Dragons Blood
February 10, 2019
Aloe Arborescens
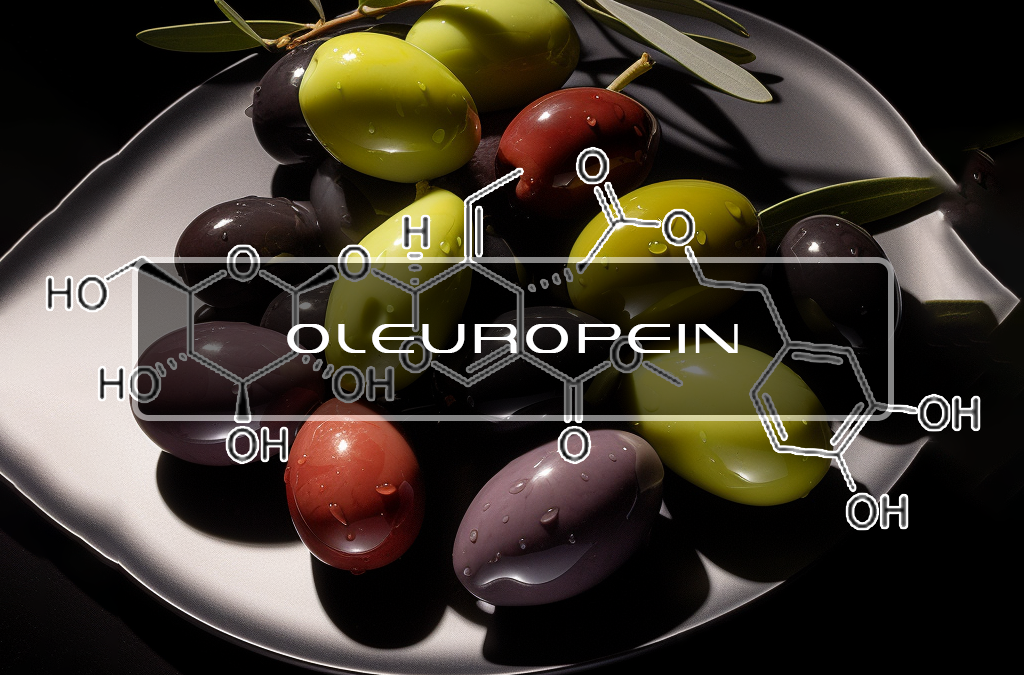
February 12, 2019Oleuropein

Scientists have been able to isolate a molecule in olive that has health and life extending properties. Oleuropein is a type of polyphenol which has been shown to reduce cholesterol, blood pressure, prevent cancer, and oxidative stress.
The compound itself is tangy and bitter that can be found in the higher quality olive oils. This compound also contains a power antioxidant , anti inflammatory and disease fighting capabilities.
The unexpected benefits and unique properties of oleuropein provide ample rationale for continued use and study of this key component of the Mediterranean diet to promote human health.

Benefits of Oleuropein
The data presently available suggest that OLE could provide a protective and therapeutic effect against a number of pathologies, including AD as well as obesity, type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic hepatitis, and other natural or experimentally-induced pathological conditions.
In particular, the recent data on the cellular and molecular correlates of OLE neuroprotection suggest it could also play a therapeutic role against AD.
Oxidative Stress - This study aimed to evaluate the significance of supplementation of oleuropein in reducing oxidative stress and hyperglycemia in alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits.
After induction of diabetes, a significant rise in plasma and erythrocyte malondialdehyde (MDA) and blood glucose as well as alteration in enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants was observed in all diabetic animals.
These results demonstrate that oleuropein may be of advantage in inhibiting hyperglycemia and oxidative stress induced by diabetes and suggest that administration of oleuropein may be helpful in the prevention of diabetic complications associated with oxidative stress.
Antioxidant - The main reaction products obtainable by the hydrolysis of commercially available oleuropein by hyperthermophilic β-glycosidase were purified and structurally characterized by UV and 1H and 13C NMR analyses.
Their antioxidant activity, in particular their capacity to inhibit the fatty acid peroxidation rate, was studied. This molecule, under the reaction conditions (pH 7.0, 60 °C) required for β-glycosidase activity, rapidly gives rise to phenylethanol.
Antimicrobial - Oleuropein, the bitter glucoside in green olives, and products of its hydrolysis were tested for antibacterial action against certain species of lactic acid bacteria involved in the brine fermentation of olives.
Oleuropein was not inhibitory, but two of its hydrolysis products, the aglycone and elenolic acid, inhibited growth of the four species of lactic acid bacteria tested.
Results of a brining experiment indicated that oleuropein is degraded to antibacterial compounds when unheated olives are brined.
mTOR Inhibition - The link between AMPK activation and mTOR inhibition was shown in the OLE-fed animal model in which we found that decreased phospho-mTOR immunoreactivity and phosphorylated mTOR substrate p70 S6K levels match enhanced phospho-AMPK levels, supporting the idea that autophagy activation by OLE proceeds through mTOR inhibition.
Antiviral - Based on laboratory tests, which were done by Dr H. Renis in 1960’s, Olive Leaf Extract has the ability to eliminate viruses like Herpes Zoster, HSV-1 and HSV-2. This ability to kill different viruses is attributed to Oleuropein.
There was also one study done 1993 on humans whose main aim was to test effectiveness of this extract for treating herpes outbreak. Since this study was private there were only 6 participants in it. Three participants, who took Olive Leaf Extract, reported that their herpes lesions disappeared within 2 days. The other participants (who didn’t noticed improvement) were given higher dosage of this extract later. After three days one participant reported that almost all of his/her lessons disappeared and other two participants said they condition improved significantly too. Based on this study it can be said that Olive Leaf Extract shows a lot of potential in treating herpes outbreaks; however more studies are needed to fully confirm effectiveness of this extract.
Advanced Glycation End Product Inhibitor - Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are readily formed and accumulated with sustained hyperglycemia, contribute to the development of diabetic complications. As a consequence, inhibition of AGE formation constitutes an attractive therapeutic/preventive target. In the current study, we explored the phytochemical composition and the in vitro effect of two different olive leaf extracts (an aqueous and a methanolic) on AGE formation. The methanolic olive leaf extract inhibited fluorescent AGE formation in a bovine serum albumin (BSA)-ribose system, whereas the aqueous extract had no effect in both BSA-fructose and BSA-ribose systems.
The phytochemical profile was investigated with liquid chromatography-ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) diode array coupled to electrospray ionization multistage mass spectrometry (LC/DAD/ESI-MSn). Quantification of the major phenolic compounds was performed with high performance liquid chromatography with UV-Vis diode array detection and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Among the major phenolic components (luteolin, hydroxytyrosol, luteolin-4′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, and oleuropein), luteolin and luteolin-4′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside were assigned as potent inhibitors of AGE formation. The extraction procedure greatly affects the composition and therefore the anti-glycation potential of olive leaves.
Anti-Candida - In the present study we investigated activity of oleuropein, a complex phenol present in large quantities in olive tree products, against opportunistic fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Oleuropein was found to have in vitro antifungal activity with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 12.5 mg·mL−1. Morphological changes in the nuclei after staining with fluorescent DNA-binding dyes revealed that apoptosis was a primary mode of cell death in the analyzed samples treated with subinhibitory concentrations of oleuropein. Our results suggest that this antifungal agent targets virulence factors essential for establishment of the fungal infection.
We noticed that oleuropein modulates morphogenetic conversion and inhibits filamentation of C. albicans. The hydrophobicity assay showed that oleuropein in sub-MIC values has significantly decreased, in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, the cellular surface hydrophobicity (CSH) of C. albicans, a factor associated with adhesion to epithelial cells. It was also demonstrated that the tested compound inhibits the activity of SAPs, cellular enzymes secreted by C. albicans, which are reported to be related to the pathogenicity of the fungi. Additionally, we detected that oleuropein causes a reduction in total sterol content in the membrane of C. albicans cells, which might be involved in the mechanism of its antifungal activity.
In this study, oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol, major phenolic compound of olive oil, was studied for its effects on growth in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells using assays for proliferation (MTT assay), cell viability (Guava ViaCount assay), cell apoptosis, cellcycle (flow cytometry). Oleuropein or hydroxytyrosol decreased cell viability, inhibited cell proliferation, and induced cell apoptosis in MCF-7 cells.
Oleuropein or hydroxytyrosol decrease of the number of MCF-7 cells by inhibiting the rate of cell proliferation and inducing cell apoptosis.
The anticancer potential of dry olive leaf extract (DOLE) represents the net effect of multilevel interactions between different biologically active compounds from the extract, cancer cells and conventional therapy. In this context, it was of primary interest to evaluate the influence of DOLE on progression of the highly malignant, immuno- and chemoresistant type of skin cancer-melanoma.
The results of this study indicate that DOLE possesses strong antimelanoma potential. When DOLE was applied in combination with different chemotherapeutics, various outcomes, including synergy and antagonism, were observed.
Neuroprotection - In TgCRND8 (Tg) mice we checked the dose–response effect of diet supplementation with oleuropein aglycone (OLE) at 12.5 or 0.5 mg kg−1 of diet.
Our results extend previous data showing that the effects of OLE on behavioural performance and neuropathology are dose‐dependent and not closely related to OLE by itself. In fact, diet supplementation with the same dose of a mix of polyphenols found in olive mill waste water resulted in comparable neuroprotection.
Lower Blood Pressure - The olive leaf extract EFLA®943, having antihypertensive actions in rats, was tested as a food supplement in an open study including 40 borderline hypertensive monozygotic twins.
Cholesterol levels decreased for all treatments with significant dose‐dependent within‐pair differences for LDL‐cholesterol.
The study confirmed the antihypertensive and cholesterol‐lowering action of EFLA®943 in humans.
Brown Fat Activation - The intravenous administration of oleuropein and oleuropein aglycone significantly increased plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline concentrations. Furthermore, oleuropein aglycone induced the secretions of noradrenaline and adrenaline about ten fold more potently than oleuropein. These results suggest that the phenolic compound oleuropein in EV-olive oil enhances thermogenesis by increasing the UCP1 content in IBAT and noradrenaline and adrenaline secretions in rats.
Protects Liver From Alcohol - The aim of the present study was to evaluate the antioxidant properties of oleuropein on ethanol-induced oxidative damage and to examine its beneficial effects on liver function. Thirty-two adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four equal groups: the first group served as untreated control. The second group of rats were given ethanol (4 g/kg) orally. Group 3 received oral oleuropein (15 mg/kg). The final group of rats were fed ethanol (4 g/kg), 120 min after oral administration of oleuropein (15 mg/kg).
All of the treatments were applied for 4 weeks via gavage. Administration of ethanol to rats induced toxicity in their liver, as shown by the significant elevation in the serum levels of transaminases, total cholesterol as well as liver histopathological findings. Elevation of glutathione peroxidase activity, the hepatic main antioxidant enzyme, and total glutathione was observed to suppress oxidative stress in the ethanol group. TBARS (an indicator of lipid peroxidation) concentration is also increased in ethanol-treated rats. In contrast, oleuropein during ethanol treatment in rats resulted in a higher antiperoxidative enzyme activity, catalase, and inhibited toxicity to the liver, as monitored by the reduction in ALT and AST levels and TBARS concentration.
It is suggested that oleuropein possesses beneficial antioxidant effects against ethanol-induced liver toxicity, and therefore use of olive leaf extract may have prophylactic value in reducing the common complications resulting from oxidative stress in alcoholism.
AMPK activation - Oleuropein significantly enhanced glucose consumption and the phosphorylation of AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase/ACC (acetyl-CoA carboxylase)) and MAPKs (mitogen-activated protein kinases), but not PI3 kinase (Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase)/Akt. However, the co-treatment of oleuropein and insulin improved the insulin sensitivity via insulin-dependent (PI3 kinase/Akt) and insulin independent (AMPK/ACC) pathways. These results could be confirmed from the findings of GLUT4 translocation which was strongly enhanced in the case of oleuropein.
Lifespan Extension - Importantly, oleuropein-treated cultures exhibit a delay in the appearance of senescence morphology and their life span is extended by approximately 15%. In summary, these data demonstrate the beneficial effect of oleuropein on human fibroblasts undergoing replicative senescence and provide new insights towards enhancement of cellular antioxidant mechanisms by natural compounds that can be easily up-taken through normal diet.

Related Products
Oleuropein (Olive Leaf)
- Anti-aging properties of the olive constituent oleuropein in human cells
- OLEUROPEIN EXERTS ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY AND REDUCES THE EXPRESSION OF COX-2 AND PROinflammatory cytokines IN CACO-2 CELLS AND …
- Dose–response study of effect of oleuropein, an olive oil polyphenol, in an ovariectomy/inflammation experimental model of bone loss in the rat
- The leishmanicidal activity of oleuropein is selectively regulated through inflammation-and oxidative stress-related genes
- Oleuropein down-regulated IL-1β-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in human synovial fibroblast cell line SW982
- Oleuropein Curtails Pulmonary inflammation and Tissue Destruction in Models of Experimental Asthma and Emphysema
- Correction: Oleuropein down-regulated IL-1β-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in human synovial fibroblast cell line SW982
- Oleuropein ameliorates airway inflammation and emphysema in a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease model
- Evaluation of the effect of oleuropein on alveolar bone loss, inflammation, and apoptosis in experimental periodontitis
- Oleuropein ameliorates cisplatin-induced oxidative damage, inflammation and apoptosis in mice kidneys by modulating CYP2E1, NF-κB and ERK1/2 expression
- OLEUROPEIN IN INHIBITION OF ARTERIAL inflammation
- Anti-inflammatory effect of oleuropein in experimental rat spinal cord trauma
- Oleuropein suppresses LPS-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 cell and zebrafish
- Hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein from olive leaves: Potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities
- Oleuropein inhibits the IL-1β-induced expression of inflammatory mediators by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes
- Oleuropein decreases cyclooxygenase-2 and interleukin-17 expression and attenuates inflammatory damage in colonic samples from ulcerative colitis patients
- Anti-inflammatory effect of oleuropein on microglia through regulation of Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission
- Oleuropein is responsible for the major anti-inflammatory effects of olive leaf extract
- Anti-inflammatory and antitumor effects of hydroxytyrosol but not oleuropein on experimental glioma in vivo. A putative role for the renin-angiotensin system
- Antioxidant Status And Anti-inflammatory Effects Of Oleuropein In Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy In Rats
- Assessment of the anti-inflammatory, analgesic and sedative effects of oleuropein from Olea europaea L.
- The efficacy of oleuropein against non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drug induced toxicity in rat kidney
- Oleuropein reduces inflammatory mediators and hepatic immune cells infiltration in a mouse model of NAFLD
- Oleuropein suppresses oxidative, inflammatory, and apoptotic responses following glycerol-induced acute kidney injury in rats
- P108 Oleuropein decreases interleukin-17 and attenuates inflammatory damage in colonic mucosa from ulcerative colitis patients
- Olive secoiridoid oleuropein and its semisynthetic acetyl-derivatives reduce LPS-induced inflammatory response in murine peritoneal macrophages via JAK-STAT …
- … aromatica (turmeric) and Zingiber officinale (ginger); the sweet compounds hernandulcin and 4-hydroxyhernandulcin; the anti-inflammatory bisabolol (that promotes …
- OC. 14.4: Oleuropein Decreases Interleukin (IL)-17 and Attenuates inflammatory Damage in Colonic Mucosa from Ulcerative Colitis Patients
- 676 OLEUROPEIN REDUCES ENDOTHELIAL PROGENITOR CELLS senescence AND PROTECTS AGAINST OXIDATIVE STRESS INDUCED BY …
- Oleuropein aglycone attenuates the pro-angiogenic phenotype of senescent fibroblasts: A functional study in endothelial cells