MDM2
January 10, 2020
Andrographis Paniculata
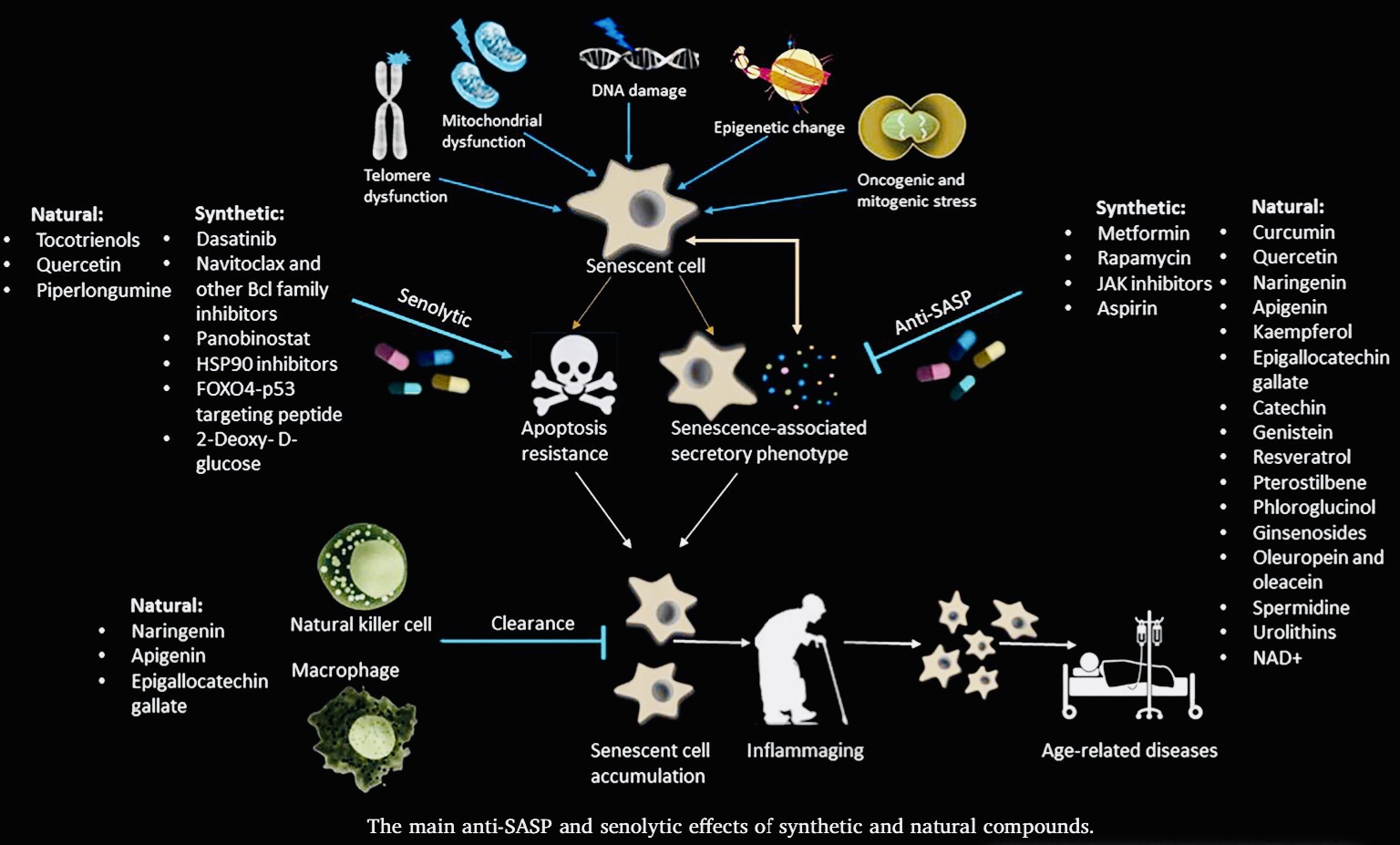
January 14, 2020Senescent cells are like retired workers in our bodies. They’ve stopped dividing due to stress or damage, which prevents uncontrolled growth and potential cancer. However, these cells don’t disappear. They unleash a mix of signaling molecules called the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP). While SASP can be helpful in wound healing,chronic SASP from accumulated senescent cells with age is linked to inflammation and age-related diseases.
This is where senolytics come in. These are drugs being developed to selectively target and eliminate senescent cells. By clearing these “troublemakers,” senolytics have the potential to improve healthspan and potentially lifespan by reducing chronic inflammation and delaying the onset of age-related diseases. Research in this area is ongoing, but the potential to combat aging and promote healthy longevity through senescent cell management is a promising avenue in human health.
Human adipocytes show a lower sensitivity to CD95-induced apoptosisthan preadipocytes.
The anti-apoptotic molecule Bcl-2 is up-regulated during adipogenic differentiation.
Overexpression of Bcl-2 rescues human preadipocytes from CD95-induced apoptosis.
Knockdown of Bcl-2 sensitizes human adipocytes to CD95-induced apoptosis.
Bcl-2 may constitute a new therapeutic target in the treatment of obesity.
-
Targeting apoptotic pathways in adipocytes has been suggested as a pharmacological approach to treat obesity. However, adipocyte apoptosis was identified as a cause for macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue. Previous studies suggest that mature adipocytes are less sensitive to apoptotic stimuli as compared to preadipocytes. Here, we aimed to identify proteins mediating apoptosis resistance in adipocytes.
Our data revealed that the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) is up-regulated during adipogenic differentiation. Bcl-2 overexpression in preadipocytes lowers their apoptosis sensitivity to the level of mature adipocytes. Vice versa Bcl-2 knockdown in adipocytes sensitizes these cells to CD95-induced apoptosis. Taken together, our findings suggest a shift in the balance of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic molecules during adipogenesis resulting in a higher apoptosis resistance. This study sheds new light on the apoptotic process in human fat cells and may constitute a new possible target for the specific regulation of adipose tissue mass.
- New dimension in therapeutic targeting of BCL-2 family proteins
- BCL2 FAMILY FUNCTIONS:
- Inhibits Apoptosis:BCL-2, BCL-XL, BCL-W, BCL-B BFL-1 (BH4 BH3 BH1 BH2)
- Promotes Apoptosis:BAX, BAK, BOK (BH3 BH1 BH2) / BID, BAD, BIM, PUMA, NOXA (BH3)
- Bad and Noxa are poor inducers of apoptosis individually because each binds only a subset of the prosurvival proteins, whereas Bim is a potent killer because it binds all of them.
- BID, BIM, and PUMA Are Essential for Activation of the BAX– and BAK-Dependent Cell Death Program
- Senescent cells normally accumulate at a rate of 0.5% or less per month as a function of total cell number in the tissues examined. Caloric restriction resulted in a 3.3 to 6.5% decrease.
- BH4 domain deletion or mutation eliminates the prosurvival activity of Bcl-2
- BH4 domain inhibits apoptosis
- Beyond a classical role in inhibiting apoptosis, BH4 domain has been characterized as a crucial regulator of other important cellular functions attributed to Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, including proliferation, autophagy, differentiation, DNA repair, cell migration, tumor progression and angiogenesis.
- p21 p27 activation is senolytic
- The role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in apoptosis.
- Treatment with a senolytic agent reduced IL17 expression and fibrosis
- BAD BH3 binds BCL-2, BCL-XL, and BCL-w a/ NOXA BH3 targets MCL-1 and BFL-1/A
- BH3 mimetic acts as a senolytic to remove senscent cells
- BNIP3 is a mitochondrial BH3-only protein that contributes to cell death through activation of the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis
- Bcl-rambo, a Novel Bcl-2 Homologue That Induces Apoptosis via Its Unique C-terminal Extension
The Bcl-2 family of proteins plays a central regulatory role in apoptosis. We have identified a novel, widely expressed Bcl-2 member which we have named Bcl-rambo. Bcl-rambo shows overall structural homology to the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 members containing conserved Bcl-2 homology (BH) motifs 1, 2, 3, and 4. Unlike Bcl-2, however, the C-terminal membrane anchor region is preceded by a unique 250 amino acid insertion containing two tandem repeats. No interaction of Bcl-rambo with either anti-apoptotic (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Bcl-w, A1, MCL-1, E1B-19K, and BHRF1) or pro-apoptotic (Bax, Bak, Bik, Bid, Bim, and Bad) members of the Bcl-2 family was observed. In mammalian cells, Bcl-rambo was localized to mitochondria, and its overexpression induces apoptosis that is specifically blocked by the caspase inhibitors, IAPs, whereas inhibitors controlling upstream events of either the ‘death receptor’ (FLIP, FADD-DN) or the ‘mitochondrial’ pro-apoptotic pathway (Bcl-xL) had no effect. Surprisingly, the Bcl-rambo cell death activity was induced by its membrane-anchored C-terminal domain and not by the Bcl-2 homology region. Thus, Bcl-rambo constitutes a novel type of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 member that triggers cell death independently of its BH motifs.
Senescent Cell Anti-Apoptotic Pathways (SCAPs)
To remove senescent cells pharmacologically from non-genetically modified individuals, “senolytic” agents, including small molecules, peptides, and antibodies, are being developed21. Since the article describing the first senolytic agents was published in March, 201522, progress in identifying additional senolytic agents and their effects has been remarkably rapid. In that first article, a hypothesis-driven senolytic agent discovery paradigm was implemented. Senescent cells are resistant to apoptosis, despite the SASP factors they release, which should trigger apoptosis. Indeed, pro-apoptotic pathways are up-regulated in senescent cells22, yet these cells resist apoptosis23. The hypothesis was therefore tested that senescent cells depend on pro-survival pathways to defend against their own pro-apoptotic SASP. Using bioinformatics approaches based on the RNA and protein expression profiles of senescent cells, five Senescent-Cell Anti-Apoptotic Pathways (SCAPs) were identified (Table 1). That SCAPs are indeed required for senescent cell viability was verified by RNA interference studies, in which key proteins in these pathways were reduced. Through this approach, survival proteins were identified as the “Achilles’ heels” of senescent cells. Knocking-down expression of these proteins causes death of senescent but not non-senescent cells. Since the discovery of the first five SCAPs, another was identified (Table 1)24. This approach and the SCAPs discovered were subsequently used by others and us to identify putative senolytic targets22, 24, 25, 26, 27.
The SCAPs required for senescent cell resistance to apoptosis vary among cell types.The Achilles’ heels, for example of senescent human primary adipose progenitors differ from those in a senescent human endothelial cell strain, implying that agents targeting a single SCAP may not eliminate all types of senescent cells. So far, the senolytics that have been tested across a wide range of senescent cell types have all exhibited a degree of cell type specificity. For example, navitoclax is senolytic in a cell culture-acclimated human umbilical vein endothelial cell strain, but is not very effective against senescent primary human fat cell progenitors27. Even within a particular cell type, human lung fibroblasts, nativoclax is senolytic in the culture-acclimated IMR-90 lung fibroblast-like cell strain, while it is less so in primary human lung fibroblasts isolated from patients19, 27. Without extensive testing across a range of truly primary cells, as opposed to cell lines or culture-acclimated cell strains, it is difficult to contend that any particular candidate senolytic drug is universally effective for all types of senescent cells. Furthermore, senolytics can act synergistically in some cell types. For example, while neither dasatinib nor quercetin was significantly senolytic in mouse embryonic fibroblasts in vitro, the combination of dasatinib and quercetin was senolytic22. Thus, different senolytics may prove to be optimal for different indications and combinations of senolytics can be used to broaden the range of senescent cell types that are targeted.
News Articles:
- Both Senolytic Molecules Are Inhibitors Of Particular Members Of The Bcl-2 Family Of Apoptosis Regulatory Proteins And Have Distinct Pharmacokinetic Profiles.
- ‘One Of The Most Important Aging Discoveries Ever’
- 100 Is The New 60: The Transformation Of Healthcare
- 12 Innovations That Could Make Reverse Aging A Reality
- 1St Age Reversal Results—Is It Hgh Or Something Else?
- 20 Technology Metatrends That Will Define The Next Decade
- 3 Most Important Breakthrough In Biology Of 2019
- 9 Ways To Stay Healthy As You Age
- A Cell-Killing Strategy To Slow Aging Passed Its First Test This Year
- A ‘One-Two Punch’ To Wipe Out Cancerous Ovarian Cells
- A True Fountain-Of-Youth Drug Combo?
- Advances In Antiaging Research: Chemistry Could Hold The Key To Better Health
- Advances In The Science Of Aging
- Ageing In Human Cells Successfully Reversed In The Lab
- Age-Related Enfeeblement Of The Immune System Speeds Build-Up Of Senescent Cells
- Anti-Ageing Drug On The Horizon: Scientists Discover Medicine Cocktail That Clears ‘Zombie Cells‘
- ‘Anti-Ageing‘ Drugs Could Be On The Market In Five Years If Clinical Trials Prove Successful
- Anti-Aging Drugs And Toxic Cells
- Anti-Aging Drugs Are Showing Promise In Human Trials
- Anti-Aging Drugs Could Be On The Market In The Next 5 Years
- Anti-Aging Field ‘Explodes’ In Pursuit Of Healthy Old Age
- Anti-Aging Mechanism May Hold Key To ‘Perfect’ Osteoporosis Treatment
- Anti-Aging Senolytic Cocktail Passes First Human Trial
- Anti-Aging Senolytics Drugs Found To Improve Mice Health And Lifespan
- Antibiotics Eliminate Senescent Cells Associated With Ageing
- Antoxerene Closes $10 Million Deal With Juvenescence To Develop Small Molecule Drugs For Diseases Of Aging
- Are Tauopathies Caused By Neuronal And Glial Senescence?
- Ascentage Pharma And Unity Biotechnology Announce Collaboration For The Development Of Senolytic Healthspan Therapies
- Ascentage Pharma, Unity Biotech Collab To ‘Cure Old Age’
- Can A Single Pill Keep You Healthy To 100?
- Can We Live Forever? | Feature
- Cell Aging In Lung Epithelial Cells
- Cellular Sickness Linked To Type 1 Diabetes Onset
- Clearing Old Cells From Mouse Brains Lowered Signs Of Anxiety
- Clearing Out Brain’S “Zombie Cells” Offers New Approach Against Dementia
- Concerns Rise Over Negative Impact Of Hev Light On Skin As Companies Delve Into Anti-Aging Therapeutics
- Could An Existing Heart Drug Help Treat Cancer?
- Could One Pill Cure A Host Of Diseases? Killing ‘Zombie‘ Cells To Improve Health In Old Age
- Cover Story: Investing In The Ageing Population Theme
- Diet, Physical Activity Among Keys To Healthy Brain
- Discovery Offers Hope For Improving Physical Performance As We Age
- Eat Glutathione
- Editor’S Letter: The Precision Medicine Issue
- Elixir Of Life: Scientists Find Way To Reverse Cell Damage Caused By Ageing
- Emerging Evidence Shows Wider Benefits Of Supplements
- Epigenetics And Aging
- Experts Propose New Healthcare Framework To Help Ageing Populations Stay Healthier Longer
- Extending Healthspan May Be Coming Soon
- Fascinating Picture Shows Anti-Ageing Drugs Really Do Work
- Finally, The Drug That Keeps You Young
- First-In-Human Trial Of Senolytic Drugs Encouraging
- Fisetin May Be An Effective Senolytic
- Fisetin Within Strawberries Clears Senescent Cells
- Fisetin—A New Senolytic
- Fountains Of Youth: Biotech Startups Emerge From Stealth Mode To ‘Take On Aging’
- Foxbio: $10M Jv Launched To Target Age-Related Disease
- Global Longevity And Anti-Senescence Therapy Market
- Global Longevity And Anti-Senescence Therapy Market 2019-2023 – Focus On Senolytic Drug Therapy, Gene Therapy, Immunotherapy And Others
- Herb Leaf Eaten By Japanese Samurai Found To Slow Down Ageing By Clearing Out Disease-Causing Cells
- Here Are 5 Things You Should Start Doing Today To Live Longer
- How Genome Sequencing And Senolytics Can Help Us Live Healthier, Longer
- How Silicon Valley Billionaires Claim They’Ve Discovered The Secret To Everlasting Life
- How This Man Genuinely Expects To Live To 200 (And Has Invested $100M To Discover The Secret)
- How To Live Longer: The Science Of Ageing, And How To Slow It Down
- Https://Endpts.Com/Harvard-Prof-David-Sinclair-Backs-Anti-Aging-Upstart-Life-Bio-Which-Just-Raised-50M-For-Research/
- Human Drug Trial In San Antonio Offers Hope To Those With Age-Related Diseases
- Humans ‘Biohacking’ Their Own Bodies With Blood Transfusions To Achieve ‘Diy Immortality’
- In Search For ‘Perfect’ Osteoporosis Treatment, Consider Key Anti-Aging Mechanism
- Ipf Treatment Options May Be Boosted By Senolytic Drugs
- Is Cellular Senescence The Key To Naked Mole Rats’ Long, Cancer-Free Life?
- Is Fasting Senolytic?
- Is Metformin The Key To Living Longer? | The Times Magazine
- Is The Cancer Drug Dasatinib The Anti-Aging Breakthrough We Have All Been Waiting For?
- Is There Any Truth To Anti-Aging Schemes?
- Journal Of The American Medical Association Shines Spotlight On Geroscience
- Juvenescence Closes First Tranche Of Series B Enabling Further Growth And Development
- Juvenescence Raises Another $100M To Invest In Longevity
- Kalter: Fountain Of Youth?
- Kidney Disease: Senescent Cell Burden Is Reduced In Humans By Senolytic Drugs
- Kill Senescent Cells Before They Kill You
- Killing ‘Zombie Cells‘ Cures Anxiety In Obese Mice
- Letter To An Incipient Cancer Survivor
- Life Biosciences Joins The Longevity Race
- Life Biosciences Raises $50M As Longevity Race Heats Up
- Life Biosciences: A New Paradigm For Approaching Longevity Research
- Lifespan Extended, Health Improved By Senolytic Drugs
- Link Between Aging, Devastating Lung Disease Discovered
- Link Between Cells Associated With Aging, Bone Loss
- Longevity And Anti-Senescence Therapy Market 2019 Global Analysis, Opportunities And Forecast To 2024
- Longevity And Anti-Senescence Therapy Market, 2023 – Emphasis On Stem Cell Research And Increasing Demand For Cell-Based Assays
- Longevity Company Unity Biotechnology Stocks Soared After Ceo Talks To Cnbc
- ‘Longevity‘ Could Reach Billions In 2019 – And Is No Longer Just The Preserve Of Billionaires
- Mayo Clinic Discovery Could Extend Quality Of Life
- Mayo Clinic May Be Onto The Fountain Of Youth
- Mayo Clinic Showcases Anti-Aging Senolytics
- Mayo Clinic Takes Next Step In Anti-Aging Research
- Molecule Kills Elderly Cells, Reduces Signs Of Aging In Mice
- Money In Aging Research, Part I
- Money In Aging Research, Part Ii
- Mouse Model Shows Success Of Senolytic Drugs In Reversing Senescent Cell Damage
- Natural Compounds That Remove Aging Cells
- Nature Medicine Study Describes A Novel Senolytic Molecule That Slows The Progression Of Osteoarthritis
- Never Grow Up: The Anti-Aging Market Is A $200B Industry
- New Cause Of Cell Aging Uncovered
- New Class Of ‘Transformative’ Anti-Aging Drugs Set For Human Trials
- Novato Startup Unity Biotechnology Tackles Arthritis, Glaucoma
- Obese Mice Lose Anxiety When ‘Zombie Cells‘ Exit Their Brain
- Osteoporosis: Potential New Drug Target Uncovered
- Parp Inhibitors Used In ‘One-Two Punch’ Strategy To Kill Oc Cells In Mouse Models, Study Shows
- Peninsula Anti-Aging Drug Company Files For $85M Ipo
- Plaques Age Glial Precursors, Stoking Inflammation
- Purging Failed Brain Insulation Cells Lessened Damage, Improved Cognition In Alzheimer’S Mouse Model
- Reducing ‘Zombie‘ Cells May Slow The Aging Process
- Rejuvenating Senolytics
- Rejuvenation At The Cell Level
- Removal Of ‘Zombie Cells‘ Alleviates Causes Of Diabetes In Obese Mice
- Removing “Zombie Fat Cells” A Way Forward For Treating Diabetes
- Research Shows It’S Possible To Reverse Damage Caused By Aging Cells
- Researchers Discover New Cause Of Cell Aging
- Researchers Discover Way To Slow Aging Process
- Researchers Identify Molecule With Anti-Aging Effects On Vascular System, Study Finds
- Researchers May Have Discovered”Fountain Of Youth” Drugs
- Restoring Brain Function In Mice With Symptoms Of Alzheimer’S Disease
- Rewinding The Clock
- Rumors Of Age Reversal: The Plasma Fraction Cure
- Scaling The Alzheimer’S Cure
- Scientists Discover Cell Aging Linked To Nucleotide Synthesis
- Scientists Harness Ai To Reverse Ageing In Billion-Dollar Industry
- Scientists Hunt Zombie Cells: ‘The Grand Challenge’
- Scientists Mark Success In First Human Test Of Novel Anti-Aging Therapy
- Scientists Pinpoint A Natural Compound That Helps Us Stave Off Aging
- Scientists Slow Ageing With Green Tea, Onions, Red Wine
- Scientists Take A Step Towards Beating The Pain Of Old Age
- Screening Method Identifies Compounds That Extend Lifespan In Mice
- Senescent Cell Burden Is Reduced In Humans By Senolytic Drugs
- Senescent Cell Research Moves Into Human Trials
- Senescent Cells May Play A Role In Thrombosis
- Senescent Cells Play An Essential Role In Wound Healing
- Senolytic Drugs Increase Lifespan, Improve Physical Function In Aging Mice | Medicine
- Senolytic Drugs May Offer New Ipf Therapy Options
- Senolytic Drugs May Reverse Damage Caused By Senescent Cells
- Senolytic Drugs Reverse Damage Caused By Senescent Cells In Mice
- Senolytic Therapeutics Kicks Off Q1 2019 With High-Profile Speaking Events
- Senolytic Therapeutics Y Quibim, Industria De La Longevidad Con Adn Valenciano
- Senolytic Therapies And The Quest To Cure Aging
- Senolytic Therapies For Healthy Longevity
- Senolytic Treatment Improves Physical Function In Ipf Patients, According To Small Pilot Study
- Senolytics Against Aging: Snapshot Of A Fast-Moving Field
- Senolytics Show Promise Against Alzheimer’S In Mice
- Senolytics: Living Healthier For Longer With A New Class Of Drugs
- Senolytics: Scientists Identify New Drug That Slows The Ageing Process And Could Dramatically Increase Our Life Expectancy
- Six Columbia Cancer Researchers Receive Seed Funding From Velocity
- ‘Sleeping Cells‘ Drive A Host Of Age-Related Diseases — And New Drugs Are Seeking To Rid Them From Our Bodies
- Steadman Philippon Research Institute To Share Four Dod Research Grants Aimed At Reducing Risk Of Osteoarthritis & Reducing Long-Term Disability Among Military Service Members And Veterans
- Study: Eating Red Meat May Not Be That Bad For You
- Sweep Away Senile Cells
- Targeting Senescent Cells Increases Bone Mass
- Tau Tangles Cleared By Senolytic Drugs In Alzheimer’S Mice
- The Biological Fountain Of Youth? ‘Anti-Aging’ Therapy Close To Clinical Trials
- The Ethics Of Anti-Ageing: Where Do We Draw The Line?
- The First Drugs Designed To Fight Aging Are Ready For Human Testing, Scientists Say
- The Future Of Aging: Bringing Hollywood To The Hospital
- The Longevity Industry Comes Of Age
- The Most Effective Personal Anti-Aging Program
- The Science Of Senolytics: How A New Pill Could Spell The End Of Ageing
- The Top 10 Companies Working To Increase Longevity
- The Transhumanists Who Want To Live Forever
- The War On Aging: An Update From The Front Lines – H+ Media
- The Wonder Drug That Could Reverse The Ageing Process
- This Drug Combo Extends Lifespan And Healthspan In Mice By Killing ‘Zombie’ Cells
- This Is An Important Step In Assessing The Role That A Senolytic Agent May Play In The Treatment Of Osteoarthritis
- This Russian Millionaire Wants To Help People Live To 200 Years Old
- To Stay Young, Kill Zombie Cells
- Top Companies Working To Extend Longevity
- Transfusions Of Young Blood Could Hold Key To Longer Life, Scientists Say
- Two Clinically-Approved Antibiotics Eliminate Senescent Cells Associated With Ageing
- Unity Takes Up Option On Ascentage Aging Drug
- Want To Live For Ever? Flush Out Your Zombie Cells
- What Is Fisetin? Product Found In Fruits And Vegetables May Slow Aging, Researchers Show
- What This Biotech’S $85 Million Ipo Tells Us About Raging Against Aging
- When Aging Is Fun
- Why A Drug For Aging Would Challenge Washington
- Why Jeff Bezos Is Backing This Silicon Valley Scientist Who Is Working On A Cure For Aging
- Why You Shouldn’T Fear The Gray Tsunami
- Will Age Soon Really Just Be A Number?
- Will We Soon Be Taking A Pill To Slow Aging?
- Wiping Out The Brain’S Retired Cells Prevents A Hallmark Of Alzheimer’S
- Wiping Out Zombie Cells In Fat May Delay Or Alleviate Diabetes
- Zombie Cell Research And Anxiety
- ‘Zombie Cells‘ Buildup In Your Body May Play Role In Aging
SCIENTIFIC STUDIES:
- The Achilles’ heel of senescent cells: from transcriptome to senolytic drugs
- The Clinical Potential of senolytic Drugs
- Chronic senolytic treatment alleviates established vasomotor dysfunction in aged or atherosclerotic mice
- Identification of a novel senolytic agent, navitoclax, targeting the Bcl‐2 family of anti‐apoptotic factors
- Clinical strategies and animal models for developing senolytic agents
- senolytic drugs target alveolar epithelial cell function and attenuate experimental lung fibrosis ex vivo
- Discovery of piperlongumine as a potential novel lead for the development of senolytic agents
- Pleiotropic Effects of Tocotrienols and Quercetin on Cellular senescence: Introducing the Perspective of senolytic Effects of Phytochemicals
- A Novel Indication for Panobinostat as a senolytic Drug in NSCLC and HNSCC
- Oxidation resistance 1 is a novel senolytic target
- Effects of senolytic drugs on human mesenchymal stromal cells
- senolytic activity of piperlongumine analogues: Synthesis and biological evaluation
- Hsp90 inhibitors as senolytic drugs to extend healthy aging
- The curcumin analog EF24 is a novel senolytic agent
- senolytic drugs in respiratory medicine: is it an appropriate therapeutic approach?
- senolytic therapy alleviates Aβ-associated oligodendrocyte progenitor cell senescence and cognitive deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease model
- Azithromycin and Roxithromycin define a new family of “senolytic” drugs that target senescent human fibroblasts
- Increased renal cellular senescence in murine high-fat diet: effect of the senolytic drug quercetin
- senolytic Cocktail Dasatinib+Quercetin (D+Q) Does Not Enhance the Efficacy of senescence-Inducing Chemotherapy in Liver Cancer
- Emerging senolytic agents derived from natural products
- senolytic treatments applied to osteoarthritis: a step towards the end of orthopedic surgery?
- Fibrates as drugs with senolytic and autophagic activity for osteoarthritis therapy
- Curcumin and o-Vanillin Exhibit Evidence of senolytic Activity in Human IVD Cells In Vitro
- senolytic helpers
- senolytic therapies for healthy longevity
- Removing Aging Cells With a New Class of senolytic Drug
- Quercetin in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Another Brick in the senolytic Wall
- SAT0053 Identification of novel drugs with senolytic activity as osteoarthritis therapeutics
- Abstract 11299: A Novel senolytic Drug for Aging and Age-Related Cardiometabolic Disorders
- Novel Classification Perspective of Geroprotective and senolytic Drugs as an Antiaging Strategy
- LSC – 2017 – senolytic drugs target alveolar epithelial cell function and attenuate experimental lung fibrosis ex vivo
- senolytic treatment targets aberrant p21-expression to restore liver regeneration in adult mice
- Augmented Inflammatory Responses in Aging are Driven by Circulating mtDNA and Ameliorated by senolytic Treatment
- senescence Signature in Skin Biopsies From Systemic Sclerosis Patients Treated With senolytic Therapy: Potential Predictor of Clinical Response?
- Fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, is a novel molecule with senolytic and autophagy activity for cartilage degeneration and osteoarthritis
- senolytic activity of small molecular polyphenols from olive restores chondrocyte redifferentiation and cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis
- Treatment of parkinson’s disease and other conditions caused or mediated by senescent astrocytes using small molecule senolytic agents
- Application of ex-vivo spheroid model system for the analysis of senescence and senolytic phenotypes in uterine leiomyoma
- AMPK-mediated senolytic and senostatic activity of quercetin surface functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles during oxidant-induced senescence in human fibroblasts
- Mitochondrial DNA-Mediated Inflammatory Injury in Old Donors Is Improved by senolytic Treatment
- The biology of senescence.
- Leaf senescence
- Cellular senescence in Aging Primates
- senescence in premalignant tumours
- senescence mechanisms
- Cancer, aging and cellular senescence.
- The essence of senescence
- Four faces of cellular senescence
- Microarray analysis of replicative senescence
- Aging, Cellular senescence, and Cancer
- Molecular aspects of leaf senescence
- Cellular senescence in Cancer and Aging
- Making Sense of senescence (Molecular Genetic Regulation and Manipulation of Leaf senescence).
- Pleiotropy, Natural Selection, and the Evolution of senescence
- Cellular senescence as a tumor-suppressor mechanism
- Ageing. The biology of senescence.
- CHLOROPHYLL DEGRADATION DURING senescence*
- The moulding of senescence by natural selection
- The molecular biology of leaf senescence
- Gene expression during leaf senescence
- A new murine model of accelerated senescence
- The biology of replicative senescence
- The senescence of leaves.
- A DNA damage checkpoint response in telomere-initiated senescence
- Cellular senescence: from physiology to pathology
- Putting the stress on senescence
- Rapamycin decelerates cellular senescence
- Inhibition of Leaf senescence by Autoregulated Production of Cytokinin
- senescence and Postharvest Physiology
- Free radicals and senescence
- Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells
- Bmi1, stem cells, and senescence regulation
- The signals and pathways activating cellular senescence
- senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM): A novel murine model of senescence
- Testosterone Secretion and Metabolism in Male senescence
- senescence in Plant Development
- Catalase, Peroxidase, and Polyphenoloxidase Activities during Rice Leaf senescence
- Replicative senescence: An Old Lives’ Tale?
- Transcriptome of Arabidopsis leaf senescence
- Nitrogen metabolism and remobilization during senescence
- Tumor Cell senescence in Cancer Treatment
- senescence Induced by Altered Telomere State, Not Telomere Loss
- senescence of Activated Stellate Cells Limits Liver Fibrosis
- Telomeres, telomerase and senescence
- LABORATORY EVOLUTION OF POSTPONED senescence IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER
- Defining senescence and death
- Chemokine Signaling via the CXCR2 Receptor Reinforces senescence
- FUNGAL senescence
- Telomeres, stem cells, senescence, and cancer
- Replicative senescence: the human fibroblast comes of age
- Evolution of senescence: late survival sacrificed for reproduction
- Cellular senescence
- SELECTION FOR DELAYED senescence IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER
- senescence in tumours: evidence from mice and humans
- Fat tissue, aging, and cellular senescence
- Inflammatory networks during cellular senescence: causes and consequences
- senescence
- Role of Ceramide in Cellular senescence
- senescence of human fibroblasts induced by oncogenic Raf
- Ethylene and flower senescence
- Cell senescence and cancer
- Therapy-Induced senescence in Cancer
- Genes involved in senescence and immortalization
- BRAFE600-associated senescence-like cell cycle arrest of human naevi
- Vascular Cell senescence
- Reversible inhibition of tomato fruit senescence by antisense RNA
- A senescent cell bystander effect: senescence‐induced senescence
- Molecular regulation of leaf senescence
- senescence in a Bacterium with Asymmetric Division
- senescence-messaging secretome: SMS-ing cellular stress
- Leaf senescence
- senescence, Apoptosis or Autophagy?
- senescence and immortalization: role of telomeres and telomerase
- senescence‐Accelerated Mouse (SAM): A Novel Murine Model of Accelerated senescence
- Regulation of cellular senescence by p53
- If not apoptosis, then what? Treatment-induced senescence and mitotic catastrophe in tumor cells
- Formation of MacroH2A-Containing senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci and senescence Driven by ASF1a and HIRA
- Oncogene-induced senescence as an initial barrier in lymphoma development
- Persistent DNA damage signalling triggers senescence-associated inflammatory cytokine secretion
- Tumor suppressors and oncogenes in cellular senescence
- senescence in human intervertebral discs
- Oncogene-Induced senescence Relayed by an Interleukin-Dependent Inflammatory Network
- Cellular senescence and its effector programs
- 15 – Whole Plant senescence
- Cellular senescence and organismal aging
- senescence-Associated Gene Expression during Ozone-Induced Leaf senescence in Arabidopsis
- Human senescence
- senescence impairs successful reprogramming to pluripotent stem cells
- Oncogenic ras Provokes Premature Cell senescence Associated with Accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a
- Programmed Cell senescence during Mammalian Embryonic Development
- Cellular senescence and the senescent secretory phenotype: therapeutic opportunities
- The case for negative senescence
- Methods to Detect Biomarkers of Cellular senescence
- senescence and tumour clearance is triggered by p53 restoration in murine liver carcinomas
- senescence‐associated β‐galactosidase is lysosomal β‐galactosidase
- Akt Determines Replicative senescence and Oxidative or Oncogenic Premature senescence and Sensitizes Cells to Oxidative Apoptosis
- Deferral of Leaf senescence with Calcium
- Experimental Modification of Plant senescence.
- The Activated Oxygen Role of Peroxisomes in senescence
- Aging, articular cartilage chondrocyte senescence and osteoarthritis
- PML regulates p53 acetylation and premature senescence induced by oncogenic Ras
- Pro-senescence therapy for cancer treatment
- senescence comes of age
- The senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype: The Dark Side of Tumor Suppression
- Oxidative DNA damage and senescence of human diploid fibroblast cells
- senescence surveillance of pre-malignant hepatocytes limits liver cancer development
- Extreme heat effects on wheat senescence in India
- Cellular senescence: putting the paradoxes in perspective
- Cellular senescence and cancer treatment
- Calcium in plant senescence and fruit ripening
- An alternative pathway for yeast telomere maintenance rescues est1− senescence
- THE TWO-STAGE MECHANISM CONTROLLING CELLULAR senescence AND IMMORTALIZATION
- Ethylene, Plant senescence and Abscission
- The molecular genetic analysis of leaf senescence
- Hallmarks of senescence in carcinogenesis and cancer therapy
- Crucial role of p53-dependent cellular senescence in suppression of Pten-deficient tumorigenesis
- Homocysteine accelerates endothelial cell senescence
- The molecular analysis of leaf senescence – a genomics approach
- A Cellular Timetable of Autumn senescence
- MicroRNA-34a regulation of endothelial senescence
- Involvement of Hydrogen Peroxide in the Regulation of senescence in Pear
- Oncogene-induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper-replication
- Obesity-induced gut microbial metabolite promotes liver cancer through senescence secretome
- Deconstructing PML-induced premature senescence
- Mortality Patterns Suggest Lack of senescence in Hydra
- Plant senescence processes and free radicals
- Role of oxidative carbonylation in protein quality control and senescence
- Measuring Wheat senescence with a Digital Camera
- Brain acetylcholine synthesis declines with senescence
- Human cell senescence as a DNA damage response
- Molecular genetics of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis
- Development and senescence of the Postnatal Bovine Ovary
- Leaf senescence in Brassica napus: cloning of senescence related genes by subtractive hybridisation
- Alveolar Cell senescence in Patients with Pulmonary Emphysema
- Functional senescence in Drosophila melanogaster
- Control of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype by NF-κB promotes senescence and enhances chemosensitivity
- The evolutionary ecology of senescence
- Replicative senescence: Implications for in Vivo Aging and Tumor Suppression
- SASP reflects senescence
- Ethylene regulates the timing of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis
- Cellular senescence, cancer and aging: the telomere connection
- Control of Jasmonate Biosynthesis and senescence by miR319 Targets
- Replicative senescence of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Continuous and Organized Process
- T-helper-1-cell cytokines drive cancer into senescence
- Cellular senescence and tumor suppressor gene p16
- Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints
- Telomeres and senescence: Ending the Debate
- Rb-Mediated Heterochromatin Formation and Silencing of E2F Target Genes during Cellular senescence
- The aging brain: morphomolecular senescence of cortical circuits
- Reversal of human cellular senescence: roles of the p53 and p16 pathways
- Molecular analysis of natural leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana
- A transcriptional timetable of autumn senescence
- Cellular senescence and cancer
- Human SIR2 deacetylates p53 and antagonizes PML/p53‐induced cellular senescence
- Telomere dysfunction and tumour suppression: the senescence connection
- Many roads lead to oncogene-induced senescence
- A negative feedback signaling network underlies oncogene-induced senescence
- The anemia of senescence
- Plant senescence and crop productivity
- Replicative senescence: a critical review
- senescence in Health and Disease
- A NAC Gene Regulating senescence Improves Grain Protein, Zinc, and Iron Content in Wheat
- Last exit: senescence, abscission, and meristem arrest in Arabidopsis.
- Memory loss in senescence.
- Cigarette Smoke Induces Cellular senescence
- Rethinking Chronic Allograft Nephropathy
The Concept of Accelerated senescence - The sound of senescence
- Oncogenic Braf Induces Melanocyte senescence and Melanoma in Mice
- What has senescence got to do with cancer?
- Targets of AtWRKY6 regulation during plant senescence and pathogen defense
- Telomerase, senescence and ageing
- Memory deficits associated with senescence: A neurophysiological and behavioral study in the rat.
- PML is induced by oncogenic ras and promotes premature senescence
- The senescence-Induced Staygreen Protein Regulates Chlorophyll Degradation
- Bypass of senescence After Disruption of p21CIP1/WAF1 Gene in Normal Diploid Human Fibroblasts
- Differential expression of senescence-associated mRNAs during leaf senescence induced by different senescence-inducing factors in Arabidopsis
- Reversible cellular senescence: implications for immortalization of normal human diploid fibroblasts.
- An attempt to prevent senescence: A mitochondrial approach
- Delayed leaf senescence induces extreme drought tolerance in a flowering plant
- senescence and Rejuvenation
- Forging a signature of in vivo senescence
- Evolutionary and Nonevolutionary Theories of senescence
- Cellular senescence revisited: a review
- Living on a break: cellular senescence as a DNA-damage response
- senescence in the whole plant.
- Mild Hyperoxia Shortens Telomeres and Inhibits Proliferation of Fibroblasts: A Model for senescence?
- Geriatric muscle stem cells switch reversible quiescence into senescence
- Physiology and molecular biology of petal senescence
- Endothelial Cell senescence in Human Atherosclerosis
- Telomere positional effects and the regulation of cellular senescence
- Role of Ethylene in senescence of Petals—Morphological and Taxonomical Relationships
- Paradoxical suppression of cellular senescence by p53
- Evidence Supporting a Role of Jasmonic Acid in Arabidopsis Leaf senescence
- Prohibitin: Potential role in senescence, development, and tumor suppression
- senescence and aging: the critical roles of p53
- senescence as a mode of tumor suppression.
- Large‐scale identification of leaf senescence‐associated genes
- NK and NK/T cells in human senescence
- Vascular endothelial senescence: from mechanisms to pathophysiology
- Regulation of p16CDKN2 expression and its implications for cell immortalization and senescence.
- When cells get stressed: an integrative view of cellular senescence
- A mutant with a defect in telomere elongation leads to senescence in yeast
- Selenium – an antioxidative protectant in soybean during senescence
- Oncogene-Induced senescence: Putting the Brakes on Tumor Development
- The power and the promise of oncogene-induced senescence markers
- The role of chondrocyte senescence in osteoarthritis
- OSTEOPOROSIS : DISEASE OR senescence ?
- The pathobiology of Parkinson’s disease: biochemical aspects of dopamine neuron senescence.
- A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence
- Growth, Maturation, and senescence in Fruits
- ORE9, an F-Box Protein That Regulates Leaf senescence in Arabidopsis
- Cell senescence and hypermitogenic arrest
- Cellular senescence mediates fibrotic pulmonary disease
- Accelerated immune senescence and HIV-1 infection
- senescence of leafy vegetables
- Mitotic and postmitotic senescence in plants.
- NaCl-induced senescence in Leaves of Rice (Oryza sativaL.) Cultivars Differing in Salinity Resistance
- Erosion of the telomeric single-strand overhang at replicative senescence
- Mechanisms of cellular senescence in human and mouse cells
- Loss of ‘Complexity’ and AgingPotential Applications of Fractals and Chaos Theory to senescence
- Id proteins in cell cycle control and cellular senescence
- A role for both RB and p53 in the regulation of human cellular senescence
- Physiological significance of anthocyanins during autumnal leaf senescence
- Lamin B1 loss is a senescence-associated biomarker
- Isolation and Identification of a senescence-promoting Substance from Wormwood (Artemisia absinthium L.)
- Oxidative stress and antioxidant activity as the basis of senescence in maize leaves
- Nutrients mobilized from leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana during leaf senescence
- Ethylene in Plant Growth, Development, and senescence
- Normal human mammary epithelial cells spontaneously escape senescence and acquire genomic changes
- Ras Proteins Induce senescence by Altering the Intracellular Levels of Reactive Oxygen Species
- Flower senescence in daylily (Hemerocallis)
- Role of Oxidative Stress in Telomere Length Regulation and Replicative senescence
- Leaf senescence: Correlated with Increased Levels of Membrane Permeability and Lipid Peroxidation, and Decreased Levels of Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase
- Deletion of Ku86 causes early onset of senescence in mice
- senescence, apoptosis and therapy — cutting the lifelines of cancer
- Cellular senescence: A Translational Perspective
- senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM): a biogerontological resource in aging research
- The timing of maize leaf senescence and characterisation of senescence‐related cDNAs
- Skp2 targeting suppresses tumorigenesis by Arf-p53-independent cellular senescence
- Human melanocyte senescence and melanoma susceptibility genes
- UV-C treatment delays postharvest senescence in broccoli florets
- Processes and control of plant senescence.
- The oncogene and Polycomb-group gene bmi-1 regulates cell proliferation and senescence through the ink4a locus
- Pollination-induced flower senescence: a review
- Structure elucidation of a senescence cross-link from human extracellular matrix. Implication of pentoses in the aging process.
- Oncogene-Induced Cell senescence — Halting on the Road to Cancer
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction Contributes to Oncogene-Induced senescence
- Opposing effects of Ets and Id proteins on p16INK4a expression during cellular senescence
- Cell cycle arrest is not senescence
- Proteolytic activity during senescence of plants
- senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotypes Reveal Cell-Nonautonomous Functions of Oncogenic RAS and the p53 Tumor Suppressor
- senescence IN NATURAL POPULATIONS OF MAMMALS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY
- Grading score system: A method for evaluation of the degree of senescence in senescence Accelerated Mouse (SAM)
- Oncogenic ras and p53 Cooperate To Induce Cellular senescence
- senescence, Abscission and Cellulase Activity in Phaseolus vulgaris
- Oncogenic BRAF Induces senescence and Apoptosis through Pathways Mediated by the Secreted Protein IGFBP7
- Early Immune senescence in HIV Disease
- The role of senescence and immortalization in carcinogenesis
- Leaf senescence: Signals, Execution, and Regulation
- Cellular senescence and chromatin structure
- Cellular senescence in vivo: a barrier to tumorigenesis
- Aging is associated with decreased maximal life span and accelerated senescence of bone marrow stromal cells,
- The shaping of senescence in the wild
- Molecular Dissection of Formation of senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci
- Short Telomeres Limit Tumor Progression In Vivo by Inducing senescence
- Zeb1 links epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cellular senescence
- Cellular senescence controls fibrosis in wound healing
- Jasmonates: Hormonal regulators or stress factors in leaf senescence?
- Effect of extrinsic mortality on the evolution of senescence in guppies
- Replicative senescence and Oxidant‐Induced Premature senescence: Beyond the Control of Cell Cycle Checkpoints
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction Accounts for the Stochastic Heterogeneity in Telomere-Dependent senescence
- Immunologic Deficiencies in senescence
- Telomeres and senescence: The history, the experiment, the future
- A senescence Program Controlled by p53 and p16INK4a Contributes to the Outcome of Cancer Therapy
- senescence As an Anticancer Mechanism
- Changes in antioxidative enzymes in cucumber cotyledons during natural senescence: comparison with those during dark‐induced senescence
- senescence-like growth arrest induced by hydrogen peroxide in human diploid fibroblast F65 cells
- MicroRNA 217 Modulates Endothelial Cell senescence via Silent Information Regulator 1
- The Role of Cellular senescence in Skin Aging
- Identification of three genetic loci controlling leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana
- Pathobiology of the senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM)
- Biochemistry of senescence
- Optimization of edible coating composition to retard strawberry fruit senescence
- Population cycles in microtines: The senescence hypothesis
- Replicative senescence of T cells: does the Hayflick Limit lead to immune exhaustion?
- In vivo alteration of telomere sequences and senescence caused by mutated Tetrahymena telomerase RNAs
- Mitochondria: are they the seat of senescence?
- senescence of red blood cells: progress and problems
- Shortened telomeres in the expanded CD28-CD8+ cell subset in HIV disease implicate replicative senescence in HIV pathogenesis.
- T cell senescence.
- Involvement of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 (INK4a) in replicative senescence of normal human fibroblasts
- Escape from senescence in human diploid fibroblasts induced directly by mutant p53.
- senescence, ageing and death of the whole plant
- Reactive Oxygen Species as Mediators of Cellular senescence
- TAp63 induces senescence and suppresses tumorigenesis in vivo
- p53, ROS and senescence in the control of aging
- Cellular senescence in aging and age-related disease: from mechanisms to therapy
- Cellular senescence: hot or what?
- Microglial senescence: does the brain’s immune system have an expiration date?
- A genetic analysis of senescence in Drosophila
- Non‐destructive optical detection of pigment changes during leaf senescence and fruit ripening
- Role of CMV in immune senescence
- JunD Protects Cells from p53-Dependent senescence and Apoptosis
- MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES ACCOMPANYING senescence OF CULTURED HUMAN DIPLOID CELLS
- Quantitative assessment of markers for cell senescence
- Caspase inhibition switches doxorubicin-induced apoptosis to senescence
- Replicative senescence of human fibroblast-like cells in culture
- Hepatocyte telomere shortening and senescence are general markers of human liver cirrhosis
- A senescence-associated gene of Arabidopsis thaliana is distinctively regulated during natural and artificially induced leaf senescence
- Impact of cellular senescence signature on ageing research
- DNA damage response and cellular senescence in tissues of aging mice
- Lack of Replicative senescence in Normal Rodent Glia
- Peroxisome senescence in Human Fibroblasts
- Effects of estrogen on growth plate senescence and epiphyseal fusion
- DNA damage, cellular senescence and organismal ageing: causal or correlative?
- Lack of Replicative senescence in Cultured Rat Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells
- Human Platelet senescence
- Feedback between p21 and reactive oxygen production is necessary for cell senescence
- Oncogene-Induced senescence Pathways Weave an Intricate Tapestry
- A Role for Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase during Leaf senescence
- senescence-induced RNases in tomato
- Identification of a transcription factor specifically expressed at the onset of leaf senescence
- PRAK Is Essential for ras-Induced senescence and Tumor Suppression
- Relation between leaf senescence and stomatal closure: senescence in light
- Protein oxidation and degradation during cellular senescence of human BJ fibroblasts: part I—effects of proliferative senescence
- Total body irradiation selectively induces murine hematopoietic stem cell senescence
- Is Petal senescence Due to Sugar Starvation?
- senescence and apoptosis: dueling or complementary cell fates?
- Cellular senescence as a tumor-protection mechanism: the essential role of counting
- AtNAP, a NAC family transcription factor, has an important role in leaf senescence
- Metabolism of Oat Leaves during senescence
V. senescence in Light - Leaf senescence in rice plants: cloning and characterization of senescence up‐regulated genes
- Premature senescence involving p53 and p16 is activated in response to constitutive MEK/MAPK mitogenic signaling
- Memory T cell homeostasis and senescence during aging
- Natal dispersal and senescence
- Cell wall metabolism during maturation, ripening and senescence of peach fruit
- senescence, sleep, and circadian rhythms
- Neurologic Signs in senescence
- Genetic regulation of embryo death and senescence
- Lysosome-mediated processing of chromatin in senescence
- The DNA damage signaling pathway is a critical mediator of oncogene-induced senescence
- senescence Is a Developmental Mechanism that Contributes to Embryonic Growth and Patterning
- Inside and out: the activities of senescence in cancer
- p16Ink4a in Melanocyte senescence and Differentiation
- Replicative senescence of human endothelial cells in vitro involves G1 arrest, polyploidization and senescence-associated apoptosis
- Replicative senescence in normal liver, chronic hepatitis C, and hepatocellular carcinomas
- Autophagy facilitates oncogene-induced senescence
- Cellular senescence: A link between cancer and age-related degenerative disease?
- senescence‐associated intrinsic mechanisms of osteoblast dysfunctions
- Mutant p53 drives metastasis and overcomes growth arrest/senescence in pancreatic cancer
- Secretion of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor by Primary Human Fibroblasts at senescence
- Transcription factors regulating leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana
- Expression of senescence‐enhanced genes in response to oxidative stress
- A Phylogenetic Evaluation of Whether Endophytes Become Saprotrophs at Host senescence
- Mitochondria, telomeres and cell senescence
- Mechanisms, Functional Consequences, and Potential Therapeutics for Cellular senescence
- Evidence for programmed cell death during leaf senescence in plants [1998]
- senescence: a new weapon for cancer therapy
- Ethylene Production During senescence of Flowers
- Die and let live: leaf senescence contributes to plant survival under drought stress
- Astrocyte senescence as a Component of Alzheimer’s Disease
- Alcohols and Carnation senescence
- AGE‐SPECIFIC SURVIVAL IN FIVE POPULATIONS OF UNGULATES: EVIDENCE OF senescence
- Fibroblast senescence in pressure ulcers
- Mental efficiency in senescence.
- Chloroplasts regulate leaf senescence: delayed senescence in transgenic ndhF-defective tobacco
- Retarded senescence in an insular population of Virginia opossums (Didelphis virginiana)
- Ink4a/Arf links senescence and aging
- Retardation of radish leaf senescence by polyamines
- Salicylic acid has a role in regulating gene expression during leaf senescence
- DNA Damage Is Able to Induce senescence in Tumor Cells in Vitro and in Vivo
- Hormone receptor changes during adulthood and senescence: significance for aging research.
- Vascular smooth muscle cell senescence in atherosclerosis
- How might replicative senescence contribute to human ageing?
- Age-related changes in learning and memory in the senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM)
- Angiotensin II accelerates endothelial progenitor cell senescence through induction of oxidative stress
- INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES, LONGEVITY, AND REPRODUCTIVE senescence IN BIGHORN EWES
- DNA damage checkpoint kinase Chk2 triggers replicative senescence
- Tumor Suppression in the Absence of p53-Mediated Cell-Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, and senescence
- Targets of the WRKY53 transcription factor and its role during leaf senescence in Arabidopsis
- Reversal of senescence in Mouse Fibroblasts through Lentiviral Suppression of p53
- senescence‐associated proteases in plants
- Cigarette Smoke Induces senescence in Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- senescence-Associated Exosome Release from Human Prostate Cancer Cells
- Aging and Cancer: The Double‐Edged Sword of Replicative senescence
- The evolution of premature reproductive senescence and menopause in human females
- senescence of an Antibody-forming Cell Clone
- miR-22 represses cancer progression by inducing cellular senescence
- Telomerase Inhibition, Telomere Shortening, and senescence of Cancer Cells by Tea Catechins
- cGAS is essential for cellular senescence
- Effect of Kinetin on Protein & Nucleic Acid Metabolism in Xanthium Leaves During senescence
- A key role for mitochondrial gatekeeper pyruvate dehydrogenase in oncogene-induced senescence
- Retardation of the senescence of Cultured Human Diploid Fibroblasts by Carnosine
- Plant senescence
- Immune Activation and CD8+ T-Cell Differentiation towards senescence in HIV-1 Infection
- Telomere Shortening Triggers senescence of Human Cells through a Pathway Involving ATM, p53, and p21CIP1, but Not p16INK4a
- Mitogen‐activated protein kinase p38 defines the common senescence‐signalling pathway
- Werner syndrome protein limits MYC-induced cellular senescence
- Identification of senescence-associated genes from daylily petals
- Cellular senescence in naevi and immortalisation in melanoma: a role for p16?
- Leaf senescence and nutrient remobilisation in barley and wheat
- Stay-green regulates chlorophyll and chlorophyll-binding protein degradation during senescence
- Overcoming cellular senescence in human cancer pathogenesis
- The matricellular protein CCN1 induces fibroblast senescence and restricts fibrosis in cutaneous wound healing
- PHOTOCONTROL OF LEAF senescence
- Hallmarks of Cellular senescence
- Inhibition of p21‐mediated ROS accumulation can rescue p21‐induced senescence
- Vascular cell senescence and vascular aging
- The p16INK4a-RB pathway : molecular link between cellular senescence and tumor suppression
- T cell anergy, exhaustion, senescence, and stemness in the tumor microenvironment
- Loss of linker histone H1 in cellular senescence
- Fibroblasts cultured from venous ulcers display cellular characteristics of senescence
- senescence and programmed cell death: substance or semantics?
- Rapid induction of senescence in human cervical carcinoma cells
- Networking senescence-Regulating Pathways by Using Arabidopsis Enhancer Trap Lines
- Synthetic lethal metabolic targeting of cellular senescence in cancer therapy
- DOES INCREASED MORTALITY FAVOR THE EVOLUTION OF MORE RAPID senescence?
- Relation between senescence and stomatal opening: senescence in darkness
- Measuring senescence in wild animal populations: towards a longitudinal approach
- Cell senescence in the Aging Kidney
- p53-independent upregulation of miR-34a during oncogene-induced senescence represses MYC
- Replicative senescence and Cell Immortality: The Role of Telomeres and Telomerase
- Cellular senescence, ageing and disease
- Effect of sugar-induced senescence on gene expression and implications for the regulation of senescence in Arabidopsis
- Dose-dependent oncogene-induced senescence in vivo and its evasion during mammary tumorigenesis
- Victorin Induction of an Apoptotic/senescence–like Response in Oats
- The oxidative hypothesis of senescence
- Accumulation of Short Telomeres in Human Fibroblasts Prior to Replicative senescence
- Stress-induced Premature senescence (SIPS)
- Significant Role for p16INK4a in p53-Independent Telomere-Directed senescence
- Is β-Galactosidase Staining a Marker of senescence in Vitro and in Vivo?
- Role of polyamines and ethylene as modulators of plant senescence
- Aging and Immortality: Quasi-Programmed senescence and Its Pharmacologic Inhibition
- Ovarian Dynamics in Heliconiine Butterflies: Programmed senescence versus Eternal Youth
- Inflammatory signaling and cellular senescence
- PROTEIN SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION DURING AGING AND senescence
- Extracellular Invertase Is an Essential Component of Cytokinin-Mediated Delay of senescence
- Physical activity and immune senescence in men.
- Reciprocal regulation of p53 and malic enzymes modulates metabolism and senescence
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induces senescence with a Distinct Secretory Phenotype
- Induction of replicative senescence biomarkers by sublethal oxidative stresses in normal human fibroblast
- Regulation of mitochondrial respiration in senescence
- Induction of EMT by Twist Proteins as a Collateral Effect of Tumor-Promoting Inactivation of Premature senescence
- Pancreatitis-Induced Inflammation Contributes to Pancreatic Cancer by Inhibiting Oncogene-Induced senescence
- Role of Cytokinins in Carnation Flower senescence
- Cellular senescence and apoptosis: how cellular responses might influence aging phenotypes
- The roles of senescence and telomere shortening in cardiovascular disease
- Vertical saccades in senescence.
- Variations in senescence and Longevity Include the Possibility of Negligible senescence
- Lipid turnover during senescence
- Mechanisms of endothelial senescence
- Natural senescence of Pea Leaves (An Activated Oxygen-Mediated Function for Peroxisomes)
- Water Stress during Seed Filling and Leaf senescence in Soybean
- Stress-induced premature senescence and tissue ageing
- Increase of deleted mitochondrial DNA in the striatum in Parkinson’s disease and senescence
- Defining cellular senescence in IMR-90 cells: a flow cytometric analysis
- Cellular senescence mechanisms in chronic wound healing
- Cellular senescence is an important mechanism of tumor regression upon c-Myc inactivation
- The role of CD8+ T‐cell replicative senescence in human aging
- Telomere Erosion and senescence in Human Articular Cartilage Chondrocytes
- Cellular senescence and DNA synthesis: Thymidine incorporation as a measure of population age in human diploid cells
- A Novel Role for High-Mobility Group A Proteins in Cellular senescence and Heterochromatin Formation
- Healing and Hurting: Molecular Mechanisms, Functions, and Pathologies of Cellular senescence
- Signal transduction in leaf senescence
- senescence in seeds.
- Growth stimulation leads to cellular senescence when the cell cycle is blocked
- Epidermal differentiation, apoptosis, and senescence: common pathways?
- Cellular senescence in the glaucomatous outflow pathway
- Leaf senescence Is Delayed in Tobacco Plants Expressing the Maize Homeobox Gene knotted1 under the Control of a senescence-Activated Promoter
- Induction of cellular senescence in immortalized cells by human chromosome 1
- senescence-associated (beta)-galactosidase reflects an increase in lysosomal mass during replicative ageing of human endothelial cells
- Stabilization of Oat Leaf Protoplasts through Polyamine-mediated Inhibition of senescence
- Androgens in male senescence
- Id1 regulation of cellular senescence through transcriptional repression of p16/Ink4a
- Mitogenic signalling and the p16INK4a–Rb pathway cooperate to enforce irreversible cellular senescence
- Programmed Cell Death during Pollination-Induced Petal senescence in Petunia
- Developmental and age-related processes that influence the longevity and senescence of photosynthetic tissues in arabidopsis.
- Are senescence and exhaustion intertwined or unrelated processes that compromise immunity?
- Reactive oxygen species and oxidative burst: Roles in stress, senescence and signal transducation in plants
- Molecular and Biochemical Characterization of Postharvest senescence in Broccoli
- TWIN STUDIES ON senescence
- senescence of the Human Immune System
- Longevity and senescence in plants
- senescence‐specific regulation of catalases in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh
- Extended culture of mouse embryo cells without senescence: inhibition by serum
- Cellular and molecular mechanisms of stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS) of human diploid fibroblasts and melanocytes
- Desiccation, Flight, Glycogen, and Postponed senescence in Drosophila metanogaster
- Klotho as a regulator of oxidative stress and senescence
- Twisted epithelial–mesenchymal transition blocks senescence
- BENZYLADENINE EFFFCTS ON BEAN LEAF GROWTH AND senescence
- The Strategy of senescence
- Differences in gene expression between natural and artificially induced leaf senescence
- Aging and Replicative senescence Have Related Effects on Human Stem and Progenitor Cells
- Requirement for p27KIP1 in Retinoblastoma Protein-Mediated senescence
- Replicative senescence in Human Uroepithelial Cells
- MTOR regulates the pro-tumorigenic senescence-associated secretory phenotype by promoting IL1A translation
- Superoxide Dismutase 1 Knock-down Induces senescence in Human Fibroblasts
- Cellular senescence in vivo: Its relevance in ageing and cardiovascular disease
- Evolutionary Perspectives on Human senescence
- T Cell Replicative senescence in Human Aging
- Possible Mechanisms of Adaptive Leaf senescence
- Sorghum stay-green QTL individually reduce post-flowering drought-induced leaf senescence
- senescence Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae With a Defect in Telomere Replication Identify Three Additional EST Genes
- senescence AND REPRODUCTIVE VALUE IN SPARROWHAWKS
- Understanding insect life histories and senescence through a resource allocation lens
- Klotho suppresses RIG-I-mediated senescence-associated inflammation
- Cardiac Muscle Changes in senescence
- Ethylene as a Regulator of senescence in Tobacco Leaf Discs
- Aspirin reduces endothelial cell senescence
- senescence IN NATURAL POPULATIONS OF MAMMALS: A REANALYSIS
- Growth and senescence of antibody‐forming cells
- Regulation of a senescence Checkpoint Response by the E2F1 Transcription Factor and p14ARF Tumor Suppressor
- INK4a-de®cient human diploid ®broblasts areresistant to RAS-induced senescence
- Response of a primary human fibroblast cell line to H2O2: senescence-like growth arrest or apoptosis?
- A senescence-like Phenotype Distinguishes Tumor Cells That Undergo Terminal Proliferation Arrest after Exposure to Anticancer Agents
- Cdk2 suppresses cellular senescence induced by the c-myc oncogene
- Identification of a promoter region responsible for the senescence-specific expression of SAG12
- Aging and osteoarthritis: the role of chondrocyte senescence and aging changes in the cartilage matrix
- ANTAGONISTIC PLEIOTROPY, MORTALITY SOURCE INTERACTIONS, AND THE EVOLUTIONARY THEORY OF senescence
- Wound chronicity and fibroblast senescence – implications for treatment
- Insect thermal tolerance: what is the role of ontogeny, ageing and senescence?
- THE CORRELATION BETWEEN OXIDATIVE STRESS AND LEAF senescence DURING PLANT DEVELOPMENT #
- p38MAPK is a novel DNA damage response‐independent regulator of the senescence‐associated secretory phenotype
- Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells
- Effect of Pod Removal on Leaf senescence in Soybeans
- On the senescence of ovules in cherries
- OsNAP connects abscisic acid and leaf senescence by fine-tuning abscisic acid biosynthesis and directly targeting senescence-associated genes in rice
- Acceleration of senescence in the collared flycatcher Ficedula albicollis by reproductive costs
- Rapid and costly ageing in wild male flies
- Transcription Analysis of Arabidopsis Membrane Transporters and Hormone Pathways during Developmental and Induced Leaf senescence
- Role of p14ARF in Replicative and Induced senescence of Human Fibroblasts
- Leaf senescence and Starvation-Induced Chlorosis Are Accelerated by the Disruption of an Arabidopsis Autophagy Gene
- The Role of Protein Synthesis in the senescence of Leaves
- Emergence, Elongation, and senescence of Maize Silks
- Hemangioblastic Derivatives from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Exhibit Limited Expansion and Early senescence
- Immune senescence
- Glucose-Induced Replicative senescence in Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- p63 deficiency activates a program of cellular senescence and leads to accelerated aging
- Weak p53 permits senescence during cell cycle arrest
- Aging and sensory senescence.
- Pathways connecting telomeres and p53 in senescence, apoptosis, and cancer
- Tumour suppression by p53: the importance of apoptosis and cellular senescence
- Chronic oxidative stress compromises telomere integrity and accelerates the onset of senescence in human endothelial cells
- Does a Sentinel or a Subset of Short Telomeres Determine Replicative senescence?
- Markers for hypersensitive response and senescence show distinct patterns of expression
- The role of nuclear lamin B1 in cell proliferation and senescence
- Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis
- Post‐traumatic osteoarthritis: The role of accelerated chondrocyte senescence
- senescence and the healing rates of venous ulcers
- The senescence‐Related Mitochondrial/Oxidative Stress Pathway is Repressed in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- senescence and Receptivity of Maize Silks
- Molecular signature of oncogenic ras-induced senescence
- senescence and Embedded-Figure Performance in Vision and Touch
- Anti-apoptotic and anti-senescence effects of Klotho on vascular endothelial cells
- Role of calcium in ripening and senescence
- Pheophytin Pheophorbide Hydrolase (Pheophytinase) Is Involved in Chlorophyll Breakdown during Leaf senescence in Arabidopsis
- Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a critical downstream target of p53 in the induction of replicative senescence
- Id-1 Delays senescence but Does Not Immortalize Keratinocytes
- Dissecting the Unique Role of the Retinoblastoma Tumor Suppressor during Cellular senescence
- Cellular aging and senescence
- Mitochondrial production of pro-oxidants and cellular senescence
- p16INK4a can initiate an autonomous senescence program
- Genetic analysis of cellular senescence
- A comparison of the expression patterns of several senescence-associated genes in response to stress and hormone treatment
- Replicative senescence Revisited
- Evolution of accelerated senescence in laboratory populations of Drosophila
- Cytoplasmic chromatin triggers inflammation in senescence and cancer
- Hormone-directed Transport of Metabolites and its possible Role in Plant senescence
- The evolution of senescence in fish
- senescence‐associated lncRNAs: senescence‐associated long noncoding RNAs
- Regulation of Leaf senescence by Cytokinin, Sugars, and Light
- Cellular senescence in the pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- A causal link between respiration and senescence in Podospora anserina
- Early Compositional Changes during Postharvest senescence of Broccoli
- HDA6 is required for jasmonate response, senescence and flowering in Arabidopsis
- Arabidopsis Cytokinin Receptor Mutants Reveal Functions in Shoot Growth, Leaf senescence, Seed Size, Germination, Root Development, and Cytokinin Metabolism
- Leaf senescence and activities of the antioxidant enzymes
- Cellular senescence drives age-dependent hepatic steatosis
- Cloning and characterization of tomato leaf senescence-related cDNAs
- Role of Telomerase in Cell senescence and Oncogenesis
- Cell senescence and telomere shortening induced by a new series of specific G-quadruplex DNA ligands
- senescence in fishes
- Methylene blue delays cellular senescence and enhances key mitochondrial biochemical pathways
- CD28 extinction in human T cells: altered functions and the program of T‐cell senescence
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the senescence Accelerated Mouse (SAM)
- Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases induce features of replicative senescence in early passage human diploid fibroblasts
- Adriamycin-induced senescence in Breast Tumor Cells Involves Functional p53 and Telomere Dysfunction
- MicroRNAs miR-146a/b negatively modulate the senescence-associated inflammatory mediators IL-6 and IL-8
- senescence in natural populations of animals: Widespread evidence and its implications for bio-gerontology
- Linkage of decreased bone mass with impaired osteoblastogenesis in a murine model of accelerated senescence.
- The Control of Autumn senescence in European Aspen
- Genetic regulation of primitive hematopoietic stem cell senescence
- DNA fragmentation is regulated by ethylene during carpel senescence in Pisum sativum
- AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR1 and AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR2 regulate senescence and floral organ abscission in Arabidopsis thaliana
- p63–microRNA feedback in keratinocyte senescence
- Role of the Ascorbate-Glutathione Cycle of Mitochondria and Peroxisomes in the senescence of Pea Leaves
- Effects of PSAG12-IPT Gene Expression on Development and senescence in Transgenic Lettuce
- Involvement of free radicals in ageing: a consequence or cause of senescence
- The Remobilization of Nitrogen Related to Leaf Growth and senescence in Rice Plants (Oryza sativa L.)
- NF-κB inhibition delays DNA damage–induced senescence and aging in mice
- Decreased beta-adrenergic responsiveness during senescence.
- Membrane phospholipid catabolism and Ca2+ activity in control of senescence
- Mechanism of Monocarpic senescence in Rice
- Oxidative stress occurs during soybean nodule senescence
- Evidence that transcriptional activation by p53 plays a direct role in the induction of cellular senescence.
- Longevity and the genetic determination of collagen glycoxidation kinetics in mammalian senescence
- High levels of antioxidant enzymes correlate with delayed senescence in nonnetted muskmelon fruits
- Relationship between Photosynthesis and Chlorophyll Content during Leaf senescence of Rice Seedlings
- The Role of Ethylene in the senescence of Oat Leaves
- Splicing into senescence: The Curious Case of p16 and p19ARF
- The Gene Expression Program of Prostate Fibroblast senescence Modulates Neoplastic Epithelial Cell Proliferation through Paracrine Mechanisms
- Cellular senescence and chromatin organisation
- Wild-type p53 triggers a rapid senescence program in human tumor cells lacking functional p53
- Telomeres are favoured targets of a persistent DNA damage response in ageing and stress-induced senescence
- DNA damage in telomeres and mitochondria during cellular senescence: is there a connection?
- Ageing, telomeres, senescence, and liver injury
- Evidence That Aging And Amyloid Promote Microglial Cell senescence
- Cellular senescence and DNA repair
- Rethinking the evolutionary theory of aging: Transfers, not births, shape senescence in social species
- Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Undergo Telomere-Based senescence in Human Atherosclerosis
- Assessing Cell and Organ senescence Biomarkers
- Molecular Regulation of Melanocyte senescence
- Premature senescence of endothelial cells: Methusaleh’s dilemma
- Resistance to Environmental Stress in Drosophila melanogaster Selected for Postponed senescence
- Oxidative stress induces senescence in chondrocytes
- p53 isoforms Δ133p53 and p53β are endogenous regulators of replicative cellular senescence
- HIF1α delays premature senescence through the activation of MIF
- Retardation of leaf senescence by benzyladenine in intact bean plants
- Cellular senescence and the aging brain
- Carnosine as a Potential Anti-senescence Drug
- The H3K36 demethylase Jhdm1b/Kdm2b regulates cell proliferation and senescence through p15Ink4b
- Cellular aging–clonal senescence. A review (Part I)
- Is Accelerated senescence a Cost of Reproduction?
- Astrocytes in the aging brain express characteristics of senescence‐associated secretory phenotype
- MicroRNAs linking inflamm-aging, cellular senescence and cancer
- senescence-associated inflammatory responses: aging and cancer perspectives
- Telomere dysfunction suppresses spontaneous tumorigenesis in vivo by initiating p53‐dependent cellular senescence
- Altered fruit ripening and leaf senescence in tomatoes expressing an antisense ethylene‐forming enzyme transgene
- Antioxidants Inhibit Nuclear Export of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase and Delay Replicative senescence of Endothelial Cells
- The DNA damage response induces inflammation and senescence by inhibiting autophagy of GATA4
- Evidence that exposure of the telomere 3′ overhang sequence induces senescence
- Physiological compensation for loss of afferent synapses in rat hippocampal granule cells during senescence.
- Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase and Proteolytic Activity in Wheat Leaves from Anthesis through senescence
- Spontaneous age-associated amyloidosis in senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM)
- Cellular senescence: Molecular Mechanisms, In Vivo Significance, and Redox Considerations
- Overexpression of Arabidopsis Hexokinase in Tomato Plants Inhibits Growth, Reduces Photosynthesis, and Induces Rapid senescence
- senescence induction; a possible cancer therapy
- Cell senescence and Its Implications for Nephrology
- Accelerated senescence: An emerging role in tumor cell response to chemotherapy and radiation
- Central Role of the Proteasome in senescence and Survival of Human Fibroblasts
INDUCTION OF A senescence-LIKE PHENOTYPE UPON ITS INHIBITION AND RESISTANCE TO STRESS UPON ITS ACTIVATION - Differential Roles for Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors p21 and p16 in the Mechanisms of senescence and Differentiation in Human Fibroblasts
- senescence-associated changes in respiration and oxidative phosphorylation in primary human fibroblasts.
- Characteristics of age-related behavioral changes in senescence-accelerated mouse SAMP8 and SAMP10
- Mammalian Prohibitin Proteins Respond to Mitochondrial Stress and Decrease during Cellular senescence
- Antisense suppression of phospholipase D alpha retards abscisic acid- and ethylene-promoted senescence of postharvest Arabidopsis leaves.
- Autophagy, senescence and tumor dormancy in cancer therapy
- senescence of immune defence in Bombus workers
- senescence-Induced Serotonin Biosynthesis and Its Role in Delaying senescence in Rice Leaves
- Role of T lymphocyte replicative senescence in vaccine efficacy
- Dental senescence in a long-lived primate links infant survival to rainfall
- The influence of sward condition on rates of herbage growth and senescence in mixed swards under continuous stocking management
- Cytokinin Activity in Rose Petals and Its Relation to senescence
- Evidence for Multiple Pathways to Cellular senescence
- Arabidopsis Nitric Oxide Synthase1 Is Targeted to Mitochondria and Protects against Oxidative Damage and Dark-Induced senescence
- Dual CDK4/CDK6 Inhibition Induces Cell-Cycle Arrest and senescence in Neuroblastoma
- Cellular senescence in cancer treatment: friend or foe?
- Human chondrocyte senescence and osteoarthritis
- Spectral Reflectance Changes Associated with Autumn senescence of Aesculus hippocastanum L. and Acer platanoides L. Leaves. Spectral Features and Relation to Chlorophyll Estimation
- BULB-TYPE FLOWER senescence
- Pathway analysis of senescence-associated miRNA targets reveals common processes to different senescence induction mechanisms
- Protein oxidation and degradation during postmitotic senescence
- Doubling potential, calendar time, and senescence of human diploid cells in culture
- Inflammatory bowel disease-like enteritis and caecitis in a senescence accelerated mouse P1/Yit strain
- Abrogation of BRAFV600E-induced senescence by PI3K pathway activation contributes to melanomagenesis
- mTOR regulates MAPKAPK2 translation to control the senescence-associated secretory phenotype
- senescence Is Induced in Individually Darkened Arabidopsis Leaves, but Inhibited in Whole Darkened Plants
- Hypoxia suppresses conversion from proliferative arrest to cellular senescence
- RNS2: a senescence-associated RNase of Arabidopsis that diverged from the S-RNases before speciation
- Interleukin‐22 induces hepatic stellate cell senescence and restricts liver fibrosis in mice
- Progerin and telomere dysfunction collaborate to trigger cellular senescence in normal human fibroblasts
- Evolutionary Biology of senescence
- Eating to exit: autophagy-enabled senescence revealed
- Loss of CD28 expression on T lymphocytes: A marker of replicative senescence
- senescence‐associated vacuoles with intense proteolytic activity develop in leaves of Arabidopsis and soybean
- senescence-associated beta-galactosidase histochemistry for the primate eye.
- Cytokine loops driving senescence
- MicroRegulators come of age in senescence
- DNA end joining becomes less efficient and more error-prone during cellular senescence
- Conditional senescence in bacteria: death of the immortals
- senescence and Death of Primitive Cells and Myocytes Lead to Premature Cardiac Aging and Heart Failure
- Isolation and analysis of cDNAs encoding tomato cysteine proteases expressed during leaf senescence
- Negligible senescence in the longest living rodent, the naked mole-rat: insights from a successfully aging species
- Mate Choice, Sexual Conflict, and Evolution of senescence
- Markers of cellular senescence. Telomere shortening as a marker of cellular senescence
- Stress-Induced Legume Root Nodule senescence. Physiological, Biochemical, and Structural Alterations
- Chlorophyll b reduction during senescence of barley seedlings
- Categories of Petal senescence and Abscission: A Re-evaluation
- Inhibition of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Pathway Induces a senescence-like Arrest Mediated by p27Kip1
- Relation between Nitrogen and Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase in Rice Leaves from Emergence through senescence
- ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3 Is a senescence-Associated Gene That Accelerates Age-Dependent Leaf senescence by Directly Repressing miR164 Transcription in Arabidopsis
- TP53 and MTOR crosstalk to regulate cellular senescence
- senescence in innate immune responses: reduced neutrophil phagocytic capacity and CD16 expression in elderly humans
- Physiological and pathological consequences of cellular senescence
- Agents that cause DNA double strand breaks lead to p16INK4a enrichment and the premature senescence of normal fibroblasts
- senescence from G2 arrest, revisited
- ORS1, an H2O2-Responsive NAC Transcription Factor, Controls senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana
- THE KINETICS OF senescence
- Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis can alleviate drought‐induced nodule senescence in soybean plants
- High-Resolution Temporal Profiling of Transcripts during Arabidopsis Leaf senescence Reveals a Distinct Chronology of Processes and Regulation
- The evolution of senescence from a comparative perspective
- Relationship between Ethylene Evolution and senescence in Morning-Glory Flower Tissue
- WRKY22 transcription factor mediates dark-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis
- senescence of nickel-transformed cells by an X chromosome: possible epigenetic control
- Hydrogen sulfide acts as a regulator of flower senescence in plants
- Gene expression during anthesis and senescence in Iris flowers
- Induced senescence of Intact Wheat Seedlings and Its Reversibility
- Oncogene-induced senescence: the bright and dark side of the response
- miR-29 and miR-30 regulate B-Myb expression during cellular senescence
- Negligible senescence during Reproductive Dormancy in Drosophila melanogaster
- Delayed Leaf senescence in Tobacco Plants Transformed with tmr, a Gene for Cytokinin Production in Agrobacterium.
- Monitoring Tumorigenesis and senescence In Vivo with a p16INK4a-Luciferase Model
- Endothelial Cell senescence
- Hormonal changes during salinity-induced leaf senescence in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.)
- Short Periods of Water Stress during Seed Filling, Leaf senescence, and Yield of Soybean
- senescence, nutrient remobilization, and yield in wheat and barley
- senescence and the Genetic-Correlation Hang-Up
- REVIEW ARTICLE. p53: GUARDIAN OF CELLULAR senescence
- Phospholipase D in cellular senescence
- Rice NON-YELLOW COLORING1 Is Involved in Light-Harvesting Complex II and Grana Degradation during Leaf senescence
- Delayed leaf senescence in ethylene‐deficient ACC‐oxidase antisense tomato plants: molecular and physiological analysis
- Source : sink ratio and leaf senescence in maize:: I. Dry matter accumulation and partitioning during grain filling
- Carotenoid catabolism during leaf senescence and its control by light
- senescence: does it all happen at the ends?
- Oxidative stress induces senescence in human mesenchymal stem cells
- DNA damage, vascular senescence and atherosclerosis
- Accelerated cellular senescence in degenerate intervertebral discs: a possible role in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration
- DNA-SCARS: distinct nuclear structures that sustain damage-induced senescence growth arrest and inflammatory cytokine secretion
- Role of p21 in Apoptosis and senescence of Human Colon Cancer Cells Treated with Camptothecin
- Oxygen free radicals in cell senescence: Are they signal transducers?
- Genetics of cellular senescence
- Regulation of E2Fs and senescence by PML nuclear bodies
- Cellular senescence and cancer chemotherapy resistance
- RNA Interference of Human Papillomavirus Type 18 E6 and E7 Induces senescence in HeLa Cells
- senescence and immortality in hepatocellular carcinoma
- senescence Processes in Leaf Abscission
- Acceleration of Membrane senescence in Cut Carnation Flowers by Treatment with Ethylene
- Oncogenic functions of tumour suppressor p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1: association with cell senescence and tumour-promoting activities of stromal fibroblasts
- WRKY54 and WRKY70 co-operate as negative regulators of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana
- Calcium regulation of senescence in rose petals
- Leaf senescence in Brassica napus: expression of genes encoding pathogenesis-related proteins
- Leaf senescence in maize hybrids: plant population, row spacing and kernel set effects
- The Effects of Ear Removal on senescence and Metabolism of Maize
- Time, telomeres and tumours: is cellular senescence more than an anticancer mechanism?
- Asexual metazoans undergo senescence.
- The biochemistry and regulation of senescence in chloroplasts
- Catalase and Peroxidase in Primary Bean Leavesduring Development and senescence
- Correlation of Xylem Sap Cytokinin Levels with Monocarpic senescence in Soybean
- Induction of senescence by oncogenic ras
- Mechanisms of polyamine action during senescence responses induced by osmotic stress
- Papillomavirus E2 induces senescence in HPV‐positive cells via pRB‐ and p21CIP‐dependent pathways
- Role of Ethylene in the senescence of Detached Rice Leaves
- senescence, Stress, and Reactive Oxygen Species
- A Role for Glutamine Synthetase in the Remobilization of Leaf Nitrogen during Natural senescence in Rice Leaves
- Predatory senescence in ageing wolves
- Hydrogen Sulfide Protects Against Cellular senescence via S-Sulfhydration of Keap1 and Activation of Nrf2
- Estrogen reduces endothelial progenitor cell senescence through augmentation of telomerase activity
- ABA receptor PYL9 promotes drought resistance and leaf senescence
- senescence-associated reprogramming promotes cancer stemness
- Arabidopsis AtNAP regulates fruit senescence
- Reversible senescence in Human CD4+CD45RA+CD27− Memory
- T Cell Activation and senescence Predict Subclinical Carotid Artery Disease in HIV-Infected Women
- Reexpression of the retinoblastoma protein in tumor cells induces senescence and telomerase inhibition
- Evolutionary mechanisms of senescence
- Changes in Capsaicinoids during Development, Maturation, and senescence of Chile Peppers and Relation with Peroxidase Activity
- The Vacuole and Cell senescence
- The role of ubiquitin in plant senescence and stress responses
- DYRK1A protein kinase promotes quiescence and senescence through DREAM complex assembly
- Induction of senescence in human malignant glioma cells by p16INK4A
- Leaf peroxisomes are directly transformed to glyoxysomes during senescence of pumpkin cotyledons
- Convergence and divergence in gene expression profiles induced by leaf senescence and 27 senescence‐promoting hormonal, pathological and environmental stress treatments
- senescence mechanisms of nucleus pulposus chondrocytes in human intervertebral discs
- Transcriptional regulation of cellular senescence
- Molecular and Cell Biology of Replicative senescence
- Ethylene-regulated expression of a carnation cysteine proteinase during flower petal senescence
- senescence and death of plant organs: Nutrient recycling and developmental regulation
- p16Ink4a overexpression in cancer: a tumor suppressor gene associated with senescence and high-grade tumors
- Chemokines Acting via CXCR2 and CXCR4 Control the Release of Neutrophils from the Bone Marrow and Their Return following senescence
- The senescence of the Immune System
- Telomere-driven replicative senescence is a stress response
- Methyl Jasmonate, Calcium, and Leaf senescence in Rice
- Murine fibroblasts lacking p21 undergo senescence and are resistant to transformation by oncogenic Ras
- Smurf2 up-regulation activates telomere-dependent senescence
- Autophagy and senescence
- Critical pathways in cellular senescence and immortalization revealed by gene expression profiling
- The evolutionary ecology of pre- and post-meiotic sperm senescence
- Inhibition of phospholipase D by lysophosphatidylethanolamine, a lipid-derived senescence retardant
- Chlorophyll-a degradation during cellular senescence and death
- Integrated Signaling in Flower senescence
- Mechanisms of Disease: role of chondrocytes in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis—structure, chaos and senescence
- Opposing roles for p16Ink4a and p19Arf in senescence and ageing caused by BubR1 insufficiency
- PML interaction with p53 and its role in apoptosis and replicative senescence
- Thidiazuron—a potent inhibitor of leaf senescence in Alstroemeria
- The disparity between human cell senescence in vitro and lifelong replication in vivo
- Ethylene receptor expression is regulated during fruit ripening, flower senescence and abscission
- T-cell senescence: a culprit of immune abnormalities in chronic inflammation and persistent infection
- Expression of Caveolin-1 Induces Premature Cellular senescence in Primary Cultures of Murine Fibroblasts
- A Systematic Screen for CDK4/6 Substrates Links FOXM1 Phosphorylation to senescence Suppression in Cancer Cells
- Stress-induced premature senescence and replicative senescence are different phenotypes, proteomic evidence
- Emerging role of NF-κB signaling in the induction of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
- Endogenous Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7 Proteins Differentially Regulate Proliferation, senescence, and Apoptosis in HeLa Cervical Carcinoma Cells
- Transcriptome analysis of senescence in the flag leaf of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Changes associated with aging and replicative senescence in the regulation of transcription factor nuclear factor-κB
- The Relation of Autoǵamy to senescence and Rejuvenescence in Paramecium aurelia
- senescence and Genetic Load: Evidence from Tribolium
- senescence, aging, and malignant transformation mediated by p53 in mice lacking the Brca1 full-length isoform
- Leaf senescence – not just a ‘wear and tear’ phenomenon
- Immune senescence: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications
- Involvement of the INK4a/Arf gene locus in senescence
- Free radical oxidation of brain proteins in accelerated senescence and its modulation by N-tert-butyl-α-phenylnitrone
- ARF functions as a melanoma tumor suppressor by inducing p53-independent senescence
- Errors in Protein Synthesis and Clonal senescence in Fungi
- The E3 SUMO Ligase PIASy Is a Regulator of Cellular senescence and Apoptosis
- miRNA-205 Suppresses Melanoma Cell Proliferation and Induces senescence via Regulation of E2F1 Protein
- Hidden costs of infection: Chronic malaria accelerates telomere degradation and senescence in wild birds
- Replicative senescence of CD8 T cells: effect on human ageing
- Studies on Soybean Nodule senescence
- Cellular senescence: Its role in tumor suppression and aging
- Evidence for the function of the free radical gas — nitric oxide (NO•) — as an endogenous maturation and senescence regulating factor in higher plants
- AtATG18a is required for the formation of autophagosomes during nutrient stress and senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana
- Propagation and senescence of human marrow stromal cells in culture: a simple colony‐forming assay identifies samples with the greatest potential to propagate and differentiate
- senescence Regulation by the p53 Protein Family
- Cell surface-bound IL-1α is an upstream regulator of the senescence-associated IL-6/IL-8 cytokine network
- mTOR Inhibition Prevents Epithelial Stem Cell senescence and Protects from Radiation-Induced Mucositis
- Cellular lifespan and senescence signaling in embryonic stem cells
- Lung fibroblasts from patients with emphysema show markers of senescence in vitro
- Future atmospheric CO2 leads to delayed autumnal senescence
- Sugars, senescence, and ageing in plants and heterotrophic organisms
- Increased p16 expression with first senescence arrest in human mammary epithelial cells and extended growth capacity with p16 inactivation
- Mutation and senescence: where genetics and demography meet
- miR-200c is upregulated by oxidative stress and induces endothelial cell apoptosis and senescence via ZEB1 inhibition
- ATR signaling can drive cells into senescence in the absence of DNA breaks
- OPTIMALITY THEORY, GOMPERTZ’ LAW, AND THE DISPOSABLE SOMA THEORY OF senescence
- Inhibition of ethylene synthesis and senescence in carnation by ethanol.
- In vitro simulation of senescence-related membrane damage by ozone-induced lipid peroxidation
- Telomere-dependent senescence
- Stress-induced senescence in human and rodent astrocytes
- The evolutionary basis of leaf senescence: Method to the madness?
- Leaf Proteolytic Activities and senescence during Grain Development of Field-grown Corn (Zea mays L.)
- Hypoxia, MTOR and autophagy
Converging on senescence or quiescence - Long‐term exogenous application of melatonin delays drought‐induced leaf senescence in apple
- Integration of soybean pod development and monocarpic senescence
- Tissue damage and senescence provide critical signals for cellular reprogramming in vivo
- Unexpected Pieces to the senescence Puzzle
- Cell senescence: Role in Aging and Age-Related Diseases
- Disposable-soma senescence mediated by sexual selection in an ungulate
- Reactive oxygen species and hematopoietic stem cell senescence
- Biochemical changes related to aging in the senescence-accelerated mouse
- Programmed senescence of plant organs
- SOCS1 Links Cytokine Signaling to p53 and senescence
- The role of ascorbic acid in the control of flowering time and the onset of senescence
- Autophagy and senescence in Cancer Therapy
- Crosstalk between chromatin state and DNA damage response in cellular senescence and cancer
- Aging in Legume Symbiosis. A Molecular View on Nodule senescence in Medicago truncatula
- A gene regulatory network controlled by the NAC transcription factor ANAC092/AtNAC2/ORE1 during salt‐promoted senescence
- DNA damaging agents and p53 do not cause senescence in quiescent cells, while consecutive re-activation of mTOR is associated with conversion to senescence
- Evidence of cell loss from the rat retina during senescence
- Evidence for a senescence-Associated Gene Induced by Darkness
- Ascorbic acid, a familiar small molecule intertwined in the response of plants to ozone, pathogens, and the onset of senescence
- Targeting cellular senescence prevents age-related bone loss in mice
- Executing Cell senescence
- Aging and senescence in plant developent.
- Cortical bone senescence and mineral bone density of the humerus
- Control of cellular senescence by CPEB
- Morphological and contractile characteristics of rat cardiac myocytes from maturation to senescence
- p16/pRb Pathway Alterations Are Required for Bypassing senescence in Human Prostate Epithelial Cells
- Vemurafenib Induces senescence Features in Melanoma Cells
- Role of growth regulators in the senescence of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves
- Pigment dynamics and autumn leaf senescence in a New England deciduous forest, eastern USA
- Suppression of tumor growth by senescence in virally transformed human fibroblasts
- Factors that accelerate or retard red blood cell senescence.
- IndependentInductionofsenescencebyp16INK4
- Multiple pathways to cellular senescence: Role of telomerase repressors
- Octopus senescence: The Beginning of the End
- A new member of the Arabidopsis WRKY transcription factor family, AtWRKY6, is associated with both senescence‐ and defence‐related processes
- Demographic Perspectives on Human senescence
- Molecular mechanisms of replicative senescence in endothelial cells
- Does Maintaining Green Leaf Area in Sorghum Improve Yield under Drought? I. Leaf Growth and senescence
- Functional Aging and Gradual senescence in Zebrafish
- A reassessment of the telomere hypothesis of senescence
- Interrelationships of Ethylene and Abscisic Acid in the Control of Rose Petal senescence
- Promotive Effect of Methyl Jasmonate on Oat Leaf senescence in the Light
- senescence in podospora anserina: Amplification of a mitochondrial DNA sequence
- Evolution of senescence in iteroparous perennial plants
- Comparison of replicative senescence and stress‐induced premature senescence combining differential display and low‐density DNA arrays
- POLLINATION-INDUCED COROLLA senescence
- The H3K27me3 demethylase JMJD3 contributes to the activation of the INK4A–ARF locus in response to oncogene- and stress-induced senescence
- Legume nodule senescence: roles for redox and hormone signalling in the orchestration of the natural aging process
- Mitochondrial-Targeted Plastoquinone Derivatives. Effect on senescence and Acute Age-Related Pathologies
- Dark‐inducible genes from Arabidopsisthaliana are associated with leaf senescence and repressed by sugars
- Nitric oxide counteracts the senescence of rice leaves induced by abscisic acid
- Cellular senescence in Type 2 Diabetes: A Therapeutic Opportunity
- senescence of the retinal pigment epithelium
- senescence-related serine protease in parsley
- The Metabolism of Oat Leaves during senescence
- Metabolic analysis of senescent human fibroblasts reveals a role for AMP in cellular senescence.
- Markers of senescence?
- Repair of telomeric DNA prior to replicative senescence
- Expression of p16INK4a and other cell cycle regulator and senescence associated genes in aging human kidney
- Regulation of detached coriander leaf senescence by 1-methylcyclopropene and ethylene
- Stress-Activated MAP Kinase Cascades in Cellular senescence
- Cellular senescence in Vitro
- Inhibition of ethylene‐induced cellular senescence symptoms by 1‐methylcyclopropene, a new inhibitor of ethylene action
- The Complex Regulation of senescence
- Posttranscriptional gene regulation by RNA-binding proteins during oxidative stress: implications for cellular senescence
- Delayed senescence of apple leaves by exogenous melatonin treatment: toward regulating the ascorbate–glutathione cycle
- High Levels of Brain Dolichols in Neuronal Ceroid‐Lipofuscinosis and senescence
- An anti-aging drug today: from senescence-promoting genes to anti-aging pill
- Homocysteine accelerates senescence and reduces proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells
- Posttranslational Modifications of p53 in Replicative senescence Overlapping but Distinct from Those Induced by DNA Damage
- Aging, life span, and senescence
- The Role of Arabidopsis Rubisco Activase in Jasmonate-Induced Leaf senescence
- Connecting autophagy to senescence in pathophysiology
- Magnesium deficiency accelerates cellular senescence in cultured human fibroblasts
- miR-335 and miR-34a Promote Renal senescence by Suppressing Mitochondrial Antioxidative Enzymes
- senescence-Accelerated Mouse (SAM) with Special References to Neurodegeneration Models, SAMP8 and SAMP10 Mice
- Glycated Collagen I Induces Premature senescence-Like Phenotypic Changes in Endothelial Cells
- Image analysis of GFA-positive astrocytes from adolescence to senescence
- Escape from Therapy-Induced Accelerated Cellular senescence in p53-Null Lung Cancer Cells and in Human Lung Cancers
- Cloning of senescent Cell-Derived Inhibitors of DNA Synthesis Using an Expression Screen
- Localization of senescent cell antigen on band 3
- A senescent cell bystander effect: senescence‐induced senescence
- senescent cell antigen is immunologically related to band 3
- Measurement of DNA content and cell volume in senescent human fibroblasts utilizing flow multiparameter single cell analysis
- A New LIM Protein Containing an Autoepitope Homologous to “senescent Cell Antigen”
- Generation of senescent cell antigen on old cells initiates IgG binding to a neoantigen.
- Mimetics of senescent cell derived inhibitors of DNA synthesis
- senescent Keratinocytes Die by Autophagic Programmed Cell Death
- Rapid disappearance of statin, a nonproliferating and senescent cell-specific protein, upon reentering the process
- Molecular Mechanisms for the senescent Cell Cycle Arrest
- Membrane Fragmentation and Ca++-Membrane Interaction : Potential Mechanisms of Shape Change in the senescent Red Cell
- Long-Term in vitro Growth of Human T Cell Clones: Can Postmitotic ‘senescent’ Cell Populations Be Defined?
- senescent cell derived inhibitors of DNA synthesis
- Antigenicity, storage, and aging: physiologic autoantibodies to cell membrane and serum proteins and the senescent cell antigen
- Aging of Cell Membrane Molecules Leads to Appearance of an Aging Antigen and Removal of senescent cells
- Growth hormone action predicts age-related white adipose tissue dysfunction and senescent cell burden in mice
- Inhibition of intimal hyperplasia after vein grafting by in vivo transfer of human senescent cell-derived inhibitor-1 gene
- Identification of senescent cell surface targetable protein DPP4
- Synthetic senescent cell antigen
- senescent vs. non-senescent cells in the human annulus in vivo: Cell harvest with laser capture microdissection and gene expression studies with microarray analysis
- senescent cell derived inhibitors of DNA synthesis
- Glucose transport protein is structurally and immunologically related to band 3 and senescent cell antigen
- senescent Human Fibroblasts Resist Programmed Cell Death, and Failure to Suppress bcl2 Is Involved
- Duration of senescent cell survival in vitro as a characteristic of organism longevity, an additional to the proliferative potential of fibroblasts
- Antibodies to senescent cell-derived inhibiters of DNA synthesis
- Expression of cell cycle-dependent genes in young and senescent WI-38 fibroblasts
- Induction of senescent cell-derived inhibitor of DNA synthesis gene, SDI1, in hepatoblastoma (HepG2) cells arrested in the G2-phase of the cell cycle by 9-nitrocamptothecin.
- Relationship between cell replication and volume in senescent human diploid fibroblasts
- p21 maintains senescent cell viability under persistent DNA damage response by restraining JNK and caspase signaling
- Cell-Cell Affinity of senescent Human Erythrocytes
- The Ability to Generate senescent Progeny as a Mechanism Underlying Breast Cancer Cell Heterogeneity
- senescent and quiescent cell inhibitors of DNA synthesis: Membrane-associated proteins
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa Transmigrates at Epithelial Cell-Cell Junctions, Exploiting Sites of Cell Division and senescent Cell Extrusion
- senescent cell antigen, band 3, and band 3 mutations in cellular aging.
- SCAMP4 enhances the senescent cell secretome
- senescent cell differentiation antigen.
- Reinitiation of DNA Synthesis and Cell Division in senescent Human Fibroblasts by Microinjection of Anti-p53 Antibodies
- Aging of cell membrane molecules: Band 3 and senescent cell antigen in neural tissue
- Impaired Cell Shortening and Relengthening with Increased Pacing Frequency are Intrinsic to the senescent Mouse Cardiomyocyte
- Dynamics of senescent Cell Formation and Retention Revealed by p14ARF Induction in the Epidermis
- Entry into S phase is inhibited in two immortal cell lines fused to senescent human diploid cells
- senescent cell death brings hopes to life
- Common senescent cell‐specific antibody epitopes on fibronectin in species and cells of varied origin
- senescent cell derived inhibitors of DNA synthesis
- Restoration of the responsiveness to growth factors in senescent cells by an embryonic cell extract
- MnSOD Upregulation Induces Autophagic Programmed Cell Death in senescent Keratinocytes
- Spontaneous cell transformation: Karyoplasts derived from multinucleated cells produce new cell growth in senescent human epithelial cell cultures
- senescent cell antigen: a terminal differentiation antigen.
- Small extracellular vesicles secreted from senescent cells promote cancer cell proliferation through EphA2
- Fibroblasts derived from Gpx1 knockout mice display senescent-like features and are susceptible to H2O2-mediated cell death
- Molecular Mapping of the Active Site of an Aging Antigen: senescent Cell Antigen Requires Lysine(s) for Antigenicity and Is Located on an Anion-Binding Segment of Band 3 Membrane Transport Protein
- Human platelet lysate stimulates high-passage and senescent human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell growth and rejuvenation in vitro
- Gerontology and drug development: The challenge of the senescent cell
- Chlorophyll Degradation in senescent Tobacco Cell Culture (Nicotiana tabacum var. «Samsun»)
- Down-regulation of Akt/PKB in senescent cardiac fibroblasts impairs PDGF-induced cell proliferation
- Type 1 interferons contribute to the clearance of senescent cell
- Robust nuclear lamina-based cell classification of aging and senescent cells
- Simvastatin suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation induced by senescent cells
- Secretome from senescent melanoma engages the STAT3 pathway to favor reprogramming of naive melanoma towards a tumor-initiating cell phenotype
- Appearance of the terminal senescent cell population in human diploid fibroblasts analyzed by flow cytometry
- Some chemotherapeutics-treated colon cancer cells display a specific phenotype being a combination of stem-like and senescent cell features
- mRNA levels of the differentiation-associated linker histone variant H1 zero in mitotically active and postmitotic senescent human diploid fibroblast cell populations
- Method To Purify and Analyze Heterogeneous senescent Cell Populations Using a Microfluidic Filter with Uniform Fluidic Profile
- Mapping of senescent cell antigen on brain anion exchanger protein (AE) isoforms using HPLC and fast atom bombardment ionization mass spectrometry (FAB‐MS)
- Evaluation of a near‐senescent human dermal fibroblast cell line and effect of amelogenin
- Level of macroautophagy drives senescent keratinocytes into cell death or neoplastic evasion
- Genes and ageing: beyond good and evil in the senescent cell
- Method of optimizing conditions for selectively removing a plurality of senescent cells from a tissue or a mixed cell population
- Complementation between senescent human diploid cells and a thymidine kinase-deficient murine cell line
- Targeting senescent cholangiocytes and activated fibroblasts with B‐cell lymphoma‐extra large inhibitors ameliorates fibrosis in multidrug resistance 2 gene knockout (Mdr2−/−) mice
- Diet-induced weight loss is sufficient to reduce senescent cell number in white adipose tissue of weight-cycled mice
- Natural killer cell recognition of in vivo drug-induced senescent multiple myeloma cells
- senescence-associated secretory factors induced by cisplatin in melanoma cells promote non-senescent melanoma cell growth through activation of the ERK1/2-RSK1 pathway
- Density-gradient centrifugation enables the purification of cultured corneal endothelial cells for cell therapy by eliminating senescent cells
- senescent cell clearance by the immune system: Emerging therapeutic opportunities
- Life and Death of Neurons: The Role of senescent Cell Antigen
- Mapping H4K20me3 onto the chromatin landscape of senescent cells indicates a function in control of cell senescence and tumor suppression through preservation of genetic and epigenetic stability
- Retroviral vectors carrying senescent cell derived inhibitors 1 (SDI-1)or antisense SDI-1 nucleotide sequences
- In Vitro Expansion of Human Nasoseptal Chondrocytes Reveals Distinct Expression Profiles of G1 Cell Cycle Inhibitors for Replicative, Quiescent, and senescent Culture Stages
- Drug-Induced senescent Multiple Myeloma Cells Elicit NK Cell Proliferation by Direct or Exosome-Mediated IL15 Trans-Presentation
- Radiation-Induced Reprogramming of Pre-senescent Mammary Epithelial Cells Enriches Putative CD44+/CD24−/low Stem Cell Phenotype
- Epigallocatechin gallate suppresses premature senescence of preadipocytes by inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and induces senescent cell death by regulation of Bax/Bcl-2 pathway
- The senescent cell epigenome
- CHAPTER 24 – senescent cell antigen and band 3 in aging and disease
- The mTORC1-autophagy pathway is a target for senescent cell elimination
- HPV-16 virions can remain infectious for 2 weeks on senescent cells but require cell cycle re-activation to allow virus entry
- Embryonic senescent cells re-enter cell cycle and contribute to tissues after birth
- Proteomics Analysis of Normal and senescent NG108-15 Cells: GRP78 Plays a Negative Role in Cisplatin-Induced senescence in the NG108-15 Cell Line
- Cell surface oligosaccharide modulation during differentiation: VI. The effect of biomodulation on the senescent and neoplastic cell phenotype
- Induction of Neointimal Formation by Local Gene Transfer of the Antisense senescent Cell-derived Inhibitor 1 (SDI) Delivered With the Needle Injection Catheter
- Antibody Dependent Cell Mediated Cytotoxicity and Phagocytosis of senescent Erythrocytes by Autologous Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Phase-space description of the cell cycle: Application to noncycling, senescent, and transformed cells
- Effect of Overproduction of Mitochondrial Uncoupling Protein 2 on Cos7 Cells: Induction of senescent-like Morphology and Oncotic Cell Death
- senescent dermal fibroblasts enhance stem cell migration through CCL2/CCR2 axis
- Red cell aging: senescent cell antigen, band 3, and band 3 mutations associated with cellular dysfunction.
- Rock Inhibition Reduces senescent Cell Size
- The senescent Cell, SC
- senescent Cell Biomarkers
- THE senescent CELL POPULATION WITHIN NEW BONE PRODUCED BY DISTRACTION OSTEOGENESIS
- Treating atherosclerosis by removing senescent foam cell macrophages from atherosclerotic plaques
- Single senescent cell sequencing reveals heterogeneity in senescent cells induced by telomere erosion
- [Establishment of senescent cell model in primary rat aortic endothelial cells].
- THE ROLE OF THE RETINOBLASTOMA PROTEIN IN senescent CELL CYCLE EXIT, SURVIVAL, AND MORPHOLOGICAL ALTERATION
- Abstract 453: senescent Cell Depletion via Abt263 Augments Experimental Aortic Aneurysm Progression
- Aging and cancer: Cell non-autonomous effects of senescent fibroblasts on tissue microenvironment
- The senescent cell induced bystander effect
- [senescent cell antigens in the clearance of senescent cells].
- Material-induced senescence (MIS): Fluidity Induces senescent Type Cell Death of Lung Cancer Cells via Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 5
- Abstract 361: Effects of Chronic, Intermittent senescent Cell Clearance in Combination with Lipid Lowering on Inflammation in Perivascular Adipose Tissue
- Active, Dormant, or on the Path to Elimination: What Does a senescent Cell Do?
- The connection between the cardiac glycoside‐induced senescent cell morphology and Rho/Rho kinase pathway
- Cloning of animals from senescent cell nuclei–what are the implications for aging research?
- Cell Cycle Traverse and Growth Arrest Control in senescent Human Fibroblasts
- senescent cells evade immune clearance via HLA-E-mediated NK and CD8+ T cell inhibition
- Aging and cancer: Cell non-autonomous effects of senescent fibroblasts on tissue microenvironment
- Klotho‐mediated targeting of CCL2 suppresses the induction of colorectal cancer progression by stromal cell senescent microenvironments
- Hydroxyurea‐induced senescent peripheral blood mesenchymal stromal cells inhibit bystander cell proliferation of JAK2V617F‐positive human erythroleukemia cells
- Aging and cancer: Cell non-autonomous effects of senescent fibroblasts on tissue microenvironment
- Antibodies to senescent Antigen and C3 Are Not Required for Normal Red Blood Cell Lifespan in a Murine Model
- Removing senescent cells from a mixed cell population or tissue using a phosphoinositide 3-kinase (pi3k) inhibitor
- Differential Regulation of Methylation-Regulating Enzymes by senescent Stromal Cells Drives Colorectal Cancer Cell Response to DNA-Demethylating Epi-Drugs
- senescent Pulmonary-Artery Smooth Muscle Cell (PA-SMC)-Derived Osteopontin Promotes PA-SMC Proliferation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 303: A role for senescent cell-derived IL6 in HER2+ breast cancer progression
- A New LIM Protein Containing an Autoepitope Homologous to ‘senescent Cell Antigen,’
- Aging and the senescent cell
- Differences between cytotoxicity of chemicals determined in vitro on young and old cells of a senescent cell line
- Modulation of Phenotype and Induction of Apoptosis in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMC) by Transfer of Human senescent Cell-Derived Inhibitor-1 Gene: 190
- Adventitial gene transfer of the antisense to senescent cell-derived inhibitor 1 results in increased neointima
- senescent CELL DERIVED INHIBITORS OF DNA SYNTHESIS
- Cell cycle and apoptosis: death of a senescent cell
- MIMETICS OF senescent CELL DERIVED INHIBITORS OF DNA SYNTHESIS
- senescent cell distribution in human skeletal muscle : Role of exercise and protein availability
- A new LIM protein containing an autoepitope homologous to’senescent cell antigen’ (vol 201, pg 1127, 1994)
- Chemotherapeutics-treated cancer cells display stem-like and senescent cell features
- Fisetin is a senotherapeutic that extends health and lifespan
- The emerging field of senotherapeutic drugs
- SA-β-Galactosidase-Based Screening Assay for the Identification of Senotherapeutic Drugs.
- Src Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: New Perspectives on Their Immune, Antiviral, and Senotherapeutic Potential
- Senotherapy: growing old and staying young?
- Senotherapy for attenuation of cellular senescence in aging and organ implantation
- Targeting normal and cancer senescent cells as a strategy of senotherapy
- Emerging role of NF-κB signaling in the induction of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
- SASP reflects senescence
- SASP mediates chemoresistance and tumor-initiating-activity of mesothelioma cells
- Unbiased analysis of senescence associated secretory phenotype (SASP) to identify common components following different genotoxic stresses
- Detection of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
- Melatonin regulates PARP 1 to control the senescence‐associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in human fetal lung fibroblast cells
- Suppression of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in human fibroblasts using small molecule inhibitors of p38 MAP kinase and MK2
- SASP: tumor suppressor or promoter? Yes!
- The experimental demonstration of a SASP-based full software radio receiver
- Anti-TNF-α treatment modulates SASP and SASP-related microRNAs in endothelial cells and in circulating angiogenic cells
- Partial sleep deprivation activates the DNA damage response (DDR) and the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in aged adult humans
- Evaluation of the mutagenicity of the anti-inflammatory drug salicylazosulfapyridine (SASP)
- Whole Chromosome Instability induces senescence and promotes SASP
- SASP gene delivery: a novel antibacterial approach
- Downregulation of cytoplasmic DNases is implicated in cytoplasmic DNA accumulation and SASP in senescent cells
- The small acid soluble proteins (SASP α and SASP β) of Bacillus weihenstephanensis and Bacillus mycoides group 2 are the most distinct among the Bacillus cereus …
- ATM, MacroH2A. 1, and SASP: the checks and balances of cellular senescence
- … absorption of 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) after administration of a 5-ASA enema and salazosulfapyridine (SASP) after an SASP suppository in Japanese volunteers
- SASP (Small, Acid-Soluble Spore Proteins) and Spore Properties in Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus
- Isolation and identification of Lom-SG-SASP, a salivation stimulating peptide from the salivary glands of Locusta migratoria
- Targeting the SASP to combat ageing: Mitochondria as possible intracellular allies?
- “Social Life” of Senescent Cells: What Is SASP and Why Study It?
- Synthesis and characterization of a 29-amino acid residue DNA-binding peptide derived from α/β-type small, acid-soluble spore proteins (SASP) of bacteria
- Effects of NAT2 polymorphism on SASP pharmacokinetics in Chinese population
- Sensitive detection and monitoring of senescence-associated secretory phenotype by SASP-RAP assay
- Another classic of EU sports jurisprudence: Legal implications of Olympique Lyonnais SASP v Olivier Bernard and Newcastle UFC (C-325/08)
- Clinical Observation on 30 Cases of Ulcerative Colitis of Damp Heat in the Large Intestine Stagnation Type Treated with Kuijieling Granules Combinated SASP [J]
- SASP regulation by noncoding RNA
- Scavenger effect of sulphasalazine (SASP), 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), and olsalazine (OAZ)
- SASP, a Senescence-Associated Subtilisin Protease, is involved in reproductive development and determination of silique number in Arabidopsis
- Symbol manipulation in FORTRAN: SASP I subroutines
- Chronic resveratrol treatment inhibits MRC5 fibroblast SASP-related protumoral effects on melanoma cells
- Pharmacokinetics of salazosulfapyridine (Sulfasalazine, SASP)(I): Plasma kinetics and plasma metabolites in the rat after a single intravenous or oral administration
- Sirt1 and Parp1 as epigenome safeguards and microRNAs as SASP-associated signals, in cellular senescence and aging
- SASP, a Production Planning and Control System for Shipbuilding on Individual Orders
- TORn about SASP regulation
- Case C-325/08, Olympique Lyonnais SASP v. Olivier Bernard and Newcastle United UFC, Judgment of the Court of Justice (Grand Chamber) of 16 March 2010
- Beneficial effect of salazosulfapyridine (SASP) in a patient with secondary renal amyloidosis
- Optical design and performance of the SASP spectrometer at TRIUMF
- Detecting the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) by high content microscopy analysis
- Pharmacokinetics of Salazosulfapyridine (Sulfasalazine, SASP)(V): Pharmacokinetics of SASP after a single intravenous or oral administration in the dog.
- Comparison of SKP (semi-automated kinetic perimetry) and SASP (suprathreshold automated static perimetry) techniques in patients with advanced glaucoma
- SIN3B, the SASP, and pancreatic cancer
- Pharmacokinetics of Salazosulfapyridine (Sulfasalazine, SASP)(III) Metabolism and biliary excretion of SASP in the rat after a single intravenous or oral administration.
- PAI-1 Regulation of TGF-β1-induced ATII Cell Senescence, SASP Secretion, and SASP-mediated Activation of Alveolar Macrophages
- Maintenance treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC) with oral 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) in patients unable to take sulphasalazine (SASP)
- Observation of curative effect of Sanguis Draxonis combined with SASP in the treatment of non-specific ulcerative colitis
- Replica exchange molecular dynamics simulations of an α/β-type small acid soluble protein (SASP)
- 98: Term fetal membranes and senescence associated secretory phenotype (SASP)-like gene expression: a signal for parturition?
- COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF SULPHASALAZINE (SASP) AND 3 5 DIPS ON GLUTATHIONE (GSH) LEVEL IN RED CELLS OF HUMAN BLOOD IN …
- Inhibition of neutral proteases from polymorphonuclear (PMN) neutrophils by salicylazosulfapyridine (SASP)
- Senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) involvement in the development of cancer, aging, and age related diseases
- RNA-binding Protein Immunoprecipitation (RIP) to examine AUF1 binding to senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) factor mRNA
- Modified bacteriophage including an alpha/beta small acid-soluble spore protein (SASP) gene
- Modified bacteriophage including an alpha/beta small acid-soluble spore protein (SASP) gene
- Arabidopsis subtilase SASP is involved in the regulation of ABA signaling and drought tolerance by interacting with OPEN STOMATA 1
- The first experimental demonstration of a SASP-based full Software Radio receiver
- A low power digitally-enhanced SASP-based receiver architecture for mobile DVB-S applications in the Ku-band (10.7–12.75 GHz)
- Senescence can be BETter without the SASP?
- Cancer cell cannibalism and the SASP: Ripples in the murky waters of tumor dormancy
- Methyl caffeate and some plant constituents inhibit age-related inflammation: effects on senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) formation
- Dissecting cellular senescence and SASP in Drosophila
- 169: IL-19, a novel SASP factor, is upregulated during senescence and in response to DSBs
- Growth arrest by sulfasalazine (SASP) of subrenal capsule prostate cancer xenografts in immuno-deficient mice is coupled to a decrease in the number of tumor …
- COMPARISON OF THE EFFICACY OF 5 ASA AND SASP IN TREATMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS
- A La Recherche of Functions for the Spore Protein SASP-E from Bacillus subtilis
- SASP: a symbolic algorithm for shortest paths
- Molecules and Clusters in Motion: Looking Back and Looking Forward, SASP and Beyond
- I no longer dread teaching physics, I now enjoy it!’Participant reflections from the SASP physics course
- The salivary gland salivation stimulating peptide from Locusta migratoria (Lom-SG-SASP) is not a typical neuropeptide
- Pharmacokinetics of Salazosulfapyridine (Sulfasalazine, SASP)(II) Tissue distribution and excretion of SASP in the rat after a single intravenous or oral administration.
- Deciphering the mechanism for induction of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) and its role in ageing and cancer development
- Optimisation of a screening platform for determining IL-6 inflammatory signalling in the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
- Overexpression of Klotho Inhibits HELF Fibroblasts SASP-related Protumoral Effects on Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells
- SASP-Dependent Interactions between Senescent Cells and Platelets Modulate Migration and Invasion of Cancer Cells
- SKYNET Applications Software Package (SASP) Operators’ and Users’ Handbook, Version 2.
- The rehabilitation village-Paper presented at SASP Congress 1993
- Designing in uncertainty: The I-SASP model for tactical and innovative risk management in the hi-performing professional practice
- Characterization of structural changes in alpha/beta-type small, acid-soluble spore proteins (SASP) upon binding to DNA.
- SASP: The future of School Psychology
- Regulation of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
- Micromanaging fibroblast senescence: The role of small non-coding RNAs in senescence associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
- Effect of sulfasalazine (SASP) on sodium flux in rat colon
- Senescence utilises inflammatory caspases to drive SASP
- Outcome of Patients with Ankylosing Spondyloarthritis Continuing Treated with Thalidomide and SASP after a Short Course of Etanercept Therapy [J]
- Study on Effect of Regulation to Th1/Th2 in AUC Patients with Chinese Medicine Combined with SASP Enema under Guidance of Synchronous Treatment of Lung …
- Effect of combine probiotics with SASP on inflammatory bowel disease
- Changes of T regulatory cells in rats with experimental colitis after drug treatment with SASP and PSL
- Clinical effects of 99Tc-2MDP combined with SASP for ankylosing spondylitis
- Ex-SASP-erating cancer
- ETDEWEB/Search Results/Proceedings of the DASS/SASP (Dual Arm Spectrometer System/Second Arm Spectrometer) workshop
- Immunological Responses and Protection in Dairy Cows Vaccinated with Staphylococcus aureus Surface Proteins (SASP) and Staphylococcus chromogenes …
- Studies on the Role of SASP in Heat and Radiation Resistance of Bacterial Spores and on Regulation of a SASP Specific Protease
- Scavenger effect of sulphasalazine (SASP)
- SASP: targeted delivery to Gram-negative pathogens
- Slow-Release 5-Aminosalicylic Acid (Pentasa) versus Sulphasalazine (SASP) in the Maintenance Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis (82)
- SKYNET Applications Software Package (SASP) Programmers’ Handbook, Version 2.
- Signatures analysis systems prototype (SASP)
- PAI-1-Stimulated AT2 Cell SASP Promotes Profibrotic Polarization of Alveolar Macrophages
- … serum antibodies to bacterial antigens may be used as markers for the likelihood of response to SASP could have implications regarding the tailoring of SASP …
- Advances in pain management and research presented at the 2015 Scientific Meeting of the Scandinavian Association for the Study of Pain (SASP)
- SASP-A digital signal processor system for speech processing applications
- Poster-abstracts from SASP–The Scandinavian Association for the Study of Pain scientific meeting, Oslo, Norway, April 7–9, 2014
- The salivary gland salivation stimulating peptide from Locusta migratoria (Lom-SG-SASP) is not a neuropeptide
- Poor attendance at the SASP annual meeting
- … OF SOLUBLE TAU AGGREGATES IN BRAIN MICROVASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL CELLS PROMOTES CELLULAR SENESCENCE/SASP AND BLOCKS ENOS …
- Senescence-Associated Secretory Pheno-type (SASP)
- Provisional programme for SASP congress
- THE MANIPULATIVE THERAPISTS’GROUP OF THE SASP
- Algorithms for arithmetic operation in a systolic array of single-bit processor (SASP)
- SASP Erwin Schrödinger Gold Medal 2010
- Lipid metabolism is involved in mitotic slippage-induced SASP upon treatment with anti-mitotic drugs
- The role of SASP in tumor microenvironment.
- Effection of Tripterygium Wilfordii Unions SASP Moves to Rheumatoid Arthritis [J]
- Prospects for (p, pi) physics in the Delta region using the SASP spectrometer
- Scientific presentations at the 2017 annual meeting of the Scandinavian Association for the Study of Pain (SASP)
- Assessing Functional Roles of the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP)
- Report of first AGM of obstetric group of SASP
- Conceptual design study Science and Application Space Platform SASP. Volume 1: Executive summary
- Pharmacokinetics of Salazosulfapyridine (Sulfasalazine, SASP)(IV): Pharmacokinetics of SASP in the rat following consecutive oral doses.
- Treating 150 Cases with Active Ankylosing Spondylitis with Chinese Peashrub Root Powder Capsule combined with SASP
- TOE MANIPULATIVE THERAPISTS’GROUP OF THE SASP
- … of long term radionuclide data for lead-210 and beryllium-7 collected at Murdoch University for the Surface Air Sampling Program (SASP) of the Environmental …
- Human SLE bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) have a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) mediated by a MAVS-IFNβ …
- Secondary amine selective Petasis (SASP) bioconjugation
- The senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) from mesenchymal stromal cells impairs growth of immortalized prostate cells but has no effect on …
- Convergent validity of the Richmond Reversal Rating in relation to visual-spatial perception as measured by the SASP
- In Search of Nutritional Anti-Aging Targets: TOR Inhibitors, SASP Modulators And BCL-2 Family Suppressors
- Non-overlapping roles of the RP and p19Arf pathways in protecting oncogenic induced HCC and their roles to modulate SASP
- XXth Symposium on Atomic, Cluster and Surface Physics 2016 (SASP 2016)
- Hep:: HepNames:: Institutions:: Conferences:: Jobs:: Experiments:: Journals:: Help Home> Conferences> DASS/SASP (Dual Arm Spectrometer System …
- 14 ANALYSIS OF SASP REFERENCES: INSIGHTS FOR EFFECTIVE CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION FOR UROLOGISTS
- Correction to: Optimisation of a screening platform for determining IL-6 inflammatory signalling in the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
- Brief Overview of the ECJ Judgement in the Case of Olympique Lyonais SASP v. Olivier Bernard and Newcastle United Football Club
- The Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) and Redox-Dependent Invasion of Metastatic Cancer Cells
- PO-112 The senescence associated secretory phenotype (SASP)-factor ccl2 fosters vascular dysfunction and endothelial cell loss in radiation-induced lung disease
- Efficacy of artemisinin and SASP on chicken coccidiosis induced by Eimeria tenella.
- AISA can control the inflammatory facet of SASP
- Momentum Calibration for the SASP Spectrometer
- … Article Folic Acid Supplementation Suppresses Sleep Deprivation-Induced Telomere Dysfunction and Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP)
- Endothelial senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) is regulated by Makorin-1 ubiquitin E3 ligase
- SASP. Contributions to the 13. Symposium on atomic and surface physics and related topics
- Folic Acid Supplementation Suppresses Sleep Deprivation-Induced Telomere Dysfunction and Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP)
- SKYNET Applications Software Package (SASP) Operator’s and User’s Handbook.
- Unmasking senescence: context-dependent effects of SASP in cancer
- VOLUME II-TECHNICAL REPORT PART A SASP SPECIAL EMPHASIS TRADE STUDIES’k
- Sexual Assault Services Program (SASP) and Sexual Offense Services (SOS)
- Review of Best Practices for ICJI Program Areas: Sexual Assault Services Program (SASP) and Sexual Offense Services (SOS)
- Chronic resveratrol treatment inhibits MRC5 fibroblast SASP-related pro-tumoral effects on melanoma cells
- P10 CELL SURFACE INTERLEUKIN-1α, WHICH DRIVES THE SENESCENCE-ASSOCIATED SECRETORY PHENOTYPE (SASP), IS TETHERED VIA IL …
- The annual meeting of the Scandinavian Association for the Study of Pain (SASP) 18-20 April 2018− S1
- Science and Applications Space Platform (SASP) End-to-End Data System Study
- … Responses and Protection in Dairy Cows Vaccinated withStaphylococcus aureusSurface Proteins (SASP) andStaphylococcus chromogenes Surface Proteins …
- … /REPERFUSION (I/R) INDUCED INFLAMMAGING BY INHIBITING SENESCENCE-ASSOCIATED SECRETORY PHENOTYPE (SASP) IN TUBULAR EPITHELIAL …
- SASP-Symposium on atomic, cluster and surface physics’ 94
- The Triumf Second Arm Spectrometer System (SASP)
- Proceedings of the DASS/SASP (Dual Arm Spectrometer System/Second Arm Spectrometer) Workshop, Vancouver, March 17-18, 1986
- The Abstracts of SASP 2001: The Seventh Annual Meeting of the Society of Australasian Social Psychologists
- SASP’86: Symposium on atomic and surface physics
- 1‐Amino‐2‐(Silyloxymethyl) Pyrrolidines (SASP)
- Address at the opening Jubilee Congress of the SASP by the Minister of Health and Welfare
- SASP. Symposium on atomic and surface physics’ 82. Contributions
[HTML] Senolytics: A Translational Bridge Between Cellular Senescence and Organismal Aging
BIOMARKERS FOR CELLULAR SENESCENCE
[HTML] Potential Role of Cellular Senescence in Asthma
The Heterogeneity of Senescent Cells
Perspectives of the potential implications of polyphenols in influencing the interrelationship between oxi-inflammatory stress, cellular senescence and …
[PDF] Special issue on “Molecular genetics of aging and longevity”: a critical time in the field of geroscience
Pharmacotherapy to gene editing: potential therapeutic approaches for Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome
[PDF] Establishment of a Temperature-Sensitive Model of Oncogene-Induced Senescence in Angiosarcoma Cells
Cancer as a disease of old age: changing mutational and microenvironmental landscapes
Preadipocyte secretory factors differentially modulate murine macrophage functions during aging which are reversed by the application of phytochemical EGCG
[PDF] Novel properties of mature adipocytes in obesity and hyperinsulinemia
[PDF] Establishment of a Temperature-Sensitive Model of Oncogene-Induced Senescence in Angiosarcoma Cells
Cancer as a disease of old age: changing mutational and microenvironmental landscapes
Preadipocyte secretory factors differentially modulate murine macrophage functions during aging which are reversed by the application of phytochemical EGCG
[PDF] Novel properties of mature adipocytes in obesity and hyperinsulinemia
Targeted reduction of senescent cell burden alleviates focal radiotherapy-related bone loss.
Treating cognitive decline and other neurodegenerative conditions by selectively removing senescent cells from neurological tissue
[HTML] Therapeutic senescence via GPCR activation in synovial fibroblasts facilitates resolution of arthritis
[HTML] SENEBLOC, a long non-coding RNA suppresses senescence via p53-dependent and independent mechanisms
Repurposing cell penetrating peptides and their novel derivatives and iopromide and iodo-aryl carbonates for treatment of senescence-related diseases and disorders
[HTML] Implications of Oxidative Stress and Cellular Senescence in Age-Related Thymus Involution
The human thymus is a primary lymphoepithelial organ which supports the production of self-tolerant T cells with competent and regulatory functions. Paradoxically, despite the crucial role that it exerts in T cell-mediated immunity …
[HTML] Taking in consideration the bystander effects of articular senescence
RNA Biology Provides New Therapeutic Targets for Human
The ageing epigenome and its rejuvenation
Ageing is characterized by the functional decline of tissues and organs and the increased risk of ageing-associated disorders. Several ‘rejuvenating’ interventions have been proposed to delay ageing and the onset of …
[PDF] Beyond Tumor Suppression: Senescence in Cancer Stemness and Tumor Dormancy
The Heterogeneity of Senescent Cells
[PDF] Regorafenib Alteration of the BCL-xL/MCL-1 Ratio Provides a Therapeutic Opportunity for BH3-Mimetics in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Models
Cellular Senescence and Tumor Promotion
[PDF] Henry Ford Health System Scholarly Common s
The role of adipose tissue senescence in obesity-and ageing-related metabolic disorders
Skip to Main Content …
[PDF] Stress-induced Cellular Senescence Contributes to Chronic Inflammation and Cancer Progression
[PDF] Tissue specificity of senescent cell accumulation during physiologic and accelerated aging of mice
Cardiac Glycosides as Senolytic Compounds
[HTML] Endothelial progeria induces adipose tissue senescence and impairs insulin sensitivity through senescence associated secretory phenotype
[HTML] Urogenital Support
[PDF] Transplanting cells from old but not young donors causes physical dysfunction in older recipients
[PDF] Preclinical Pharmacological Activities of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate in Signaling Pathways: An Update on Cancer
Senolytic compositions and uses thereof
Impaired Myofibroblast Dedifferentiation Contributes to Non-Resolving Fibrosis in Aging
[HTML] Browsed by Tag: Mitochondrial mutations
[PDF] Cellular senescence contributes to age‐dependent changes in circulating extracellular vesicle cargo and function
Therapy-induced senescence—an induced synthetic lethality in liver cancer?
Dasatinib plus quercetin prevents uterine age-related dysfunction and fibrosis in mice.
[HTML] CMV-independent increase in CD27− CD28+ CD8+ EMRA T cells is inversely related to mortality in octogenarians
Dasatinib, a second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces melanogenesis via ERK-CREB-MITF-tyrosinase signaling in normal human melanocytes
[PDF] The role of the microbiota in sedentary life style disorders and ageing: Lessons from the animal kingdom
[HTML] Browsed by Tag: cancer
Pharmacological or genetic depletion of senescent astrocytes prevents whole brain irradiation–induced impairment of neurovascular coupling responses protecting …
[HTML] Astrocyte Support for Oligodendrocyte Differentiation can be Conveyed via Extracellular Vesicles but Diminishes with Age
[HTML] TGF-β1/IL-11/MEK/ERK signaling mediates senescence-associated pulmonary fibrosis in a stress-induced premature senescence model of Bmi-1 deficiency
[HTML] Underlying Histopathology Determines Response to Oxidative Stress in Cultured Human Primary Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells
[HTML] Metabolic Syndrome Support
PDF] Senescent Colon and Breast Cancer Cells Induced by Doxorubicin Exhibit Enhanced Sensitivity to Curcumin, Caffeine, and Thymoquinone
Targeting defective pulmonary innate immunity–A new therapeutic option?
Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease
Cellular senescence: from anti-cancer weapon to anti-aging target
[PDF] Targeting Age-Related Pathways in Heart Failure
[HTML] Autophagy Reprograms Alveolar Progenitor Cell Metabolism in Response to Lung Injury
[HTML] A Newly Synthesized Rhamnoside Derivative Alleviates Alzheimer’s Amyloid-β-Induced Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Cell Senescence through …