anxiety. The previous study is revealed significant of antidepressant activity of ethanolic extract of leaves of A. salvifolium (EASL) by stress -induced depression through forced swim test and tail suspension test models in Swiss albino mice. Aims and Objectives: The present study was designed to explore Learning and memory Enhancing activity leaves of A. salvifolium in Swiss albino mice.
Materials and Methods: EASL of two divided doses (EASL-100 and 250 mg/kg orally) and scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg i.p.) per kg body weight was administrated for 7 days to individual groups of mice. The sensitivity behavioral models such as Elevated plus maze and Morris water maze were used to appraise Learning and memory. However, scopolamine is the natural agent that is elicited Cognitive state served as interoceptive models. The results area unit expressed as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical analysis was done by one-way analysis of variance test followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests. P < 0.05 was measured as statistically significant.
Results: The results of this study showed that Alangiumsalvifoliumat the doses of 100–250 mg/kg significantly (P < 0.05) improved abstraction short-term and memory, the exceptional reduction in transfer latency of the 6th and 7th days as a region of Learning and memory. Within the elevated maze and reducing the escape latency within the Morris water maze.
Conclusion: The results concluded, leaves of A. salvifoliumhave revealed as a significant memory Enhancing activity altogether the screening models used. The consequences of this examine show that the EASL stabilized scopolamine-prompted memory impairment and also may be oxidative stress . As a consequence, it will be terminated that A. Salvifolium might exist a precious herb aid for the management of dementia, in trendy, associate age-related psychological feature deficit of Alzheimer’s type principally. Though, larger studies with A. salvifoliumtargeted on totally different hypotheses of advert are needed to clarify the exact mechanism of motion of the plant.
Nootropic activity of Albizzia lebbeck in mice
The effect of saponin containing n-butanolic fraction (BF) extracted from dried leaves of Albizzia lebbeck on Learning and memory was studied in albino mice using passive shock avoidance paradigm and the elevated plus maze. Significant improve ment was observed in the retention ability of the normal and amnesic mice as compared to their respective controls. We have also studied the effects of BF on the Behavior influenced by serotonin (5-HT), noradrenaline and dopamine. The Brain levels of serotonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and dopamine were also estimated to correlate the Behavior with neurotransmitter levels. The Brain concentration s of GABA and dopamine were decreased, whereas the 5-HT level was increased. The data indicate the involvement of monoamine neurotransmitter s in the Nootropic action of BF of A. lebbeck.
Alpha-GPC is suggested to be synergistic with cholinergic Nootropics including the racetam family of Nootropics.
Alpha-GPC and other choline donors are also considered to be synergistic with antiacetylcholine sterase Nootropics for a similar effect.
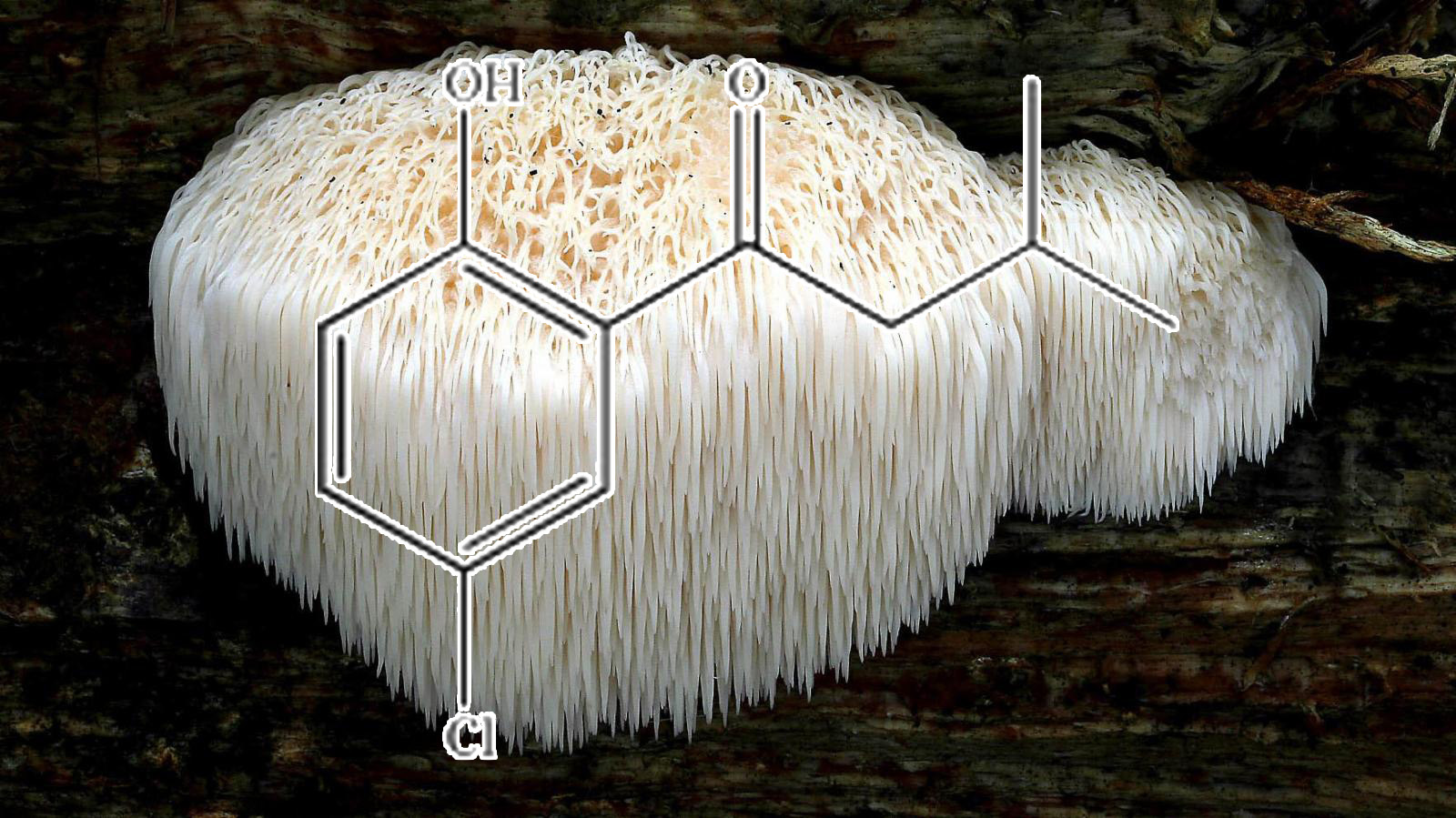
Amycenone (Hericium erinaceum)
Amycenone, a Nootropic found in Hericium erinaceum
The current paper describes the physiological and Nootropic actions of Amycenone, which is an activator of Brain function that is obtained from extracts of the Yamabushitake (Hericium erinaceum).
Kawagishi and his group have studied compounds that are derived from medicinal mushrooms and their use in the treatment of dementia from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages dementia since 1991. They have found that H. erinaceum exerts important bio-activities, including the induction of nerve growth factor (NGF) synthesis, the inhibition of the cytotoxicity of beta-amyloid peptide, and the protection against neuronal cell death caused by oxidative or stres.
Since NGF was first discovered in the 1940s, it has garnered attention as a substance in the Brain that curbs the degeneration and loss of neurons and that promotes the repair and regeneration of nerve function. However, NGF cannot pass through the Brain Barrier. Amysenone (Amyloban®3399, which contains a standardized extract of H. erinaceum) has been found to pass through the blood–Brain barrier, and its safety as a health food is currently being ascertained.
On the basis of the author’s first-hand experiences, Amyloban®3399 was found to clearly increase alertness. The actions of Amyloban®3399 in treating sleep-related breathing disorders were examined. Amyloban®3399 was effective in improving sleep apnea and hypopnea syndrome.
Andrographolide (Andrographis Paniculata)
Results: A significant (P<0.05) increase in Cognitive function was observed in both normal and type 2 diabetic rats. Nootropic activity in terms of per cent reduction in latency period was more in type 2 diabetic rats. A significant increase in blood lymphocyte count, splenic lymphocyte count and peritoneal macrophage count was observed in both normal and type 2 diabetic rats. Immunostimulant activity was observed more in type 2 diabetic rats. The per cent decrease in cerebral infarction was more in type 2 diabetic rats when compared to normal rats. The per cent increase in superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels was more in type 2 diabetic rats.
Interpretation & conclusions: The Antioxidant activity of the methanolic extract of A. paniculata leaves was evident by decreased tissue malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and increased SOD levels. These properties may be responsible for the observed cerebroprotective activity. The methanolic leaf extract of A. paniculata showed significant immunostimulant, cerebroprotective and Nootropic activities in normal and type 2 diabetic rats.
Effects of Aniracetam, a Nootropic agent , in Senile dementia
Three female patients with dementia were given aniracetam 500 mg, 1000 mg, and placebo for 4-week periods in a double-blind, cross-over study. EEGs and psychometric tests were performed before and during the treatment. From the power percentage of EEGs, aniracetam 500 mg produced an increase of α and fast wave activities but a decrease of slow wave activity. With aniracetam 1000 mg, neither an increase of α activity nor a decrease of slow wave activity were observed. In the psychometric tests, only the patient with a mild dementia responded favorably, according to performance on the tests.
However, the scores with aniracetam 500 mg were higher than those with aniracetam 1000 mg. These results indicate that aniracetam may only be effective when dementia is mild and when the dose is carefully titrated.
Evaluation of the Nootropic activity of arabica coffee pulp extract (Coffea arabica)
The Nootropic activity has the purpose of optimizing the Cognitive functions of the brain, which entails, to fight againts the lack of concentration, memory loss and Brain fatigue, which are age-dependent symptoms. This study evaluated the Nootropic activity of the extract of the pulp of the Arabica coffee (Coffea arabica). In the first stage we performed a quality control of the arabica coffee pulp and the quantification of total phenols. It was determined that the extract obtained by dynamic maceration and using ethanol as solvent: water (50:50), contains a greater quantity of total phenols.
In a second stage, an in vivo study was carried out with mice of the speciesmus musculus as experimental subjects. These mice were divided into 4 groups with the purpose of administering water, Ginkgo Biloba and two different doses of pulp extract coffee. The results obtained, using Learning tests such as Morris water maze and the radial 8 arms maze, allowed to evaluate the spatial Learning and the animal’s memory.
Argyreia Speciosa
Evaluation of Nootropic Effect of Argyreia speciosa in Mice
Dementia is a Brain disorder that seriously affects a person’s ability to carry out daily activities. The most common form of dementia among older people is alzheimer’s disease (AD), which initially involves the parts of the Brain that control thought, memory, and language, ending with severe Brain damage. Nootropic agents like, piracetam, and cholinesterase inhibitors like, donepezil are commonly used for improving memory, mood and behavior but their adverse effects have made their use limited and it is worthwhile to explore the utility of traditional medicines in the treatment of various Cognitive disorders. Argyreia speciosa (AS) commonly known as Vridha daraka is widely used in ayurveda for the treatment of neurological disorders. The present work was undertaken to assess the potential of AS as a Nootropic and anti-cholinesterase agent in mice. Effectiveness of aqueous extract of AS on ageing, scopolamine and diazepam induced memory deficits in mice was evaluated.
Elevated plus maze and passive avoidance paradigm were employed to assess short-term and long term memory. In order to delineate the possible mechanism through which AS elicits the anti-amnesic effects, the whole Brain acetyl cholinesterase (AChE) activity, was also assessed. Two doses (100 and 200 mg/kg, p.o.) of aqueous extract of AS were administered orally for 6 successive days to both young and aged mice. AS decreased transfer latencies and increased step down latencies in both young and aged mice AS (100 and 200 mg/kg, p.o.) successfully reversed amnesia induced by diazepam, scopolamine and natural ageing. AS significantly decreased AChE levels in the whole Brain homogenate indicating its potential in the attenuation of Learning and memory deficits especially in the aged mice.
Chemical Composition and Biological Uses of Artemisia absinthium (Wormwood)
Nootropic potential of Ashwagandha leaves: Beyond traditional root extracts
Rapidly increasing aging population and environMental stress ors are the two main global concerns of the modern society. These have brought in light rapidly increasing incidence of a variety of pathological conditions including Brain tumors, neurodegenerative & neuropsychiatric disorders, and new challenges for their treatment. The overlapping symptoms, complex etiology and lack of full understanding of the Brain structure and function to-date further complicate these tasks. On the other hand, several herbal reagents with a long history of their use have been asserted to possess neurodifferentiation, neuroregenerative and neuroprotective potentials, and hence been recommended as supplement to enhance and maintain Brain health and function.
Although they have been claimed to function by holistic approach resulting in maintaining body homeostasis and Brain health, there are not enough laboratory studies in support to these and mechanism(s) of such beneficial activities remain largely undefined. One such herb is Ashwagandha, also called “Queen of Ayurveda” for its popular use in Indian traditional home medicine because of its extensive benefits including anticancer, anti-stress and remedial potential for aging and neurodegenerative pathologies. However, active principles and underlying mechanism(s) of action remain largely unknown.
Here we provide a review on the effects of Ashwagandha extracts and active principles, and underlying molecular mechanism(s) for Brain pathologies. We highlight our findings on the Nootropic potential of Ashwagandha leaves. The effects of Ashwagandha leaf extracts are multidimensional ranging from differentiation of neuroblastoma and glioma cells, reversal of Alzheimer and Parkinson’s pathologies, protection against environMental neurotoxins and enhancement of memory.
Neuropharmacological Review of the Nootropic Herb Bacopa monnieri
This review synthesizes behavioral research with neuromolecular mechanisms putatively involved with the low-toxicity Cognitive Enhancing action of Bacopa monnieri (BM), a medicinal Ayurvedic herb. BM is traditionally used for various ailments, but is best known as a neural tonic and memory enhancer. Numerous animal and in vitro studies have been conducted, with many evidencing potential medicinal properties. Several randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have substantiated BM’s Nootropic utility in humans. There is also evidence for potential attenuation of dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy. Current evidence suggests BM acts via the following mechanisms—anti-oxidant neuroprotection (via redox and enzyme induction), acetylcholine sterase inhibition and/or choline acetyltransferase activation, β-amyloid reduction, increased cerebral blood flow, and neurotransmitter modulation (acetylcholine [ACh], 5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT], dopamine [DA]).
BM appears to exhibit low toxicity in model organisms and humans; however, long-term studies of toxicity in humans have yet to be conducted. This review will integrate molecular neuroscience with behavioral research.
Nootropic potential of Bauhinia variegata: A systematic study on murine model
Objectives: Bauhinia variegata Linn (leguminosae) is one of the important medicinal herbs used traditionally to treat fever, as tonic, astringent, diarrhea, dysentery, hemorrhoids, piles, edema. Recent findings on Bauhinia variegata Linn have demonstrated its Antioxidant , anti-hyperlipidemic, and hepatoprotective potential. The present work is focused to evaluate Nootropic potential of Bauhinia variegata Linn in rats.
Materials and Methods: The leaves of Bauhinia variegata were collected in the month of January from Jawaharlal Nehru Krishi Vishwavidyalaya Jabalpur (Madhya Pradesh). Leaves were subjected for isolation of crude flavonoids and characterized by total flavonoid content assay. Flavonoid -rich extract of Bauhinia variegata was studied for acute oral toxicity as per revised Organization for Economic Cooperation & Development guidelines No. 423. Nootropic activity was determined by elevated plus maze, rotating rod apparatus, baclofen-induced catatonia, diazepam-induced amnesia.
Results: flavonoid -rich fraction of Bauhinia variegata caused no alteration in locomotion in animals. In the current study, animals treated with flavonoid -rich fraction of Bauhinia variegata (400 mg/kg) showed a significant decrease in transfer latency as compared to the control group, which indicates Cognitive enhancement effect flavonoid -rich fraction of Bauhinia variegata. In rota rod studies, flavonoid -rich fraction of Bauhinia variegata increased fall of time as compared to diazepam. In baclofen-induced catatonia, administration of flavonoid -rich fraction of Bauhinia variegata demonstrated protective effect on rats. Over all, flavonoid -rich fraction of Bauhinia variegata was found to enhance the performance of murine models.
Conclusion: Thus, it could be concluded that flavonoids from Bauhinia variegata possess Nootropic potential. However, more systematic studies are required to determine its exact mechanism of action.
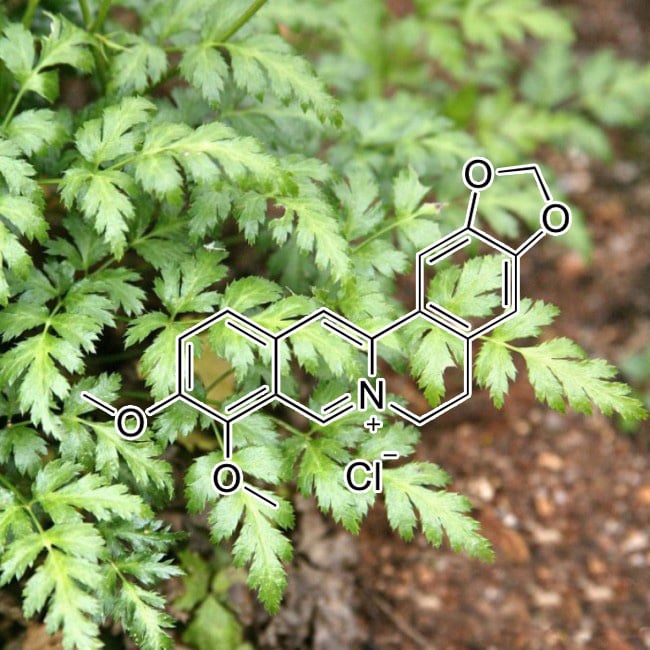

Berberine (Coptis chinensis Franch.)
Background & Objectives: Colchicineadministration by ICV is well known model which shows sporadic dementia of the Alzheimer type in humans, causing Cognitive impairmentand oxidative damage. Berberine (BBR) is a naturally occurring flavonoi . Literature suggests multiple activitiesberberine. Hence it may act as a promising agent to combat AD. The present study has been designed to investigate the protective effects of berberine against the colchicine-induced cognitive impairment by modulating cholinergic neurotransmission in mice.
Methods: Colchicine(15 microg/5 microL), administered intracerebroventricularly, resulted in poor memory retention in both the Morris water maze task paradigms. Mice received chronic treatment of BBR at a subeffectiveandeffective dose of (5 and 40 mg/kg per day, PO respectively) along with nicotine and mechamylamine respectively for a period of 25 days beginning 4 days prior to colchicineadministration. For cholinergic system modulation study Nicotine and Mecamylamine was given I.C.V as agonist and antagonistrespectively.
Results: In present investigation, BBR in sub effective dose do not show any ant amnesic activity but when it is given along with Nicotine it significantly decreases the latency time on as compared to BBR alone in MWM task. Similarly is the case with mecamylamine and BBR at effective.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that BBR provides ant amnesic effects and that may be through modulation of nicotinergic receptors in colchicine’s induced memory impairment model and further investigation of the BBR for therapeutic use in treating AD is warranted.
The aim of present study is to investigate neuroprotective and Nootropic activity of Petroleum Ether Extract of Carica papaya seeds (PEECPS) on diabetic induced Cognitive decline rats. Rectangular maze and morris water maze models were used to evaluate Nootropic activity and neuroprotective effects were studied by estimating acetyl cholinesterase (AchE), malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), nitric oxide (NO), catalase (CAT) and glutathione (GSH) levels in the brains of diabetic rats.
In rectangular maze and morris water maze models, 400 mg/kg of PECPS were shown the significant effect when compared with diabetic control on day 75. Significant decrease in AchE (P<0.001), MDA (P<0.01), NO (P<0.05) and significantly (P<0.01) increased levels of SOD, CAT and GSH with PECPS (200 and 400 mg/kg) when compared with diabetic control. There is a need of further studies on Carica papaya seeds as it showed protection against diabetes induced Cognitive decline to reveal its mode of action.
Phytochemical Screening and invivo Nootropic Evaluation of Carissacarandus linn. Roots
The present investigation was planned with an objective to screen phytochemically andneuropharmacologically the roots of Carissa carandus Linn.in rats. Carissa carandus Linn.(karaunda), common herb of dogbane family Apocynaceae. It has been used as additive in Indian pickles1. The extraction of Carissa carandus Linn. roots was carried out by Soxhlet apparatus by successive solvent extraction in the order of increasing polarity with solvents such as hexane, methanol and water respectively for 24 hours. Phytochemical screening of the extracts reveals the presence of following chemical constituents such as carbohydrates, proteins, lignans, flavonoids, terpenes, saponins glycosides, cardiac glycosides etc. Nootropic activity was carried out with methanolic extract (200 mg/kg) in albino rats by using object recognition test.
The rats of all the groups are placed one by one in an empty object recognition test chamber to get habituated to the environment for a period of 5 minutes before the test session. The rats were allowed to explore a familiar object (F) and a new object (F1) on first day test trail for a period of 5 minutes. Second day test trial includes exploration of a previous familiar (F) object and a new object (N). The result obtained indicate that discrimination index with control rats were found to be 0.0470±0.113 sec, whereas with test treated rats discrimination index was found to be 0.2042 ±0.412 sec. This increase in discrimination index with Carissa carandus Linn. methanolic root extract treated rats in object recognition test suggests that Carissa carandus Linn. roots posseses significant memory Enhancing potential.
Carnosine
Previously, using in vivo models hystidine containing dipeptide carnosine (β-alanyl-L-hystidine) was shown to inhibit the development of oxidative stress induced by such effects like hypoxia, ischemia and neurotoxin administration. These studies showed that animals having undergone oxidative stress in the settings of carnosine administration preserve habits developed in open field, holeboard and Morris water maze. We investigated the effect of carnosine on Cognitive processes in Brain in the settings unrelated to the action of damaging factors. Carnosine administration prevented the increase of lipid hydroperoxides levels and increased the antioxidative state of the Brain in rats under development of active avoidance response in the shuttle box.
In these settings the acceleration of habit development and the increase in ratio of successfully trained animals was reported. At the same time the level of glutamate—the main transmitter amino acid related to the function of brain’s flexibility—in the Brain of rats receiving carnosine increased. The results obtained indicate the Nootropic properties of carnosine.
In the present investigation the aqueous extract of Carum carvi was evaluated for antistress activity in normal and stress induced rats. The extract was studied for Nootropic activity in rats and in vitro Antioxidant potential to correlate its antistress activity. For the evaluation of antistress activity groups of rats were subjected to forced swim stress one hour after daily treatment of Carum carvi extract. Urinary vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and ascorbic acid were selected as non invasive biomarkers to assess the antistress activity. The 24 h urinary excretion of vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and ascorbic acid was determined in all groups under normal and stressed conditions. The Nootropic activity of the extract as determined from acquisition, retention and retrieval in rats was studied by conditioned avoidance response using Cook’s pole climbing apparatus. The in vitro Antioxidant activity was determined based on the ability of Carum carvi to inhibit lipid peroxidation in liver and Brain homogenates.
Daily administration of Carum carvi at doses of 100, 200 and 300 mg/kg body weight one hour prior to induction of stress inhibited the stress induced urinary biochemical changes in a dose dependent manner. However no change in the urinary excretion of VMA and ascorbic acid was observed in normal animals at all the doses studied. The cognition, as determined by the acquisition, retention and recovery in rats was observed to be dose dependent. The extract produced significant inhibition of lipid peroxide formation in comparison with ascorbic acid in a dose dependent manner in both liver and brain.
The present study provides scientific support for the antistress (adaptogenic), Antioxidant and Nootropic activities of Carum carvi extract and substantiates its traditional use as a culinary spice in foods as beneficial and scientific in combating stress induced disorders.
Effect of CDP-choline on Learning and memory processes in rodents
The effects of cytidine (5′) diphosphocholine (CDP-choline) on Learning and memory were studied using conditioned reflex methods for passive avoidance and active avoidance with punishment reinforcement (step-through, step-down, shuttle box and maze), for active avoidance with alimentary reinforcement (staircase maze), and the Morris water maze. The majority of experiments involved comparative studies of the Nootropic agents meclofenoxate and/or piracetam. CDP-choline was administered orally, in some of the experiments also intraperitoneally, at doses of 10-500 mg/kg body weight once or twice daily for 5 or 7 days. In separate cases only single doses were administered. Trainings started one hour after the last dose of the agents.
Retention tests were given 3 h, 24 h, 7 days or 10 days after training. The results obtained with the different methods document CDP-choline’s ability to improve Learning and memory in rats and mice. No essential differences in the effects of CDP-choline were established upon oral and intraperitoneal administration of the agent. The learning- and memory-facilitating effects of CDP-choline were similar to those of meclofenoxate and piracetam. The results of the present study permit us to define CDP-choline as a substance capable of improving Cognitive levels.
Nootropic activity of Celastrus paniculatus seed
The effect of Celastrus paniculatus Willd. (Celastraceae) seed aqueous extract on Learning and memory was studied using elevated plus maze and passive avoidance test (sodium nitrite induced amnesia rodent model). The aqueous seed extract was administered orally in two different doses to rats (350 and 1050 mg/kg) and to mice (500 and 1500 mg/kg). The results were compared to piracetam (100 mg/kg, p.o.) used as a standard agent . Chemical hypoxia was induced by subcutaneous administration of sodium nitrite (35 mg/kg), immediately after acquisition training. In elevated plus maze and sodium nitrite-induced amnesia model, Celastrus paniculatus extract has showed statistically significant improve ment in memory process when compared to control.
The estimation of acetylcholine sterase enzyme in rat Brain supports the plus maze and passive avoidance test by reducing acetylcholine sterase activity which helps in memory performance. The study reveals that the aqueous extract of Celastrus paniculatus seed has dose-dependent cholinergic activity, thereby improving memory performance. The mechanism by which Celastrus paniculatus enhances cognition may be due to increased acetylcholine level in rat brain.
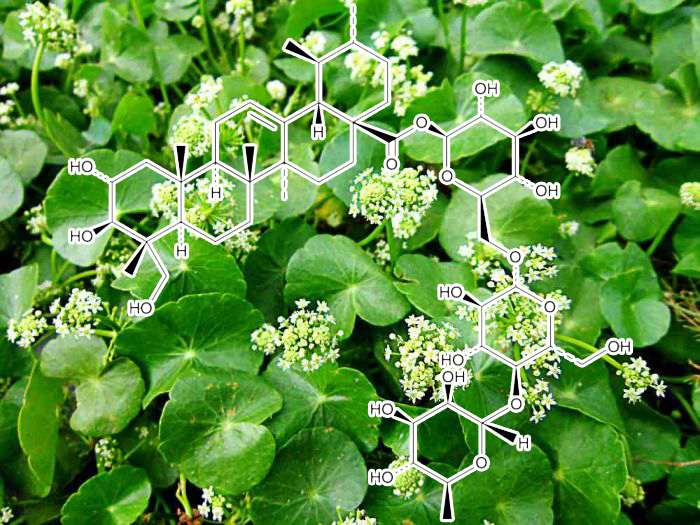

asiaticoside (Centella Asiatica
Centella asiatica treatment during postnatal period enhances Learning and memory in mice
Present investigation was planned to evaluate the Nootropic effect of Centella asiatica. Three months old male Swiss albino mice were injected orally with graded doses (200, 500, 700, 1000 mg/kg body weight) of C. asiatica aqueous extract for 15 days to select an effective dose for Nootropic studies. Animals were tested in radial arm maze to assess the Learning and memory performance.
Based on these results, mice were treated orally with 200 mg/kg of C. asiatica for 15 days from day 15 to day 30 post partum (p.p.) and the Nootropic effect was evaluated on the 31st day and 6 months p.p. The behavioral (open field, dark/bright arena, hole board and radial arm maze tests), biochemical (acetylcholine esterase activity) and histological studies (dendritic arborization) were carried out. Performance of juvenile and young adult mice was significantly improved in radial arm maze and hole board tests, but locomotor activity did not show any change compared to control. Treatment resulted in increased acetylcholine esterase activity in the hippocampus. Dendritic arborization of hippocampal CA3 neurons was also increased in terms of intersections and branching points, both at one month and 6 months. Results of the present investigation show that treatment during postnatal developMental stage with C. asiatica extract can influence the neuronal morphology and promote the higher Brain function of juvenile and young adult mice.
Citicoline
Herein, a novel validated potentiometric method is presented for the first time for citicoline determination. The method is based on measuring the potential using new constructed citicoline electrodes. The electrodes are based on the use of citicolinium/phosphomolybdate [Cit]2[PM] (sensor I) and citicolinium/tetraphenylborate [Cit][TPB] (sensor II) ion association complexes. These sensory materials were dispersed in plasticized polyvinyl chloride (PVC) polymeric membranes. The sensors revealed a Nernstian response with the slopes 55.9 ± 1.8(r2 = 0.9994) and 51.8 ± 0.9 (r2 = 0.9991) mV/decade over a linearity range of 6.3 × 10−6–1.0 × 10−3 and 1.0 × 10−5–1.0 × 10−3 M and detection limits of 3.16 × 10−6 and 7.1 × 10−6 M for sensors I and II, respectively.
To ensure the existence of monovalent citicoline, all measurements were performed in 50 mM acetate buffer at pH 3.5. All presented electrodes showed good performance characteristics such as rapid response, good selectivity, high potential-stability and long life-span. Method verification and validation in terms of response linearity, quantification limit, accuracy, bias, trueness, robustness, within-day variability and between-days variability were evaluated. The method was introduced for citicoline determination in different pharmaceutical formulations and compared with the standard high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method.
Citicoline improves memory performance in elderly subjects.
Citicoline is a choline donor involved in the biosynthesis of brain phospholipids and acetylcholine extensively used in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. In this study we investigated the effects of the oral administration of citicoline alone (C1000:1000 mg/day; C500:500 mg/day) or in combination with nimodipine (C +NI:300 + 90 mg/day) during 4 weeks on memory performance in elderly subjects with memory deficits and without dementia (N = 24; age = 66.12 +/- 10.78 years; MMS score = 31.69 +/- 2.76). Results indicated that citicoline in comparison with placebo improves memory in free recall tasks, but not in recognition tests. A significant improve ment in word recall (5.17 +/- 1.1 vs. 3.95 +/- 1.2 omissions; p < 0.005), immediate object recall (6.5 +/- 1.6 vs. 5.5 +/- 1.2 omission; p < 0.05) and delayed object recall (8.5 +/- 2.1 vs. 6.7 +/- 2.4 omissions; p < 0.005) was observed after citicoline treatment.
Similar results were found in the three subgroups of treatment (8 subjects per group), suggesting that citicoline possesses memory-enhancing activity at doses of 300-1000 mg/day. A decrease in systolic blood pressure and minor changes in lymphocyte cell counting were also observed in old subjects after receiving citicoline. These effects are consistent with the vasoregulatory and neuroimmune actions of citicoline and suggest that this compound may improve memory by acting on mechanisms of brain neurotropism and cerebrovascular regulation. According to the present results, showing that citicoline improves memory performance in elderly subjects, we concluded that this molecule is suitable for the treatment of memory deficits in old people.
Background: Clitoria ternatea (CT) is an herbal plant that has been used as a memory booster in folk medicine. CT root extract has been proven to restore chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH)-induced memory deficits in a rat model, but the underlying mechanisms and the toxicity profile following repeated exposure have yet to be explored.
The aim of the study: To investigate the effects of the chronic (28 days) oral administration of CT root extract on CCH-induced Cognitive impairment, neuronal damage and cholinergic deficit, and its toxicity profile in the CCH rat model.
Materials and methods: The permanent bilateral occlusion of common carotid arteries (PBOCCA) surgery method was employed to develop a CCH model in male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats. Then, these rats were given oral administration of CT root extract at doses of 100, 200, and 300 mg/kg, respectively for 28 days and subjected to behavioural tests. At the end of the experiment, the Brain was harvested for histological analysis and cholinesterase activities. Then, blood samples were collected and organs such as liver, kidney, lung, heart, and spleen were procured for toxicity assessment.
Results: Chronic treatment of CT root extract at doses of 200 and 300 mg/kg, restored memory impairments induced by CCH. CT root extract was also found to diminish CCH-induced neuronal damage in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. High dose (300 mg/kg) of the CT root extract was significantly inhibited the increased acetylcholine sterase (AChE) activity in the frontal cortex and hippocampus of the PBOCCA rats. In toxicity study, repeated doses of CT root extract were found to be safe in PBOCCA rats after 28 days of treatment.
Conclusions: Our findings provided scientific evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of CT root extract in the treatment of vascular dementia (VaD)-related cholinergic abnormalities and subsequent Cognitive decline.
COMPARATIVE Nootropic EFFECT OF EVOLVULUS ALSINOIDES AND CONVOLVULUS PLURICAULIS.
The aim of the present study was to highlight the comparative Nootropic effects of Evolvulus alsinoides and Convolvulus pluricaulis using two validated models of memory namely jumping box and elevated plus maze. Evolvulus alsinoides and Convolvulus pluricaulis are regarded as the botanical source of Shankhpushpi along with Clitorea ternatea and Canscoradecussata. Shankhpushpi, an important agent of indigenous system of medicine is known as a Brain tonic, alterative and laxative. However various authors on Indian medicinal plants have different opinion about its correct botanical source.
Rats were treated orally with vehicle (2% Tween 80 suspension), standard treatment (Piracetam, 200mg/kg body weight), alcoholic extracts of Evolvulous alsinoides and Convolvulus pluricaulis (250mg/kg body weight) respectively, one hour prior to the evaluation of behavioral parameters. The results indicate that alcoholic extracts of Evolvulous alsinoidesexhibited superior Nootropic activity as compared to Convolvulus pluricaulis in terms of time spent in the enclosed arm in plus maze model and the mean avoidance response on the jumping box model.
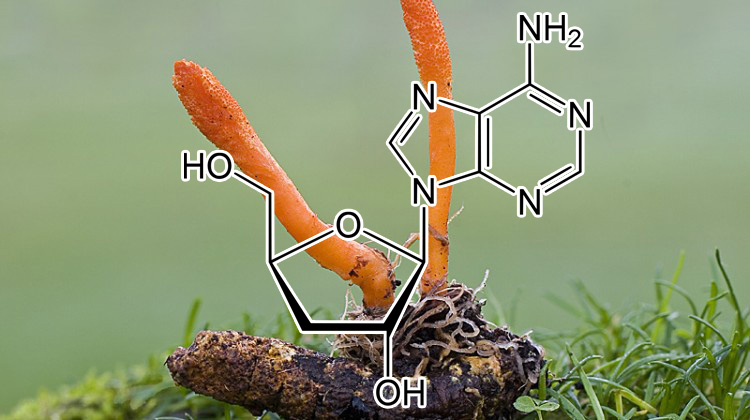
Cordycepin ( Cordyceps sinensis (Berk.)
Bioactive principles from Cordyceps sinensis: A potent food supplement – A review
Cordyceps sinensis (CS) is a well-known entamophagus fungus, naturally distributed in the Tibetan Plateau of Asia and Himalayas. Recently this synonym is transferred to Ophiocordyceps by both scientific and non-scientific communities. It is widely used as a tonic and medicinal food in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), as it possess wonderful health benefits. To support its functional attributes, various investigations have been carried out to find out its adaptogenic, aphrodisiac, anti-oxidant, anti-aging, neuroprotective, Nootropic, immunomodulatory, anti-cancer and hepatoprotective role. Its fruiting portion as well as the larvae possesses potent bio-active fractions and their composition almost found to be similar in both. The bioactive principles are nucleosides, exo-polysaccharides, sterols and, proteins, among others. Among nucleosides, adenosine and cordycepin are the major biochemical markers.
Further, different types of solvent extracts and their mixtures exhibit wide range of pharmacological activities, while the water and methanol extracts with the richest sources of nucleosides and polysaccharides also show wide range of pharmacological activities. This review gives a panoramic view of potential health benefits of various classes of bio-active fractions along with the need for sustainable management of CS for human wellness.
A TRADITIONAL APPROACH TO HERBAL Nootropic AGENTS
Nootropic agents used as a memory enhancer can improve thinking, memory, and alertness in people with Alzheimer’s disease andother disease that affect the mind. Memory is perhaps the most vital of all aspects that differentiates human beings from other animals.
However, memory can become faulty due to several reasons, and in that case the person is not able to make full use of his or her potentials. Since ages, agents and natural remedies have been prescribed to enhance memories in people. 4 million people are thought to be suffering from age related memory and increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Although several Nootropic agents are available to treat memory problems.
In recent years research on medicinal plants have been studied for Nootropic activity. Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi), Evolvulus alsinoides (Shankhpushpi),Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha),Acorus calamus(Bach)etc.,are used as a memory enhancer agents. The abstract refers to several plants with their activity. The main aim of this article isto give up the data reviews on plants with Nootropic properties.
Nootropic activity of Crataeva nurvala Buch-Ham against scopolamine induced Cognitive impairment
Loss of cognition is one of the age related Mental problems and a characteristic symptom of neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s. Crataeva nurvala Buch-Ham, a well explored traditional Indian medicinal plant of Westernghats, is routinely used as folkloric medicine to treat various ailments in particular urolithiasis and neurological disorders associated with Cognitive dysfunction. The objective of the study was to evaluate the Nootropic activity of Crataeva nurvala Buch-Ham stem bark in different Learning and memory paradigm viz. Elevated plus maze and Y-maze against scopolamine induced Cognitive impairment.
Moreover, to elucidate possible mechanism, we studied the influence of Crataeva nurvala ethanolic extract on central cholinergic activity via estimating the whole Brain acetyl cholinesterase enzyme. Ethanolic extracts of Crataeva nurvala (100, 200 and 400 mg/kg body weight) were administered to adult Wistar rats for successive seven days and the acquisition, retention and retrieval of spatial recognition memory was determined against scopolamine (1 mg/kg, i.p.) induced amnesia through exteroceptive behavioral models viz. Elevated plus maze and Y-maze models. Further, whole Brain acetyl cholinesterase enzyme was estimated through Ellman’s method. Pretreatment with Crataeva nurvala ethanolic extract significantly improve d spatial Learning and memory against scopolamine induced amnesia.
Moreover, Crataeva nurvala extract decreased rat Brain acetyl cholinesterase activity in a dose dependent manner and comparable to the standard agent Piracetam. The results indicate that ethanolic extract of Crataeva nurvala might be a useful as Nootropic agent to delay the onset and reduce the severity of symptoms associated with dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. The underlying mechanism of action of its Nootropic potentiality might be attributed to its anticholinesterase property.
Evaluation of Nootropic activity of Cressa creticain scopola-mine-induced memory impairment in mice
The present investigation was undertaken to assess the pharmacological effects of Cressa creticaon Learning and memory in mice. Mor-ris water maze was used to test Learning and memory. Two doses (200 and 400 mg/kg, p.o.) of ethanolic extract of Cressa creticawere administered for 28 successive days in mice. The dose of 400 mg/kg p.o. of CCE (Cressa creticaextract) significantly enhanced Learning and memory of mice.
This dose significantly opposed the memory loss caused by Scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg, i.p.). The effect of CCE on whole Brain MDA, SOD, GSH, Catalase, NO activity was estimated to analyze how CCE shows Nootropic activity. CCE reduced wholeBrain MDA, NO levels. Antioxidant properties and presence of flavonoids in Cressa creticamay be responsible for Nootropic activity. Piracetam (200 mg/kg, i.p) was utilized as standard Nootropic agent . Hence Cressa creticaseems to be a potent candidate for Enhancing Learning and memory and it would be beneficial for the treatment of amnesia and Alzheimer’s disease.

Dangsheng Polysaccharide (radix codonopsis)
Nootropic EFFECT OF DANGSHENG, CODONOPSIS PILOSULA (FRANCH.) NANNF
Twenty Percent alcohol extract of Dangshen (DS-A) was used for facilitation of memory tested by one trail passive avoidance response (step down test) in mice and operant conditional reflex (fixed ratio) in rats. The extract reduced the impairment of acquisition of memory produced by scopolamine (SCPL), the disruption of consolidation of memory caused by sodium nitrite and the deficit of retrieval of memory induced by alcohol. And also, DS-A could improve operant conditional reflex impaired by SCPL. Similar effects were observed with the n-butyl alcohol extrect (DS-FIII), further purified from DS-A, of the agent . It suggested that the active components of Dangshen may be in DS-FIII. Effect of DS-FIII on M-cholinergic receptors were measured by radioligand receptor assay (RRA).
No specific binding; of DS-FIII to M-receptor was observed. However, 5 days after ip injection of DS-FIII higher Bmax values were observed. Effects of DS-FIII and SCPL on Ach content of cortex and hippocampus were measured by radioimmunoassay(RIA) .SCPL reduced the Ach content in cortex and hippocampus markedly. Whereas, DS-FIII could not affect the reduction and raise the Ach content.
The results suggested that one of mechanisms of action of Dangshen on memory facilitation may be related to cholinergic system. But, the mechanism of the Nootropic action of Dangshen is very complicate and need to be further studied.
Alzheimer’s disease the most common form of dementia in the elderly is a neurodegenerative disease that affects 44 millions of people worldwide. The first treatments against Alzheimer’s disease are acetylcholine sterase inhibitors; however, these medications are associated with many side effects. Dichrocephala integrifolia is a traditional herb widely used by indigenous population of Cameroon to treat and prevent Alzheimer’s disease and for memory improvement. In this study, we evaluated the effect of the decoction prepared from leaves of D. integrifolia, on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Seven groups of six animals were used. The first two groups received distilled water for the distilled water and scopolamine groups.
The four test groups received one of the four doses of the decoction of the plant (35, 87.5, 175 or 350 mg/kg p.o.) and the positive control group received tacrine (10 mg/kg), a cholinesterase inhibitor used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, during 10 consecutive days. Scopolamine (1 mg/kg), a cholinergic receptor blocker, administered 30 min after treatments, was used to induce memory impairment to all groups except the distilled water group on day 10 of agent treatment. The behavioral paradigms used to evaluate the effects of the treatment were the elevated plus maze for Learning and memory, Y maze for spatial short-term memory, the novel object recognition for recognition memory and Morris water maze for the evaluation of spatial long-term memory.
After behavioral tests, animals were sacrificed and brains of a subset were used for the assessment of some biomarkers of oxidative stress (malondialdehyde and reduced glutathione levels) and for the evaluation of the acetylcholine sterase activity. From the remaining subset brains, histopathological analysis was performed. The results of this study showed that, D. integrifolia at the doses of 87.5 and 350 mg/kg significantly (p < 0.01) improved spatial short-term and long-term memory, by increasing the percentage of spontaneous alternation in the Y maze and reducing the escape latency in the Morris water maze. Furthermore, the results of histopathological evaluation showed that D. integrifolia attenuated the neuronal death in the hippocampus induced by scopolamine. The main finding of this work is that D. integrifolia improves Learning capacities and counteracts the memory impairment induced by scopolamine. Thus, D. integrifolia can be a promising plant resource for the management of Alzheimer’s disease and memory loss.

Docosahexaenoic acid (marine microalgae)
DOCOSAHEXAENOIC ACID ADMINISTRATION AMELIORATES SCOPOLAMINE-INDUCED memory IMPAIRMENT IN MICE
Neuropharmacological profile of Eclipta alba (Linn.) Hassk
The present study deals with the investigation of standardized and phytochemically evaluated aqueous and hydroalcoholic extracts of the plant Eclipta alba for sedative, muscle-relaxant, anxiolytic, Nootropic and anti-stress activities. The hydrolyzed fraction of the aqueous extract was also subjected to similar studies in rats. The aqueous and hydroalcoholic extracts were administered in a dose of 150 and 300 mg/kg, p.o., while the hydrolyzed fraction was administered in a dose of 30 mg/kg, p.o. The findings indicated Nootropic activity of the aqueous extract (300 mg/kg, p.o.) and its hydrolyzed fraction (30 mg/kg, p.o.).
The effect of the extracts on stress -induced alterations was evaluated. The aqueous extract and the hydrolyzed fraction provided protection against cold restraint induced gastric ulcer formation and also normalized the white blood cell count in the milk induced leukocytosis challenge model. The hydroalcoholic extract on the other hand demonstrated a significant effect only in the milk induced leukocytosis challenge model. The results point towards the potential neuropharmacological activity of the plant Eclipta alba as a Nootropic and also having the property of attenuating stress induced alterations. Further neurochemical investigations can unravel the mechanism of action of the plant agent with respect to Nootropic activity and help to establish the plant in the armamentarium of Nootropic agents.
Eclipta prostrata has been used as a traditional medicinal plant to prevent dementia and to enhance memory in Asia. Its potential as a Nootropic and as an Antioxidant have been reported in mice. We hypothesized that Eclipta may affect the formation of neurotransmitter s and the inhibition of oxidative stress. Charles River cesarean-derived rats (male, 180 ± 10 g) were fed experimental diets supplemented with 0 mg (control), 25 mg (E25), 50 mg (E50), or 100 mg (E100) of a freeze-dried butanol fraction of E prostrata per kilogram of diet for 6 weeks. The acetylcholine level was significantly increased by 9.6% and 12.1% in the brains of E50 and E100 groups, respectively, as compared with the control group that was fed standard diet alone.
The acetylcholine esterase activity was significantly increased by 13.1% and 19.7% in the brains of E50 and E100 groups, respectively, compared with the control group. Monoamine oxidase-B activity was significantly decreased by 10.5% in the brains of the E100 group, and the superoxide radical level was significantly reduced by 9.4% in the serum of the E100 group compared with the control group. Superoxide dismutase activity was significantly increased by 9.6% and 11.6% in the serum of E50 and E100 groups, respectively, compared with the control group. These results clearly demonstrate the effects of E prostrata on the formation of acetylcholine in the Brain and the inhibition of oxidative stress in the Brain and serum of rats. These findings may have implications for preventing dementia and Enhancing memory function in humans.
Embelin (2,5-dihydroxy-3-undecyl-1,4-benzoquinone) is one of the active components (2.3%) found in Embelia ribes Burm fruits. As determined via in vitro AChE inhibition assay, embelin can inhibit the acetylcholine sterase enzyme. Therefore, embelin can be utilized as a therapeutic compound, after further screening has been conducted for its use in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In this study, the Nootropic and anti-amnesic effects of embelin on scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats were evaluated. Rats were treated once daily with embelin (0.3 mg/kg, 0.6 mg/kg, 1.2 mg/kg) and donepezil (1 mg/kg) intraperitoneally (i.p.) for 17 days. During the final 9 days of treatment, a daily injection of scopolamine (1 mg/kg) was administered to induce Cognitive deficits. Besides that, behavioral analysis was carried out to assess the rats’ Learning and memory functions.
Meanwhile, hippocampal tissues were extracted for gene expression, neurotransmitter, and immunocytochemistry studies. Embelin was found to significantly improve the recognition index and memory retention in the novel object recognition (NOR) and elevated plus maze (EPM) tests, respectively. Furthermore, embelin at certain doses (0.3 mg/kg, 0.6 mg/kg, and 1.2 mg/kg) significantly exhibited a memory–Enhancing effect in the absence of scopolamine, besides improving the recognition index when challenged with chronic scopolamine treatment. Moreover, in the EPM test, embelin treated rats (0.6 mg/kg) showed an increase in inflection ratio in Nootropic activity.
However, the increase was not significant in chronic scopolamine model. In addition, embelin contributed toward the elevated expression of BDNF, CREB1, and scavengers enzymes (SOD1 and CAT) mRNA levels. Next, pretreatment of rats with embelin mitigated scopolamine-induced neurochemical and histological changes in a manner comparable to donepezil. These research findings suggest that embelin is a Nootropic compound, which also possesses an anti-amnesic ability that is displayed against scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats. Hence, embelin could be a promising compound to treat AD.
Epicatechin
Evaluation of Nootropic and Anti-Nociceptive Activity of Green Tea inComparison with Medhya Rasayana
memory retrieval deficits: Alleviation by etiracetam, a Nootropic agent
Etiracetam, a nonanaleptic agent related to the Nootropic substance piracetam, was found to facilitate memory retrieval in rats in several experimental situations, when injected 30 min prior to retention testing. The agent was active when memory deficits were induced by electroconvulsive shock, undertraining, or by a long training-to-test interval. The behavioral paradigms included a one-trial inhibitory avoidance task and a complex multitrial, spatially discriminated approach task. The clinical interest of agents which facilitate retrieval processes is also discussed.
COMPARATIVE Nootropic EFFECT OF EVOLVULUS ALSINOIDES AND CONVOLVULUS PLURICAULIS.
The aim of the present study was to highlight the comparative Nootropic effects of Evolvulus alsinoides and Convolvulus pluricaulis using two validated models of memory namely jumping box and elevated plus maze. Evolvulus alsinoides and Convolvulus pluricaulis are regarded as the botanical source of Shankhpushpi along with Clitorea ternatea and Canscoradecussata. Shankhpushpi, an important agent of indigenous system of medicine is known as a Brain tonic, alterative and laxative.
However various authors on Indian medicinal plants have different opinion about its correct botanical source. Rats were treated orally with vehicle (2% Tween 80 suspension), standard treatment (Piracetam, 200mg/kg body weight), alcoholic extracts of Evolvulous alsinoides and Convolvulus pluricaulis (250mg/kg body weight) respectively, one hour prior to the evaluation of behavioral parameters. The results indicate that alcoholic extracts of Evolvulous alsinoidesexhibited superior Nootropic activity as compared to Convolvulus pluricaulis in terms of time spent in the enclosed arm in plus maze model and the mean avoidance response on the jumping box model.
Fasoracetam – An anxiety -Reducing Nootropic
Fasoracetam is a fascinating Nootropic with a novel mechanism of action (relative to the other racetams). It has powerful anti-anxiety and anti-depressant effects, in addition to its ability to improve memory and focus.
As more and more research is done on fasoracetam, the more likely it will continue to grow in popularity. Right now, it’s hard to find and a little more expensive than most of the other racetams.
A TRADITIONAL APPROACH TO HERBAL Nootropic AGENTS: ANOVERVIEW
Nootropic agents used as a memory enhancer can improve thinking, memory, and alertness in people with Alzheimer’s disease andother disease that affect the mind. Memory is perhaps the most vital of all aspects that differentiates human beings from other animals. However, memory can become faulty due to several reasons, and in that case the person is not able to make full use of his or her potentials. Since ages, agents and natural remedies have been prescribed to enhance memories in people. 4 million people are thought to be suffering from age related memory and increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Although several Nootropic agents are available to treat memory problems. In recent years research on medicinal plants have been studied for Nootropic activity. Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi), Evolvulus alsinoides (Shankhpushpi),Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha),Acorus calamus(Bach)etc.,are used as a memory enhancer agents. The abstract refers to several plants with their activity. The main aim of this article isto give up the data reviews on plants withNootropic properties.
Nootropic Effect of Meadowsweet (Filipendula vulgaris) Extracts
The effects of the extracts of the aboveground parts of Filipendula vulgaris Moench on the Behavior and memory of mice after hypoxic injury and their physical performance in the open-field test were studied using the models of hypoxia in a sealed volume, conditioned passive avoidance response (CPAR), and forced swimming with a load. The extracts improved animal resistance to hypoxia, normalized orientation and exploration activities, promoted CPAR retention after hypoxic injury, and increased physical performance. Aqueous extract of meadowsweet had the most pronounced effect that corresponded to the effect of the reference agent piracetam. These effects were probably caused by modulation of hippocampal activity.
cholinergic Basis of memory -Strengthening Effect of Foeniculum vulgare Linn.
alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder associated with a decline in Cognitive abilities. dementia is one of the age-related Mental problems and a characteristic symptom of alzheimer’s disease. Nootropic agents are used in situations where there is organic disorder in Learning abilities. The present work was undertaken to assess the potential of Foeniculum vulgare Linn. extract as a Nootropic and anticholinesterase agent in mice. Methanolic extract of the whole plant of F. vulgare Linn. administered for eight successive days ameliorated the amnesic effect of scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg) and aging- induced memory deficits in mice. The passive avoidance paradigm served as the exteroceptive behavioral model for assessing memory. F. vulgare extract increased step-down latency and acetylcholine sterase inhibition in mice significantly. Hence, F. vulgare can be employed in treatment of Cognitive disorders such as dementia and alzheimer’s disease.
Evaluation of Nootropic effects of galantamine and sildenafil as a combination in mice
Cognitive decline is one of the age related Mental problems and a characteristic symptom of various neurodegenerative disorders. Nootropic effects of combination of sildenafil and galantamine was evaluated in different Learning and memory paradigms viz. Elevated plus maze (EPM) and Morris water maze (MWM) against scopolamine induced Cognitive impairment. Moreover, the influence on central cholinergic activity via estimating the whole Brain acetylcholine sterase enzyme was also assessed. Sildenafil (8 mg/kg, i.p.) and galantamine (3 mg/kg, i.p.) were administered per se to Swiss albino mice for successive 14 days. In addition, combination of sildenafil (4 mg/kg, i.p.) and galantamine (1.5 mg/kg, i.p.) were administered. Scopolamine (1 mg/kg, i.p.) was used to induce amnesia. Inflexion ratio and time spent in target quadrant were determined in EPM and MWM, respectively.
Further, whole Brain acetylcholine sterase enzyme was estimated through Ellman’s method. Treatment with sildenafil and galantamine combination significantly increased inflexion ratio and time spent in target quadrant in EPM and MWM, respectively. Combination treatment also showed reduction in Brain acetylcholine sterase enzyme activity when compared separately against sildenafil and galantamine per se. The present study results suggest the augmentation of benefits of galantamine and sildenafil combination in the treatment of Cognitive impairments.
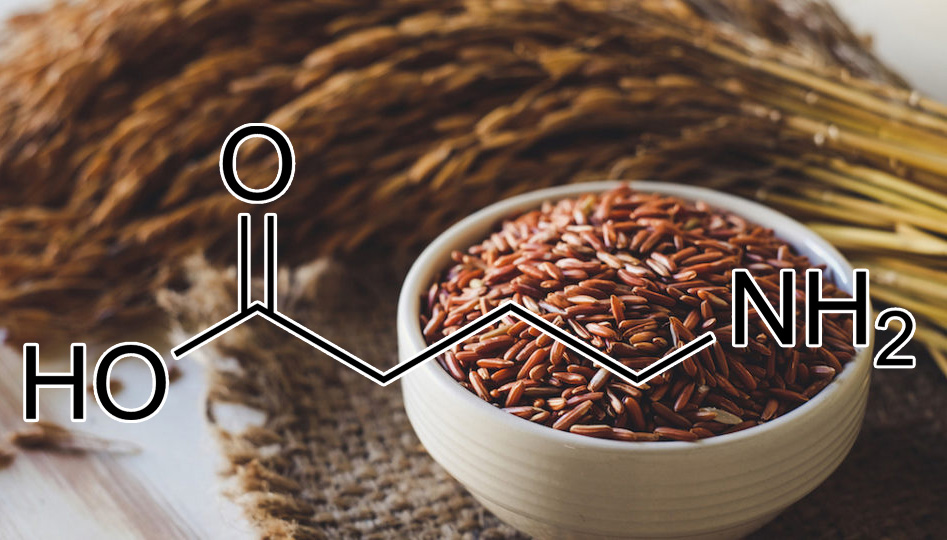
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (Gaba) 56-12-2
Nootropic properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid derivatives
Experiments on rats and mice were made to study the antianamnestic and antihypoxic effects of some GABA derivatives. Cetyl GABA, sodium and lithium hydroxybutyrates and phenibut were shown to be able to decrease the retrograde amnesia caused by electroshock in passive avoidance performance. As regards the degree of the antianamnestic effect, the above-mentioned non-cyclic derivatives of GABA are not inferior to the standard Nootropic agent piracetam, a derivative of cyclic GABA. antihypoxic activity of sodium hydroxybutyrate, cetyl GABA, phenibut and lioresal studied in experimental hypoxic hypoxia compares very favourably with that of piracetam.
The compounds under consideration manifest their protective action against damaging factors in doses which do not provoke muscle relaxation or any types of central depression. According to the data obtained one may conclude that the Nootropic effect is exhibited by not only piracetam, a derivative of cyclic GABA, but also by some of its non-cyclic derivatives.
Ginkgo biloba has been shown to have chronic memory Enhancing effects in healthy subjects and patients with dementia. There is limited research on the acute Nootropic effects of Ginkgo biloba in humans. The current study aimed to examine the acute effects of Ginkgo biloba (120 mg) on memory functioning in healthy older volunteers using the Cognitive agent research (CDR) battery of memory tests and the Rey auditory verbal Learning task (AVLT).
The study was a double‐blind placebo‐controlled design, with each participant tested under both placebo and Ginkgo biloba treatment conditions. Testing was conducted pre‐ and 90 min post‐agent administration for each treatment condition. Treatment conditions were separated by a 7 day wash out period. No acute effects of Ginkgo biloba were found for any of the memory tests examined. The findings suggest that 120 mg of Ginkgo biloba has no acute Nootropic effects in healthy older humans.
Nootropic Activity of Calyces of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Linn
Nootropic acitivity of calyces of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn. was studied in mice. Elevated plus maze and passive avoidance paradigm were employed to evaluate Learning and memory parameters. Scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg, i.p.) was used to induce amnesia in mice. The aqueous extracts of calyces of Hibiscus sabdariffa (HS-100 and 200 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly attenuated amnestic deficits induced by scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg, i.p.) and natural aging. HS (100 and 200 mg/kg) decreased the transfer latencies and increased step down latencies significantly in the aged mice and scopolamine induced amnesic mice as compared with Piracetam (200 mg/kg, i.p.). To delineate the possible mechanism through which H. sabdariffa elicits the anti-amnesic effects, we studied its influence on central cholinergic activity by estimating the whole Brain acetylcholine sterase activity. H. sabdariffa significantly decreased acetyl cholinesterase activity in mice.
The results indicate that, the aqueous extract of calyces of H. sabdariffa might prove to be a useful memory restorative agent in the treatment of dementia seen in elderly. The underlying mechanism of action can be attributed to its anti acetylcholine sterase property.
The Nootropic components of Hovenia dulcis.
Objective: To investigate the Nootropic components of Hovenia dulcis.
Methods: Six saponins were isolated from Hovenia dulcis and Step-down test was used to examine the memory ability of mice. The escape latency and the times of wrong performance within 3 min were used to evaluate the memory ability of mice. To study the effects of saponins on learning and memory in mice, we divided the mice into 6 groups; youth group, aged group, aged plus piracetam (0.3 g/kg) group, aged plus saponins (0.6 g/kg) group, aged plus saponins (0.3 g/kg) group, and aged plus saponins (0.15 g/kg) group. To study the influence of saponins on impairment of memory acquirement, consolidation, and reoccurrence (induced by scopolamine, sodium nitrite and 40% ethanol, respectively), mice were also divided into the following 7 groups: control group, untreated group, piracetam group (0.3 g/kg), compound 3 group (0.3 g/kg), compound 4 group (0.3 g/kg), compound 5 group (0.3 g/kg), and compound 6 group (0.3 g/kg).
Results: The chemical structures of six saponins were elucidated as 3-O-stigmasterol-(6-O-palmitoyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside (1), β-daucosterin (2), hovenidulcioside A1 (3), hoduloside I (4), hoduloside IV (5), and saponins C2 (6). Among them, compounds 1 and 2 were isolated from this plant for the first time. Compounds 5 and 6 had Enhancing effect on the Learning and memory ability of natural senile mice, and they could improve the impairment of memory acquirement, consolidation and recurrence in mice induced by scopolamine, sodium nitrite and 40% ethanol, respectively.
Conclusion: The aglycone of jujubogenin might be the main saponins contributing to the Nootropic effect of total saponins from Hovenia dulcis.
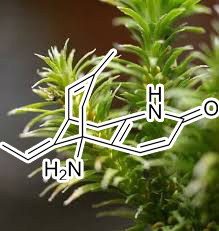
Huperzine A (Lycopodium serratum Thunb)
Huperzine A, a Nootropic from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages Nootropic alkaloid isolated from a Chinese herb, has been proposed as one of the most promising agents to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Recently, the agent was found to inhibit the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in rat cerebral cortex in addition to causing an inhibitory effect on acetylcholine sterase from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages acetylcholine sterase. In the present study, the mechanisms underlying NMDA receptor inhibition were investigated using whole-cell voltage-clamp recording in CA1 pyramidal neurons acutely dissociated from rat hippocampus. Huperzine A reversibly inhibited the NMDA-induced current (IC50=126 μM, Hill coefficient=0.92), whereas it had no effect on the current induced by α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate or kainate. The effect was non-competitive, and showed neither ‘voltage-dependency’, nor ‘use-dependency’. The IC50 values of huperzine A were neither altered by changing the concentrations of glycine (2–0.2 μM) and pH (7.4–6.7) in the external solution, nor by addition of Zn2+ (5 μM) and dithiothreitol (5 mM) to the external solution. However, addition of spermine (200 μM) to the external solution caused a parallel shift to the right of the huperzine A concentration –response curve.
From these we suggest that huperzine A acts as a non-competitive antagonist of the NMDA receptors, via a competitive interaction with one of the polyamine binding sites. The potential relevance of NMDA Receptor Antagonist from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages NMDA receptor antagonist activity of huperzine A to the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease is discussed.
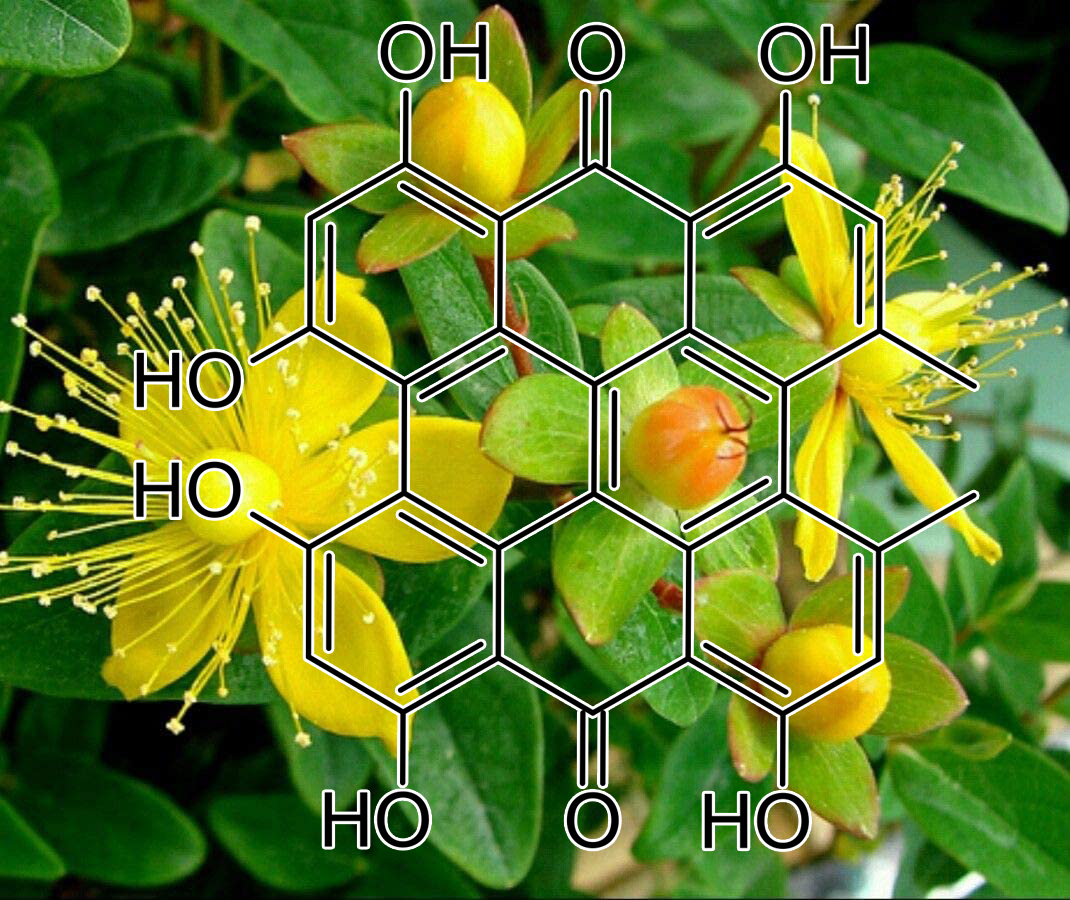
Hypericin (Hypericum Perforatum)
Depression, among other non-Cognitive symptoms, is common in patients with dementia. The effect of Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort) extract, with well-documented antidepressant activity, was tested on memory retrieval 24 h after training on a one-trial passive avoidance task in mice. Acute administration of Hypericum extract (4.0, 8.0, 12.0, and 25.0 mg/kg i.p.) before retrieval testing increased the step-down latency during the test session. The same doses of Hypericum extract, on the other hand, failed to reverse scopolamine-induced amnesia of a two-trial passive avoidance task. The involvement of serotonergic, adrenergic, and dopamine rgic mechanisms in the facilitatory effect of Hypericum extract on retrieval memory was investigated.
Pretreatment of the animals with serotonergic 5-HT1A receptor antagonist (−)-pindolol (0.3, 1.0, and 3.0 mg/kg), serotonergic 5-HT2A receptor blocker spiperone (0.01, 0.03, and 0.1 mg/kg), alpha adrenoceptor antagonist phentolamine (1, 5, and 10 mg/kg), beta receptor antagonist propranolol (5, 7.5, and 10 mg/kg), dopamine rgic D1 receptor antagonist SCH 23390 (0.01, 0.05, and 0.1 mg/kg), and dopamine rgic D2 receptor antagonist sulpiride (5, 7.5, and 10 mg/kg) revealed the involvement of adrenergic and serotonergic 5-HT1A receptors in the facilitatory effect of Hypericum extract on retrieval memory.
It is concluded that Hypericum extract may be a better alternative for treatment of depression commonly associated with dementia than other antidepressants known to have anticholinergic side effects causing delirium, sedation and even exacerbating already existing impaired cognition. In dementias of old age, Hypericum perforatum would, therefore, serve as one medication targeting both depression and amnesia with lower potential side effects.
The effects of idebenone and various Nootropic agents on lipid peroxidation in rat Brain homogenate were examined. Idebenone inhibited lipoperoxide (LPO) production in Brain homogenate in a concentration -dependent manner, with an IC50 of 38 microM. The inhibition was strongly enhanced (about 100-fold) by adding succinate, a substrate in the mitochondrial respiration. The optimal concentration of succinate was 0.5 mM. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation in Brain homogenate by various Nootropic agents in the presence or absence of succinate was then examined. agents added to the Brain homogenate at 100 microM in the absence of succinate inhibited LPO production in the order: idebenone greater than vinpocetine greater than bifemelane greater than indeloxazine greater than calcium hopantenate. However, when the agents were added at 1 microM in the presence of succinate, only idebenone demonstrated inhibition.
These results suggest that although almost all of the agents tested inhibit lipid peroxidation in Brain homogenate, only idebenone is activated by succinate, the other agents being insensitive to this compound.
Ipomoea Aquatic Forsk
Nootropic EFFECT OFIPOMOEA AQUATICAFORSK INRAT HIPPOCAMPUS
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a primary degenerative disease of the central nervous system.The progression of disease will ultimately lead to dementia, behavioral and Cognitive impairments.AD ischaracterized by selective neuron al cell death, the presence of extra cellular amyloid deposits in the coreof neuritic plaques and the formation of intraneuron al neurofibrillary tangles in the Brain of affectedindividuals.AD affects up to 15% of people over age 65 years and nearly half of people age 85 years.Prevalence rates for more than 20 million people worldwide including 4.5 million Americans.In AD, thesevere loss of cholinergic neurons in the nucleus basalis and associated areas that form the cholinergicforeBrain area and their projections to the cerebral cortices are marked with decreased levels ofacetylcholine (ACh). The aim of the study is to elvaluate the acetylcholine Enhancing activity ofmethanol leaf extract ofIpomoea aquaticaForsk(MEIA), is known to posses various therapeuticproperties.We found that treatment with 200 and 400 mg/kg of MEIA, for 30 days in neonatal and youngadult age groups of rat, significantly increased acetylcholine (ACh) content in their hippocampus ascompared to age matched controls. Increase in ACh content in their hippocampus may be theneurochemical basis for their improved learning and memory.
Background: Currently, available therapy for the treatment of memory impairment is far from satisfactory. Therefore, the agents of natural origin may serve as potential therapies. Objective: The present study was designed to evaluate the memory –Enhancing effect of Juniperus recurva extract.
Materials and Methods: The methanol extract of J. recurva was prepared by Soxhlet extraction and characterized by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The in vitro Antioxidant activity of the extract was corroborated by diphenyl picryl hydrazine scavenging, nitric oxide scavenging, metal chelating, and reducing power activity. Memory impairment was induced by the administration of scopolamine (1 mg/kg i.p) on 3 consecutive days to mice and assessment of memory acquisition and memory retention was done using Morris water maze test, passive avoidance test, elevated plus maze test, and light and dark box test, motor coordination was evaluated using the rotarod test and inclined plane test; and depression was evaluated by forced swim test. Serum acetylcholine sterase (AChE) activity was quantified by Ellman’s method.
Results: The HPLC analysis of J. recurva extract revealed gallic acid as a prominent peak. The extract was found to have an excellent antioxidant effect in all the tests employed. The in vivo studies revealed memory Enhancing and improve d motor coordination activity of the extract in mice. Serum AChE activity was decreased on the administration of the extract.
Conclusion: The inhibition of the AChE enzyme contributes to the memory–Enhancing activity of J. recurva extract.
Leontopodium alpinum (‘Edelweiss’) was phytochemically investigated for constituents that might enhance cholinergic neurotransmission. The potency to increase synaptic availability of acetylcholine (ACh) in rat Brain served as key property for the bioguided isolation of cholinergically active compounds using different chromatographic techniques. The dichlormethane (DCM) extract of the root, fractions and isolated constituents were injected i.c.v. and the effect on Brain ACh was detected via the push–pull technique. The DCM extract enhanced extracellular ACh concentration in rat Brain and inhibited acetylcholine sterase (AChE) in vitro. The extracellular level of Brain ACh was significantly increased by the isolated sesquiterpenes, isocomene and 14-acetoxyisocomene, while silphiperfolene acetate and silphinene caused a small increasing tendency. Only silphiperfolene acetate showed in vitro AChE inhibitory activity, thus suggesting the other sesquiterpenes to stimulate cholinergic transmission by an alternative mechanism of action. Isocomene was further investigated with behavioural tasks in mice. It restored object recognition in scopolamine-impaired mice and showed Nootropic effects in the T-maze alternation task in normal and scopolamine-treated mice.
Additionally, this sesquiterpene reduced locomotor activity of untreated mice in the open field task, while the activity induced by scopolamine was abolished. The enhancement of synaptic availability of ACh, the promotion of alternation, and the amelioration of scopolamine-induced deficit are in accordance with a substance that amplifies cholinergic transmission. Whether the mechanism of action is inhibition of AChE or another pro-cholinergic property remains to be elucidated. Taken together, isocomene and related constituents of L. alpinum deserve further interest as potential antidementia agents in Brain diseases associated with cholinergic deficits.
A TRADITIONAL APPROACH TO HERBAL Nootropic AGENTS: ANOVERVIEW
Nootropic agents used as a memory enhancer can improve thinking, memory, and alertness in people with Alzheimer’s disease andother disease that affect the mind. memory is perhaps the most vital of all aspects that differentiates human beings from other animals. However, memory can become faulty due to several reasons, and in that case the person is not able to make full use of his or her potentials. Since ages, agents and natural remedies have been prescribed to enhance memories in people. 4 million people are thought to be suffering from age related memory and increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Although several Nootropic agents are available to treat memory problems. In recent years research on medicinal plants have been studied for Nootropic activity. Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi), Evolvulus alsinoides (Shankhpushpi),Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha),Acorus calamus(Bach)etc.,are used as a memory enhancer agents. The abstract refers to several plants with their activity. The main aim of this article isto give up the data reviews on plants withNootropic properties.
Context: Marsilea minuta Linn (Marsileaceae) is a common Indian hydrophytic plant. Traditionally, the plant has been used as a sedative for the treatment of insomnia and other Mental disorders. Background information of this plant has encouraged us to investigate its antiamnesic activity in rat.
Objective: Standardized ethanol extract of M. minuta was investigated for their putative role in Learning and memory performance in normal and amnesic rats.
Materials and methods: Ethanol extract of M. minuta (EMM) was standardized for marsiline using HPLC. The effect of standardized extract of M. minuta (1.15% w/w marsiline) was tested in amnesic rat using elevated plus maze (EPM) and passive avoidance (PA) test. Amnesia was induced after scopolamine (1 mg/kg, s.c.) and electroconvulsive shock (150 mA, 0.2 s) treatment. Behavioral studies were further substantiated with acetylcholine sterase (AChE) activity and radioligand muscarinic receptor binding studies in rat Brain regions.
Results: Oral administration of EMM at 200 and 400 mg/kg/day for 3 days significantly reversed the amnesia whereas, no per se effect was observed. In comparison to control, AChE activity in frontal cortex and hippocampus was found to be significantly (P < 0.05) inhibited by EMM. EMM at doses 200 and 400 mg/kg has significantly (P < 0.05) increased (+34 % and +40 % change in affinity, respectively) the binding of 3H-QNB in frontal cortex indicating the up regulation of the muscarinic receptors.
Discussion and conclusion: These findings suggest that standardized extract of M. minuta have excellent antiamnesic activity, probably mediating through central cholinergic system.
1. The effects of Adafenoxate (Adf), meclofenoxate (Mf) and citicholine (CCh) administered at a daily dose of 100 mg/kg for 7 days on the levels of noradrenaline (NA), dopamine (DA) and serotonin (5-HT) in the frontal cerebral cortex, striatum, hippocampus and hypothalamus of rats were studied.
2. Adafenoxate increased the NA level in the striatum and decreased it in the hypothalamus; it increased the DA level in the cerebral cortex and hypothalamus and decreased it in the striatum; it increased the 5-HT level in the cerebral cortex and decreased it in the hippocampus.
3. Meclofenoxate decreased the NA level in the cerebral cortex and hypothalamus; it increased the DA level in the hippocampus and hypothalamus and the 5-HT level in the cerebral cortex, striatum, hippocampus and hypothalamus.
4. Citicholine increased the NA level in the cerebral cortex and hypothalamus; it increased the DA level in the striatum and the 5-HT level in the cerebral cortex, striatum and hippocampus.
5. An attempt is made to explain some similarities and differences in the behavioral effects of the agents tested (and those observed in other studies) by the changes they induce in Brain biogenic monoamines.
Adaptogenic and Nootropic activity of Mimosa pudica in albino wistar rats
Aim: To evaluate the adoptogenic activity of ethanolic extract of Mimosa pudica L. in chronic alzheimer’s model.
Materials and Methods: The dried whole part of the plant were subjected to hot continuous extraction method using ethanol as solvent and were standardized using pharmacognostical and phytochemical screening. The in-vitro Antioxidant studies were conducted by super oxide scavenging assay and hydrogen peroxide scavenging assay. Satisfactory IC 50 values were obtained for both assays. Dose selection for in-vivo study was made on the basis of already conducted acute toxicity studies (500 mg/kg body weight). Oral administration of extract of M. pudica was continued for 21 consecutive days. Adaptogenic activity was assessed by using oral dose of 500 mg/kg of EEMP and 2 mg/kg diazepam as test and standard compound respectively.
Results: There was a significant improve ment in memory, which was observed from the test paradigms viz., morris water maze, radial arm maze. Forced swim test was used as the observation paradigm for the adaptogenic activity and EEMP caused significant reduction in swimming endurance time.
Conclusion: It was concluded that ethanolic extract of M. pudica at the dose of 500 mg/kg p.o produces potential changes in chronic alzheimer’s model and stress.
Nootropic activity of Moringa oleifera leaves
Objective: To study the Nootropic activity of leaves of Moringa oleifera.
Methods: Toluene–ethylacetatefraction of methanolic extract of Moringa oleifera (MOE) leaves was assessed for its Nootropic activityusing passive shock avoidance paradigm and elevated plus maze. MOE ( 50 and 100 mg/kg ) was comparedwith Piracetam (100 mg/kg ). Scopolamine (1 mg/kg) was used to induce Cognitive dysfunction. Theextract was also studied for its effect on gross behaviour.
Results: MOE (50 and 100 mg/kg ) significantlydecreased Transfer Latency(TL) on Day 2. The extract reduced the latency to reach the SFZ and thenumber of mistakes. No adverse effects were observed upto a dose of 200 mg/kg.
Conclusion: Thus theleaves of Moringa oleifera possess a potential for exploring the Nootropic principle.
Nootropic Potential of Murraya koenigii leaves in Rats
Murraya koenigii leavescommonly known as ‘curry patta’ are routinely added to Indian gravy andvegetarian dishes by south Indian as a favourate condiment. The present study was undertaken toinvestigate the effects of Murraya koenigii leaves (MKL) on memory in rats. Elevated plus-maze andHebb-Williams maze served as the exteroceptive behavioral models for testing memory. Diazepam-,scopolamine- and ageing-induced amnesia served as the interoceptive behavioral models. MKL fedorally to various groups of young and aged rats with diet containing 2, 4 and 8% w/w of MKL for 30days consecutively were investigated. The MKL diets produced a significant dose-dependentimprove ment in memory scores of young and aged rats and significantly reduced the amnesiainduced by scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg, i.p.) and diazepam (1 mg/kg, i.p.). Therefore, it would be worthwhile to specifically investigate the therapeutic potential of MKL in the management of dementia patients.
Nardostachys jatamansi improves Learning and memory in Mice
Cure of Cognitive disorders such as amnesia, attention deficit, and alzheimer’s disease is still far from being realized in the field of medicine. Nootropic agents such as piracetam, aniracetam, and choline esterase inhibitors like donepezil are being used for improving memory, mood, and behavior, but the resulting side effects associated with these agents have made their applicability limited. In Ayurveda, the roots of Nardostachys jatamansi have been clinically employed for their anti-ischemic, Antioxidant, anticonvulsant, and neuroprotective activities. The present study was undertaken to assess the potential of N. jatmansi as a memory enhancer. The elevated plus maze and the passive avoidance paradigm were employed to evaluate learning and memory parameters. Three doses (50, 100, and 200 mg/kg, p.o.) of an ethanolic extract of N. jatamansi were administered for 8 successive days to both young and aged mice. The 200 mg/kg dose of N. jatmansi ethanolic extract significantly improved learning and memory in young mice and also reversed the amnesia induced by diazepam (1 mg/kg, i.p.) and scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg, i.p.).
Furthermore, it also reversed aging-induced amnesia due to natural aging of mice. As scopolamine-induced amnesia was reversed, it is possible that the memory improve ment may be because of facilitation of cholinergic transmission in the brain. Hence, N. jatmansi might prove to be a useful memory restorative agent in the treatment of dementia seen in elderly persons. The underlying mechanism of action can be attributed to its Antioxidant property.
EFFECTS OF THE Nootropic NEFIRACETAM ON RAT hippocampal GABA RELEASE
The ventral hippocampus plays an important role in generalizing seizures. We have previously reported antiepileptic effects of the Nootropic nefiracetam in epileptic mutant EL mice with an ED50 of 7.5 mg/kg in p.o. In the present study, we used the microdialysis method for exploring the role of hippocampal GABAergic system under the influence of nefiracetam. Application of nefiracetam (10 mg/kg, p.o.) markedly increased GABA release to a level 3 times as high as the base line level. Then, the release gradually decreased to almost zero-level in 2 hr. With a higher dose (30 mg/kg, p.o.) of nefiracetam, GABA release sharply decreased to a quarter of the base line level and then gradually recovered in 40 min. An after-potentiation (about 1.5x base line level) was observed for 20 min.
The results suggest that nefiracetam at low, clinical doses potentiates hippocampal GABA release whereas at high doses it suppresses the GABA release.
This study was conducted to evaluate Cognitive Enhancing effect and ameliorative effects of black seed oil in scopolamine induced rat model of Cognitive impairment. These effects were investigated on scopolamine-induced dementia model in Morris water maze test (MWM) and Y maze test. The hippocampal histoarchitectural responses to scopolamine and Nigella sativa oil were also examined.
Scopolamine (1 mg/kg ip) was given to induce dementia , followed by oral administration of BSO (1 ml/kg) for 14 consecutive days. MWM and Y-maze paradigms were used to assess hippocampal and frontal dependent memory respectively, thereafter the rats were sacrificed and brains were removed for histopathologic studies.
Scopolamine resulted in memory impairment, by delayed latency in the MWM, reduced percentage alternation in the Y maze that was coupled by alterations in the cortico-hippocampal neuron s. Posttreatment of rats with BSO mitigated scopolamine-induced amnesia, by reducing latency period and increasing percentage alternation and histological changes. The observed anti-amnestic effect of BSO makes it a promising anti-amnesic agent for clinical trials in patients with Cognitive impairment.
Spontaneous alteration Behavior (SAB) is a viable measure of memory .37 BSO from this study significantly increased percentage alternation when given only and/or after scopolamine, thus confirming its anti-amnesic efficacy and its Nootropic property. This effect is strengthened by the report of Rashid and colleagues where a similar increase in percentage alternation was reported of thymoquinone, the active component of BSO against scopolamine38 also its Enhancing effect on spatial working memory performance on the radial arm maze.
The effects of the novel proline-containing Nootropic and neuroprotective dipeptide, noopept (GVS-111, N-phenylacetyl-L-prolylglycine ethyl ester) were investigated in NMRI mice following olfactory bulbectomy. We have shown previously that these animals developed alzheimer’s disease (AD)-like behaviour, morphology and biochemistry including impairment of spatial memory , regional neuron al degeneration and elevated Aβ peptide Brain levels. In the current investigation, spatial memory was assessed using the Morris water maze and serum antibodies to in vitro morphologically characterized amyloid structures of both Aβ(25—35) peptide and equine lysozyme, as well as to neurotrophic glial factor S100b, were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Noopept (administered at a dose of 0.01 mg/kg for a period of 21 days and during a further 5 days training) restored spatial memory and increased serum antibody levels to oligomers of Aβ(25—35) peptide but not to equine lysozyme amyloid or S100b protein in bulbectomized animals. The positive immunotropic effect of noopept to Aβ(25—35) peptide prefibrillar aggregates was more marked in sham-operated compared to the bulbectomized subjects which were characterized by an overall suppression of immunoreactivity. Enhancement of the immune response to Aβ(25—35) peptide prefibrils caused by noopept may attenuate the neurotoxic consequences of amyloid fibrillization and also be associated with an improve ment in spatial memory in bulbectomized mice. These actions of noopept, combined with it’s previously reported neuroprotective and cholinomimetic properties, suggests that this dipeptide may well be useful for improving Cognitive deficits induced by neurodegenerative diseases.
Anti-stress anxiolytic and Nootropic activity of Nyctanthes arbour tritis leaves
Reports suggest that stress is the most common etiological factor in CNS disorders like anxiety, Schizophrenia, Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer disease for which effective treatment strategies are inadequate due to complexities of the ailment and the limitations of allopathic medications. There are scanty reports1 on the putative Neuro pharmacological effects of the leaves of Nyctanthes arbor tristis Linn. (Family: Oleaceae) [NAT]; hence the present work investigated gamut of its neuro-pharmacological effects. The methanolic extract was evaluated for anxiolytic activity using plus maze model, open field test and light dark model. Further, the Nootropic potential2 of extract was evaluated using Morris water maze test and plus maze model. Antistress potential3 was evaluated in Wistar rats by subjecting the animals to chronic cold restraint stress followed by biochemical estimation of plasma corticosterone, glucose, triglycerides; dopamine, 5-Hydroxy Tryptamine and nor epinephrine from brain. Diazepam 1mg/kg was used as a positive control. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was applied for statistical significance.
Pretreatment with NAT extract resulted in preference to open arm in plus maze test, increased exploratory Behavior in open field test and increased number of crossings in light dark model. Further it improved Cognitive function with respect to spatial and working memory processes. The treatment with NAT extract ameliorated the stress -induced variations in the biochemical levels of corticosterone, glucose, triglycerides; dopamine , 5-HT and nor epinephrine. In conclusion, the NAT extract exhibited anxiolytic, antistress and Nootropic activity with utility in oxidative Cognitive impairment due to its Antioxidant potential.
Evaluation of Nootropic potential of Ocimum sanctum Linn. in mice
dementia is one of the age related Mental problems and a characteristic symptom of various neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer’s disease. Certain agents like diazepam, barbiturates and alcohol disrupt Learning and memory in animals and man. However, a new class of agents known as Nootropic agents is now used in situations where there is organic disorder in Learning abilities. The present work was undertaken to assess the potential of O. sanctum extract as a Nootropic and anti-amnesic agent in mice. Aqueous extract of dried whole plant of O. sanctum ameliorated the amnesic effect of scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg), diazepam (1 mg/kg) and aging induced memory deficits in mice. Elevated plus maze and passive avoidance paradigm served as the exteroceptive behavioral models. O. sanctum extract decreased transfer latency and increased step down latency, when compared to control (piracetam treated), scopolamine and aged groups of mice significantly. O. sanctum preparations could of beneficial in the treatment of Cognitive disorders such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Gallic acid (Olive Olea europaea L. Fruit)
Nootropic and Anti-anxiety Effects of Olive Oil: Relationship with dopamine and Serotonin Metabolism
In recent years, interest in the use of nutraceuticals hasrisen substantially. Olive oil has been shown to produce anumber of therapeutically important effects due to itsAntioxidant property. The present study concernsneurochemical and behavioral effects of long termadministration of low and high doses (0.1 mL/kg and 0.25mL/kg) of olive oil and associated Antioxidant effects inrats. Long term administration of low dose of olive oilincreased motor activity in an open field, decreasedanxiety in elevated plus maze test, and enhanced memory in Morris water maze test.
Whole Brain levels of serotoninincreased with low dose of olive oil while homovanillicacid (HVA), a metabolite of dopamine increased with bothdoses of olive oil. Low dose of olive oil increased glutathione peroxidase activity whereas high dose of oliveoil decreased malondialdehyde levels in plasma. Theresults show that particularly low doses of olive oil reduceanxiety and improve Learning and memory together withAntioxidant properties, Brain dopamine and serotoninalso play important role in the therapeutically importanteffects of olive oil.
Brain Entry and Direct Central Pharmacological Effects of the Nootropic agent Oxiracetam
Oxiracetam administered systemically to rats as a 14C radiolabelled agent (200 mg/kg p. o. or 100 mg/kg intra-artery) enters the Brain and is found unmetabolized above all in some of the Brain areas functionally involved in the modulation of Cognitive processes. Among the Brain areas examined, the largest amount of compound was recovered in septum, followed by hippocampus; a smaller amount was found in cerebral cortex and striatum. 14C oxiracetam administered directly into the lateral ventricles of the Brain presented a similar pattern of distribution, indicating that the tropism of the agent for the above Brain areas does not depend on its route of administration. The amounts of oxiracetam that could reach the Brain after systemically administered pharmacologically active doses were also estimated.
These amounts (1.9 to 19 nmols/rat) were delivered through a permanently implanted cannula, into the lateral ventricles of the brains of conscious, freely moving rats. In this experimental condition oxiracetam dose-dependently antagonized the amnesia induced by scopolamine (0.66 mg/kg s. c.). The above findings clearly indicate that oxiracetam enters the Brain and directly exerts its pharmacological activity there.
Panax Ginseng Ginsenoside
Study on the Nootropic mechanism of ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1–influence on mouse Brain development
Weaning mice were supplied drinking water containing Rb1 or Rg1 0.125 or 0.25 mg.ml-1 for 4 weeks. Rb1 (28.6 and 56.1 mg.kg-1) and Rg1 (27.4 and 53.9 mg.kg-1) were found to accelerate young mice body and Brain development as well as facilitate memory acquisition in step down and step through avoidance response tests. With the technique of quantitative measurement synapses, we found for the first time that Rb1 and Rg1 administration for 4 weeks can increase synapse number in the hippocampal CA3 region of mice. This is the morphological basis for explaining Rb1 and Rg1 induced facilitation of Learning and memory.
Hydroethanol (HE) and methanol (ME) extracts obtained from the leaves of Passiflora actinia Hooker were evaluated for behavioral effects in mice. Single-dose oral administration of HE (300 and 600 mg/kg) or ME (100 and 300 mg/kg) resulted in anxiolytic-like effects in the elevated plus-maze. The anxiolytic-like effects were also seen after the repeated administration of the HE (100 and 300 mg/kg). Flumazenil (10 mg/kg, i.p.), a GABAA-benzodiazepine receptor antagonist, blocked the effects of ME (300 mg/kg, p.o.) and HE (600 mg/kg). At higher doses, a sedative effect produced by acute administration of HE (600 mg/kg) or ME (300 mg/kg) was indicated by the potentiation of pentobarbital-induced sleep.
With regard to memory-disrupting effects of anxiolytics, mice were evaluated by measuring the retest step-down latency 24 h after foot-shock in a passive avoidance task. In contrast to diazepam (0.5 mg/kg) or piracetam (200 mg/kg), ME (30, 100 and 300 mg/kg) or HE (100, 300 and 600 mg/kg) did not influence the step-through latency in the acquisition or retention memory tasks. The present results show an anxiolytic profile for HE and ME of Passiflora actinia. There are also indications of an involvement of GABAA system in this effect.
Phenlypiracetam
Nootropics are cognition –Enhancing compounds, whose use has both clinical and suppleMental potential. One such compound, phenylpiracetam, has been shown to ameliorate deficits resulting from disease and trauma as well as improve cognition in healthy individuals. Despite numerous investigations into its mechanistic action, ambiguity persists and is thus suggestive of the need for a new mode of inquiry. The present study seeks to validate a novel animal model for Nootropic research; larval Danio rerio are growing in popularity as a model organism for the testing of psychotropic compounds, and were evaluated for behavioral congruency with existing rodent models. Treatment with phenylpiracetam was found to increase the locomotor activity of 7 d.p.f. (days post fertilization) larval zebrafish at doses of 10 μg (n = 14) and 15 μg (n = 14). Such Behavior is suggestive of stimulation, a consistently reported effect in the extant literature. Thus, the findings presented support the further development of this novel model for Nootropic research.
Phloretin (PHL), a dihydrochalcone flavonoid usually present in the roots and leaves of apple tree. In vitro study on GT1-7 immortalized hypothalamic neuron s exposed to amyloid beta (25–35), demonstrated that PHL significantly influenced membrane fluidity and potential. PHL also significantly decreased excitotoxicity by restoring the calcium homeostasis in the same. Thus, PHL proves to be a promising therapeutic moiety which should be further screened in the treatment of alzheimer’s disease. The objective of the present study was to evaluate the Nootropic, neuroprotective and neurotrophic roles of PHL in the subacute scopolamine induced amnesia in mice. In this study, mice were pretreated with PHL 2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg and Donepezil (DON) 1 mg/kg intraperitoneally (i.p) for 14 days.
The last 7 days of treatment regimen included daily injection of SCP 1.5 mg/kg to induce Cognitive deficits. Mice were subjected to behavioral analysis. Biochemical estimation of the Brain homogenates for acetylcholine sterase and oxidative stress biomarkers were conducted. Furthermore, immunohistochemical analysis for the Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) was carried out particularly in the hippocampus. PHL was found to significantly improve the performance of mice in Morris water maze test (P < 0.001) and significantly decreased the acetylcholine sterase activity (P < 0.001) at all doses compared to SCP treated mice. Also, PHL significantly elevated the activity of Antioxidant enzymes viz. superoxide dismutase, catalase, reduced glutathione levels (P < 0.001) and decreased malonaldehyde levels (P < 0.001) in comparison with the SCP group.
Immunohistochemistry revealed that PHL treatment dose dependently improve d BDNF levels in the hippocampus which were found to be significantly depleted (P < 0.001) in the SCP group. Additionally, PHL (10 mg/kg) significantly enhanced the spatial memory formation (P < 0.05) and neurotrophicity (P < 0.001) compared to DON (1 mg/kg). The aforementioned research findings suggested that PHL has Nootropic, neuroprotective and neurotrophic activities in SCP induced memory impaired mice and hence, is a promising therapeutic moiety in the treatment of AD.
There is increasing evidence that microglial activation is one of the major pathogenic factors for alzheimer’s disease (AD) and the inhibition of the inflammatory activation of the microglia thus appears to be neuroprotective and a potentially useful treatment for AD. Phospholipids such as phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylcholine (PC) have been reported to modulate the immune function of phagocytes. In addition, PS has been reported to be a nootropics that can be used as nonprescription memory or Cognitive enhancers.
We therefore evaluated the effects of liposomes, which comprise both PS and PC (PS/PC liposomes), on the microglial production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), nitric oxide (NO), and superoxide (radical dotO2−) induced by amyloid β (Aβ) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ). Pretreatment of microglia with PS/PC liposomes considerably inhibited the TNF-α, NO and radical dotO2− production induced by Aβ/IFN-γ. These results suggest that PS/PC liposomes have both neuroprotective and antioxidative properties through the inhibition of microglial activation, thus supporting the nootropic and antidementia effect of PS.
Oxidative stress is intensely linked with neurodegenerative disorders, especially Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Searching for medicinal plant with the Nootropic activity for controling the development and progression of AD has received extensive consideration. The plant Phyllanthus reticulatus (PR) Poir. is known in Bengali as Panjuli belongs to family Euphorbiaceae. Previous studies have shown the Antioxidant , analgesic, anti-inflammatory, etc. activities of this plant. Therefore, the objective of this study was to examine the Nootropic effect of ethanolic extracts of Phyllanthus reticulatus (EEPR) on Cognitive functions, Brain antioxidatant enzymes and acetylcholine sterase activity in aluminium-induced rats of Cognitive impairment and oxidative stress . The effects of EEPR fruit (i.e., 100 and 200 mg/kg b.w.) were examined for 30 days and its Nootropic effect was determined in aluminium treated Swiss albino male rats by behavioral studies such as Passive Avoidance (PA) test, Rewarded Alternation (RA) test and biochemical studies such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), contents of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and acetylcholine sterase (AChE) activity in rats Brain tissue homogenates. In PA test, administration of EEPR fruit (i.e., 100 and 200 mg/kg, b.w.) significantly (P < 0.05, P < 0.01) increased step-through latency (STL) in rats on 30th day with respect to disease control group.
The percentage of memory retention (MR) for this test was pointedly (P < 0.05) increased in rats treated with EEPR fruit (i.e., 200 mg/kg b.w.) as compared with disease control group. For RA test, EEPR fruit (i.e., 200 mg/kg b.w.) markedly (P < 0.01) increased the correct responses (CR) in rats on 30th day related to disease control group. In case of this test the percentage of MR was significantly (P < 0.05, P < 0.01) increased in rats treated with EEPR fruit (i.e., 100 and 200 mg/kg b.w.) with respect to disease control group. Administration of EEPR fruit (i.e., 100 and 200 mg/kg b.w.) considerably (P < 0.05, P < 0.01) increased the level of SOD, CAT and expressively (P < 0.05) decreased TBARS level compared to disease control group. Treatment with EEPR fruit (i.e., 100 and 200 mg/kg b.w.) markedly (P < 0.05, P < 0.01) decreased the level of AChE activity to that of disease control group. The present study shows that EEPR fruit has excellent nootropıc effect on Cognitive performance and Brain Antioxidant markers in aluminium-induced rats of Cognitive impairment and oxidative stress which could be developed in the management of neurodegenerative diseases especially AD.
Anti-stress , Nootropic and anticonvulsant potential of fruit extracts of Piper longum L
An aqueous extract [AE] of fruits of Piper longum L. [PL] was investigated for its anti-stress activity in chronic cold restraint stress [(4±0.5 oC) for 1h daily for 7 days induced biochemical perturbations in Sprague Dawley rats. The Nootropic potential of PL[AE] was assessed using a passive avoidance model and an elevated plus maze model in Swiss Albino mice. Further, the anticonvulsant activity of the extract was studied against seizures induced by pentylenetetrazole (PTZ), strychnine and 4-aminopyridine in mice. Stimulation of hypothalamus pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis in stress ful condition alters plasma levels of glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol, total proteins and corticosterone.
Pretreatment with the extract (250mg/kg and 500mg/kg p.o.) for 21 days significantly ameliorated the stress -induced biochemical perturbations in rats. PL[AE] treatment significantly increased step-down-latency and shortened the transfer latency in the passive avoidance model and the elevated plus maze model, respectively, suggesting Nootropic potential. Further, treatment of groups with both doses offered protection against PTZ-induced convulsions but failed to protect against strychnine and 4-aminopyridine-induced convulsions in mice. Dimunition in gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) levels in Brain of extract treated mice compared to vehicle treated mice learly indicated involvement of GABAergic mechanisms in the anticonvulsant activity. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s or Bonferroni test was applied to verify statistical significance.
The present study thus provides scientific support for anti-stress (adaptogenic), Nootropic and anticonvulsant potential of an a aqueous extract of fruits of Piper longum in animal models.
Nootropic agents in alzheimer’s disease Symptomatic treatment with pramiracetam
The cognitive-Enhancing effects of pramiracetam in animal models of Learning and memory are characterized by an inverted U-shaped dose-response curve. We evaluated antidementia efficacy of this agent in 10 patients with probable alzheimer’s disease employing a 2-phase, placebo-controlled, enrichment-type trial design. Eight patients evidenced a best dose in the dose-finding phase, but in the subsequent replication phase only two again improve d to a similar degree. PETs with fluorodeoxyglucose obtained in two individuals showed no definite change. Doses up to 4,000 mg pramiracetam are unlikely to confer symptomatic benefit to alzheimer’s disease patients.
Nootropic and hypophagic effects following long term intake of almonds(Prunus amygdalus)in rats
Introduction: Over a period of time researchers havebecome more interested in finding out the potential ofvarious foods to maintain the general health and to treatdiseases. Almonds are a very good source of many nutri-ents which may help to sharpen the memory and toreduce cardiovascular risk factors.
Objective: The present study was conducted to evaluatethe Nootropic effects of almonds. Effect of oral intake ofalmond was also monitored on food intake and plasmacholesterol levels. Methods:Rats were given almond paste orally with thehelp of feeding tube for 28 days. memory function in ratswas assessed by Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) and RadialArm Maze (RAM). Brain tryptophan, 5-HT and 5-HIAAwere estimated at the end of the treatment by HPLC-ECmethod.
Results: A significant improve ment in Learning andmemory of almond treated rats compared to controls wasobserved. Almond treated rats also exhibited a significantdecrease in food intake and plasma cholesterol levelswhile the change in growth rate (in terms of percentage)remained comparable between the two groups. Analysisof Brain tryptophan (TRP) monoamines exhibitedenhanced TRP levels and serotonergic turnover in ratBrain following oral intake of almonds.
Conclusion: The findings show that almonds possesssignificant hypophagic and Nootropic effects. Results arediscussed in context of enhanced 5-HT metabolismfollowing almond administration.
memory retrieval improve ment by Ptychopetalum olacoides in young and aging mice
Amazonian peoples use traditional remedies prepared with Ptychopetalum olacoides (PO) roots for treating various age-related conditions. This study shows that a single intraperitoneally (i.p.) administration of Ptychopetalum olacoides ethanol extract (POEE, 50 and 100 mg/kg) improve d memory retrieval in step-down inhibitory avoidance (P ≤ 0.05 and P ≤ 0.01, test session latency 102 [19.38–300] and 192 [91.3–300] s, respectively versus control 24.7 [12.9–89.6]), without interfering with acquisition or consolidation in adult (2.5-month-old) mice. Comparable results were obtained with POEE given p.o. at 800 and 1000 mg/kg (P ≤ 0.05 and P ≤ 0.01, 52.7 [19.5–297.2] and 85.7 [44.4–260.4] versus control 20.5 [8–92.6]).
Moreover, memory amelioration was also observed (P ≤ 0.01) in aging (14 months) mice presenting memory deficit (14.95 [10.8–41]) as compared to adult (2.5 months) mice (57 [15.7–141.2]), with the extract given acutely i.p. 100 mg/kg (300 [133.1–300] versus control 14.95 [10.8–41]) or p.o. 800 mg/kg (28.4 [15.1–84.6] versus control 11.5 [7.8–23.3]). Indeed, aging mice treated with POEE (800 mg/kg, p.o.) performed as well as adult mice. Consistently with its traditional use, the data suggest that POEE facilitates memory retrieval. Although the Antioxidant and acetylcholine sterase inhibitory properties previously described for this extract may be of relevance, the molecular mechanism(s) underlying the improve ment in memory retrieval here reported merit further scrutiny.
Nootropic activity of tuber extract of Pueraria tuberosa (roxb)
Nootropic effect of alcoholic (ALE; 50, 75, 100 mg/kg) and aqueous (AQE; 100, 200, 400 mg/kg) extracts of P. tuberosa was evaluated by using Elevated Plus Maze (EPM), scopolamine-induced amnesia (SIA), diazepam-induced amnesia (DIA), clonidine-induced (NA-mediated) hypothermia (CIH), lithium-induced (5-HT mediated) head twitches (LIH) and haloperidol-induced (DA- mediated) catalepsy (HIC) models. Piracetam was used as the standard agent . A significant increase in inflexion ratio (IR) was recorded in EPM, SIA and DIA models.
A significant reversal effect was observed on rectal temperature in CIH model, reduction of head twitches in LIH models. However no significant reduction in catalepsy scores in HIC models were observed with test extracts and standard piracetam. The results indicate that Nootropic activity observed with ALE and AQE of tuber extracts of P. tuberosa could be through improved Learning and memory either by augmenting the noradrenaline (NA) transmission or by interfering with 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) release. Further, the extracts neither facilitated nor blocked release of the dopamine (DA).
Thus ALE and AQE elicited significant Nootropic effect in mice and rats by interacting with cholinergic, GABAnergic, adrenergic and serotonergic systems. Phytoconstituents like flavonoids have been reported for their Nootropic effect and these are present in both ALE and AQE extracts of tubers of P. tuberosa (Roxb) and these active principles may be responsible for Nootropic activity.
Investigations on the binding properties of the Nootropic agent pyroglutamic acid
The two stereoisomers of pyroglutamic acid (PCA), a Nootropic or cognition –Enhancing agent, and classic reference compounds were investigated for their ability to interact with 27 neurotransmitter receptors and agent binding sites prepared from selected areas of the central nervous system and labelled with high affinity and selectivity with specific radioligands. L-PCA significantly interacted with the rat foreBrain excitatory amino acid receptors labelled with 3H-L-glutamic acid. The IC50 of L-PCA was 28.11 microM, that of cold L-glutamic acid was 1.68 microM. The corresponding figure for L-aspartic acid was 16.95 microM. The indirect Hill plot gave coefficients of 0.48, 1.08 and 0.75 for L-PCA, L-glutamic and L-aspartic acids, respectively.
Only very high concentration s (10(-4) M) of L-PCA were able to slightly antagonize the specific binding of 3H-clonidine to alpha 2-adrenergic receptors, of 3H-dihydroalprenolol to beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors of the heart and of the lung and of 3H-diazepam to benzodiazepine receptors. The D-isomer of PCA was practically as active as the L-isomer on these receptors. Finally, L-PCA (10(-5) to 10(-4) M) was unable to antagonize the specific binding of all the other radioligands to their respective receptors and binding sites. D-PCA did not significantly interact with excitatory amino acid receptors or with any of the other sites studied here.
Decline of Cognitive function is the hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), regardless of the pathological mechanism. Traditional Chinese medicine has been used to combat Cognitive impairments and has been shown to improve Learning and memory. Radix Polygalae (RAPO) is a typical and widely used herbal medicine. In this study, we aimed to follow the β-amyloid (Aβ) reduction activity to identify active constituent(s) of RAPO. We found that Onjisaponin B of RAPO functioned as RAPO to suppress Aβ production without direct inhibition of β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) and γ-secretase activities. Our mechanistic study showed that Onjisaponin B promoted the degradation of amyloid precursor protein (APP).
Further, oral administration of Onjisaponin B ameliorated Aβ pathology and behavioral defects in APP/PS1 mice. Taken together, our results indicate that Onjisaponin B is effective against AD, providing a new therapeutic agent for further agent discovery.

Red Ginseng Ginsenoside Rg1 Rb1
Effects of single and repeated administration of red ginseng total saponins (ROTS) and Nootropic agents were examined on impairment of acquisition induced by single oral administration of 3 g/kg ethanol (EtOH) in a step through test. The inhibitory effect of EtOH on acquisition was significantly reduced following single or repeated RGTS administration. The Nootropic agents , piracetam and N-methyl-d-glucamine, given orally significantly reduced impairment of acquisition induced by EtOH.
On the other hand, the inhibitory effect of repeated RGTS on the EtOH-induced amnesia was blocked by the pretreatment of α-methyl-ρ-tyrosine (α-MT), an inhibitor of catecholamine synthesis, in a dose-dependent manner but not ρ-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA), an inhibitor of serotonin synthesis, whereas the inhibitory effect of repeated N-methyl-d-glucamine on the EtOH-induced amnesia was blocked neither by α-MT nor PCPA. These results suggest that repeated RGTS and N-methyl-d-glucamine ameliorate the impairing effect of EtOH on acquisition, and the effect of RGTS on EtOH-induced amnesia is dependent on the catecholaminergic but not serotonergic neuron al activity, while RGTS and N-methyl-d-glucamine seem to have a different mechanism on EtOH-induced amnesia.

Reishi mushroom Polysaccharide
Background: As the standard clinically used hypotensive medicines have many undesirable side effects, there is a need for new therapeutic agents, especially ones of a natural origin.
Purpose: One possible candidate is extract from the mushroom Reishi (Ganoderma lucidum), which is used in the treatment and prevention of many chronic diseases.
Study design and methods: To study the effectiveness of Reishi, which grows in the Altai Mountains, as an antihypertensive agent, we intragastrically administered Reishi water extract to adult male hypertensive ISIAH (inherited stress -induced arterial hypertension) rats.
Results: After seven weeks, Reishi therapy reduced blood pressure in experimental animals at a level comparable to that of losartan. Unlike losartan, intragastric Reishi introduction significantly increases Brain Blood Flow from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages cerebral blood flow and affects cerebral cortex metabolic patterns, shifting the balance of inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitter from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages”
Conclusion: Changes in cerebral blood flow and ratios of neurometabolites suggests Reishi has a potential Nootropic effect.
Rhodiola Rosea: Nootropic Powerhouse?
Quality evidence has been mounting for Rhodiola Rosea’s efficacy as an adaptogen and an all natural Nootropic. It is being used by an increasing number of people to help them cope with heavy work loads, alleviate headaches, improve their concentration , reduce anxiety , enhance their memory , regulate their appetites (too little or too much), bolster their immune systems, and reduce irritability. As an herb that helps the body better cope with stress , none of these benefits should be surprising. Better yet, a sizeable chunk of the claims about Rhodiola have been subject to double-blind studies – meaning there is solid evidence to support many of the claims about it.
Rhodiola is an herbal Nootropic, a natural Brain booster. Subjects in the verum group made far fewer errors in proofreading tasks than the control or those given Siberian ginseng (Rathee, 2008).
Nootropic and anti-stress effects of rice bran oil in male rats
Rice bran oil (RBO) is an important product of rice bran. It is considered to be one of the most important nutritious oil due to its favorable fatty acid composition and unique composition of naturally occurring biologically active Antioxidant compounds. This study was designed to monitor the effects of oral intake of RBO on stress response in rats. RBO was extracted using hexane. Rats were divided into Control and test (RBO-treated). RBO-treated rats were given 0.2 ml/day RBO for 6 weeks. Food intake and body weight changes were monitored weekly. After 6 weeks open field activity and Morris Water Maze (MWM) test were performed. Results showed that weekly cumulative food intake but not body weight were lower in RBO-treated rats during 1st to 5th week of treatment, which were normalized at the end of treatment. Exploratory activity of RBO-treated rats in an open field was increased.
Spatial memory in Morris water maze was enhanced in RBO-treated than control rats. An episode of 2 h restraint stress decreased the 24 h food intake of both control and RBO-treated animals. Behavioral deficits were lower in RBO-treated rats. Exposure of 2 h restraint stress increased Brain serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine: 5-HT) metabolism. These increases were lower in RBO-treated restrained than their respective control animals. Serotonergic neurotransmitter mechanism is implicated in stress .
The findings of the study show beneficial effects of RBO in Learning and memory functions. Moreover, the study also highlights the attenuating effect of RBO on stress induced behavioral and neurochemical effects in rats.
Antihyperglycemic, antistress and Nootropic activity of roots of Rubia cordifolia Linn
Effect of alcoholic extract of roots of Rubia cordifolia was studied on elevated blood glucose level in alloxan treated animals. The extract reduced the blood sugar level raised by alloxan. Effect of alcoholic extract was also investigated on cold restraint induced stress and on scopolamine-induced memory impairment. Alcoholic extract enhanced Brain γ-amino-n-butyric acid (GABA) levels and decreased Brain dopamine and plasma corticosterone levels.
Acidity and ulcers caused due to cold restraint stress were inhibited by alcoholic extract. Animals treated with alcoholic extract spent more time in open arm in elevated plus maze model. It also antagonized scopolamine induced Learning and memory impairment. Baclofen induced catatonia was potentiated by alcoholic extract.
Rhizoma Anemarrhena, a widely used traditional Chinese medicine, has previously been shown to have neuroprotective effect. Sarsasapogenin-AA13 (AA13) is a novel synthetic derivative of Sarsasapogenin, which is extracted from Rhizoma Anemarrhena. The aim of this study is to investigate the Nootropic and neurotrophic effects of AA13 and underlying mechanisms. In vitro, cell viability of rat primary astrocytes treated with AA13 and neurons cultured with conditioned medium of AA13-treated rat primary astrocytes was tested by MTT assays.
In vivo, a pharmacological model of Cognitive impairment induced by scopolamine was employed and spatial memory of the mice was assessed by Morris water maze. This study found that AA13 increased cell viability of primary astrocytes and AA13-treated astrocyte-conditioned medium enhanced the survival rate of primary neuron s. Interestingly, AA13 markedly enhanced the level of BDNF in astrocytes. Furthermore, AA13 (6 mg/kg) improved the Cognitive deficits in animal models (p<0.05) and BDNF and PSD95 levels were increased in brain.
Therefore, we hypothesize that AA13 exerts Nootropic and neurotrophic activities through astrocytes mediated upregulation of BDNF secretion. The results suggest that AA13 could be a potential compound for Cognitive impairment after further research.
Nootropic, anxiolytic and CNS-depressant studies on different plant sources
Context: Shankhpushpi, a well-known agent in Ayurveda, is extensively used for different central nervous system (CNS) effects especially memory enhancement. Different plants are used under the name shankhpushpi in different regions of India, leading to an uncertainty regarding its true source. Plants commonly used under the name shankhpushpi are: Convolvulus pluricaulis Chois., Evolvulus alsinoides Linn., both from Convolvulaceae, and Clitoria ternatea Linn. (Leguminosae).
Objective: To find out the true source of shankhpushpi by evaluating and comparing memory –Enhancing activity of the three above mentioned plants. Anxiolytic, antidepressant and CNS-depressant activities of these three plants were also compared and evaluated.
Materials and methods: The Nootropic activity of the aqueous methanol extract of each plant was tested using elevated plus-maze (EPM) and step-down models. Anxiolytic, antidepressant and CNS-depressant studies were evaluated using EPM, Porsolt’s swim despair and actophotometer models, respectively.
Results: C. pluricaulis extract (CPE) at a dose of 100 mg/kg, p.o. showed maximum Nootropic and anxiolytic activity (p < 0.001). E. alsinoides extract (EAE) and C. ternatea extract (CTE) showed maximum memory –Enhancing and anxiolytic activity (p < 0.001) at 200 and 100 mg/kg, respectively. Amongst the three plants, EAE and CTE showed significant (p < 0.05), while CPE did not exhibit any antidepressant activity. All the three plants showed CNS-depressant action at higher dose levels.
Conclusions: The above results showed all the three plants possess Nootropic, anxiolytic and CNS-depressant activity. The results of memory –Enhancing activity suggest C. pluricaulis to be used as true source of shankhpushpi.
Evaluation of Nootropic activity of Sida cordifolia in mice
Introduction: In the present study, Nootropic effect of aqueous and hydroethanolic extracts of Sida cordifolia (AESC and EESC, respectively) was investigated in mice using transfer latency (TL) and step-down latency (SDL) tests. S. cordifolia is a well-known Ayurvedic plant which has been administered anciently for the various nervous disorders including loss of memory .
Materials and Methods: Varying doses (50, 100, 250 mg/kg; p.o.) of AESC and EESC were administered along with standard agent (donepezil; 5 mg/kg) for 15 successive days to different groups. They were subjected TL and SDL tests on the 16th day.
Results: EESC dose dependently increased the SDL and decreased the TL in mice as compared to control group, and this effect was comparable to the standard agent . No significant effect on TL and SDL was observed following varying dose treatment of AESC.
Conclusion: These findings suggest the Nootropic effect of EESC and predict its scope in the possible treatment of diseases associated with memory dysfunctions such as Alzheimer’s disease.
In today’s life of stress and strain, the need of agent called Nootropic having neuroprotective and neuropharmacological activity, Enhancing Learning and memory functions of Brain has directed the interest of scientific community to validate the claims made about herbs in the official books of Ayurveda [1, 2]. The Caralluma fimbriata (CF) family Asclepiadaceae is an edible succulent that is claimed to promote Learning and memory but not documented so far[3] hence we have undertaken the evaluation of Nootropic activity of Slimaluma (SL), branded product and an enriched phytochemical composition developed from CF in mice using four different paradigms.
Each model had six groups consisting of six male albino mice each, including vehicle treated control, reference standard Piracetam and four different doses (100, 250, 500 and 1000mg/kg) of SL. The mice were pretreated as per the standard protocol [1, 4, 5, 6] and the data obtained was analysed by using ANOVA followed by the Dunnetts test.
The SL 250, 500mg/kg (P<0.05) and 1000mg/kg (P<0.01) significantly increased the discrimination index Indicating an improve ment in nonspiatal memory with the characteristic of episodic memory [7]. In Morris water maze, all the doses were equally significant in reducing the escape latency while SL 500 and 1000mg/kg significantly reduced the distance traveled and thereby reported its effectiveness towards the memory based upon spatial navigation [6]. The SL-250, 500 and 1000mg/kg were significant in reducing the time spent in open arm and thereby exhibited anxiolytic activity [4]. In radial arm maze, none of the dose was significant, which may be due to the appetite suppression [3]. To conclude, SL significantly facilitated spatial and non-spatial memory functions and exhibited anxiolytic action. Hence may be used to treat the related disorders of Learning and memory and to relive anxiety without affecting the Cognitive function.
The role of the synthetic B1 Vitamin sulbutiamine on health – a review
Sulbutiamine is a thiamine derivative developed in Japan in the mid-60 ́s as a beriberi treatment agent . Since then, different potential applications have been described. For instance, there is some evidence that sulbutiamine can have anti-fatigue, Nootropic and Antioxidant effects, which led to its use as a sport supplement (although some authors argue it is actually a masking doping strategy). Moreover, this molecule has been proposed as a possible treatment for some microsporidial infections and even for certain types of cancer.
Despite these potential effects, sulbutiamine is still a relatively unknown molecule, which justifies the present review, where we discuss its history and the existing literature on its health applications. We conclude that there is a great potential for sulbutiamine use, well beyond its first described function (to increase thiamine tissue concentration ). Indeed, new mechanisms of action have been found, mainly associated with its derivatives.
Nevertheless, and although the research on sulbutiamine started 50 years ago, only a limited number of studies were conducted during this time frame. As so, methodological concerns need to be addressed and new studies are necessary, especially randomized controlled trials. Only then, will the full potential of this versatile molecule be identified.
DM235 (sunifiram): a novel Nootropic with potential as a Cognitive enhancer
DM235 (sunifiram), a new compound structurally related to piracetam, prevented the amnesia induced by scopolamine (1.5 mg kg–1 i.p.), after intraperitoneal (0.001–0.1 mg kg–1) or oral (0.01–0.1 mg kg–1) administration, as shown by a passive avoidance test in mice. The antiamnesic effect of DM235 was comparable to that of well-known Nootropic agents such as piracetam (30–100 mg kg–1 i.p.), aniracetam (100 mg kg–1 p.o.) or rolipram (30 mg kg–1 p.o.). DM235 also prevented mecamylamine (20 mg kg–1 i.p.)-, baclofen (2 mg kg–1 i.p.)- and clonidine (0.125 mg kg–1 i.p.)-induced amnesia in the same test. In the Morris water maze test with rats, scopolamine (0.8 mg kg–1 i.p.) inhibited the reduction of escape latency in both acquisition and retention/retraining tests. DM235 (0.1 mg kg–1 i.p.), 20 min before each daily acquisition training, prevented the scopolamine-induced memory impairment. DM235 (1 mg kg–1 i.p.) also reduced the duration of pentobarbitone-induced hypnosis in mice without modifying the induction time of hypnosis. At the highest effective doses, the investigated compound neither impaired motor coordination (rota-rod test), nor modified spontaneous motility and inspection activity (Animex and hole board tests).
These results indicate that DM235, a compound structurally related to piracetam, is a novel Nootropic endowed with the capability to prevent Cognitive deficits at very low doses. Indeed, its potency is about 1,000 times higher than that of the most active piracetam-like compounds.
Ethnophamacological relevance:
Tabernaemontana divaricata (TD), a Thai medicinal herb, has been widely used as an analgesic, sedative, or a cough syrup. Moreover, it has been used in traditional rejuvenation remedies as for preventing forgetfulness and improving the memory .
Aim of study:
The present study aimed to determine the effect of TD on Aβ25–35 peptides induced Cognitive deficits and acetylcholine sterase activity in mice.
Materials and methods:
Mice were pretreated with TDE (250, 500 and 1000 mg/kg body weight) for 28 days and then received i.c.v. injection of Aβ25–35 peptides. Cognitive performance was evaluated using the Morris water maze (MWM) and step-down avoidance test. The Ellman’s colorimetric method was used to investigate the levels of cortical and hippocampal AChE activity.
Results:
Aβ25–35 peptides induced the memory impairment and the increased levels of cortical and hippocampal AChE activity. The consumption of TDE significantly improve d the memory impairment and attenuated the Brain levels of AChE activity induced by Aβ25–35 peptides.
Conclusions:
These findings suggest that subchronic administration of TDE might prevent the Aβ25–35 peptides induced memory deficits by decreasing the AChE activity level. Therefore TDE could potentially be one of Nootropic supplements for those elderly people suffering from dementia such as the AD patients.
Screening of Taxillus Tomentosus Ethanolic Extract for Nootropic and Antistress Activity in Rats
In recent years, attempts have been made to develop agents for treatment of dementia and attention deficit disorders to improve memory and learning. Some Nootropic agents (eg: Piracetam) are widely used but the resulting chemo phobia associated with them and other similar agents has made their use limited. So it is worthwhile to explore medicines from the traditional system in the treatment of these Cognitive disorders.stress is a broad, ambiguous, and often poorly understood concept. In its most simplified Sense, stress is what one feels when life’s demands exceed one’s ability to meet those demands. The objective of the study is to study the effect of ethanolic extract of Taxillus tomentosus for Nootropic and antistress activity in experimental animals.
It has been documented in traditional system that Taxillus tomentosusplant belonging to family loranthaceaeeffective in nervine disorders, acts as a nervine tonic. In a survey of ethnobotanical literature, numerous plant preparations have been used in the treatment of age related Cognitive disorders in human beings in European countries; so in present study is to evaluate the same on Taxillus tomentosusalone by using various screening models in rats.However, this plant has not been scientifically investigated for the same. Therefore, the present study is designed to evaluate effect of whole plant extract on Learning and memory.
Pharmacological actions of Thespesia populnea relevant to alzheimer’s disease
Thespesia populnea (Malvaceae) is a large tree found in the tropical regions and coastal forests of India. Various parts of T. populnea are found to possess useful medicinal properties, such as antifertility, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant , purgative and hepatoprotective activity. The present study was undertaken to investigate the effects of T. populnea bark on Cognitive functions, total cholesterol levels and cholinesterase activity in mice. A total of 312 mice divided into 52 different groups were employed in the present investigation.
The ethanolic extract of T. populnea (TPE) was administered orally in three doses (100, 200 and 400 mg/kg) for 7 successive days to different groups of young and aged mice. The Learning and memory parameters were assessed using elevated plus maze and passive avoidance apparatus. TPE (200 and 400 mg/kg, p.o.) showed significant improve ment in memory of young and aged mice. TPE also reversed the amnesia induced by scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg, i.p.) and diazepam (1 mg/kg, i.p.). Furthermore, TPE reduced significantly the central (brain) cholinesterase activity in mice. TPE exhibited a remarkable cholesterol lowering property comparable to simvastatin (a standard agent ) in the present study.
Furthermore, we observed that, T. populnea bark possessed a powerful memory Enhancing activity in mice. Since diminished cholinergic Receptor Stimulating Agent from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages cholinergic transmission and increased cholesterol levels appear to be responsible for development of amyloid plaques and dementia from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages dementia in Alzheimer patients, TPE may prove to be a useful medicine on account of its multifarious beneficial effects, such as memory improving property, cholesterol lowering, acetylcholine sterase Inhibitor from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages anticholinesterase and anti-inflammatory activity. Therefore, T. populnea bark appears to be a promising candidate for improving memory and it would be worthwhile to explore the potential of this plant in the management of Alzheimer patients.
The antibacterial and Antioxidant potential of Tiliacora racemosa leaf extracts in various solvents (methanolic, hexane, chloroform and ethyl acetate) was determined. Additionally, the presence of bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids in the plant prompted us to evaluate the Nootropic activity of the methanolic extract in mice. Further, we seek to verify the Nootropic effect by examining the acetylcholine sterase Inhibitor from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages nticholinesterase inhibition potential of the methanolic extract. The leaf extracts in various solvents were evaluated for their antibacterial and Antioxidant activity by agar diffusion technique and α, α-diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging method, respectively. The ex vivo acetylcholine sterase from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages acetylcholine esterase inhibitory activity of the methanolic extract was carried out by Ellman’s method in male Wistar rats. The Nootropic capacity of the methanolic extract was examined in Swiss albino mice by utilizing the diazepam induced acute amnesic model.
The chloroform/n-hexane and ethyl acetate fraction showed promising Antioxidant and antibacterial (Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria) property, respectively. The methanolic extract was able to diminish the amnesic effect induced by diazepam (1 mg/kg i.p.) in mice. The extract also showed significant acetyl cholinesterase inhibition in rats. The findings prove that the memory Enhancing capability is due to increased acetylcholine from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages acetyl choline level at the nerve endings. The strong Antioxidant nature and potential Nootropic activity shown by the extract suggests its future usage in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders such as dementia from ScienceDirect’s AI-generated Topic Pages dementia and Alzheimers.
The present study was designed to evaluatethe Nootropic property of n-butanolic (TBF) fraction of ethanolic extract of Tinospora cordifoliastem which contain saponin. The TBF was administered at 100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg. The Nootropic effect was evaluated using different models like elevated plus mazein mice to determine the transfer latency on day-2 and Day-9. The passive avoidance test was carried out in mice to evaluate the step down latencyon day-2 and Day-9. The object recognition test carried out to determine the recognition index. Scopolamine(1 mg/kg) was used as amnesic agent and piracetam (250 mg/kg) was used as a standard Nootropic agent.
The results of the present study showed significant increase in transfer latency by TBF on day -2 and Day-9. The TBF also increases step down latency, object recognition index significantly.Scopolamine was used to produce amnesia significantly decreased transfer latency, step down latency, object recognition index.The TBF antagonised the amnesic effects of scopolamine in the above experimental models. Anti-cholinesterase activity of TBF was evaluated by estimation of acetylcholine steras (AchE) concentration in mice Brain after 7-days treatment with TBF. The result showed decreased in AchE concentration indicating involvement of cholinergic system in Nootropic activity of TBF.
Nootropic activity of hydroalcoholic extract of Trapa bispinosa
The effect of hydroalcoholic extract of fruits of Trapa bispinosa (TB) was investigated for its Nootropic activity using various experimental paradigms of Learning and memory, viz. transfer latency (TL) on elevated plus-maze, passive avoidance response (PAS) and object recognition test. The investigation reported that TB 500 mg/kg significantly reduced the TL on 2nd and 9th day while TB 250 mg/kg was found effective on 9th day. TB 250 and 500mg/kg significantly increased the step down latency in the PAS at acquisition and retention test. Moreover the TB (250 & 500mg/kg) increased discrimination index in the object recognition test indicating Nootropic activity.
To conclude TBextract showed significant facilitatory effect on aversively motivated Learning and memory in mice as well as improve ment of memory in absence of Cognitive deficit.
The novel Nootropic compound DM232 (UNIFIRAM) ameliorates memory impairment in mice and rats
The favorable pharmacological profile exhibited by piracetam stimulated the synthesis of related compounds potentially endowed with a higher Nootropic potency. The antiamnesic and proCognitive activity of DM232 (unifiram), a new compound structurally related to piracetam, was investigated. Mouse passive avoidance and rat Morris water maze and Social Learning tests were employed. DM232 (0.001–1 mg kg−1 i.p. – 0.01–0.1 1 mg kg−1 p.o.) prevented amnesia induced by scopolamine (1.5 mg kg−1 i.p.), mecamylamine (20 mg kg−1 i.p.), baclofen (2 mg kg−1 i.p.), and clonidine (0.125 mg kg−1 i.p.). Furthermore, The antiamnesic effect of the investigated compound was comparable to that exerted by well‐known Nootropic agents such as piracetam (30–100 mg kg−1 i.p.), aniracetam (100 mg kg−1 p.o.), rolipram (30 mg kg−1 p.o.), and nicotine (5 mg kg−1 i.p). DM232 (0.1 mg kg−1 i.p.) was also able to prevent amnesia induced by scopolamine (0.8 mg kg−1 i.p.) in the rat Morris watermaze test. In the rat social Learning test, DM232 (0.1 mg kg−1 i.p.) injected in adults rats reduced the duration of active exploration of the familiar partner in the second session of the test.
DM232, similarly to piracetam, reduced the duration of hypnosis induced by pentobarbital. At the highest effective doses, the investigated compound did not impair motor coordination (rota rod test), nor modified spontaneous (Animex). These results indicate DM232 (unifiram) as a novel cognition enhancer, strictly related to piracetam‐like compounds, able to ameliorate memory impairment at doses about 1,000 times lower than the most active available Nootropic compounds.

Vateria Indica Vitis vinifera L.
Purpose: To investigate the neuroprotective and memory-boosting properties of ethanol extract of Vateria indica bark on scopolamine-mediated defects in Learning and memory in young mice.
Methods: The ethanol extract of V. indica bark was prepared via Soxhlet extraction and subjected to qualitative and quantitative phytochemical assessment. The acute toxicity of the extract was also evaluated in mice. Six groups of 3-month-old Swiss albino mice (6 per group) were used: normal control, negative control, piracetam group, 250 mg/kg V. indica extract alone group, 500 mg/kg V. indica extract alone group, 250 mg/kg V. indica extract + scopolamine group and 500 mg/kg V. indica extract + scopolamine group. The mice were pretreated with piracetam (standard Nootropic agent ) or varied doses of the extract for 14 days prior to induction of amnesia. With the exception of normal control group, amnesia induction using scopolamine (3 mg/kg) i.p. on day 14 at 1½ h after the last extract dose. Mice in normal and negative control groups received 0.5 % tragacanth orally at a dose of 10 mL/kg. Cognitive deficit was assessed using elevated plus maze (EPM), step-down avoidance, and Morris water maze (MWM) tests.
Results: Qualitative phytochemical screening of V. indica bark extract showed flavonoid s, phenolics, glycosides, tannins, carbohydrate, saponins and steroids. The total phenol and total flavonoid contents were 580.96 ± 0.95 mg GAE/g extract and 66.89 ± 0.56 mg RE/g extract, respectively. The mice tolerated the extract up to 5000 mg/kg bwt. They all survived during and after the acute toxicity study and no significant changes in appearance or general behavior were noticed. The extract significantly enhanced Learning and memory, and improve d spatial recognition in scopolamine-induced amnesic mice (p < 0.05). acetylcholine sterase (AChE) activity and levels of dopamine and noradrenaline were markedly higher in negative control mice than in normal control, but were significantly reduced after pretreatment with ethanol extract of V. indica bark (p < 0.05). The results of histopathological examination provided evidence in support of the protective effect of the extract on hippocampal and cortical neurons.
Conclusion: Pretreatment with ethanol extract of V. indica bark confers neuroprotection and enhances memory in young amnesic mice. Therefore, the extract of the plant can potentially be develpoed for the management of degenerative Brain conditions.
Nootropic EFFECT OF VIGNA MUNGO(L.) HEPPER SEEDS EXTRACT IN SCOPOLAMINE INDUCED AMNESIC RATS
Aim of the Study: Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper seeds extract consisted of flavonoids, phenolic compounds and Vitamin C etc. have important Antioxidant functions that can protect against oxidative stress in the Brain and damage associated with neurodegenerative disorders. The present study was investigated the protective effect of ethanolic extract of Vignamungo (L.) Hepper seeds on Learning and memory functions in scopolamine induced memory deficits rats.
Materials and Methods: In scopolamine induced Cognitive deficit rat model Wistar albino rats of either sex weighing 200-300 g were divided into 8 groups (6 animals per group). Group 1 served as normal control (NC), Group 2 received SCO (2 mg/kg i.p.), Groups 3, 4 and 5 served as per se groups received piracetam (PR) (200 mg/kg i.p.), EVME (200mg/kg p.o.) and EVME (400 mg/kg p.o.), Groups 6, 7 and 8 servedas Cognitive deficit groups which received PR (200 mg/kg i.p), EVME (200 mg/kg p.o.) and EVME (400 mg/kg p.o.) for 28 days respectively followed by SCO (2 mg/kg i.p.). The protective and Cognitive Enhancing effects of EVME on Cognitive deficit rats induced by scopolamine were investigated by assessingthe elevated plus mazeand the Morris water maze test. In order to confirm the underlying mechanisms of memory Enhancing effects of EVME, activities of AChE.
The alkaloid derivative vinpocetine (14-ethoxycarbonyl-(3α,16α-ethyl)-14,15-eburnamine; Cavinton) has a well known beneficial effect on Brain function in hypoxic and ischemic conditions. While it increases CNS blood flow and improves cellular metabolism, relatively little is known about vinpocetine’s underlying molecular mechanisms on the single cell level. Since apoptotic and necrotic cell damage is always preceded by an increase in [Ca2+]i, this study investigated the effect of vinpocetine on [Ca2+]i increases in acute Brain slices. Sodium influx is an early event in the biochemical cascade that takes place during ischemia. The alkaloid veratridine can activate this Na+ influx, causing depolarization and increasing [Ca2+]i in the cells.
Therefore, it can be used to simulate an ischemic attack in Brain cells. Using a cooled CCD camera-based ratio imaging system and cell loading with fura 2/AM, the effect of vinpocetine on [Ca2+]i changes in single pyramidal neurons in the vulnerable CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices was investigated. Preperfusion and continuous administration of vinpocetine (10 μM) significantly inhibited the elevation in [Ca2+]i induced by veratridine (10 μM). When the agent was administered after veratridine, it could accelerate the recovery of cellular calcium levels. Piracetam, another Nootropic used in clinical practice, could attenuate the elevation of [Ca2+]i only at a high, 1 mM, concentration. We have concluded that vinpocetine, at a pharmacologically relevant concentration, can decrease pathologically high [Ca2+]i levels in individual rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons; this effect might contribute to the neuroprotective property of the agent.
Background: The aerial parts of Vitis vinifera (common grape or European grape) have been widely used in Ayurveda to treat a variety of common and stress related disorders. In the present investigation, the seed extract of V. vinifera was evaluated for antistress activity in normal and stress induced rats. Furthermore, the extract was studied for Nootropic activity in rats and in-vitro Antioxidant potential to correlate its antistress activity.
Methods: For the evaluation of anti-stress activity, groups of rats (n = 6) were subjected to forced swim stress one hour after daily treatment of V. vinifera extract. Urinary vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and ascorbic acid were selected as non-invasive biomarkers to assess the antistress activity. The 24 h urinary excretion of vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and ascorbic acid were determined by spectrophotometric methods in all groups under normal and stress ed conditions. The Nootropic activity of the extract as determined from acquisition, retention and retrieval in rats was studied by conditioned avoidance response using Cook’s pole climbing apparatus. The in vitro Antioxidant activity was determined based on the ability of V. vinifera to scavenge hydroxyl radicals.
Results: Daily administration of V. vinifera at doses of 100, 200 and 300 mg/kg body weight one hour prior to induction of stress inhibited the stress induced urinary biochemical changes in a dose dependent manner. However, no change in the urinary excretion of VMA and ascorbic acid was observed in normal animals at all the doses studied. The cognition , as determined by the acquisition, retention and recovery in rats was observed to be dose dependent. The extract also produced significant inhibition of hydroxyl radicals in comparison to ascorbic acid in a dose dependent manner.
Conclusion: The present study provides scientific support for the antistress (adaptogenic), Antioxidant and Nootropic activities of V. vinifera seed extract and substantiate the traditional claims for the usage of grape fruits and seeds in stress induced disorders.
Yashtimadhu is one of the “Medhya Rasayan” agents advocated to achieve desired effect on Cognitive functions especially when given with Cow milk. In present study two dosage forms of Yashtimadhu i.e. Choorna [Powder] and Kshirapaka[Medicated Milk] were prepared as per standard guidelines given in ayurvedic classical text and were analysed with API parameters. Therefore, it can be saidthat a preparation method of both formulations is developed and validated with physic-chemical analysis. In extension, comparative assessment of Nootropic activity of both formulations was done by usingtwo animal models, viz. Diazepam induced amnesia using elevated plus maze [EPM] in young mice and spatial learning and memory in radial arm maze [RAM] in aged mice. In EPM test and RAM test agent administration was done daily for 15 and 7 days respectively.
Study finding suggests that Yashtimadhu Kshirpaka at therapeutic dose exhibited anti-amnesic effect and learning-memory enhancement action in EPM test and RAM test (P<0. 001). The result also specified comparative significant effect of Yashtimadhu Choorna with cow milk on animal’s cognition than Yashtimadhu Choorna withwater. Thus it can be concluded that addition of cow milk as Anupana to Yashtimadhu or processing of Yashtimadhu Choorna with cow milk in ‘’Kshirapaka formulation’’ has potential to maintain healthy Cognitive process in animals’. Hence both potent formulations can be employed as Nootropic agents to maintain human cognition in balanced state or can be utilized as adjuvant to conventional treatment.
Gingerol (Zingiber Officinale)
ZINGIBER OFFICINALE: EVALUATION OF ITS Nootropic EFFECT IN MICE
Dementia is one of the age-related Mental problems, and a characteristic symptom of Alzheimer’s disease. Nootropic agents and cholinesterase inhibitors like donepezil® are clinically used in situations where there is organic disorder in Learning abilities and for improving memory, Mood and behavior, but the resulting side-effects associated with these agents have made their utility limited. Ayurveda emphasizes use of herbs, nutraceuticals or life-style changes for controlling age related neurodegenerative disorders. The present study was undertaken to assess the potential of an ayurvedic rasayana (rejuvenator) agent Zingiber officinale Roscoe as a memory enhancer . Elevated plus maze and passive avoidance paradigm were employed to evaluate Learning and memory parameters. Z. officinale extract (50 and 100 mg/kg, p.o.) were administered for 8 successive days to both young and aged mice.
The dose of 100 mg/kg of Z. officinale extract significantly improved Learning and memory in young mice and also reversed the amnesia induced by diazepam (1 mg/kg, i.p.), and scopolamine (0.4 mg/kg, i.p.). Furthermore, it also reversed aging induced amnesia due to natural aging of mice. Z. officinale significantly increased whole Brain acetyl cholinesterase inhibition activity. Hence, Z. officinale might prove to be a useful memory restorative agent in the treatment of dementia seen in the elderly. The underlying mechanism of its action may be attributed to its Antioxidant and acetyl cholinesterase inhibition property.
| Size | 50g, 100g, 200g, 300g |
|---|
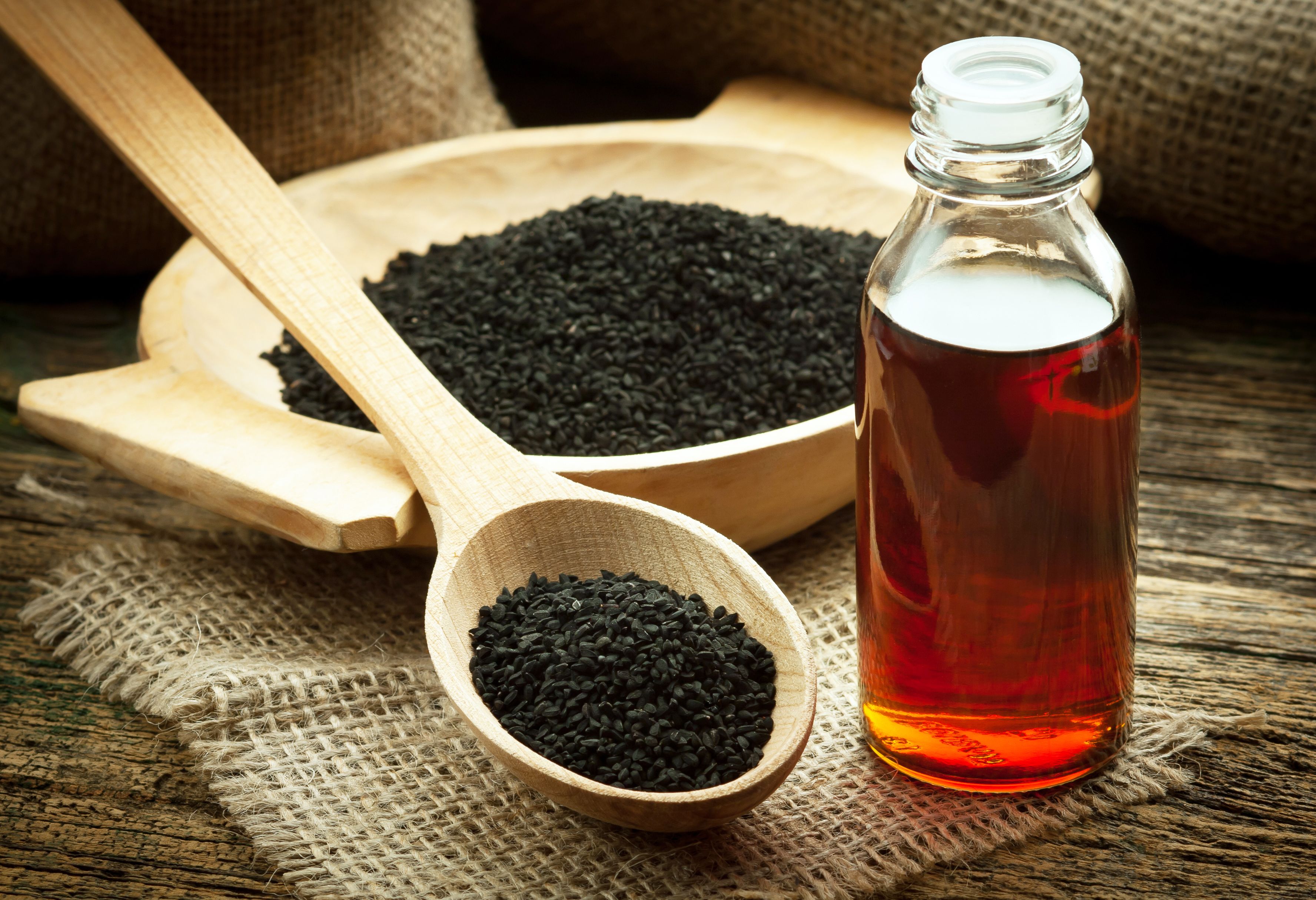
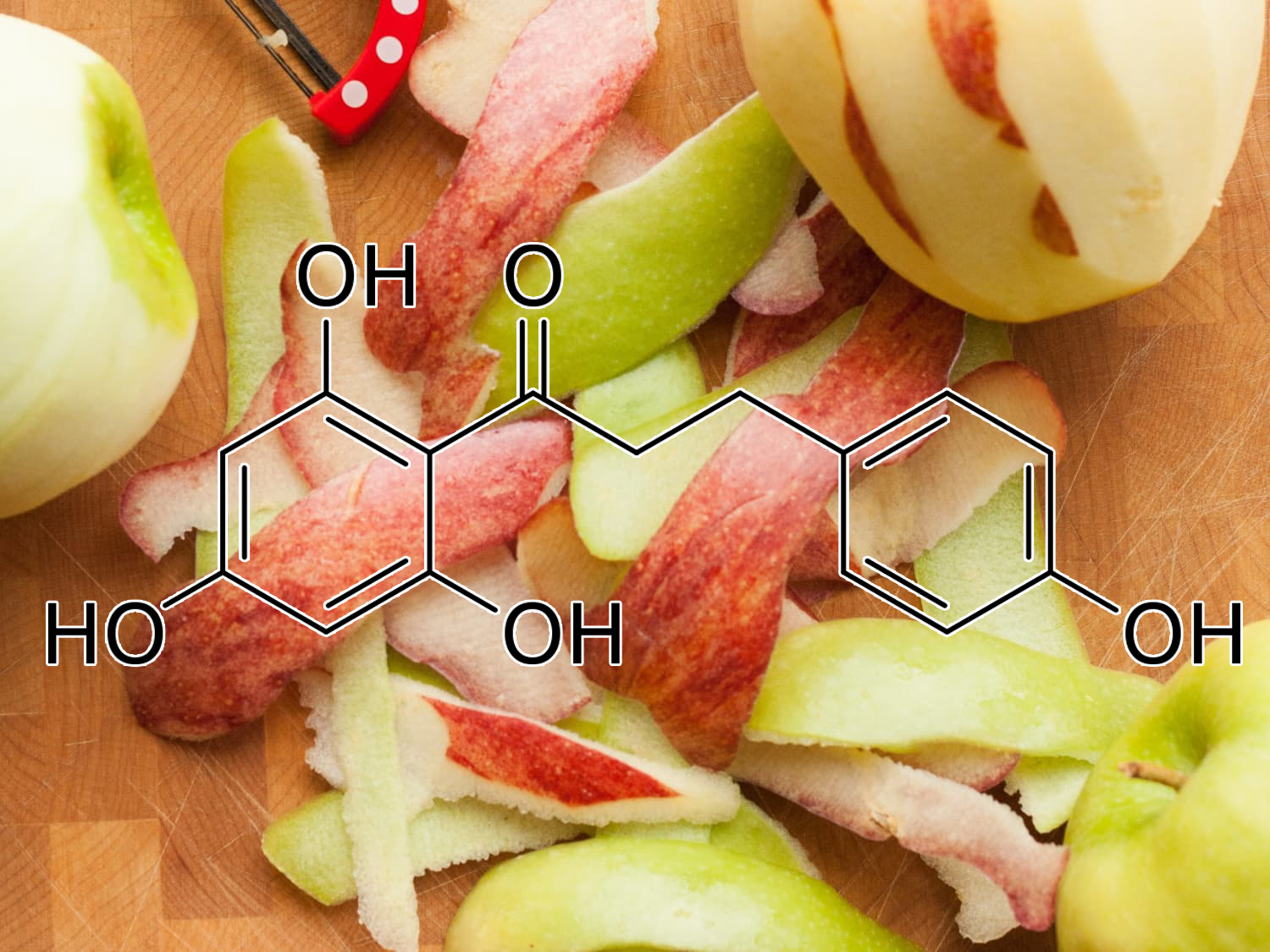









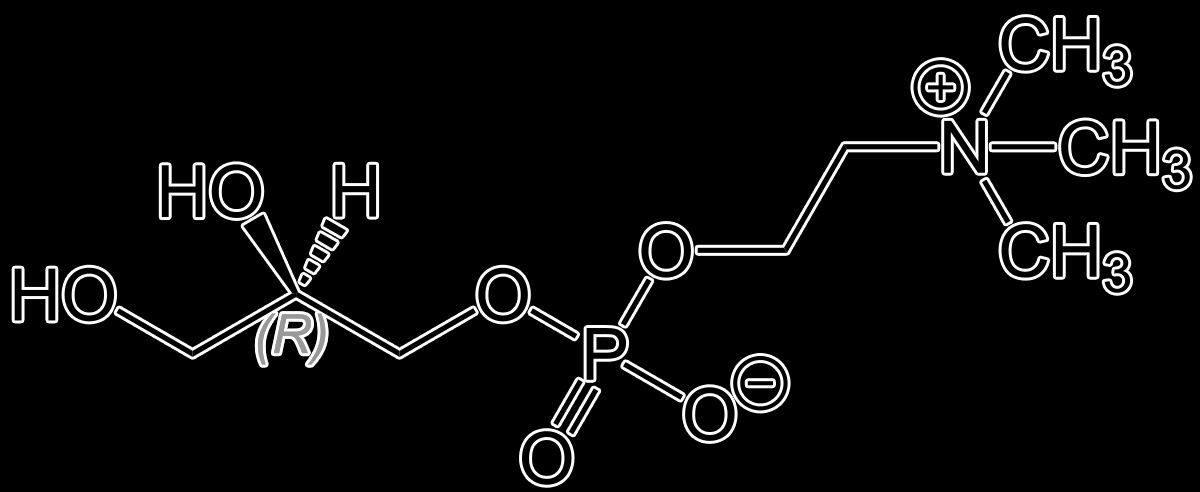




















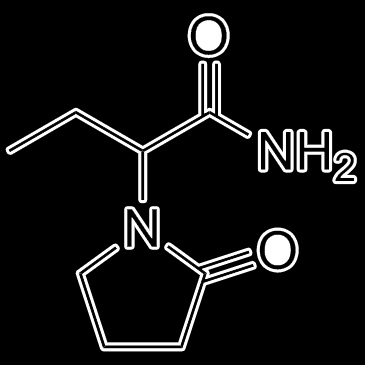



















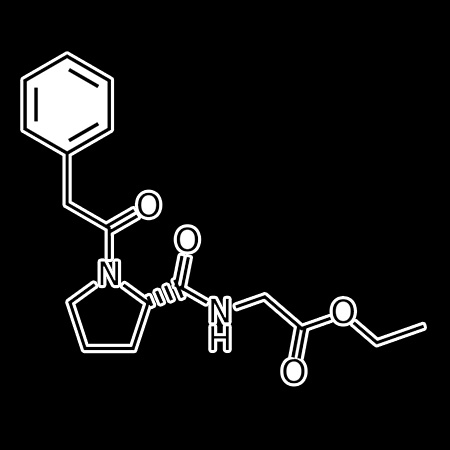











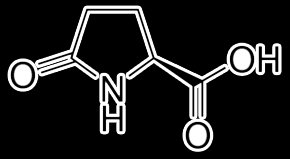

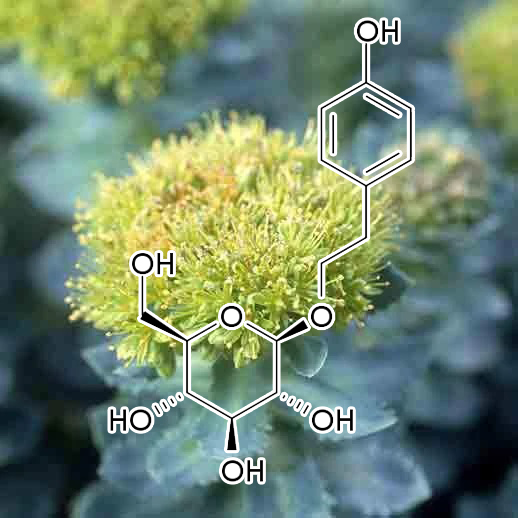


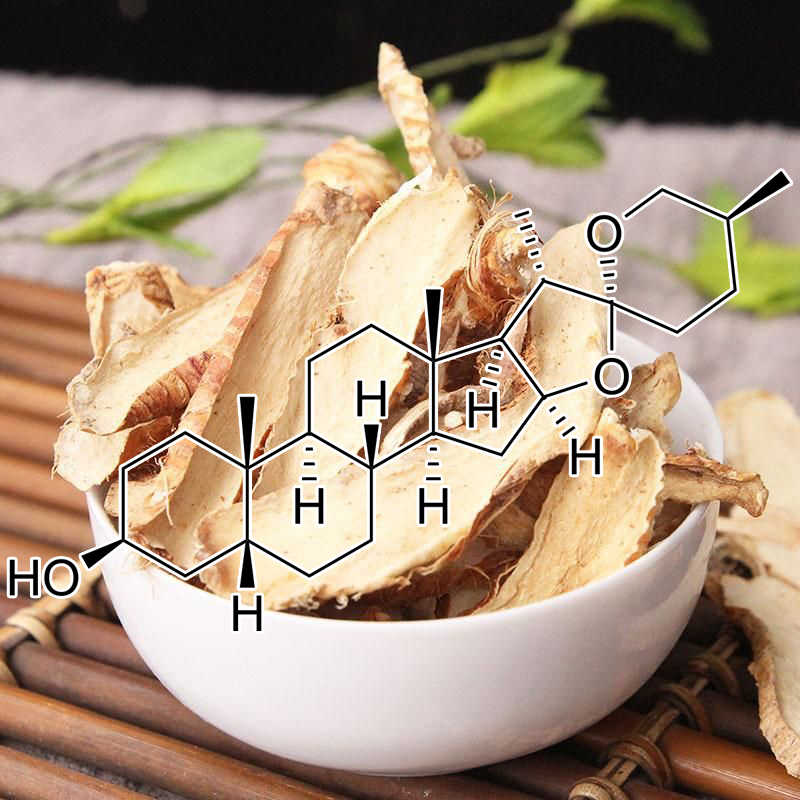



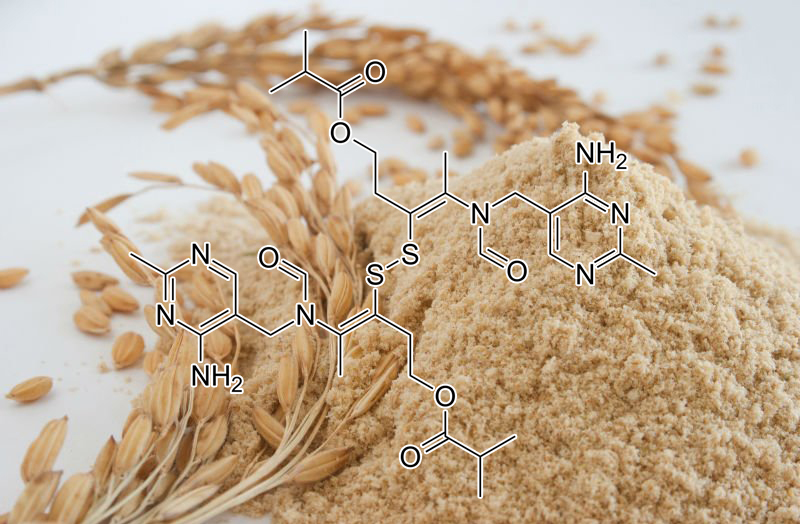














T –
First off, I have to say that Gavin and his blends are life changing. I honestly do not think I will ever stop taking them.
In the almost two months I have been taking blends, I have asked Gavin all kinds of questions and he is always so helpful. He asks you about your goals, and helps you get the right mix of blends for you. At first, I started taking a little bit of everything, but after speaking with Gavin, I have found the right blends, dosages and times of the day to take them. In less than two months, I have taken myself off prescription medications(my own decision) and stopped taking allergy meds and other things of that nature. I feel like a whole new person!
Personally, my go to blends are Trinity, Nebula and thanks to Gavin for allowing me to sample, this nootropic blend AUTONOMOUS. This blend has helped me so much while I’m at work. I am so much more productive and have LASER-SHARP FOCUS! As someone who used to have to take medication to feel this way, it is AMAZING to have even more focus NATURALLY! My field of work is quite demanding, and when I am in a fog, it is easy to get lost and overwhelmed with all I need to do. Not anymore! The fog has lifted and I am able to get through my days without being tired, or stuck in stress-mode. This is huge for me. I cannot thank you enough, Gavin!
If you are thinking about it, stop. JUST DO ITTT! You will NOT regret it, and your body and brain will thank you!
Rich Ryan –
Wow, this blend really makes a difference. I could feel it in 15 min. My brain fog lifted and I had increased focus and massive clarity and brain activity the rest of the day.
Incredible for productivity!
Perfect companion blend for Trinity, Sages, Original or Thermo. Super strong blend so you don’t need that much. 1/4 tsp is a strong dose.
You can’t achieve this with herbs at Amazon or Wal-Mart. Only super concentrated herb blends can do this. And there’s only one company that does it this way that I’m aware of.
The One And Only INTERSTELLAR BLENDS!
Worth Every Penny!
Priscila Saldivar –
WOOOWW that is all I can say! I have been taking the blends for a couple of weeks now and my life has completely change. Still lately I started going to hot yoga again and to be honest it has not been easy and I started to hate it because I was not being able to focus or last long in each pose. I asked Gavin if I could be part of his early trial of people to try the new blend Nootropic. Around 4 years ago I started to hear the word Nootropic around the tech community and I cave in and bought a lot of supposed nootropics throughout the years but nothing really surprised me UNTIL TODAY. Within 15 minutes of me taking the blend I could feel my whole vision expanding just like the movie limitless. I was aware of everything and everyone around me and I felt so powerful. My brain felt like it was rewired as I knew exactly what I have to do and in what order without feeling any pressure or anxiety. NOW wait to hear this, I went to yoga that day 2 hours after taking 1/4 tsp of Nootropic and I was laser focus, I was able to mentally challenge myself and push myself and every pose was 1100% better than last week. ALL I can saw is how lucky I am to be alive and have access to these blends. Although I have a long journey to go to loose all the weight I gained during quarantine, I feel 100% better than I did a month ago and my mind is getting sharper and sharper and I am getting strong and stronger physically, emotionally and spiritually.
Daniel Ding –
Thank you so much for the Autonomous sample Gavin!!!!! ❤️❤️❤️.
5 days after using it and My brains are overclocked and running on overdrive mode. Its literally like the NZT pill in Limitless movie. Neuroplasticity increases. I have heighten focus and clarity. Not to mention the ability to learn, decode and remember information faster. Pairing it with Trinity gives the ultimate synergy effect. I feel calm, composed and calibrated.
When are you gonna release it? I really need Autonomous. No, I think humans all need these blends. Tired of big pharma cartel and their scam rubbish products. Feels like I can take over this fucking world after having this magic blend. Please release it earlier Gavin… We all really need this for world domination. Time to take back our superhuman powers again!!!
Dylan E –
Autonomous, what else to say besides WOW. A life changing blend. First of all I had been blown away by seven sages and trinity, and after taking those two i had decided to get on many other blends like lutolin, spice and peel (some of my other favorites) Interstellar is my life style this past year, so when Autonomous came out i knew i had to grab some so i placed a large order so that I could get one of the samples and im glad I did. Autonomous makes you feel like you are in the flow state all day. Before this blend i thought i could only focus on one business and maintain a high quality focus and function. Boy was I wrong, since starting Autonomous along with my other blends I am now starting 3 other companies and flying through life. These arent just simple companies either. Im taking my life from one simple business paying me well to a potential 500 million dollars in holdings companies in the matter of a few months. If that doesnt sell you on this blend, I dont know what will! Just try it!!! Flow baby,,flowww.
Jason E (verified owner) –
So ive been on trinity, Seven Sages, and autonomous from about 2 months now, I do have other blends but these 3, I think are amazing together. I take it with black coffee and I add a very little amount of almond milk and when I say you stay focused. You Stay FOCUSED. The best result is when im fasted, I don’t eat in the morning but I also mean fasted from the night before. When I stop eating at 7pm the night before and I drink it in the morning I do feel the blends more intensely.
Im sure you can eat and still feel these blends but If you want the best results you should fast, and you don’t need to go days without eating just hours. Im focusing on doing 22/2 and with the blends its very easy to achieve. I am going to get my grandparents on these blends as well. Also going to get my parents some blends. Ive been a customer since December and I love these blends. Also the research provided from Gavin and his team on this website is unreal. If you have a question you will have it answered almost instantly.
Autonomous lifts your brain fog, clears your mind, helps you stay focused. But you have to put in the work as well, if you think you can just drink these blends and have a magical transformation your coming in with the wrong thinking. Use these blends, they can help you but you have to help yourself. You can’t eat trash food, drink the blends and think your going to feel like superman. But you can fast, drink the blends, walk, or workout and then you will feel INCREDIBLE. Thats how it really makes you feel, So if your on the verge of buying it. Go through with it. My favorite are Trinity, Seven Sages, and autonomous. I will be getting nebula soon so I want to add that to the mix. But thank you Gavin for everything!!
Philippe Tjantele (verified owner) –
I have been using the blends and the teachings of gavin to become a lot sharper then I was before. Mentally and physically I feel truely empowered since I have been in contact through telegram and using the blends as stated. When this blend came out I couldn’t be more excited because I was already feeling great and felt this would take it all to the next level. I was not wrong at all!
When fasted and on this blend I feel hyper focused! I live in Belgium (extremely fast delivery also to here) there have been lasting lockdowns and this blend has taking my focus during this time to another level. I truely feel what is good for me and have even stopped doing other things that were not aiding my full development! I am actually on this site right now to order another batch because I feel amazing.
I have advance my business more in the last 2 months then the entire past year while also starting 2 other businesses. I truely feel blessed to be on this wave of momentum and I urge you reading this to atleast give it a try. You’ll love it!
ALBERTO CAMPOS LOPEZ (verified owner) –
Autonomous is the last version that I have added to the set of blends (trinity and nebula) and I have to say that it really has its effects. It is very powerful, for me just one dose in the morning is enough and I can feel it within 15-20 minutes of taking it. Its really worth it as bag last a lot.
It’s hard to explain what it feels like, I can just focus more when I’m analyzing the charts (traders would know). Much less distractions than before. I wake up very early and after taking the blends its like I have slept 8 hours, when I rarely get over 4 every day during the week.
My latest acquisition has been Luteolin, Apigenin and ALZ, since my goal for now is to improve concentration and cognitive functions as much as possible and end with the daily stress we all have to deal with. Today is the first day combining all of them in the morning. Feel a pump.
I will leave another review in one of those last blends with an update of the final result.
Thanks Gavin, 5 * as always.
Jay Gurung –
I have been taking a combination of Autonomous, Luteolin, ALZ and seven sages for the past 2 weeks and the combo has been extremely beneficial for my memory clarity and concentration overall. I am a business major who got interested in software developing last year. I took some online classics to learn about the basics of the particular field last year but fond it extremely tough as I was having difficulty understanding even the basic terminologies.
Fast forward, I dwelled into the subject again after I started my aforementioned blends combination and it has definitely made a vast difference in my learning curve. I grasp terminologies and their logics more easily and my mind feels sharp & happy when watching tutorials cause normally I find video tutorials boring and have tendencies to feel sleepy and procrastinate. Definitely improved my productivity, also I recall memories random ass memories of when I was young. Some good memories, some memories, all pretty random that just makes me think ” What the heck” in a good way of course.
Kaye Orina –
For those who are sceptic ,or are on the verge of purchasing the blends , but didn’t do it yet, please read this, I URGE YOU:
Current pharma medecine is nothing to be compared to with this natural blends, to change your life and body for the better. You have one life and one body to maintain and nobody would care less to help you out, but here is Gavin to your rescue! Gavin responds lighthing fast to your problems and gives you the right directions on the combinations (or fasting routines) you’ll have to take.
I suffer from acne problems for 2 years I can’t find any organic solutions, ANY! I found SPICE and PEEL and always believed in natural herbs, but nowhere to be found…I asked Gavin for help and the dosage to see some effect. Believe it or not but within 5-ish days my skin started to look smoother, less bumbs, less redness & pimps didn’t pop up every next day that makes me more confident and happy to see it working out for the better.
My boyfriend too is amazed about AUTONOMOUS. He is less stressed, much more concentrated, makes his descisions faster without being concerned (or having a cloudy mind) & confident in what he is doing. He’s finishing his daily tasks and is not delaying it, just does it till it finshed. You could say it’s a limitless drug, but if you work on yourself and learn more and doing what you like you can be limitless with Gavin’s herbs.
I hope for you who read this to make a conscious decision in purchasing different herbs (samples of 50g) and see the effect and help yourself out with the problems you’re facing at this moment.
Ajay Taparia (verified owner) –
Want to go into a meeting with clear head?
Have a problem to solve and need the extra mental space ?
Want to day trade and need peak performance ?
Too many uses of this awesome blend. Start small (1/16) is a lot in the beginning.
Sudevika Okeahi –
I Highly recommend Autonomous!
This is my favorite blend so far!
It’s amazing and I’ve not been sick since taking it.
I’ve been around people who were ill and didn’t catch anything and that is very rare for me.
I have an extremely sensitive immune system and body type, also suffer from fibromyalgia, sugar in all forms makes my system weaker very fast too. But since I’ve been on Autonomous I’ve been able to bounce back almost immediately after having negative symptoms. I also take the Victorious blend but when I add Autonomous it’s like bringing in the entire army!
My best friend and I had what we all believe to have been Covid or whatever that virus is, my doctor does too.
However they weren’t testing for the virus back then here in Hawaii yet.
We both had severe chest and lung damage during and after also breathing difficulties and scary chest pains. Since I’ve been taking Autonomous for just over a month all pain and symptoms are 100 percent gone!
My friend has not yet tried the blends and she is still suffering with symptoms a year later.
So without a doubt I know this product works!
You need very little as it is strong, extremely affective and will last you a long time.
It is truly priceless as is your health.
It is very easy to take in coffee or tea and doesn’t upset the tummy at all.
Also I’ve not had a cold sore since taking Autonomous and I was getting them regularly.
I’m so grateful for these blends.
Thank you 🙏🏽
Elizabeth Paez –
so, ive been seeing these blends around with my peers for years, never jumped in, i was skeptical because of price. Time had passed and i was looking for nootropics, i figured id check Interstellarblends for some herbal blends, and to my surprise Autonomous had just come out. perfect timing, it was time to jump in. Id always known about fasting and the power of herbs. Like i said i was SKEPTICAL. i took the leap of faith. All i can say is WOW.
Most supplements are very subtle, or just placebos. This is NOT the case with Gavins blends. Truly another league. i wanted to wait atleast two weeks, and take them every day. Its been about 3 weeks now. I MUST SAY Im not only convinced, im IMPRESSED. Ive been taking Shilajit and Autonomous everyday upon rising with Black Tea.and Fasting Daily. Shilajit is a legendary substance for Longevity and Qigong practice. Autonomous is a real life NZT pill. Mental Clarity is up tremendously, so is my Emotional Intelligence. Significantly more power and strength in my body. Definitely learning concepts, assimilating info, and having breakthroughs at an accelerated pace. i Trade and Study Qigong Intensely. The results have been more than remarkable. Gavins perspicacity is reflected in the quality and power of these blends. He has earned a lifetime customer.
Life changing. I havent tried every blend yet. But i can tell you, Nebula is a power house, Autonomous is a Mental upgrade. These are my current favorites, and im very eager to buy some more blends. Gavin was also nice enough to include a Free sample along with my order. If your on the fence. I implore you, TRY it. You wont be disappointed. This is coming from someone who was very skeptical. Almost every facet of my life has had significant improvement since i started taking the blends just three weeks ago. Happy to be a part of the Interstellar blend Family! MEGA THANK YOU for your work Gav. To Infinity and Beyond!!!
Armando Paez (verified owner) –
I first heard of Interstellar Blends through a trading friend of mine, very interested from the get. Been into Fasting since my first spiritual awakening at 18. So I knew the power of proper nutrition and auto-immunity. Never had the money to try until recently. SO WORTH IT.
Gavins Blends exceeded my expectations (which were high to begin with). Needed a Nootropic for the extremely concentrated work that I do. I have a very high level of mind body awareness. So any changes in my body no matter how slight are ever overlooked. The effects of these blend are not only noticeable, they’re remarkable.
Since taking the blends I can say I’m definitely Mentally Stronger, Sharper, and overall more intelligent and clever. This has translated over to my fitness endeavors and musical endeavors.
Autonomous gave me a CLEAN BOOST, my creativity is through the roof. My favorite combination right now is Nebula, Autonomous, and Trinity. ITCHING to get my hands on more of this powdered gold that they serve here at Interstellar Blends. GODSPEED FAMILY!!! >:)
Frizz Lowry –
Autonomous is the first blend I have tried from Gavin and I absolutely love it ! Autonomous is something I highly recommend for anyone who is in need of supreme concentration, I myself struggle to naturedly get into the flow state but with autonomous I am mentally sharper, way more focused then I have ever been, I live in a loud house and sometimes that can be very distracting when I am trying to study but literately within 10 mins after consuming this I just zone out ( in a good way of course ) lol its like I get tunnel vision and I am just able to complete the task I have set for myself by the end of the day.
This product worked so great that I shared it with my friend and he himself said the same thing, this product is very well delivered and it does everything it says it does in the description, autonomous is something I see myself taking for life and I am definitely an lifetime customer 100 percent !
Another thing I will also add in is that I was taking super nova as well which is also an 5 star product these two blends mixed together absolutely phenomenal !!!!
I don’t think it gets better then those two combined but Autonomous is definitely my go to blend though! But for my next purchase I will be trying Trinity blend with Autonomous just to give a shot at the blends!
However if your looking for an product that well delivered fast guaranteed results with no jitteriness what so ever I promise you these blends are the way to go ! And the prices are not expensive for the high quality that’s delivered I PROMISE YOU THAT ! And also very very fast shipping I received my order within two days of my purchase and I didn’t pay for any fast delivery or anything like that, also Gavin is customer friendly if you have any questions about these blends you can reach him on telegram and he will respond answering all of your questions! THANK YOU GAVIN
Kevin –
After a year of suffering of much stress and anxiety a friend of mine told me about atonomous. I’m now 2 months in and I noticed that my stress and anxiety levels went down immediately.
Beside a reduce in anxiety and stress it also helps me concentrate better and I noticed a strong increase in creativity and a better concentration.
I have to thank Gavin for these amazing products and I take them probably for the rest of my life.
B.A. –
AUTONOMOUS is incredible!! Talk about next level. I’ve been really intrigued by nootropics and the ingredient list for this blend is out of this world. A lot of customers have been raving about AUTONOMOUS. Customers with demanding careers that require laser sharp focus and high mental acuity seem to gravitate towards AUTONOMOUS. Traders, analysts, executives, students, etc. The testimonials suggest that AUTONOMOUS blows most other nootropics out of the water.
So I knew I had to try it. I took the plunge, purchased AUTONOMOUS, and OH.MY.GOD. I have not previously had issues with brain fog, but let me tell you. If you have any issues with brain fog, this blend will ERADICATE IT swiftly. You want to talk about leveling up?! This blend makes you bionic. Notice I did not say “this blend makes you FEEL bionic”. AUTONOMOUS is like this magical brain stimulator that actually makes you BIONIC. You’re smarter, sharper, and operating at high levels of productivity and efficiency on AUTONOMOUS.
I could feel the shift from my very FIRST dose. Suddenly I was in the ZONE. Even my hearing was sharp!!! All five senses were on high alert but without feeling anxious or jittery. I believe anyone who — regardless of profession — is juggling this thing called life needs to absolutely have this blend in their arsenal. The level of efficiency and elevated brain functioning you get from this blend ALONE is invaluable. Even if you do not take every day although small DAILY dose is ideal. Like most of Interstellar Blends, it’s extremely potent so a little goes a long way. I will never tackle projects without AUTONOMOUS again! You don’t want to miss out on this blend – AUTONOMOUS offers the very epitome of living your BEST LIFE!
Finally, can we talk about price?!! As I mentioned a small dose goes an extremely long way, so with 100g you’re looking at OVER 600 DOSES for only $300!! That’s $0.50 PER DOSE!!! Larger sizes (200g and 300g) offer more savings, even cheaper than $0.50 per dose!! Wah?!! Say that again!!
I am now bionic and it costs me less than $1 per day. #micdrop
Always available to answer questions on FB (bfbfit) or IG (naijabu_fit). Feel free to reach out!
Patrick –
Yes, Tour The Force is the correct name for Autonomous! I am a fulltime trader who have been trading for 7 years and focus/the ability to do your analysis is very important in order to succeed in this job! I have been trying various Nootropics in the past with no groundbreaking results, which led me to believe that many Nootropics were just “hype”. Well, I was wrong after trying this blend!
This blend gives me the perfect amount of focus & clarity. The mix of Nootropics in this blend are carefully crafted by Gavin.. Want to stay in the zone? Go ahead and buy Autonomous.
My thoughts feel more sharp and I can do my job better than I normally could. I also noticed that the perfect words just come straight out without even thinking when talking to other people.
Best is to combine it with Trinity, Seven Sages! It has been my morning routine now for several weeks and I love it! Highly recommended, and thank you so much for the samples!
Luke Reynolds (verified owner) –
I purchased AUTONOMOUS along with Trinity, Spice and a few other blends and can say that I’ve been extremely happy and impressed with the results. Every morning I mix all my blends together in a tea to get me going for the day, and boy does it get me going for the day.
After taking the blend for the first time I quickly felt a surge of energy, not in an overpowering or jittery way however, a calm and controlled energy and focus which would last the whole day. Its as though the blend allows my brain to operate at 100% efficiency, not putting my brain into overdrive as stimulants do but just giving my brain everything it needs to operate as best as it can and actually giving me better functionality than stimulants do.
My job requires much concentration and decision making which prior to taking autonomous Id find Id burn out rather quickly and begin making poorer decisions, something this blend has greatly helped me with, I am able to work for longer and more efficiently, taking in much more information as I work allowing me to make better decisions.
I will definitely be purchasing more of these blends and other blends, cant wait to try out some of the new blends in stock. If anyone is on the fence about purchasing I would definitely recommend you try it, if you have anywhere near the same results I’ve had you will not be disappointed.
Rafael A. –
Before purchasing any of the blends I emailed Gavin to see what he recommended me since I started my Master program in Nursing and I was also going through some anxiety for the last few months. He recommended me taking Autonomous along with Trinity and later in the afternoon to take Nebula. I can see its the best mix of blends ever. I take it those two first thing in the morning with my coffee before going to class and I truly feel more focused and I feel that I retain more information during lectures.
Later in the afternoon if I am studying I’ll take the Nebula and it keeps me going through the rest of the day staying focused. I noticed a big difference taking the blends staying awake and more focused rather than just drinking any coffee or energy drink. It’s definitely a game changer. Not only do I feel more confident of myself taking an exam or staying focused and awake while studying but I noticed a huge difference in my anxiety not being there anymore. It sounds crazy but I am able to take things more calm and I feel more confident, if there is a situation where before I would panic a lot about now I am more chill and think things through in the moment rather than not being able what to do at all and my anxiety going through the roof.
I know that I will be buying more products to keep my studying sharp and my anxiety at its lowest level. I definitely recommend trying out the products and if you have any questions about what you should buy, email Gavin because he is super helpful and gets back to you very quickly. I am also recommending some of the products to my family and friends because I know they will love them.
Marc Tomkins (verified owner) –
Like most people, I told Gavin my life situation and he got back to me with the exact things I should do and take for my specific situation. He is a wealth of knowledge about all things concerned with health. Aside from the blends, he gave other dietary advice which since implementing, has shown almost instant benefits. Looking at all of the reviews before purchasing, I thought “there is no way these are all real” but having finally bit the bullet and ordered my own blends, I can see why he only gets good feedback.
There is nothing bad to say, the blends are amazing. You won’t hear about interstellar on TV or radio because this is not a brand that needs advertising, the results speak for themselves. I purchased autonomous because at times I have extreme difficulty staying focused and my mind just runs away with itself. I have tried things like modafinil which had an ok effect, but the side effects were simply not worth it. After taking autonomous, I see why there is a rave about these products. My mind is clear, but not wired, I can focus on whatever I want for as long as is needed without feeling unnatural or getting headaches or anything negative. I use autonomous with trinity, seven sages and a free sample of supernova that Gavin sent with my order.
I didn’t get a massive order because it was my first order but needless to say, my next order I will be ordering the whole damn shop. You are not going to find these products in your local health shop or supermarket. I can only imagine the difficulty it took to craft such perfect blends to deliver such amazing benefits, and Gavin is continuously improving and striving to create better and more helpful blends. Fuck your pills and medicines, this is the future.
Bilal Yousaf –
Let me give you a little back story about myself. I am a design engineer and my job requires me to sit at the computer for 8 hours straight. One of the things that I always struggled with was a sudden crash in my energy around 10 AM. Then I would always consume high amounts of sugar just to feel a bit energised only to crash again. The first day, and I mean literally the first day that I took Autonomous, I sat through my day without feeling drowsy and fatigue for a single moment. My focus was so sharp, I just wanted to do more and more. I wasn’t getting bored or distracted. It was super easy for me on that day to get through my work without being dependent on sugar for my energy. Autonomous truly is like your brainpower on steroids. I don’t think it’s possible for me to continue my work without the boost of Autonomous. Highly recommended for someone that struggles with lack of focus or low energy. You won’t regret it.
Luca Dall’Agnese (verified owner) –
I would wake up every morning feeling super groggy, no matter what I did (coffee, pre-workout, you name it). The grogginess would last until early afternoon and there didnt seem to be anything I could do about it. Autonomous actually changed my life. 1/8 teaspoon in my coffee/tea (fasted) every morning and it was like colours were brighter, sounds were louder and I have a level of motivation that just usually isnt there.
I have been taking automonous for over 6 months and although the effects are now more subtle than at first, it definitely changes the way I feel from the get go. Whenever I miss a day, I can tell. The best part? Im not dependent on autonomous. It supplements my day to day activities and makes me way more productive, but in NO WAY am I LESS productive than when I was before I discovered this blend.
If you are someone who has a hard time fully waking up in the morning, OR if you are someone who needs that extra level of focus on those mundane tasks, this blend is definitely for you. Ive tried many nootropics in my day, and it is definitely the best one Ive ever had bar-none. Will be buying this blend consistently going forward.
Nicolas C (verified owner) –
First of all I want to clarify that I am not the kind of person who will quickly be enthusiastic without having a real feedback on the products I bought. That’s why I write this comment almost 3 months after receiving my orders. And this in order to share my experience with you with as much hindsight as possible
I have to admit that I am really impressed by the results I was able to achieve using Gavin’s different packages. To put it simply I think these packages are clearly life changers, the reason for this is clear, I apply the protocol strictly as Gavin recommends.
After a few days I really felt a change both physically and mentally. To give more details, I bought several products: Nebula Trinity Thermo and Autonomous. The combination of these 4 products in an efficient way, adding to a regular sport practice clearly gave me a huge boost in my professional and personal life. I emphasize this point, these are not empty words, it is important to rigorously apply the various protocols and to have a good lifestyle to maximize the results. Thanks to the different packages a clear improvement will be felt.
In terms of feeling and taking. I usually take the morning fasting in a black coffee. 15 to 20 minutes after taking my mind is clear ,I am motivated, I have the ideas well in place .
I have no hesitation about the different actions I need to take to achieve my goals. Thank you so much. Thank you for allowing us to significantly improve our quality of life.
Johnny (verified owner) –
As a software developer entrepreneur I was always on the lookout for things that can optimize my performance. Been trying to stick to natural herbs and adaptogens most of the time but to get just the little edge in business and to maintain focus I was using kratom and modafinil on a weekly basis. When I didn’t use those stimulants I was just slacking off or sleeping a lot in order to regenerate. It was a vicous cycle and I was never really satisfied with my performance. On the weekend I was often lacking the energy to enjoy myself.
Now with Nebula, Trinity and Autonomous in my arsenal I have much more energy, focus, confidence, emotional resilience, less anxiety, less stress and am all in all more happy. These are benefits that come from the acute intake of the blends. On a deeper level I could challenge and neutralize limitations in my mindset. It’s the days when I use Rewire that I get better insights on what I should do and what opportunities I can’t let slip by. I’ve got this feeling of doing the right thing more often.
I really love how adaptable I have become. Limiting beliefs are left in the dust and new doors open up everywhere. Projects I have been too arrogant about before are now invigorating to me. Learning new things became enjoyable again.
So with the Holy Trinity (Nebula, Trinity, Autonomous) you can power through anything but to make the right decisions there is nothing better to recommend than REWIRE.
Anthony Verhagen –
Before I take any supplements or put anything in my body I do my due diligence to make sure everything is ok by my standards. I was looking to get into nootropics for focus so I could work for extended periods of time more than usual. To be honest they were kind of intimidating seeing as they are directly affecting the brain. Nonetheless, a public figure by the name of Shaun Lee recommended using the blends while fasting noting the definitive benefits. Once I decided to check the website out I was really impressed with the amount of information that was displayed.
There has never been a website that I’ve seen that provides such quality of information about their products and studies done to back the claims. This is what made me open into trying the products so I decided to go and get some of the samples that are provided. I got a sample of Autonomous and Trinity. I didn’t know what to expect when taking these and at first I was a little skeptical but after the first couple times of taking them I could definitely notice a big difference. I would find myself after taking Autonomous just locked into my work. The way it comes on is hard to notice for me and all of a sudden a good amount of time has passed in which I have just been very focused on what I was trying to get done. Absolutely love it.
With respect to Trinity, I work a very stressful job and this definitely chills me out. I feel a sense of zen after taking this and calmness. It is a very nice thing to have in your back pocket depending on your situation and would recommend it to just about everyone! Very happy with Autonomous and I can’t wait to try Nebula next! Worth every dollar and I’ve told those close to me to check it out because it just works.
Robby Co –
At first when I was my old self, I was skeptical to try things that increase brain function and cognitive enhancement. Ego is always getting in the way, of course. I find myself having the skills in my career but the decision making process and impulsivity can overwhelm me and I made poor quality decisions, until, that is, I tried Autonomous; this blend is my #1 go to followed by Trinity and Supernova. It’s the sweet combo for me in my nature of work.
I had a hard time focusing and taking a grasp of reality before. Autonomous brought me to a peaceful state of mind with TOP CLARITY of thoughts so I can make TOP QUALITY decisions with ease. This is truly a MAGICAL thing for lack of better term. It opens up new doors of possibility I couldn’t even think of before. I did not even know I had this much potential in me before Autonomous. Since I am a trader for a certain firm, before, when money is flowing rapidly on my screen I couldn’t control the amount of energy and emotion it sends to my brain. With AUTONOMOUS this job fixes it instantly. I go into a certain headspace where I can see things clearly and rationally. Finally now, I have broken the threshold of human programming. I am a free soul and all thanks to Gavin and his blends. truly JOB WELL DONE.
Truly AMAZING! 100/100!
Niko –
Holy shiiittt!?!¡!
I can not express my gratitude for these blends enough… When I first came to the website it looked fake af, and as if Gavin (the owner) fakes reviews as well, cause there are only good reviews… Then I have bought my first sample of Nebula and Trinity, and experienced such freakin progress in sports and daily basis operating I decided to go for more…
Autonomous made me into a machine. I went from having a focus of 0, of less than an hour to now doing 8-14h ow concentrated work, more potent that a nuclear reactor…
Autonomous
Trinity
Rewire
Nebula
Spaceborn
I can’t imagine my life without them anymore… They make me into the best version of myself, self-actualised and truly inhumane… Combined with 22/2 && 20/4 fasting, my life has never been better, I have never been happier, my mind has never been so clear and I am never taking another synthetically made supplement…
Everything you need is here, just combine with proper food, fruit, sleep, enough oil intake and have a blast… You can become a interstellar traveller as well. I give everyone reading this my personal promise that you will become 100x better and 1000x happier… Go take some samples to test out the reviews and you will see WHY THERE ARE NO BAD REVIEWS
Much love, take care and see you on the other side 🙂
Klaus (verified owner) –
In 2017 or 2018 I tried Trinity through a good friend who had been ordering from Gavin for ages and couldn’t believe what happened to him. He is a completely new person and sees the world through different eyes now. I have also recommended the blends to people suffering from cancer, diabetes and various other diseases. I bought it for my family and we all love it. After so many years, I often think to myself, it can’t believe how effective they still are. Now I have ordered Autonomous for the first time and my expectations have been exceeded by far. But it’s not just the mixes that outshine everything else, it’s Gavin as well. I have NEVER met anyone who is so reliable. It’s incredible. Gavin when he says something it is so and he does it. Gavin thank you so much for being who you are.
Kamran Sabri (verified owner) –
Hello, I was introduced to Intersellar blends through one my friend’s brother. I am currently out of employment for 4 months due to a very serious work-related injury that forced me to resign. I find it difficult to concentrate and
not easily get distracted, when filling job applications, preparing for job interviews, specially when you experience a lot application rejections. Autonomous helps me get in THE ZONE. I am on autopilot . I noticed two changes straight away. Firstly my level concentration has gone up by at least 50% if not more. Secondly, once I set myself a goal I will not stop until that task has been fulfilled. Yesterday I was scheduled to apply for 3 jobs, instead I sat down for 4 hrs nonstop and wrote cover letters for 7 jobs.
What I would say, it also helps to eliminate all other distraction to get maximum benefit. My phone is on silent, on my desk I only have my laptop and nothing else. I also put an alarm on my phone to remind, when my next blend is due to to drink.
I highly highly recommend, specially if you suffer from procrastination or poor productivity. It makes me feel great at the end of the day, knowing I completed all tasks I that needed to finish.
Kamran (verified owner) –
Hello again, I just wanted to add an extension to the review I left yesterday. After having completed all my tasks yesterday evening I went out to do my weekly shopping. As I was walking in, I felt this sheer level self confidence, tunnel vision focus and something very unique. Most people when they look at a person or an object they have tendency to twist their body, however last night I felt like Terminator, when I would only move my neck to look at an object with high level of focus. I also noticed I walked with an open chest, eye looking straight ahead, I felt like I am 6′ 5″, where actually I am 5′ 11″.
As I left supermarket, I thought what if everyday I accomplish my goals, this is how it will be everyday. Autonomous can literally change not only your productivity, but how you PERCEIVE yourself as a successful goal achiever.
Matthew W –
“I spent 9 years in pain searching for how to get back to going after what I really wanted. Finally after taking blends for a few months, I’m completely back to it. You don’t want to know the number of issues I was having from hiding from my dreams but all of them are solved. Depression, anxiety, muddled and cloudy thinking, emotional pain. I was really praying hard for something to help me. Finally found it.
Luteolin helped me think normally again.
Trinity allowed and eased my nervous system to work out the trauma.
Spaceborn put my mind and body in a higher place.
Seven Sages allowed me to see subtleties in what was going on with me.
Autonomous let my mind be unencumbered when understanding.
Rewire eased the process of changing habits.
Supernova gave me that kick to keep working through it.
Matcha let me focus in a relaxed state.
Stomach reset really seemed to remove a lot of issues automatically, like a fresh slate with how emotions, brain, and gut are connected.
Thunder is making me less controllable and under others’ influence. Big D energy.
The others are just as powerful.
Not to mention fasting making me push through it without physical distraction and coffee to keep me energized. Never would drink coffee before now it’s the best part of my day. I did combine it also with a healing technique called NET but I doubt it’s necessary unless you’re as fucked up as I was lol.
Blends are it man. Buy them.”
[email protected] (verified owner) –
The blends are just incredible, I usually take around 7 of them everyday and they keep me going smoothly and efficiently, I’m able to do more while fasting. Lifting heavy, looking sexy, skin is getting better, unreal energy, laser focus and ability to excel in everything I put my mind to!
What I wasn’t expecting is for Autonomous to work while I was full of food, I mean I stopped eating about 3 hours ago (its 9pm here, uk) and still had to do some stuff on my laptop. I was already tired because I was working on it for half a day and my brain was fried, I thought, “Screw it, I’m just gonna hit 1/8 of Autonomous, if it works, nice, if not, no drama cause I am just after my eating window.”
I’m aware that the blends work best if we take them solo fasting, these are herbs, not drugs so I never set high expectations for them.
Surprisingly, 15mins later Im organising myself, doing three things in a row, sorting my bedroom out (had some stuff to tidy up) going back to computer and continuing to work. I honestly forgot how burnout I felt and Im just going strong for an hour now, work is done now so Im gonna wind down and get ready for tomorrow.
The blends just keep surprising me! They are packed with so many good, healthy ingredients that every time I indulge in them, my brain is like exploding with nourishment, my body feels complete, cravings are gone and my mind is sharp like a Japanese katana. can’t wait to use my 50% birthday code to get more blends which Im eyeing up!
if you’re reading this, don’t be dumb and get some samples, they last months anyway, go ALL IN, thank me later 😉
Ivonne Bohorquez (verified owner) –
This is probably my new favorite blend – second only to Trinity. I have suffered from anxiety and panic attacks in the past and this caused me to have a lot of health issues in recent years. Unmanaged anxiety can wreck havoc on the body and mind in every way. I am currently using this blend in combination with Trinity to help me get past mornings where my mental focus is non existent and after experiencing the results of this blend, I can say with confidence it is one of the best nootropics on the market.
It truly helped me to concentrate with laser focus during stock trading work sessions and this was evident within only the first few days of taking it. I also noticed a direct improvement in my overall mood as well with grogginess, short temper, and negative emotions all almost entirely eliminated. I’ve also begun to have less headaches which I used to get from time to time due to ongoing struggles managing stress and anxiety.
Overall, I highly recommend this blend for anyone looking to have more clarity in their daily lives without any side effects. There are many many nootropics out there on the market but none really come close to this formula. Pair this blend with Trinity & Rewire and you will have an unparalleled “blend stack” that helps you with focus, anxiety issues, depression, panic attacks and PTSD – to name a few benefits.
Natural is the way to go, that’s the Interstellar way!!!
Lori (verified owner) –
I can’t express enough how Interstellar Blends’ combo of Rewire, Trinity, and Autonomous has completely transformed my life. These are not just products; They are a catalyst for clarity and change.
We all have those moments when things suddenly become clear, right? The haze dissipates, and what was there all along becomes obvious. But with Trinity, Rewire, and Autonomous, those moments aren’t just occasional flashes of insight; they’re a way of life.
The solution to problems that used to keep me awake at night now presents itself effortlessly. Those things I’d heard a million times, half-believed, or dismissed as impossible? Trinity, Rewire and Autonomous has a way of making them as real as my own existence.
The issues I’d been wrestling with, struggling to find answers to, they dissolved like morning mist. My heart caught fire with inspiration, and I immediately knew what I had to do. I can’t help but wonder how I ever missed what is now so plainly apparent.
The cobination of these 3 blends promises these moments, and boy, does it deliver. I took the plunge, following the guidance of Interstellar Blends’ Gavin, and it was almost immediate. I’ve honestly never felt better in my entire life.
The benefits of these blends are immeasurable. My mind feels sharper, my heart feels lighter, and I have an unshakable sense of purpose. It’s like my entire being has been rewired for success and happiness.
If you’re on the fence, let me be the one to tell you – take that leap of faith with this powerful combo. They are not just products;They are a life-altering experience. Trust me; you won’t regret it.
Thank you, Interstellar Blends andGavin, for giving me the gift of clarity, purpose, and an immeasurably improved life. 🚀💫
scooter –
Discovering these blends especially Autonomous has been a game-changer in my life. From the moment I integrated it into my daily routine, I experienced a significant improvement in my focus and productivity. SERIOUSLY. Its beneficial components seem perfectly tailored to my needs, allowing me to take tasks with clarity and extreme efficiency. I feel like I have unlocked a higher level of cognitive function, enabling me to accomplish more in less time while maintaining a sense of mental clarity and alertness forreal.
The impact of Autonomous on my life has been profound. Tasks that once seemed daunting now feel manageable, and I find myself approaching challenges with a newfound sense of confidence. Pairing it with others blends like Trinity or Nebula, not only my productivity skyrocketed, but I also feel more engaged and present in every aspect of my life. Whether it’s work, hobbies, or personal relationships, they’ve enabled me to be more attentive and proactive, leading to a more fulfilling and satisfying life.
With a range of supplements that Gavin designed to various aspects of cognitive function and wellness, there are endless possibilities for someone to excel in any fields. From memory and mood to energy to overall health benefits, Gavin truly changed the game in optimizing mental and health performance. Exploring the other supplements within the brand promises even more opportunities for improvement and a better quality of life for anyone seeking to unlock their full potential.
believe me and just try them out for yourself and just notice how much u elevate