Chlorogenic Acid (CGA)
March 21, 2019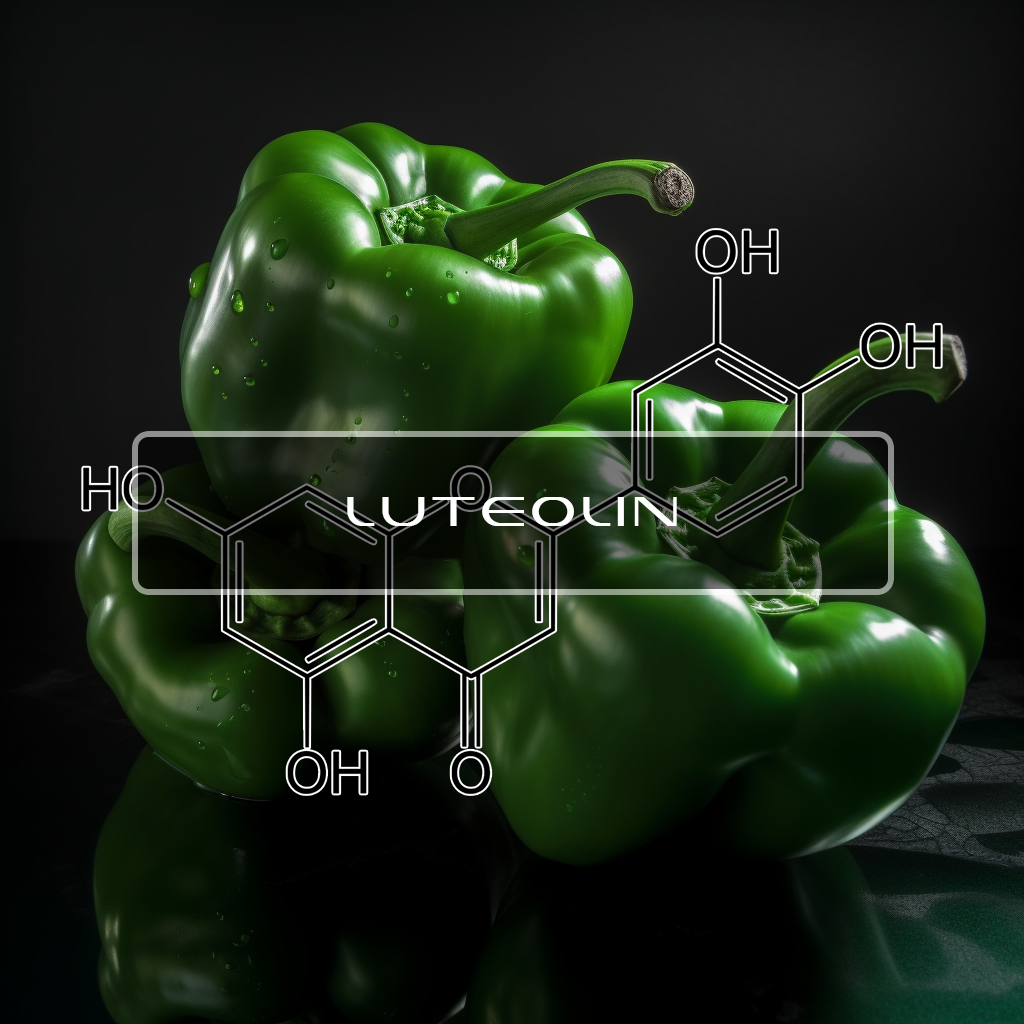
Luteolin
April 11, 2019MTOR: The Rapid Aging Pathway
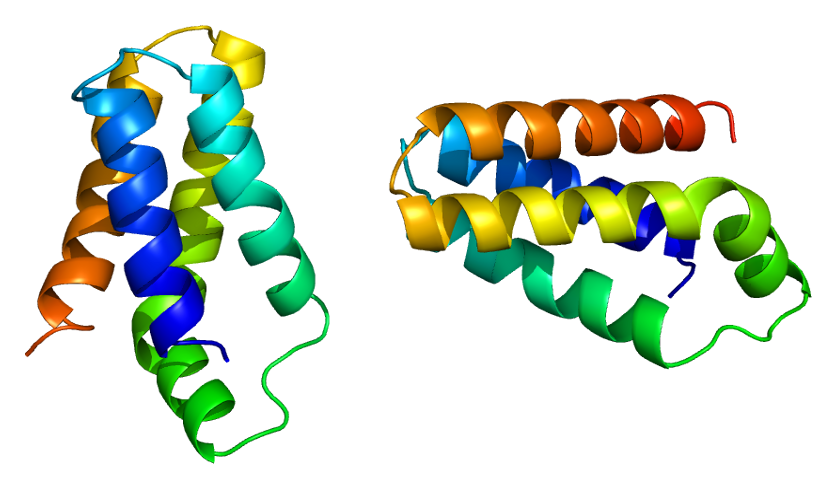
“The mammalian target of rapamycin(mTOR), also known as the mechanistic target of rapamycin and FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1 (FRAP1), is a kinase that in humans is encoded by the MTOR gene.[5][6][7] mTOR is a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase family of protein kinases.[8]
mTOR links with other proteins and serves as a core component of two distinct protein complexes, mTOR complex 1 and mTOR complex 2, which regulate different cellular processes.[9] In particular, as a core component of both complexes, mTOR functions as a serine/threonine protein kinase that regulates cell growth, cell proliferation, cell motility, cell survival, protein synthesis, autophagy, and transcription.[9][10] As a core component of mTORC2, mTOR also functions as a tyrosine protein kinase that promotes the activation of insulin receptors and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors.[11]mTORC2 has also been implicated in the control and maintenance of the actin cytoskeleton.[9][12]
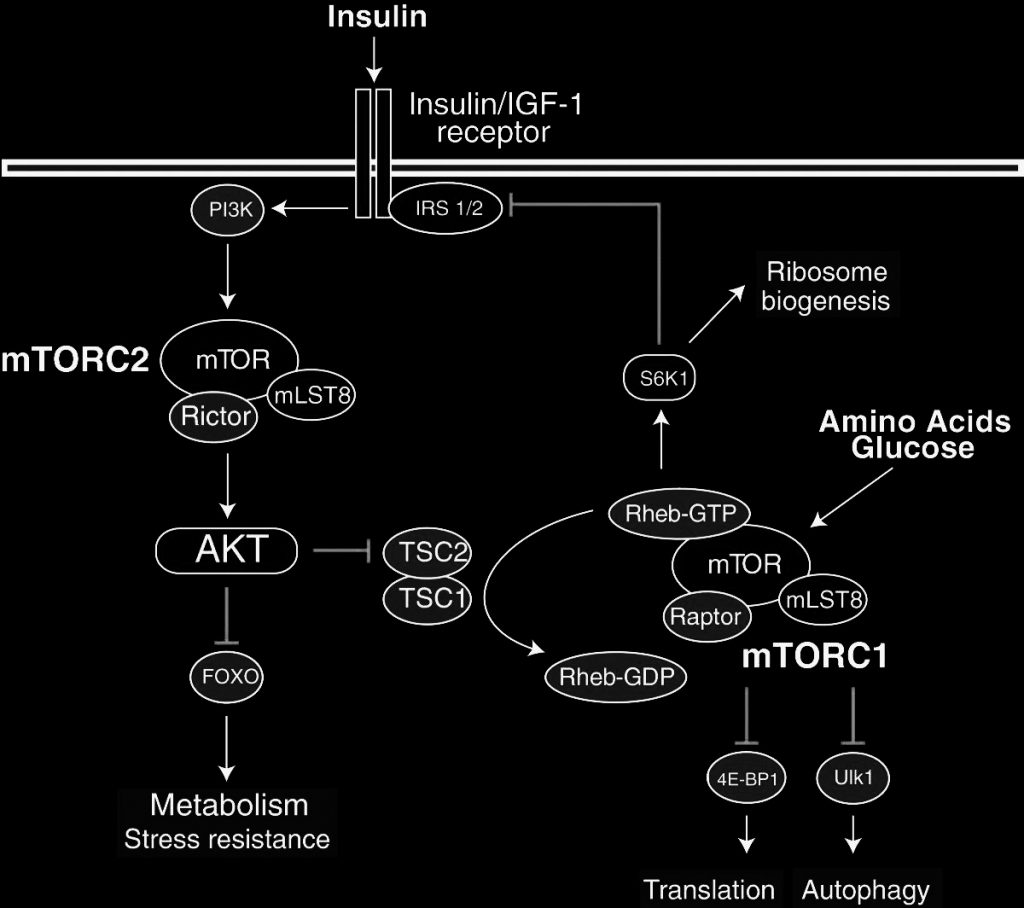
mTOR integrates the input from upstream pathways, including insulin, growth factors (such as IGF-1 and IGF-2), and amino acids.[10] mTOR also senses cellular nutrient, oxygen, and energy levels.[27] The mTOR pathway is a central regulator of mammalian metabolism and physiology, with important roles in the function of tissues including liver, muscle, white and brown adipose tissue,[28] and the brain, and is dysregulated in human diseases, such as diabetes, obesity, depression, and certain cancers.[29][30]
Decreased TOR activity has been found to increase life span in S. cerevisiae, C. elegans, and D. melanogaster.[61][62][63][64] The mTOR inhibitor rapamycin has been confirmed to increase lifespan in mice.[65][66][67][68][69]
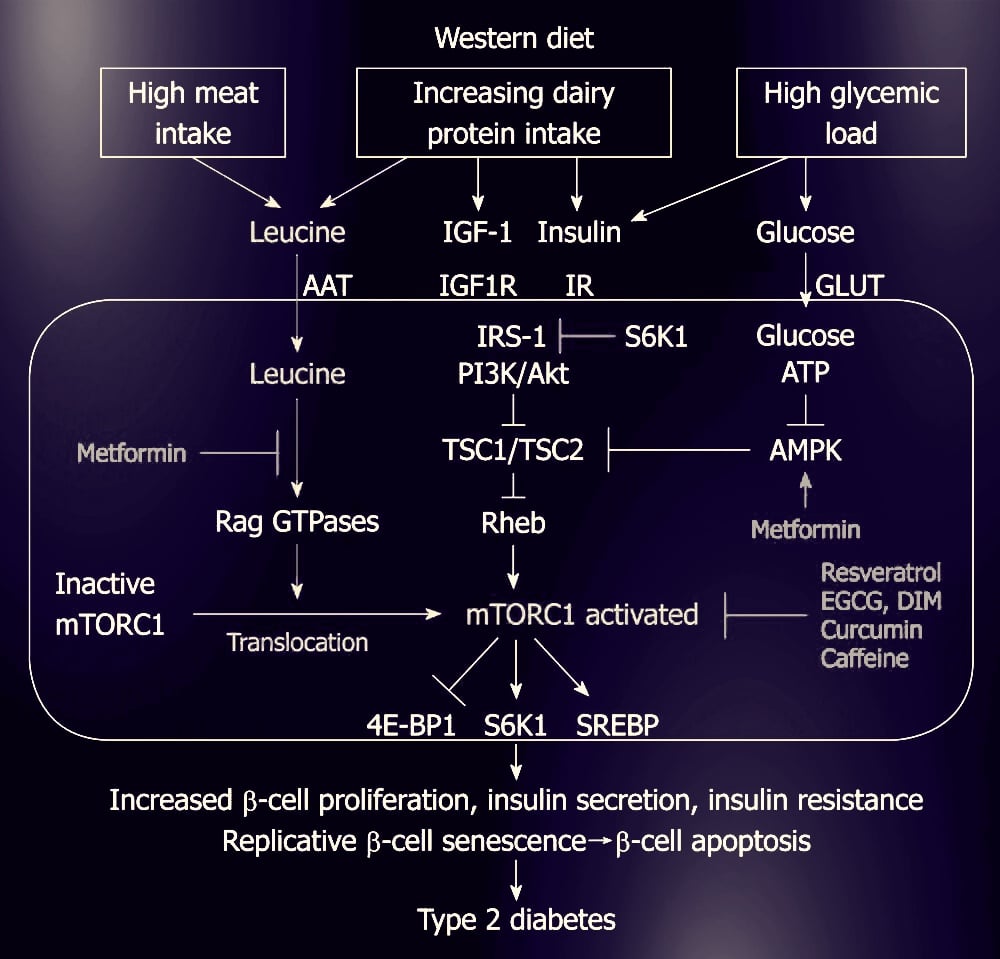
It is hypothesized that some dietary regimes, like caloric restriction and methionine restriction, cause lifespan extension by decreasing mTOR activity.[61][62] Some studies have suggested that mTOR signaling may increase during aging, at least in specific tissues like adipose tissue, and rapamycin may act in part by blocking this increase.[70] An alternative theory is mTOR signaling is an example of antagonistic pleiotropy, and while high mTOR signaling is good during early life, it is maintained at an inappropriately high level in old age. Calorie restriction and methionine restriction may act in part by limiting levels of essential amino acids including leucine and methionine, which are potent activators of mTOR.[71] The administration of leucine into the rat brain has been shown to decrease food intake and body weight via activation of the mTOR pathway in the hypothalamus.[72]
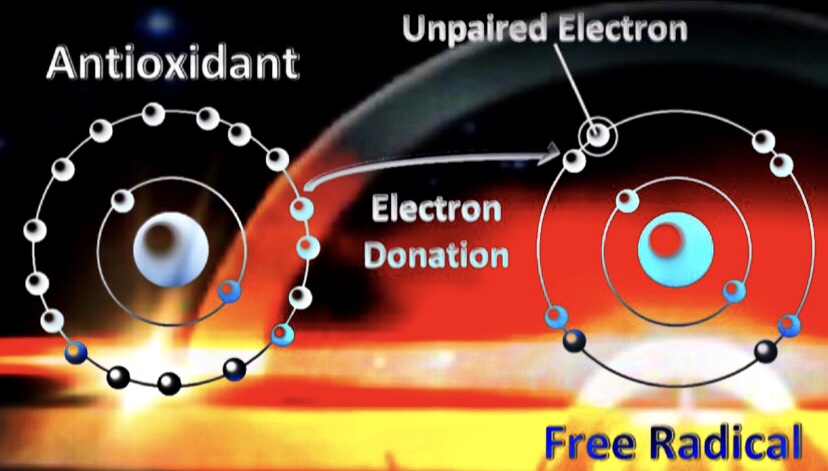
According to the free radical theory of aging,[73] reactive oxygen species cause damage of mitochondrial proteins and decrease ATP production. Subsequently, via ATP sensitive AMPK, the mTOR pathway is inhibited and ATP consuming protein synthesis is downregulated, since mTORC1 initiates a phosphorylation cascade activating the ribosome.[16] Hence, the proportion of damaged proteins is enhanced. Moreover, disruption of mTORC1 directly inhibits mitochondrial respiration.[74]These positive feedbacks on the aging process are counteracted by protective mechanisms: Decreased mTOR activity (among other factors) upregulates glycolysis[74] and removal of dysfunctional cellular components via autophagy.[73]“ — Wikipedia
Simplified in plain English:
KEEP MTOR TURNED OFF as often as possible.
MTOR = RAPID AGING.
You want ZERO amino acids (ie. protein), glucose or MCT fats during fasting window as these all require insulin and ACTIVATE MTOR. You want ZERO CALORIES. ZERO INSULIN SECRETION.
Whats left?
Interstellar Blends, matcha green tea, and black coffee are ok and all inhibit mTOR; utilize these during your fasting window to remain energized, mentally clear, emotionally elevated and feeling all around amazing while staying young by keeping mTOR turned OFF.
1000 SCIENTIFIC STUDIES
- mTOR in Aging , metabolism, and cancer
- mTOR Regulation and Therapeutic Rejuvenation of Aging Hematopoietic Stem Cells
- Rapalogs and mTOR inhibit ors as anti-Aging therapeutics
- mTOR Mediates Wnt-Induced Epidermal Stem Cell Exhaustion and Aging
- Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK and Pi3k /PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathways in controlling growth and sensitivity to therapy-implications for cancer and Aging
- calorie restriction : Decelerating mTOR -driven Aging from cells to organisms (including humans)
- BMAL1-dependent regulation of the mTOR signaling pathway delays Aging
- Increased Mammalian Lifespan and a Segmental and Tissue-Specific Slowing of Aging after Genetic Reduction of mTOR Expression
- PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling: Impaired on/off switches in Aging , cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease
- Molecular damage in cancer : an argument for mTOR -driven Aging
- mTOR signaling in Aging and neurodegeneration: At the crossroad between metabolism dysfunction and impairment of autophagy
- Caveolin-1 and Accelerated Host Aging in the Breast Tumor Microenvironment: Chemoprevention with Rapamycin, an mTOR inhibit or and Anti-Aging Drug
- mTOR activation is a biomarker and a central pathway to autoimmune disorders, cancer , obesity, and Aging
- Potential anti-Aging agents suppress the level of constitutive mTOR – and DNA damage- signaling
- mTOR signalling: the molecular interface connecting metabolic stress, Aging and cardiovascular diseases
- mTOR Signaling from Cellular Senescence to Organismal Aging
- Modulating mTOR in Aging and Health
- Ral and Rheb GTPase Activating Proteins Integrate mTOR and GTPase Signaling in Aging , Autophagy, and Tumor Cell Invasion
- mTOR and autophagy in normal brain Aging and caloric restriction ameliorating age-related cognition deficits
- From growing to secreting: New roles for mTOR in Aging cells
- mTOR inhibit ion: From Aging to Autism and Beyond
- Mechanistic or mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) may determine robustness in young male mice at the cost of accelerated Aging
- Effects of Aging and gender on muscle mass and regulation of Akt-mTOR -p70s6k related signaling in the F344BN rat model
- M(o)TOR of Aging : mTOR as a universal molecular hypothalamus
- mTOR -driven quasi-programmed Aging as a disposable soma theory: Blind watchmaker vs. intelligent designer
- longevity Pathways (mTOR , SIRT, insulin /IGF-1) as Key Modulatory Targets on Aging and Neurodegeneration
- Aging and cancer : can mTOR inhibit ors kill two birds with one drug?
- mTOR and its link to the picture of Dorian Gray – re-activation of mTOR promotes Aging
- Aberrant mTOR activation in senescence and Aging : A mitochondrial stress response?
- The proliferation of amplifying neural progenitor cells is impaired in the Aging brain and restored by the mTOR pathway activation
- Kinase mTOR : Regulation and role in maintenance of cellular homeostasis, tumor development, and Aging
- HMGA2 regulates the in vitro Aging and proliferation of human umbilical cord blood-derived stromal cells through the mTOR /p70S6K signaling pathway
- Angiotensin II blockade: how its molecular targets may signal to mitochondria and slow Aging . Coincidences with calorie restriction and mTOR inhibit ion
- Coenzyme Q10 inhibit s the Aging of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induced by D-Galactose through Akt/mTOR Signaling
- Cell cycle arrest is not yet senescence, which is not just cell cycle arrest: terminology for TOR-driven Aging
- Ampelopsin attenuates brain Aging of D-gal-induced rats through miR-34a-mediated SIRT1/mTOR signal pathway
- Vascular mTOR -dependent mechanisms linking the control of Aging to Alzheimer’s disease
- mTOR as Regulator of Lifespan, Aging , and Cellular Senescence: A Mini-Review
- restriction on an Energy-Dense Diet Improves Markers of Metabolic Health and Cellular Aging in Mice Through Decreasing Hepatic mTOR Activity
- mTOR : at the crossroads of Aging , chaperones, and Alzheimer’s disease
- Adaptation to chronic mTOR inhibit ion in cancer and in Aging
- The Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/mTOR Pathway as a Therapeutic Target for Brain Aging and Neurodegeneration
- Alleviation of senescence and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in Aging kidney by short-term caloric restriction and caloric restriction mimetics via modulation of AMPK /mTOR signaling
- Erythropoietin and mTOR : A “One-Two Punch” for Aging -Related Disorders Accompanied by Enhanced Life Expectancy
- mTOR Signaling Fades POMC Neurons during Aging
- mTOR signaling plays a critical role in the defects observed in muscle‐derived stem/progenitor cells isolated from a murine model of accelerated Aging
- The role of mTOR signaling in Alzheimer disease
- Conservative Growth Hormone/IGF-1 and mTOR Signaling Pathways as a Target for Aging and cancer Prevention: Do We Really Have an AntiAging Drug
- Gene expression analysis of mTOR pathway: association with human longevity
- Rapamycin-Induced insulin Resistance Is Mediated by mTOR C2 Loss and Uncoupled from longevity
- Diminished mTOR signaling: a common mode of action for endocrine longevity factors
- The Role of mTOR Signaling in Controlling Mammalian Life Span: What a Fungicide Teaches Us About longevity
- longevity Pathways (mTOR , SIRT, insulin /IGF-1) as Key Modulatory Targets on Aging and Neurodegeneration
- PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling: Impaired on/off switches in Aging , cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease
- The role of mitochondria in mTOR ‐regulated longevity
- Augmented autophagy pathways and mTOR modulation in fibroblasts from long-lived mutant mice
- hNAG-1 increases lifespan by regulating energy metabolism and insulin /IGF-1/mTOR signaling
- Rapamycin preserves the follicle pool reserve and prolongs the ovarian lifespan of female rats via modulating mTOR activation and sirtuin expression
- SIRT1 activator (SRT1720) improves the follicle reserve and prolongs the ovarian lifespan of diet-induced obesity in female mice via activating SIRT1 and suppressing mTOR signaling
- Chronic inhibit ion of mTOR by rapamycin modulates cognitive and non-cognitive components of behavior throughout lifespan in mice
- Differential control of ageing and lifespan by isoforms and splice variants across the mTOR network
- mTOR , cancer and Transplantation
- Defining the Role of mTOR in cancer
- Single amino-acid changes that confer constitutive activation of mTOR are discovered in human cancer
- mTOR and cancer : insights into a complex relationship
- mTOR , translation initiation and cancer
- mTOR and cancer therapy
- The Akt-mTOR tango and its relevance to cancer
- mTOR -targeted therapy of cancer with rapamycin derivatives
- An expanding role for mTOR in cancer
- The mTOR Signalling Pathway in Human cancer
- Targeting mTOR signaling for cancer therapy
- Targeting the mTOR Signaling Network for cancer Therapy
- The translational landscape of mTOR signalling steers cancer initiation and metastasis
- Hypoxia signalling through mTOR and the unfolded protein response in cancer
- Targeting Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling in cancer
- Hypoxia-inducible factor determines sensitivity to inhibit ors of mTOR in kidney cancer
- mTOR and cancer : many loops in one pathway
- mTOR , a novel target in breast cancer : the effect of CCI-779, an mTOR inhibit or, in preclinical models of breast cancer .
- mTOR in Aging , metabolism, and cancer
- mTOR inhibit ors in cancer therapy
- Targeting the mTOR signaling network in cancer
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a target for cancer therapy. therapy
- mTOR signaling and drug development in cancer
- Akt-dependent and -independent mechanisms of mTOR regulation in cancer
- mTOR Complex1–S6K1 signaling: at the crossroads of obesity, diabetes and cancer
- Targeting mTOR : prospects for mTOR complex 2 inhibit ors in cancer therapy
- NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, prevents PI3K signaling and inhibits the growth of cancer cells with activating PI3K mutations.
- Molecular targets for cancer therapy in the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway
- Targeting the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ): a new approach to treating cancer
- mTOR signaling: implications for cancer and anticancer therapy
- GOLPH3 modulates mTOR signalling and rapamycin sensitivity in cancer
- Will mTOR inhibitors make it as cancer drugs?
- Activation of the PTEN/mTOR /STAT3 pathway in breast cancer stem-like cells is required for viability and maintenance
- Inhibition of mTOR activity restores tamoxifen response in breast cancer cells with aberrant Akt Activity.
- Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Escalated Doses of Weekly Intravenous Infusion of CCI-779, a Novel mTOR inhibit or, in Patients With cancer
- Inhibitors of mTOR reverse doxorubicin resistance conferred by PTEN status in prostate cancer cells.
- Targeting AKT/mTOR and ERK MAPK signaling inhibit s hormone-refractory prostate cancer in a preclinical mouse model
- mTOR Complex 2 Is Required for the Development of Prostate cancer Induced by Pten Loss in Mice
- Targeting tumorigenesis: development and use of mTOR inhibit ors in cancer therapy
- Targeting the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer
- Oral mTOR inhibit or Everolimus in Patients With Gemcitabine-Refractory Metastatic Pancreatic cancer
- mTOR mediated anti-cancer drug discovery
- Targeting PI3 Kinase/AKT/mTOR Signaling in cancer
- Phase II Study of Temsirolimus (CCI-779), a Novel inhibit or of mTOR , in Heavily Pretreated Patients With Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast cancer
- AKT and mTOR phosphorylation is frequently detected in ovarian cancer and can be targeted to disrupt ovarian tumor cell growth
- inhibit ion of Pi3k /mTOR Leads to Adaptive Resistance in Matrix-Attached cancer Cells
- Dual inhibition of mTOR and estrogen receptor signaling in vitro induces cell death in models of breast cancer.
- PI 3-kinase, mTOR , protein synthesis and cancer
- The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in endometrial cancer.
- Current treatment strategies for inhibit ing mTOR in cancer
- Targeted Therapy for Advanced Prostate cancer : inhibit ion of the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway
- Not all substrates are treated equally: Implications for mTOR , rapamycin-resistance, and cancer therapy
- mTOR inhibit ors in the treatment of cancer
- Role of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR signaling in the cell cycle progression of human prostate cancer
- The Molecular Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) as a Therapeutic Target Against cancer
- Targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway in castration-resistant prostate cancer
- Expression of mTOR signaling pathway markers in prostate cancer progression
- mTOR Pathway and mTOR inhibit ors as Agents for cancer Therapy
- The Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway in breast cancer : targets, trials and biomarkers
- A Link between mir-100 and FRAP1/mTOR in Clear Cell Ovarian cancer
- Targeting mTOR globally in cancer : Thinking beyond rapamycin
- Aspirin inhibit s mTOR Signaling, Activates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase, and Induces Autophagy in Colorectal cancer Cells
- The mTOR Pathway: A New Target in cancer Therapy
- Phosphatidic acid signaling to mTOR : Signals for the survival of human cancer cells
- Adiponectin inhibit s colorectal cancer cell growth through the AMPK /mTOR pathway
- The clinical effect of the dual-targeting strategy involving PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAS/MEK/ERK pathways in patients with advanced cancer.
- G1 cell cycle progression and the expression of G1 cyclins are regulated by Pi3k /AKT/mTOR /p70S6K1 signaling in human ovarian cancer cells
- Targeting Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway in non small cell lung cancer
- Specific apoptosis induction by the dual Pi3k /mTOR inhibit or NVP-BEZ235 in HER2 amplified and PIK3CA mutant breast cancer cells
- Pi3k and mTOR Signaling Pathways in cancer : New Data on Targeted Therapies
- Targeting the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in the treatment of breast cancer
- A Diverse Array of Cancer-Associated MTOR Mutations Are Hyperactivating and Can Predict Rapamycin Sensitivity
- Effects of the mTOR inhibit or sirolimus in patients with hepatocellular and cholangiocellular cancer
- Overcoming cisplatin resistance by mTOR inhibitor in lung cancer.
- Enhancing mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-targeted cancer therapy by preventing mTOR/raptor inhibition-initiated, mTOR/rictor-independent Akt activation.
- Mechanisms of mTOR inhibit or resistance in cancer therapy
- The tumor suppressive microRNA miR-218 targets the mTOR component Rictor and inhibits AKT phosphorylation in oral cancer.
- Pi3k /Akt/mTOR inhibit ors in breast cancer
- mTOR signaling for biological control and cancer
- The Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in ovarian cancer
- Acquisition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotypes is associated with activation of the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway in prostate cancer radioresistance
- Novel Expression Patterns of Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway Components in Colorectal cancer
- Targeting mTOR for cancer Treatment
- mTOR Signaling Pathway Is a Target for the Treatment of Colorectal cancer
- mTOR signal and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha regulate CD133 expression in cancer cells.
- mTOR Signaling Pathway and mTOR inhibit ors in cancer Therapy
- Alternative phospholipase D/mTOR survival signal in human breast cancer cells
- Quercetin induces protective autophagy in gastric cancer cells: Involvement of Akt-mTOR – and hypoxia-induced factor 1α-mediated signaling
- inhibit ors of the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway: New Hope for Breast cancer Patients
- A phase 2 study with a daily regimen of the oral mTOR inhibit or RAD001 (everolimus) in patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell cancer
- mTOR inhibit ors in cancer therapy
- GDC-0980 Is a Novel Class I Pi3k /mTOR Kinase inhibit or with Robust Activity in cancer Models Driven by the Pi3k Pathway
- mTOR kinase inhibit ors as potential cancer therapeutic drugs
- Expanding therapeutic targets in bladder cancer : the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway
- Control of PD-L1 Expression by Oncogenic Activation of the AKT-mTOR Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
- Genetic Variations in the Pi3k /PTEN/AKT/mTOR Pathway Are Associated With Clinical Outcomes in Esophageal cancer Patients Treated With Chemoradiotherapy
- AKT and cancer —Is it all mTOR ?
- Targeting the Pi3k -AKT-mTOR signaling network in cancer
- Fisetin induces autophagic cell death through suppression of mTOR signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells
- New targets for therapy in breast cancer: Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) antagonists
- The Potential Role of mTOR inhibit ors in Non-Small Cell Lung cancer
- Potential Targets for Prevention of Colorectal cancer : a Focus on Pi3k /Akt/mTOR and Wnt Pathways
- Oxygen-independent Regulation of HIF-1: Novel Involvement of Pi3k / AKT/mTOR Pathway in cancer
- Decreased lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by mTOR inhibition in head and neck cancer.
- mTOR pathway in colorectal cancer : an update
- mTOR complex component Rictor interacts with PKCzeta and regulates cancer cell metastasis.
- JAK2/STAT5 inhibit ion Circumvents Resistance to Pi3k /mTOR Blockade: A Rationale for Cotargeting These Pathways in Metastatic Breast cancer
- PIK3CA mutation, but not PTEN loss of function, determines the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to mTOR inhibit ory drugs
- Targeting mTOR signaling in lung cancer
- Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cancer stem cells: from basic research to clinical application
- mTOR signaling in human cancer
- Compound C induces protective autophagy in cancer cells through AMPK inhibit ion-independent blockade of Akt/mTOR pathway
- Pi3k -AKT-mTOR signaling in prostate cancer progression and androgen deprivation therapy resistance
- mTOR and cancer : reason for dancing at the crossroads?
- Enhancing mTOR -targeted cancer therapy
- Targeting mTOR pathway: A new concept in cancer therapy
- Hypoxia inhibit s Protein Synthesis through a 4E-BP1 and Elongation Factor 2 Kinase Pathway Controlled by mTOR and Uncoupled in Breast cancer Cells
- Autophagy upregulation by inhibit ors of caspase-3 and mTOR enhances radiotherapy in a mouse model of lung cancer
- Suppression of PTEN function increases breast cancer chemotherapeutic drug resistance while conferring sensitivity to mTOR inhibit ors
- Combined PI3K/mTOR and MEK inhibition provides broad antitumor activity in faithful murine cancer models.
- Dysfunctional AMPK activity, signalling through mTOR and survival in response to energetic stress in LKB1-deficient lung cancer
- Deciphering the Role of Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway in Breast cancer Biology and Pathogenesis
- Targeting mTOR dependency in pancreatic cancer
- Role of the Akt/mTOR survival pathway in cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells
- mTOR as a Target for cancer Therapy
- PLC and Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signalling in disease and cancer
- Downregulation of miR-144 is associated with colorectal cancer progression via activation of mTOR signaling pathway
- Down‐regulation of Notch‐1 and Jagged‐1 inhibit s prostate cancer cell growth, migration and invasion, and induces apoptosis via inactivation of Akt, mTOR , and NF‐κB signaling pathways
- Activation of mTOR signaling pathway contributes to survival of cervical cancer cells
- In vivo antitumor effect of the mTOR inhibit or CCI‐779 and gemcitabine in xenograft models of human pancreatic cancer
- Antidiabetic Drug Metformin Prevents Progression of Pancreatic cancer by Targeting in Part cancer Stem Cells and mTOR Signaling
- The oral mTOR inhibit or RAD001 (everolimus) in combination with letrozole in patients with advanced breast cancer : Results of a phase I study with pharmacokinetics
- mTOR inhibit ors for hepatocellular cancer : a forward-moving target
- Rapamycin and mTOR : a serendipitous discovery and implications for breast cancer
- Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors as Anti-cancer Agents
- Metformin promotes progesterone receptor expression via inhibit ion of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) in endometrial cancer cells
- Relation between outcomes and localisation of p-mTOR expression in gastric cancer
- Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in advanced pancreatic cancer: results of two phase II studies.
- Development of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway inhibit ors and Their Application in Personalized Therapy for Non–Small-Cell Lung cancer
- A phase II trial of the mTOR inhibit or AP23573 as a single agent in advanced endometrial cancer
- Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic cell death through inhibit ion of Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway in human pancreatic cancer stem cells
- MicroRNA-193a-3p and -5p suppress the metastasis of human non-small-cell lung cancer by downregulating the ERBB4/PIK3R3/mTOR /S6K2 signaling pathway
- Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway inhibit ors in cancer : A Perspective on Clinical Progress
- The Pharmacology of mTOR inhibit ion
- PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor VS-5584 preferentially targets cancer stem cells.
- The Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase-Akt-mTOR Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Breast cancer
- Simvastatin inhibit s Renal cancer Cell Growth and Metastasis via AKT/mTOR , ERK and JAK2/STAT3 Pathway
- The Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway is activated in gastric cancer with potential prognostic and predictive significance
- Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptosis in prostate cancer stem cells via Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Recent Clinical Trials of mTOR -Targeted cancer Therapies
- Docosahexaenoic acid induces autophagy through p53/AMPK /mTOR signaling and promotes apoptosis in human cancer cells harboring wild-type p53
- Dietary flavonoid fisetin: A novel dual inhibit or of Pi3k /Akt and mTOR for prostate cancer management
- Thioridazine induces apoptosis by targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway in cervical and endometrial cancer cells
- Identification of S664 TSC2 phosphorylation as a marker for extracellular signal-regulated kinase mediated mTOR activation in tuberous sclerosis and human cancer.
- Diosgenin, a naturally occurring steroid, suppresses fatty acid synthase expression in HER2‐overexpressing breast cancer cells through modulating Akt, mTOR and JNK phosphorylation
- The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in ovarian cancer: therapeutic opportunities and challenges.
- The VEGF pathway and the AKT/mTOR /p70S6K1 signalling pathway in human epithelial ovarian cancer
- Phase I trial of oral mTOR inhibit or everolimus in combination with trastuzumab and vinorelbine in pre-treated patients with HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer
- Effects of a combined treatment with mTOR inhibit or RAD001 and tamoxifen in vitro on growth and apoptosis of human cancer cells
- The Importance of the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway in the Progression of Ovarian cancer
- Blocking on the CXCR4/mTOR signalling pathway induces the anti-metastatic properties and autophagic cell death in peritoneal disseminated gastric cancer cells
- Metformin sensitizes chemotherapy by targeting cancer stem cells and the mTOR pathway in esophageal cancer
- Molecular damage in cancer : an argument for mTOR -driven Aging
- mTOR in renal cell cancer : modulator of tumor biology and therapeutic target
- mTOR activation is a biomarker and a central pathway to autoimmune disorders, cancer , obesity, and Aging
- Allosteric and ATP-competitive kinase inhibit ors of mTOR for cancer treatment
- A review of oral toxicity associated with mTOR inhibit or therapy in cancer patients
- LKB1/AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway in hematological malignancies: From metabolism to cancer cell biology
- Current clinical regulation of Pi3k /PTEN/Akt/mTOR signalling in treatment of human cancer
- Deciphering downstream gene targets of Pi3k /mTOR /p70S6K pathway in breast cancer
- Requirement of the mTOR Kinase for the Regulation of Maf1 Phosphorylation and Control of RNA Polymerase III-dependent Transcription in cancer Cells
- Pi3k /AKT/mTOR signaling pathway as a therapeutic target for ovarian cancer
- Temsirolimus, an mTOR inhibit or, enhances anti-tumour effects of heat shock protein cancer vaccines
- Metformin potentiates the effects of paclitaxel in endometrial cancer cells through inhibit ion of cell proliferation and modulation of the mTOR pathway
- Silibinin inhibit s hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and mTOR /p70S6K/4E-BP1 signalling pathway in human cervical and hepatoma cancer cells: implications for anticancer therapy
- mTOR Signaling in cancer Cell Motility and Tumor Metastasis
- Activation of the mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer and its correlation with the clinicopathologic variables
- Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway inhibit ors enhance radiosensitivity in radioresistant prostate cancer cells through inducing apoptosis, reducing autophagy, suppressing NHEJ and HR repair pathways
- The expanding role of mTOR in cancer cell growth and proliferation
- mTOR as a therapeutic target in patients with gastric cancer
- mTOR -independent 4E-BP1 phosphorylation is associated with cancer resistance to mTOR kinase inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit or Treatment of Pancreatic cancer in a Patient With Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
- Discovery of a Potent, Selective, and Orally Available Class I Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (Pi3k )/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) Kinase inhibit or (GDC-0980) for the Treatment of cancer
- The Dual Pi3k /mTOR inhibit or NVP-BEZ235 Induces Tumor Regression in a Genetically Engineered Mouse Model of PIK3CA Wild-Type Colorectal cancer
- TGF-β Effects on Prostate cancer Cell Migration and Invasion Are Mediated by PGE2 through Activation of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway
- Targeting the deregulated spliceosome core machinery in cancer cells triggers mTOR blockade and autophagy.
- Fucoidan from Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus inhibit s Migration and Invasion of Human Lung cancer Cell via Pi3k -Akt-mTOR Pathways
- Integrated preclinical and clinical development of mTOR inhibit ors in pancreatic cancer
- Targeting YB-1 in HER-2 overexpressing breast cancer cells induces apoptosis via the mTOR/STAT3 pathway and suppresses tumor growth in mice.
- Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is associated with prostate cancer metastasis and chemo/radioresistance via the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Genetic variations in Pi3k -AKT-mTOR pathway and bladder cancer risk
- Targeting Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in the treatment of prostate cancer radioresistance
- Simultaneous inhibit ion of mTOR C1 and mTOR C2 by mTOR kinase inhibit or AZD8055 induces autophagy and cell death in cancer cells
- Targeting mTOR network in colorectal cancer therapy
- Targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Axis by Apigenin for cancer Prevention
- Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling in medullary thyroid cancer : a promising molecular target for cancer therapy
- Genomic Loss of Tumor Suppressor miRNA-204 Promotes cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Activating AKT/mTOR /Rac1 Signaling and Actin Reorganization
- Therapeutic targeting of the mTOR ‐signalling pathway in cancer : benefits and limitations
- From Rapa Nui to rapamycin: targeting Pi3k /Akt/mTOR for cancer therapy
- Pi3k /AKT/mTOR inhibit ors In Ovarian cancer
- Metformin and the mTOR inhibit or Everolimus (RAD001) Sensitize Breast cancer Cells to the Cytotoxic Effect of Chemotherapeutic Drugs In Vitro
- Resveratrol enhances the anti-tumor activity of the mTOR inhibit or rapamycin in multiple breast cancer cell lines mainly by suppressing rapamycin-induced AKT signaling
- A liaison between mTOR signaling, ribosome biogenesis and cancer
- Effects of mTOR inhibitor everolimus (RAD001) on bladder cancer cells.
- Dual inhibit ion of EGFR and mTOR pathways in small cell lung cancer
- Exploiting the Head and Neck Cancer Oncogenome: Widespread PI3K-mTOR Pathway Alterations and Novel Molecular Targets
- Repurposing of Metformin and Aspirin by Targeting AMPK-mTOR and Inflammation for Pancreatic Cancer Prevention and Treatment
- Licorice and Licochalcone-A Induce Autophagy in LNCaP Prostate cancer Cells by Suppression of Bcl-2 Expression and the mTOR Pathway
- LKB1/AMPK /mTOR Signaling Pathway in Non-small-cell Lung cancer
- Different Patterns of Akt and ERK Feedback Activation in Response to Rapamycin, Active-Site mTOR inhibit ors and Metformin in Pancreatic cancer Cells
- Concomitant BRAF and PI3K/mTOR blockade is required for effective treatment of BRAF(V600E) colorectal cancer.
- Prognostic role of p‐mTOR expression in cancer tissues and metastatic lymph nodes in pT2b gastric cancer
- E2F1 inhibit s c-Myc-Driven Apoptosis via PIK3CA/Akt/mTOR and COX-2 in a Mouse Model of Human Liver cancer
- mTOR Signaling in Protein Translation Regulation: Implications in cancer Genesis and Therapeutic Interventions
- miR-99b-targeted mTOR induction contributes to irradiation resistance in pancreatic cancer
- Genetic variation in a metabolic signaling pathway and colon and rectal cancer risk: mTOR , PTEN , STK11 , RPKAA1 , PRKAG2 , TSC1 , TSC2 , Pi3k and Akt1
- Synergistic action of a RAF inhibitor and a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor in thyroid cancer.
- Curcumin inhibit s the mammalian target of rapamycin‐mediated signaling pathways in cancer cells
- Novel phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mTOR dual inhibitor, NVP-BGT226, displays potent growth-inhibitory activity against human head and neck cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
- Targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway for Breast cancer Therapy
- Nuclear reprogramming of luminal-like breast cancer cells generates Sox2-overexpressing cancer stem-like cellular states harboring transcriptional activation of the mTOR pathway
- Overcoming acquired resistance to letrozole by targeting the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway in breast cancer cell clones
- Dissecting the role of mTOR : Lessons from mTOR inhibit ors
- 6-Shogaol, an Active Constituent of Dietary Ginger, Induces Autophagy by inhibit ing the AKT/mTOR Pathway in Human Non-Small Cell Lung cancer A549 Cells
- Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase by a selective small molecule inhibitor, QLT0254, inhibits the PI3K/PKB/mTOR, Stat3, and FKHR pathways and tumor growth, and enhances gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in human orthotopic primary pancreatic cancer xenografts.
- Glucose metabolism and cancer
- Rhodiola rosea extract s and salidroside decrease the growth of bladder cancer cell lines via inhibit ion of the mTOR pathway and induction of autophagy
- Targeted Regulation of Pi3k /Akt/mTOR /NF-κB Signaling by Indole Compounds and their Derivatives: Mechanistic Details and Biological Implications for cancer Therapy
- Current Status and Challenges Associated with Targeting mTOR for cancer Therapy
- Pi3k -AKT-mTOR Pathway is Dominant over Androgen Receptor Signaling in Prostate cancer Cells
- The mTOR Pathway in Breast cancer
- mTOR inhibit ion reverses acquired endocrine therapy resistance of breast cancer cells at the cell proliferation and gene‐expression levels
- Inhibition of tumor growth progression by antiandrogens and mTOR inhibitor in a Pten-deficient mouse model of prostate cancer.
- HIF1α Regulates mTOR Signaling and Viability of Prostate cancer Stem Cells
- Involvement of Akt-1 and mTOR in Sensitivity of Breast cancer to Targeted Therapy
- inhibit ion of mTOR Signaling by Quercetin in cancer Treatment and Prevention
- Plumbagin induces apoptotic and autophagic cell death through inhibit ion of the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Overexpression of the μ-Opioid Receptor in Human Non-Small Cell Lung cancer Promotes Akt and mTOR Activation, Tumor Growth, and Metastasis
- AKT/mTOR pathway activation and BCL-2 family proteins modulate the sensitivity of human small cell lung cancer cells to RAD001.
- mTOR inhibition by rapamycin prevents beta-cell adaptation to hyperglycemia and exacerbates the metabolic state in type 2 diabetes.
- Attenuated mTOR Signaling and Enhanced Autophagy in Adipocytes from Obese Patients with Type 2 diabetes
- Posttransplant diabetes mellitus in kidney transplant recipients receiving calcineurin or mTOR inhibitor drugs.
- The Tuberin/mTOR Pathway Promotes Apoptosis of Tubular Epithelial Cells in diabetes
- mTOR inhibit ors and diabetes
- The role of mTOR in the adaptation and failure of β‐cells in type 2 diabetes
- mTOR : Driving apoptosis and autophagy for neurocardiac complications of diabetes mellitus
- The role of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) in the regulation of pancreatic β-cell mass: implications in the development of type-2 diabetes
- Insights for oxidative stress and mTOR Signaling in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury under diabetes
- Phospho-mTOR : A novel target in regulation of renal lipid metabolism abnormality of diabetes
- mTOR and tau phosphorylated proteins in the hippocampal tissue of rats with type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease
- Hyperactivation of Akt/mTOR and deficiency in tuberin increased the oxidative DNA damage in kidney cancer patients with diabetes
- Novel nervous and multi-system regenerative therapeutic strategies for diabetes mellitus with mTOR
- Leucine Stimulates insulin Secretion via Down-regulation of Surface Expression of Adrenergic α2A Receptor through the mTOR (Mammalian Target of Rapamycin) Pathway
IMPLICATION IN NEW-ONSET diabetes IN RENAL TRANSPLANTATION - The role of mTOR in lipid homeostasis and diabetes progression
- Reciprocal regulation of mTOR complexes in pancreatic islets from humans with type 2 diabetes
- The mTOR Signaling Pathway in Myocardial Dysfunction in Type 2 diabetes Mellitus
- Investigation of Pi3k /PKB/mTOR /S6K1 signaling pathway in relationship of type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease
- Association of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway genetic variants with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese
- diabetes Diminishes Phosphatidic Acid in the Retina: A Putative Mediator for Reduced mTOR Signaling and Increased Neuronal Cell Death
- mTOR and Cardiovascular Diseases: Diabetes Mellitus.
- Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms implicate mTOR signalling in the development of new-onset diabetes after transplantation
- microRNA-503 contribute to pancreatic beta cell dysfunction by targeting the mTOR pathway in gestational diabetes mellitus
- 1,25(OH)2D3 improves cardiac dysfunction, hypertrophy, and fibrosis through PARP1/SIRT1/mTOR ‐related mechanisms in type 1 diabetes
- High glucose induces formation of tau hyperphosphorylation via Cav-1-mTOR pathway: A potential molecular mechanism for diabetes -induced cognitive dysfunction
- Supplementation with polyunsaturated fatty acids in pregnant rats with mild diabetes normalizes placental PPARγ and mTOR signaling in female offspring developing gestational diabetes
- Associations between INSR and mTOR polymorphisms in type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy in a Northeast Chinese Han population
- Anabolic resistance does not explain sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, compared with healthy controls, despite reduced mTOR pathway activity
- Tuberin and mTOR , a key apoptotic pathway indiabetes
- inhibit ion of mTOR activity in diabetes mellitus reduces proteinuria but not renal accumulation of hyaluronan
- Amino Acid and insulin Signaling via the mTOR /p70 S6 Kinase Pathway
A NEGATIVE FEEDBACK MECHANISM LEADING TO insulin RESISTANCE IN SKELETAL MUSCLE CELLS - Down-regulation of placental mTOR , insulin /IGF-I signaling, and nutrient transporters in response to maternal nutrient restriction in the baboon
- A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway mediates and PTEN antagonizes tumor necrosis factor inhibit ion of insulin signaling through insulin receptor substrate-1
- Nutrients Suppress Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Signaling via Raptor-Dependent mTOR -Mediated insulin Receptor Substrate 1 Phosphorylation
- insulin and amino-acid regulation of mTOR signaling and kinase activity through the Rheb GTPase
- Stimulation of the insulin /mTOR pathway delays cone death in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa
- mTOR ‐dependent stimulation of the association of eIF4G and eIF3 by insulin
- MAP kinases and mTOR mediate insulin -induced phosphorylation of insulin Receptor Substrate-1 on serine residues 307, 612 and 632
- Leucine deprivation increases hepatic insulin sensitivity via GCN2/mTOR/S6K1 and AMPK pathways.
- Amino Acids and insulin Control Autophagic Proteolysis through Different Signaling Pathways in Relation to mTOR in Isolated Rat Hepatocytes
- Distinct Signaling Events Downstream of mTOR Cooperate To Mediate the Effects of Amino Acids and insulin on Initiation Factor 4E-Binding Proteins
- Regulation of insulin signalling by hyperinsulin aemia: role of IRS-1/2 serine phosphorylation and the mTOR /p70 S6K pathway
- Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ion activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt by up-regulating insulin -like growth factor-1 receptor signaling in acute myeloid leukemia: rationale for therapeutic inhibit ion of both pathways
- Long‐chain omega‐3 fatty acids regulate bovine whole‐body protein metabolism by promoting muscle insulin signalling to the Akt–mTOR –S6K1 pathway and insulin sensitivity
- Activation of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) by insulin Is Associated with Stimulation of 4EBP1 Binding to Dimeric mTOR Complex 1
- insulin – and Leptin-Mediated Control of Aquaglyceroporins in Human Adipocytes and Hepatocytes Is Mediated via the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Signaling Cascade
- Insulin growth factor-receptor (IGF-1R) antibody cixutumumab combined with the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus in patients with refractory Ewing’s sarcoma family tumors.
- Chronic mTOR inhibit ion by rapamycin induces muscle insulin resistance despite weight loss in rats
- Insulin Stimulates Mitochondrial Fusion and Function in Cardiomyocytes via the Akt-mTOR-NFkB-Opa-1 Signaling Pathway
- Glycerolipid signals alter mTOR complex 2 (mTOR C2) to diminish insulin signaling
- insulin promotes dendritic spine and synapse formation by the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR and Rac1 signaling pathways
- The TSC-mTOR Pathway Mediates Translational Activation of TOP mRNAs by insulin Largely in a Raptor- or Rictor-Independent Manner
- insulin Receptor Substrate-2 Proteasomal Degradation Mediated by a Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR )-induced Negative Feedback Down-regulates Protein Kinase B-mediated Signaling Pathway in β-Cells
- IKKβ suppression of TSC1 function links the mTOR pathway with insulin resistance
- The Cardioprotection of the insulin -Mediated Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
- Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) is involved in the neuronal differentiation of neural progenitors induced by insulin
- Maternal Protein restriction in the Rat inhibit s Placental insulin , mTOR , and STAT3 Signaling and Down-Regulates Placental Amino Acid Transporters
- Hepatitis C Virus Activates the mTOR /S6K1 Signaling Pathway in inhibit ing IRS-1 Function for insulin Resistance
- The insulin -like Growth Factor-I–mTOR Signaling Pathway Induces the Mitochondrial Pyrimidine Nucleotide Carrier to Promote Cell Growth
- insulin growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) antibody cixutumumab combined with the mTOR inhibit or temsirolimus in patients with metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma
- Glucose phosphorylation is required for insulin -dependent mTOR signalling in the heart
- Activation of mTOR /p70S6 kinase by ANG II inhibit s insulin -stimulated endothelial nitric oxide synthase and vasodilation
- mTOR inhibit ion with rapamycin causes impaired insulin signalling and glucose uptake in human subcutaneous and omental adipocytes
- Amino acids are necessary for the insulin -induced activation of mTOR /S6K1 signaling and protein synthesis in healthy and insulin resistant human skeletal muscle
- Amino acids and leucine allow insulin activation of the PKB/mTOR pathway in normal adipocytes treated with wortmannin and in adipocytes from db/db mice
- insulin -Like Growth Factor I-Mediated Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy Is Characterized by Increased mTOR -p70S6K Signaling without Increased Akt Phosphorylation
- The Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway mediates insulin -like growth factor 1-induced E-cadherin down-regulation and cell proliferation in ovarian cancer cells
- insulin ‐like growth factor‐1 (IGF‐1) and leucine activate pig myogenic satellite cells through mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) pathway
- mTOR Complex 2 Regulates Proper Turnover of insulin Receptor Substrate-1 via the Ubiquitin Ligase Subunit Fbw8
- Both Wnt and mTOR signaling pathways are involved in insulin -stimulated proto-oncogene expression in intestinal cells
- Zinc stimulates the activity of the insulin – and nutrient-regulated protein kinase mTOR
- Resistin Promotes Cardiac Hypertrophy via the AMP-activated Protein Kinase/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (AMPK /mTOR ) and c-Jun N-terminal Kinase/insulin Receptor Substrate 1 (JNK/IRS1) Pathways
- Role of the PI3-kinase/mTOR pathway in the regulation of the stearoyl CoA desaturase (SCD1) gene expression by insulin in liver
- Exercise training reduces insulin resistance and upregulates the mTOR /p70S6k pathway in cardiac muscle of diet‐induced obesity rats
- Leucine Activates Pancreatic Translational Machinery in Rats and Mice through mTOR Independently of CCK and insulin
- Akt/mTOR Counteract the Antitumor Activities of Cixutumumab, an Anti-insulin –like Growth Factor I Receptor Monoclonal Antibody
- insulin Potentiates Ca2+ Signaling and Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate Hydrolysis Induced by Gq Protein-Coupled Receptor Agonists through an mTOR -Dependent Pathway
- insulin -induced stimulation of JNK and the PI 3-kinase/mTOR pathway leads to phosphorylation of serine 318 of IRS-1 in C2C12 myotubes
- Tissue-Specific Responses of IGF-1/insulin and mTOR Signaling in calorie Restricted Rats
- mTOR C2 promotes type I insulin -like growth factor receptor and insulin receptor activation through the tyrosine kinase activity of mTOR
- insulin -like growth factor-I inhibit s dexamethasone-induced proteolysis in cultured L6 myotubes through Pi3k /Akt/GSK-3β and Pi3k /Akt/mTOR -dependent mechanisms
- The role of AMPK /mTOR /S6K1 signaling axis in mediating the physiological process of exercise-induced insulin sensitization in skeletal muscle of C57BL/6 mice
- Glucose Induces Mouse β-Cell Proliferation via IRS2, MTOR, and Cyclin D2 but Not the Insulin Receptor.
- insulin Promotes Glucose Consumption via Regulation of miR-99a/mTOR /PKM2 Pathway
- insulin -induced serine phosphorylation of IRS-2 via ERK1/2 and mTOR : studies on the function of Ser675 and Ser907
- Protein Ingestion Induces Muscle Insulin Resistance Independent of Leucine-Mediated mTOR Activation.
- Salmonella enterica Typhimurium infection causes metabolic changes in chicken muscle involving AMPK , fatty acid and insulin /mTOR signaling
- inhibit ion of the mTOR /p70S6K pathway is not involved in the insulin -sensitizing effect of AMPK on cardiac glucose uptake
- Acute mTOR inhibit ion induces insulin resistance and alters substrate utilization in vivo
- Knockdown of insulin receptor substrate 1 reduces proliferation and downregulates Akt/mTOR and MAPK pathways in K562 cells
- Antiproliferation of cardamonin is involved in mTOR on aortic smooth muscle cells in high fructose-induced insulin resistance rats
- Implication of RICTOR in the mTOR inhibit or-mediated induction of insulin -like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (Her2) expression in gastrointestinal cancer cells
- Cardiac overexpression of insulin -like growth factor 1 attenuates chronic alcohol intake-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction but not hypertrophy: Roles of Akt, mTOR , GSK3β, and PTEN
- Palmitate Induced insulin Resistance by PKCtheta-Dependent Activation of mTOR /S6K Pathway in C2C12 Myotubes
- insulin fails to enhance mTOR phosphorylation, mitochondrial protein synthesis, and ATP production in human skeletal muscle without amino acid replacement
- Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR ): a point of convergence in the action of insulin /IGF-1 and G protein-coupled receptor agonists in pancreatic cancer cells
- Raptor Binds the SAIN (Shc and IRS-1 NPXY Binding) Domain of insulin Receptor Substrate-1 (IRS-1) and Regulates the Phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser-636/639 by mTOR
- Quantification of the effect of amino acids on an integrated mTOR and insulin signaling pathway
- The Mechanism of insulin -stimulated 4E-BP Protein Binding to Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) Complex 1 and Its Contribution to mTOR Complex 1 Signaling
- Activation of placental insulin and mTOR signaling in a mouse model of maternal obesity associated with fetal overgrowth
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Suppresses Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling in Prostate Cancer Cells by Activating mTOR Signaling
- Adipocyte-specific deletion of mTOR inhibit s adipose tissue development and causes insulin resistance in mice
- insulin inhibit ion of apolipoprotein B mRNA translation is mediated via the PI-3 kinase/mTOR signaling cascade but does not involve internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) initiation
- PKCζ Is Essential for Pancreatic β-Cell Replication During Insulin Resistance by Regulating mTOR and Cyclin-D2.
- Cardamonin Ameliorates insulin Resistance Induced by High insulin and High Glucose through the mTOR and Signal Pathway
- inhibit ion of PI-3 kinase/Akt/mTOR , but not calcineurin signaling, reverses insulin -like growth factor I-induced protection against glucose toxicity in cardiomyocyte contractile function
- Evodiamine inhibit s insulin -Stimulated mTOR -S6K Activation and IRS1 Serine Phosphorylation in Adipocytes and Improves Glucose Tolerance in Obese/Diabetic Mice
- insulin and mTOR Pathway Regulate HDAC3-Mediated Deacetylation and Activation of PGK1
- mTOR -Independent autophagy inducer trehalose rescues against insulin resistance-induced myocardial contractile anomalies: Role of p38 MAPK and Foxo1
- The inhibit ion of insulin -stimulated Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Rosiglitazone Is Mediated by the Akt-mTOR -P70S6K Pathway
- insulin regulation of hepatic insulin -like growth factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) gene expression and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) signalling is impaired by the presence of hydrogen peroxide
- Anthocyanin-rich mulberry fruit improves insulin resistance and protects hepatocytes against oxidative stress during hyperglycemia by regulating AMPK /ACC/mTOR pathway
- mTOR and neuronal cell cycle reentry: How impaired brain insulin signaling promotes Alzheimer’s disease
- Impaired overload-induced hypertrophy is associated with diminished mTOR signaling in insulin -resistant skeletal muscle of the obese Zucker rat
- Anti-inflammatory action of insulin via induction of Gadd45-β transcription by the mTOR signaling pathway
- In Human Endothelial Cells Amino Acids Inhibit Insulin-induced Akt and ERK1/2 Phosphorylation by an mTOR-dependent Mechanism
- Activation of the hexosamine pathway leads to phosphorylation of IRS-1 on Ser307 and Ser612 and impairs the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR insulin biosynthetic pathway in RIN pancreatic {beta}-cells
- Essential Amino Acids Improve insulin Activation of Akt/mTOR Signaling in Soleus Muscle of Aged Rats
- Akt/mTOR Role in Human Foetoplacental Vascular insulin Resistance in Diseases of Pregnancy
- Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase-4-deficient mice are protected from diet-induced insulin resistance by the enhanced association of mTOR and rictor
- The Regulation of Lipid Deposition by insulin in Goose Liver Cells Is Mediated by the Pi3k -AKT-mTOR Signaling Pathway
- Pectic Bee Pollen Polysaccharide from Rosa rugosa Alleviates Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis and insulin Resistance via Induction of AMPK /mTOR -Mediated Autophagy
- Reduction of insulin signalling pathway IRS‐1/IRS‐2/AKT/mTOR and decrease of epithelial cell proliferation in the prostate of glucocorticoid‐treated rats
- Flavanol‐rich lychee fruit extract alleviates diet‐induced insulin resistance via suppressing mTOR /SREBP‐1 mediated lipogenesis in liver and restoring insulin signaling in skeletal muscle
- insulin -like growth factor 1 receptor-mediated cell survival in hypoxia depends on the promotion of autophagy via suppression of the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Melanocortin-4 receptor activation promotes insulin -stimulated mTOR signaling
- Heparin-Binding EGF-Like Growth Factor (HB-EGF) Mediates 5-HT-Induced insulin Resistance Through Activation of EGF Receptor-ERK1/2-mTOR Pathway
- Zinc stimulates glucose consumption by modulating the insulin signaling pathway in L6 myotubes: essential roles of Akt–GLUT4, GSK3β and mTOR –S6K1
- Amino acid-sensing mTOR signaling is involved in modulation of lipolysis by chronic insulin treatment in adipocytes
- Overexpression of Kinase-Dead mTOR Impairs Glucose Homeostasis by Regulating Insulin Secretion and Not β-Cell Mass.
- Combination of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit or everolimus (E) with the insulin like growth factor-1-receptor (IGF-1-R) inhibit or NVP-AEW-541: A mechanistic based anti-tumor strategy
- Exercise improves skeletal muscle insulin resistance without reduced basal mTOR /S6K1 signaling in rats fed a high-fat diet
- insulin stimulates IGFBP-2 expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through the Pi3k /mTOR pathway
- The dual targeting of insulin and insulin -like growth factor 1 receptor enhances the mTOR inhibit or-mediated antitumor efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma
- insulin activation of vacuolar protein sorting 34 mediates localized phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate production at lamellipodia and activation of mTOR /S6K1
- Attenuation of insulin resistance in rats by agmatine: role of SREBP-1c, mTOR and GLUT-2
- mTOR partly mediates insulin resistance by phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 on serine307 residues after burn
- Development of a model describing regulation of casein synthesis by the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) signaling pathway in response to insulin , amino acids, and acetate
- Judicious Toggling of mTOR Activity to Combat insulin Resistance and cancer : Current Evidence and Perspectives
- Genetically reducing mTOR signaling rescues central insulin dysregulation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
- insulin Stimulates Goose Liver Cell Growth by Activating Pi3k -AKT-mTOR Signal Pathway
- The effects of amino acids on glucose metabolism of isolated rat skeletal muscle are independent of insulin and the mTOR /S6K pathway
- Exercise and dietary change ameliorate high fat diet induced obesity and insulin resistance via mTOR signaling pathway
- insulin -like growth factor binding protein-3 mediates interleukin-24-induced apoptosis through inhibit ion of the mTOR pathway in prostate cancer
- insulin Increases Sestrin 2 Content by Reducing Its Degradation through the Pi3k /mTOR Signaling Pathway
- calorie restriction : Decelerating mTOR -driven Aging from cells to organisms (including humans)
- mTOR and autophagy in normal brain Aging and caloric restriction ameliorating age-related cognition deficits
- Effects of Intermittent and Chronic calorie restriction on Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) and IGF-I Signaling Pathways in Mammary Fat Pad Tissues and Mammary Tumors
- Effect of caloric restriction on the SIRT1/mTOR signaling pathways in senile mice
- Angiotensin II blockade: how its molecular targets may signal to mitochondria and slow Aging . Coincidences with calorie restriction and mTOR inhibit ion
- Linking calorie restriction to longevity through sirtuins and autophagy: any role for TOR
- Systematic gene expression profile of hypothalamus in calorie -restricted mice implicates the involvement of mTOR signaling in neuroprotective activity
- mTOR signaling and ubiquitin-proteosome gene expression in the preservation of fat free mass following high protein, calorie restricted weight loss
- fasting Increases Human Skeletal Muscle Net Phenylalanine Release and This Is Associated with Decreased mTOR Signaling
- Muscle Wasting in fasting Requires Activation of NF-κB and inhibit ion of AKT/Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) by the Protein Acetylase, GCN5
- fasting glucose and triglycerides as biomarkers of mTOR inhibit ion, evidence of a categorical response.
- mTOR C1 controls fasting -induced ketogenesis and its modulation by ageing
- The ketogenic diet inhibit s the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) pathway
- Rapamycin passes the torch: a new generation of mTOR inhibit ors
- Pi3k /AKT/mTOR inhibit ors in Patients With Breast and Gynecologic Malignancies Harboring PIK3CA Mutations
- Next-generation mTOR inhibit ors in clinical oncology: how pathway complexity informs therapeutic strategy
- mTOR inhibit ors: An overview
- Updates of mTOR inhibit ors
- PIK3CA Mutations in Patients with Advanced cancer s Treated with Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Axis inhibit ors
- Enhanced radiation damage of tumor vasculature by mTOR inhibit ors
- AKT Activity Determines Sensitivity to Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors by Regulating Cyclin D1 and c-myc Expression
- Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and Pi3k /PTEN/Akt/mTOR inhibit ors: Rationale and Importance to inhibit ing These Pathways in Human Health
- Picking the Point of inhibit ion: A Comparative Review of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway inhibit ors
- Targeting the mTOR kinase domain: the second generation of mTOR inhibit ors
- Pilot study of the combination of EGFR and mTOR inhibit ors in recurrent malignant gliomas
- mTOR Signaling, Function, Novel inhibit ors, and Therapeutic Targets
- Strategies for the management of adverse events associated with mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors-induced proteinuria: mechanisms, significance, and management
- PIK3CA/PTEN mutations and Akt activation as markers of sensitivity to allosteric mTOR inhibitors.
- Response of a Neuronal Model of Tuberous Sclerosis to Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors: Effects on mTOR C1 and Akt Signaling Lead to Improved Survival and Function
- Combinations of BRAF, MEK, and Pi3k /mTOR inhibit ors Overcome Acquired Resistance to the BRAF inhibit or GSK2118436 Dabrafenib, Mediated by NRAS or MEK Mutations
- Assessing PIK3CA and PTEN in Early-Phase Trials with Pi3k /AKT/mTOR inhibit ors
- Pi3k and mTOR inhibit ors — a new generation of targeted anticancer agents
- mTOR inhibit or/proliferation signal inhibit ors: entering or leaving the field?
- PIK3CA mutation H1047R is associated with response to PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway inhibitors in early-phase clinical trials.
- Predicted mechanisms of resistance to mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
- The role of mTOR inhibitors in the management of posttransplant malignancy.
- Pushing the Envelope in the mTOR Pathway: The Second Generation of inhibit ors
- IRS-1: Auditing the effectiveness of mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors are synergistic with methotrexate: an effective combination to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- mTOR inhibit ors in Polycystic Kidney Disease
- mTOR inhibit ors in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
- inhibit ors of mTOR
- mTOR inhibit ors in renal cell carcinoma
- The pleiotropic effects of mTOR inhibit ors.
- The emerging safety profile of mTOR inhibit ors, a novel class of anticancer agents
- Combination of PI3K/mTOR inhibitors: antitumor activity and molecular correlates.
- Rapamycin and mTOR kinase inhibit ors
- Current development of the second generation of mTOR inhibit ors as anticancer agents
- Morpholine Derivatives Greatly Enhance the Selectivity of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors
- Potent antifibrotic activity of mTOR inhibit ors sirolimus and everolimus but not of cyclosporine A and tacrolimus in experimental liver fibrosis
- Replacing calcineurin inhibit ors with mTOR inhibit ors in children
- Aspects of mTOR biology and the use of mTOR inhibit ors in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Differentiating mTOR inhibit ors in renal cell carcinoma
- Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors Alone and in Combination with JAK2 inhibit ors Effectively inhibit Cells of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
- Targeted inhibit ion of mTOR C1 and mTOR C2 by active-site mTOR inhibit ors has cytotoxic effects in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Increased Incidence of Angioedema with ACE inhibit ors in Combination with mTOR inhibit ors in Kidney Transplant Recipients
- mTOR inhibit ors and their clinical application in cervical, endometrial and ovarian cancer s: A critical review
- Kinome-wide Selectivity Profiling of ATP-competitive Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors and Characterization of Their Binding Kinetics
- Bcl-2 and CCND1/CDK4 expression levels predict the cellular effects of mTOR inhibit ors in human ovarian carcinoma
- Review of combination therapy with mTOR inhibit ors and tacrolimus minimization after transplantation
- Therapeutic polymeric nanoparticles with mTOR inhibit ors and methods of making and using same
- Pneumonitis associated with mTOR inhibit ors therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Incidence, radiographic findings and correlation with clinical outcome
- MYC Cooperates with AKT in Prostate Tumorigenesis and Alters Sensitivity to mTOR inhibit ors
- Third-Line Sorafenib After Sequential Therapy With Sunitinib and mTOR inhibit ors in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Updating progress in sarcoma therapy with mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors Synergize on Regression, Reversal of Gene Expression, and Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Current Scientific Rationale for the Use of Somatostatin Analogs and mTOR inhibit ors in Neuroendocrine Tumor Therapy
- Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors
- Synergic antiproliferative and antiangiogenic effects of EGFR and mTOR inhibit ors on pancreatic cancer cells
- Metabolic complications with the use of mTOR inhibit ors for cancer therapy
- A critical review of mTOR inhibit ors and epilepsy: from basic science to clinical trials
- mTOR inhibit ors in breast cancer : A systematic review
- Biologic rationale and clinical activity of mTOR inhibit ors in gynecological cancer
- Defining biomarkers to predict sensitivity to Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway inhibit ors in breast cancer
- Comparison of the effects of the Pi3k /mTOR inhibit ors NVP-BEZ235 and GSK2126458 on tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells
- Discovery of (Thienopyrimidin-2-yl)aminopyrimidines as Potent, Selective, and Orally Available Pan-PI3-Kinase and Dual Pan-PI3-Kinase/mTOR inhibit ors for the Treatment of cancer
- Focus on mTOR inhibit ors and tacrolimus in renal transplantation: Pharmacokinetics, exposure–response relationships, and clinical outcomes
- Preclinical evaluation of dual Pi3k –mTOR inhibit ors and histone deacetylase inhibit ors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Induction of autophagy with catalytic mTOR inhibit ors reduces huntingtin aggregates in a neuronal cell model
- Comparative Analysis of Adverse Events Requiring Suspension of mTOR inhibit ors: Everolimus versus Sirolimus
- Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors slow skin carcinogenesis, but impair wound healing
- Systemic and nonrenal adverse effects occurring in renal transplant patients treated with mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR pathway and mTOR inhibit ors in head and neck cancer
- Alterations in glucose metabolism by cyclosporine in rat brain slices link to oxidative stress : interactions with mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors at a Glance
- Do wound complications or lymphoceles occur more often in solid organ transplant recipients on mTOR inhibit ors? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials
- Clinical development of mTOR inhibitors in breast cancer
- inhibit ors of mTOR and Risks of Allograft Failure and Mortality in Kidney Transplantation
- Incomplete inhibit ion of phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 as a mechanism of primary resistance to ATP-competitive mTOR inhibit ors
- Incidence and risk of pulmonary toxicity in patients treated with mTOR inhibit ors for malignancy. A meta-analysis of published trials
- Cancer and mTOR Inhibitors in Transplant Recipients.
- Antitumor activity of pimasertib, a selective MEK 1/2 inhibit or, in combination with Pi3k /mTOR inhibit ors or with multi‐targeted kinase inhibit ors in pimasertib‐resistant human lung and colorectal cancer cells
- The Role of mTOR inhibit ors in Liver Transplantation: Reviewing the Evidence
- Pyrazolopyrimidines as highly potent and selective, ATP-competitive inhibit ors of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ): Optimization of the 1-substituent
- [Pi3k -AKT-mTOR pathway inhibit ors].
- inhibit ion of Pi3k -Akt-mTOR Signaling in Glioblastoma by mTOR C1/2 inhibit ors
- Emergent toxicities associated with the use of mTOR inhibitors in patients with advanced renal carcinoma.
- Differentiating the mTOR inhibit ors everolimus and sirolimus in the treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex
- Treatment outcome with mTOR inhibit ors for metastatic renal cell carcinoma with nonclear and sarcomatoid histologies
- mTOR inhibit ors: Do They Help Preserve Renal Function?
- mTOR , p70S6K, AKT, and ERK1/2 levels predict sensitivity to mTOR and Pi3k /mTOR inhibit ors in human bronchial carcinoids
- The therapeutic potential of mTOR inhibit ors in breast cancer
- Pi3k -AKT-mTOR inhibit ors in breast cancer s: From tumor cell signaling to clinical trials
- Maximizing the clinical outcome with mTOR inhibit ors in the renal transplant recipient: defining the role of calcineurin inhibit ors
- Thymic stromal-derived lymphopoietin induces proliferation of pre-B leukemia and antagonizes mTOR inhibitors, suggesting a role for interleukin-7 Ralpha signaling.
- Catalytic mTOR inhibit ors can overcome intrinsic and acquired resistance to allosteric mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibitors block Kaposi sarcoma growth by inhibiting essential autocrine growth factors and tumor angiogenesis.
- Antitumor activities of ATP-competitive inhibitors of mTOR in colon cancer cells.
- Role of mTOR inhibit ors in epilepsy treatment
- “Overcoming breast cancer drug resistance with mTOR inhibit ors”. Could it be a myth or a real possibility in the short-term future?
- Safety of mTOR inhibit ors in adult solid organ transplantation
- mTOR inhibit ors and its Role in the Treatment of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Synergistic antiproliferative effect of mTOR inhibit ors in combination with 5‐fluorouracil in scirrhous gastric cancer
- Predictive biomarkers for the activity of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors and the anti-diabetic biguanide metformin: new insights into the molecular management of breast cancer resistance to the HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibit or lapatinib (Tykerb®)
- Methylnaltrexone Potentiates the Anti-Angiogenic Effects of mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors as a new therapeutic option for epilepsy
- mTOR inhibit ors in the management of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer : the latest evidence and future directions
- mTOR Inhibitors Suppress Homologous Recombination Repair and Synergize with PARP Inhibitors via Regulating SUV39H1 in BRCA-Proficient Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
- Incorporation of water-solubilizing groups in pyrazolopyrimidine mTOR inhibit ors: Discovery of highly potent and selective analogs with improved human microsomal stability
- FBXW7 Mutations in Patients with Advanced cancer s: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics and Outcomes with mTOR inhibit ors
- Use of APO2L/TRAIL with mTOR inhibit ors in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme
- Discovery and Assembly-Line Biosynthesis of the Lymphostin Pyrroloquinoline Alkaloid Family of mTOR inhibit ors in Salinispora Bacteria
- Benchmarking effects of mTOR , Pi3k , and dual Pi3k /mTOR inhibit ors in hepatocellular and renal cell carcinoma models developing resistance to sunitinib and sorafenib
- The role of mTOR inhibit ors for treatment of sarcomas
- Combining mTOR inhibit ors With Rapamycin-resistant T Cells: A Two-pronged Approach to Tumor Elimination
- mTOR inhibit ors and sorafenib for recurrent heptocellular carcinoma after orthotopic liver transplantation
- inhibit ors of Pi3k /Akt and/or mTOR inhibit the Growth of Cells of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms and Synergize with JAK2 inhibit or and Interferon,
- Neuroprotective, immunosuppressant and antineoplastic properties of mTOR inhibit ors: current and emerging therapeutic options
- Combining mTOR inhibit ors with Chemotherapy and Other Targeted Therapies in Advanced Breast cancer : Rationale, Clinical Experience, and Future Directions
- Novel imidazolopyrimidines as dual PI3-Kinase/mTOR inhibit ors
- inhibit ion of mTOR Pathway Sensitizes Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells to Aurora inhibit ors by Suppression of Glycolytic Metabolism
- Paronychia and Pyogenic Granuloma Induced by New Anticancer mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors counteract tamoxifen-induced activation of breast cancer stem cells
- Resistance to mTOR Kinase inhibit ors in Lymphoma Cells Lacking 4EBP1
- The inhibit ion of MAPK potentiates the anti-angiogenic efficacy of mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors in pediatric kidney transplantation
- mTOR inhibit ors and dyslipidemia in transplant recipients: A cause for concern?
- The Role of mTOR inhibit ors in the Treatment of Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: Evidence-based and Expert Opinions
- mTOR inhibit ors in advanced breast cancer : Ready for prime time?
- Innovations therapy: mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ors for the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors
- mTOR inhibit ors induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells via CHOP-dependent DR5 induction on 4E-BP1 dephosphorylation
- Therapeutic activity of mTOR inhibit ors in mantle cell lymphoma: Clues but no clear answers
- Use of mTOR inhibit ors in chronic heart transplant recipients with renal failure: Calcineurin-inhibit ors conversion or minimization?
- Is There a Role for Proliferation Signal/mTOR inhibit ors in the Prevention and Treatment of De Novo Malignancies After Heart Transplantation? Lessons Learned From Renal Transplantation and Oncology
- Development of ATP-Competitive mTOR inhibit ors
- The role of mTOR inhibit ors in the inhibit ion of growth and cortisol secretion in human adrenocortical carcinoma cells
- Fused bicyclic mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors radiosensitize PTEN‐deficient non‐small‐cell lung cancer cells harboring an EGFR activating mutation by inducing autophagy
- Conformationally-restricted cyclic sulfones as potent and selective mTOR kinase inhibit ors
- Dual Pi3k /mTOR inhibit ors Induce Rapid Overactivation of the MEK/ERK Pathway in Human Pancreatic cancer Cells through Suppression of mTOR C2
- Potential of mTOR inhibit ors for the treatment of subependymal giant cell astrocytomas in tuberous sclerosis complex
- Identification of 2-oxatriazines as highly potent pan-Pi3k /mTOR dual inhibit ors
- Recent advances in the development of selective, ATP-competitive inhibit ors of mTOR .
- ATP-Competitive inhibit ors of mTOR : An Update
- Can mTOR inhibit ors reduce the risk of late kidney allograft failure?
- inhibit ion of mTOR pathway by everolimus cooperates with EGFR inhibit ors in human tumours sensitive and resistant to anti-EGFR drugs
- Everolimus and mTOR inhibit ors in liver transplantation: Opening the “box”
- Skin cancer in solid organ transplant recipients: are mTOR inhibit ors a game changer?
- mTOR inhibit ors Control the Growth of EGFR Mutant Lung cancer Even after Acquiring Resistance by HGF
- Discovery of 2-ureidophenyltriazines bearing bridged morpholines as potent and selective ATP-competitive mTOR inhibit ors
- The pros and the cons of mTOR inhibit ors in kidney transplantation
- Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and Pi3k /PTEN/Akt/mTOR Cascade inhibit ors: How Mutations Can Result in Therapy Resistance and How to Overcome Resistance
- The mTOR kinase inhibit ors polarize glioma-activated microglia to express a M1 phenotype
- Discovery and optimization of potent and selective imidazopyridine and imidazopyridazine mTOR inhibit ors
- Ophthalmic compositions comprising calcineurin inhibit ors or mTOR inhibit ors
- Management of side effects of mTOR inhibit ors in tuberous sclerosis patients
- Clinical efficacy of mTOR inhibit ors in solid tumors: a systematic review
- inhibit ors of mTOR overcome drug resistance from topoisomerase II inhibit ors in solid tumors
- mTOR inhibit ors (Rapamycin and its Derivatives) and Nitrogen Containing Bisphosphonates: Bi-Functional Compounds for the Treatment of Bone Tumours
- Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibit ors activate the AKT kinase in multiple myeloma cells by up-regulating the insulin -like growth factor receptor/insulin receptor substrate-1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascade
- mTOR inhibit ors in hematologic malignancies.
- Thymoma Patients Treated in a Phase I Clinic at MD Anderson cancer Center: Responses to mTOR inhibit ors and Molecular Analyses
- inhibit ion of autophagy sensitizes malignant pleural mesothelioma cells to dual Pi3k /mTOR inhibit ors
- mTOR inhibit ors in Castration-Resistant Prostate cancer : A Systematic Review
- Gerosuppression by pan-mTOR inhibit ors
- A novel mTOR activating protein protects dopamine neurons against oxidative stress by repressing autophagy related cell death
- Leptin induces cardiac fibrosis through galectin-3, mTOR and oxidative stress : potential role in obesity
- Pi3k /Akt and mTOR /p70S6K pathways mediate neuroprotectin D1-induced retinal pigment epithelial cell survival during oxidative stress -induced apoptosis
- Bridges between mitochondrial oxidative stress , ER stress and mTOR signaling in pancreatic β cells
- Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) inhibit ion with Rapamycin Improves Cardiac Function in Type 2 Diabetic Mice
POTENTIAL ROLE OF ATTENUATED oxidative stress AND ALTERED CONTRACTILE PROTEIN EXPRESSION - Cytotoxicity of withaferin A in glioblastomas involves induction of an oxidative stress -mediated heat shock response while altering Akt/mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways
- inhibit ion of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR axis disrupts oxidative stress -mediated survival of melanoma cells
- Melatonin represses oxidative stress ‐induced activation of the MAP kinase and mTOR signaling pathways in H4IIE hepatoma cells through inhibit ion of Ras
- Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Activity Is Required to Control Neuronal Stress Responses in an mTOR -Dependent Manner
- Resveratrol exerts antidepressant properties in the chronic unpredictable mild stress model through the regulation of oxidative stress and mTOR pathway in the rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex
- Salvianolic acid B protects human endothelial progenitor cells against oxidative stress -mediated dysfunction by modulating Akt/mTOR /4EBP1, p38 MAPK/ATF2, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways
- Particulate matter exposure induces the autophagy of macrophages via oxidative stress -mediated Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway
- Insights for oxidative stress and mTOR Signaling in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury under diabetes
- Neuroprotection Through Rapamycin-Induced Activation of Autophagy and Pi3k /Akt1/mTOR /CREB Signaling Against Amyloid-β-Induced oxidative stress , Synaptic/Neurotransmission Dysfunction, and Neurodegeneration in Adult Rats
- Radiation persistently promoted oxidative stress , activated mTOR via Pi3k /Akt, and downregulated autophagy pathway in mouse intestine
- The regulation of energy metabolism and the IGF-1/mTOR pathways by the p53 protein
- Glucose Regulation of Load‐Induced mTOR Signaling and ER Stress in Mammalian Heart
- Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone protects retinal pigment epithelium cells from oxidative stress through activation of melanocortin 1 receptor–Akt–mTOR signaling
- Sestrin2 integrates Akt and mTOR signaling to protect cells against energetic stress-induced death
- Modulation of oxidative stress and tau phosphorylation by the mTOR activator phosphatidic acid in SH‐SY5Y cells
- oxidative stress plays a key role in butyrate-mediated autophagy via Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatoma cells
- Induction of autophagy by salidroside through the AMPK –mTOR pathway protects vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress -induced apoptosis
- Tumor Cells Switch to Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation under Radiation via mTOR -Mediated Hexokinase II inhibit ion – A Warburg-Reversing Effect
- Ivabradine Prevents Low Shear Stress Induced Endothelial Inflammation and oxidative stress via mTOR /eNOS Pathway
- The role of CAPE in Pi3k /AKT/mTOR activation and oxidative stress on testis torsion
- Hydrogen sulfide restores a normal morphological phenotype in Werner syndrome fibroblasts, attenuates oxidative damage and modulates mTOR pathway
- mTOR , AMPK , and Sirt1: Key Players in Metabolic Stress Management
- Oxidant Stress and Signal Transduction in the Nervous System with the PI 3-K, Akt, and mTOR Cascade
- The Role of AKT/mTOR Pathway in Stress Response to UV-Irradiation: Implication in Skin Carcinogenesis by Regulation of Apoptosis, Autophagy and Senescence
- Growth Control Under Stress: mTOR Regulation through the REDD1-TSC Pathway
- Albumin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and ER stress are regulated through a common ROS-c-Src kinase-mTOR pathway: effect of imatinib mesylate
- Anthelminthic drug niclosamide sensitizes the responsiveness of cervical cancer cells to paclitaxel via oxidative stress -mediated mTOR inhibit ion
- Molecular mechanisms of mTOR regulation by stress
- α-Solanine induces ROS-mediated autophagy through activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibit ion of Akt/mTOR pathway
- Liquiritigenin reverses depression-like behavior in unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced mice by regulating Pi3k /Akt/mTOR mediated BDNF/TrkB pathway
- An α-Acetoxy-Tirucallic Acid Isomer inhibit s Akt/mTOR Signaling and Induces oxidative stress in Prostate cancer Cells
- Lp-PLA2 silencing protects against ox-LDL-induced oxidative stress and cell apoptosis via Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human THP1 macrophages
- Endosulfan induces autophagy and endothelial dysfunction via the AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway triggered by oxidative stress
- Oxidative cytotoxic agent withaferin A resensitizes temozolomide-resistant glioblastomas via MGMT depletion and induces apoptosis through Akt/mTOR pathway inhibit ory modulation
- Alcohol Dehydrogenase Protects against Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Myocardial Contractile Dysfunction via Attenuation of oxidative stress and Autophagy: Role of PTEN-Akt-mTOR Signaling
- Metformin-induced protection against oxidative stress is associated with AKT/mTOR restoration in PC12 cells
- Proteasome inhibit ors Activate Autophagy Involving inhibit ion of Pi3k -Akt-mTOR Pathway as an Anti-Oxidation Defense in Human RPE Cells
- FNDC5 Alleviates Hepatosteatosis by Restoring AMPK/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy, Fatty Acid Oxidation, and Lipogenesis in Mice
- mTOR plays a critical role in p53-induced oxidative kidney cell injury in HIVAN
- Huperzine A Alleviates Oxidative Glutamate Toxicity in Hippocampal HT22 Cells via Activating BDNF/TrkB-Dependent Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
- The Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway mediates retinal progenitor cell survival under hypoxic and superoxide stress
- Anti‐leukaemic effects induced by APR‐246 are dependent on induction of oxidative stress and the NFE2L2/HMOX1 axis that can be targeted by Pi3k and mTOR inhibit ors in acute myeloid leukaemia cells
- Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 inhibit s TGF-β1-induced EMT through the inhibit ion of the mTOR pathway by reducing the expression of PKM2 and is closely linked to oxidative stress
- Rapamycin Confers Neuroprotection against Colistin-Induced oxidative stress , Mitochondria Dysfunction, and Apoptosis through the Activation of Autophagy and mTOR /Akt/CREB Signaling Pathways
- The effects of melatonin on oxidative stress and prevention of primordial follicle loss via activation of mTOR pathway in the rat ovary
- inhibit ion of Rac1 ameliorates neuronal oxidative stress damage via reducing Bcl-2/Rac1 complex formation in mitochondria through Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway
- Linalool induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HepG2 cells through oxidative stress generation and modulation of Ras/MAPK and Akt/mTOR pathways
- Aurora kinase A suppresses metabolic stress-induced autophagic cell death by activating mTOR signaling in breast cancer cells
- Subtoxic concentrations of benzo[a]pyrene induce metabolic changes and oxidative stress in non-activated and affect the mTOR pathway in activated Jurkat T cells
- TGF-β1 stimulates mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and generation of reactive oxygen species in cultured mouse podocytes, mediated in part by the mTOR pathway
- Melatonin Combined with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induces Cell Death via the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway in B16F10 Melanoma Cells
- Thioredoxin-1 maintains mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR ) function during oxidative stress in cardiomyocytes
- Glucocorticoids Modulate the mTOR Pathway in the Hippocampus: Differential Effects Depending on Stress History
- Spironolactone promotes autophagy via inhibit ing Pi3k /AKT/mTOR signalling pathway and reduce adhesive capacity damage in podocytes under mechanical stress
- Honokiol induces autophagy of neuroblastoma cells through activating the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR and endoplasmic reticular stress/ERK1/2 signaling pathways and suppressing cell migration
- Effects of ketamine administration on mTOR and reticulum stress signaling pathways in the brain after the infusion of rapamycin into prefrontal cortex
- Global Proteomics Revealed Klebsiella pneumoniae Induced Autophagy and oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans by inhibit ing Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway during Infection
- Gold nanoparticles reduce high glucose-induced oxidative-nitrosative stress regulated inflammation and apoptosis via tuberin-mTOR /NF-κB pathways in macrophages
- oxidative stress and Decreased Mitochondrial Superoxide Dismutase 2 and Peroxiredoxins 1 and 4 Based Mechanism of Concurrent Activation of AMPK and mTOR in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Osmotic Stress Regulates Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) Complex 1 via c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK)-mediated Raptor Protein Phosphorylation
- The mTOR promotes oxidative stress -induced apoptosis of mesangial cells in diabetic nephropathy
- Autophagy protects gastric mucosal epithelial cells from ethanol-induced oxidative damage via mTOR signaling pathway
- AKT/mTOR as novel targets of polyphenol piceatannol possibly contributing to inhibit ion of proliferation of cultured prostate cancer cells
- Targeting mTOR signaling by polyphenol s: A new therapeutic target for ageing
- Protective effects of a green tea polyphenol , epigallocatechin-3-gallate, against sevoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis involve regulation of CREB/BDNF/TrkB and Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signalling pathways in neonatal mice
- Sorghum polyphenol suppresses the growth as well as metastasis of colon cancer xenografts through co-targeting jak2/STAT3 and Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathways
- Curculigoside and polyphenol -rich ethyl acetate fraction of Molineria latifolia rhizome improved glucose uptake via potential mTOR /AKT activated GLUT4 translocation
- inhibit ion of Akt/mTOR Signaling by the Dietary flavonoid Fisetin
- flavonoid myricetin inhibit s TNF-α-stimulated production of inflammatory mediators by suppressing the Akt, mTOR and NF-κB pathways in human keratinocytes
- DUAL inhibit ION OF Pi3k /AKT AND mTOR SIGNALING IN HUMAN NON-SMALL CELL LUNG cancer CELLS BY A DIETARY flavonoid FISETIN
- Rutin, A Natural flavonoid Protects PC12 Cells Against Sodium Nitroprusside-Induced Neurotoxicity Through Activating Pi3k /Akt/mTOR and ERK1/2 Pathway
- flavonoid s inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis and autophagy through downregulation of Pi3k γ mediated Pi3k /AKT/mTOR /p70S6K/ULK signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells
- Luteolin, a natural flavonoid , inhibit s methylglyoxal induced apoptosis via the mTOR /4E-BP1 signaling pathway
- Abstract 1586: Tumor regression in a 3-D melanoma model by the dietary flavonoid fisetin is associated with inhibit ion of Akt/mTOR signaling
- [Effect of total flavonoid s in Scutellaria barbata in mediating autophagy in tumor cells via Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway].
- Dietary flavonoid tangeretin induces reprogramming of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells by targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- LZ205, a newly synthesized flavonoid compound, exerts anti-inflammatory effect by inhibit ing M1 macrophage polarization through regulating Pi3k /AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Anti-inflammatory effects of water extract of Taraxacum mongolicum hand.-Mazz on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury by suppressing Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Ethanolic Ginkgo biloba leaf extract prevents renal fibrosis through Akt/mTOR signaling in diabetic nephropathy
- Lactobacillus casei extract Induces Apoptosis in Gastric cancer by inhibit ing NF-κB and mTOR -Mediated Signaling
- Huaier extract Induces Autophagic Cell Death by inhibit ing the mTOR /S6K Pathway in Breast cancer Cells
- Rosemary extract reduces Akt/mTOR /p70S6K activation and inhibit s proliferation and survival of A549 human lung cancer cells
- PBI-05204, a supercritical CO2 extract of Nerium oleander, inhibit s growth of human pancreatic cancer via targeting the Pi3k /mTOR pathway
- Mechanism of Chemoprevention against Colon Cancer Cells Using Combined Gelam Honey and Ginger Extract via mTOR and Wnt/β-catenin Pathways.
- Bisebromoamide, an extract from Lyngbya species, induces apoptosis through ERK and mTOR inhibit ions in renal cancer cells
- Arecoline and the 30–100 kDa fraction of areca nut extract differentially regulate mTOR and respectively induce apoptosis and autophagy: a pilot study
- Ethanol extract of Remotiflori radix induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death through AMPK /mTOR signaling in human prostate cancer cells
- An enzymatically fortified ginseng extract inhibit s proliferation and induces apoptosis of KATO3 human gastric cancer cells via modulation of Bax, mTOR , PKB and IκBα
- Celastrus Orbiculatusextract could inhibit human colorectal carcinoma HT-29 cells metastasis via suppression of the mTOR signaling pathway
- Huaier aqueous extract sensitizes cells to rapamycin and cisplatin through activating mTOR signaling
- Cell Cycle Arrest of extract from Artemisia annua Linné. Via Akt-mTOR Signaling Pathway in HCT116 Colon cancer Cells
- Auraptene, a Major Compound of Supercritical Fluid extract of Phalsak (Citrus Hassaku Hort ex Tanaka), Induces Apoptosis through the Suppression of mTOR Pathways in Human Gastric cancer SNU-1 Cells
- Centipeda minima (Ebushicao) extract inhibit s Pi3k -Akt-mTOR signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-1 cells
- extract from Astragalus membranaceus inhibit breast cancer cells proliferation via Pi3k /AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Suppression of mTOR Signaling Pathways in Skeletal Muscle of Finishing Pigs by Increasing the Ratios of Ether extract and Neutral Detergent Fiber at the Expense of Starch in Iso-energetic Diets
- Apocynum leaf extract inhibit s the progress of atherosclerosis in rats via the AMPK /mTOR pathway
- AMPK and mTOR coordinate the regulation of Ulk1 and mammalian autophagy initiation
- AMPK and mTOR in Cellular Energy Homeostasis and Drug Targets
- mTOR , AMPK , and GCN2 coordinate the adaptation of hepatic energy metabolic pathways in response to protein intake in the rat
- Metformin, independent of AMPK, induces mTOR inhibition and cell-cycle arrest through REDD1.
- Folliculin encoded by the BHD gene interacts with a binding protein, FNIP1, and AMPK , and is involved in AMPK and mTOR signaling
- The autophagy initiating kinase ULK1 is regulated via opposing phosphorylation by AMPK and mTOR
- A possible linkage between AMP‐activated protein kinase (AMPK ) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) signalling pathway
- Selective activation of AMPK -PGC-1α or PKB-TSC2-mTOR signaling can explain specific adaptive responses to endurance or resistance training-like electrical muscle stimulation
- Discrete mechanisms of mTOR and cell cycle regulation by AMPK agonists independent of AMPK
- The regulation of AMPK beta1, TSC2, and PTEN expression by p53: stress, cell and tissue specificity, and the role of these gene products in modulating the IGF-1-AKT-mTOR pathways.
- The Role of AMPK and mTOR in Nutrient Sensing in Pancreatic β-Cells
- Cross-Talk between AMPK and mTOR in Regulating Energy Balance
- Therapeutic metformin/AMPK activation blocked lymphoma cell growth via inhibit ion of mTOR pathway and induction of autophagy
- A central role for neuronal AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in high-protein diet-induced weight loss.
- The LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway has tumor suppressor activity in acute myeloid leukemia through the repression of mTOR -dependent oncogenic mRNA translation
- Antroquinonol displays anticancer potential against human hepatocellular carcinoma cells: A crucial role of AMPK and mTOR pathways
- Coordinated time-dependent modulation of AMPK /Akt/mTOR signaling and autophagy controls osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- Resveratrol engages AMPK to attenuate ERK and mTOR signaling in sensory neurons and inhibit s incision-induced acute and chronic pain
- Berberine alleviates ox-LDL induced inflammatory factors by up-regulation of autophagy via AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway
- Chondrocyte autophagy is stimulated by HIF-1 dependent AMPK activation and mTOR suppression
- Differentiated mTOR but not AMPK signaling after strength vs endurance exercise in training‐accustomed individuals
- Central Exercise Action Increases the AMPK and mTOR Response to Leptin
- AMPK -Mediated inhibit ion of mTOR Kinase Is Circumvented during Immediate-Early Times of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection
- Hypoxia-Induced Energy Stress inhibit s the mTOR Pathway by Activating an AMPK /REDD1 Signaling Axis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Perivascular fat-mediated vascular dysfunction and remodeling through the AMPK /mTOR pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese rats
- GLP-1 analogue improves hepatic lipid accumulation by inducing autophagy via AMPK /mTOR pathway
- Resveratrol enhances prostate cancer cell response to ionizing radiation. Modulation of the AMPK , Akt and mTOR pathways
- Betulinic acid alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver by inhibit ing SREBP1 activity via the AMPK –mTOR –SREBP signaling pathway
- Repression of protein synthesis and mTOR signaling in rat liver mediated by the AMPK activator aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleoside
- The AMPK stress response pathway mediates anoikis resistance through inhibit ion of mTOR and suppression of protein synthesis
- Altered LKB1/AMPK /TSC1/TSC2/mTOR signaling causes disruption of Sertoli cell polarity and spermatogenesis
- AMPK /mTOR -mediated inhibit ion of survivin partly contributes to metformin-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cell
- Stabilization and activation of p53 downregulates mTOR signaling through AMPK in mantle cell lymphoma
- Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Induces Autophagy via the AMPK /ERK/TSC2/mTOR Signaling Pathway in PK-15 Cells
- P2X7 Integrates Pi3k /AKT and AMPK -PRAS40-mTOR Signaling Pathways to Mediate Tumor Cell Death
- The human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue liraglutide regulates pancreatic beta-cell proliferation and apoptosis via an AMPK /mTOR /P70S6K signaling pathway
- Autophagic cell death induced by resveratrol depends on the Ca2+/AMPK /mTOR pathway in A549 cells
- Akt activation protects pancreatic beta cells from AMPK -mediated death through stimulation of mTOR
- GLUT1 enhances mTOR activity independently of TSC2 and AMPK
- Activation of AMPK and inactivation of Akt result in suppression of mTOR -mediated S6K1 and 4E-BP1 pathways leading to neuronal cell death in in vitro models of Parkinson’s disease
- NAD Blocks High Glucose Induced Mesangial Hypertrophy via Activation of the Sirtuins-AMPK –mTOR Pathway
- ARG2 impairs endothelial autophagy through regulation of mTOR and PRKAA/AMPK signaling in advanced atherosclerosis
- Resveratrol Enhances the Antitumor Effects of Temozolomide in Glioblastoma via ROS‐dependent AMPK ‐TSC‐mTOR Signaling Pathway
- Feeding Uninvited Guests: mTOR and AMPK Set the Table for Intracellular Pathogens
- 4-Nonylphenol induces apoptosis, autophagy and necrosis in Sertoli cells: Involvement of ROS-mediated AMPK /AKT-mTOR and JNK pathways
- Warming Up to New Possibilities with the Capsaicin Receptor TRPV1: mTOR , AMPK , and Erythropoietin
- Alcohol and PRAS40 knockdown decrease mTOR activity and protein synthesis via AMPK signaling and changes in mTOR C1 interaction
- Silencing of Twist1 sensitizes NSCLC cells to cisplatin via AMPK -activated mTOR inhibit ion
- Quercetin Regulates Sestrin 2-AMPK –mTOR Signaling Pathway and Induces Apoptosis via Increased Intracellular ROS in HCT116 Colon cancer Cells
- Glucose stimulates protein synthesis in skeletal muscle of neonatal pigs through an AMPK – and mTOR -independent process
- A combination of four active compounds alleviates cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury in correlation with inhibit ion of autophagy and modulation of AMPK /mTOR and JNK pathways
- Reduced AMPK -ACC and mTOR signaling in muscle from older men, and effect of resistance exercise
- l-Glutamine enhances enterocyte growth via activation of the mTOR signaling pathway independently of AMPK
- Glucose promotes cell proliferation, glucose uptake and invasion in endometrial cancer cells via AMPK /mTOR /S6 and MAPK signaling
- Antifungal drug itraconazole targets VDAC1 to modulate the AMPK /mTOR signaling axis in endothelial cells
- Adiponectin attenuates the osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells through the AMPK /mTOR pathway
- Tanshinone IIA Induces Autophagic Cell Death via Activation of AMPK and ERK and inhibit ion of mTOR and p70 S6K in KBM‐5 Leukemia Cells
- Activation of autophagy via Ca2+-dependent AMPK /mTOR pathway in rat notochordal cells is a cellular adaptation under hyperosmotic stress
- Mesenchymal stem cells promote colorectal cancer progression through AMPK /mTOR -mediated NF-κB activation
- Docosahexaenoic Acid Induces Cell Death in Human Non-Small Cell Lung cancer Cells by Repressing mTOR via AMPK Activation and Pi3k /Akt inhibit ion
- FK866-induced NAMPT inhibit ion activates AMPK and downregulates mTOR signaling in hepatocarcinoma cells
- Resveratrol-induced autophagy and apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant human oral cancer CAR cells: A key role of AMPK and Akt/mTOR signaling
- Berberine induces autophagy in glioblastoma by targeting the AMPK /mTOR /ULK1-pathway
- A Novel Dual AMPK Activator/mTOR inhibit or inhibit s Thyroid cancer Cell Growth
- Autophagy facilitates lung adenocarcinoma resistance to cisplatin treatment by activation of AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway
- Activation of Autophagic Flux against Xenoestrogen Bisphenol-A-induced Hippocampal Neurodegeneration via AMP kinase (AMPK )/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) Pathways
- Hydrogen sulfide reduces serum triglyceride by activating liver autophagy via the AMPK –mTOR pathway
- miR-124 regulates cell apoptosis and autophagy in dopaminergic neurons and protects them by regulating AMPK /mTOR pathway in Parkinson’s disease
- Effects of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK ) signaling and essential amino acids on mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR ) signaling and protein synthesis rates in mammary cells
- Thyroid hormone improves the mechanical performance of the post-infarcted diabetic myocardium: A response associated with up-regulation of Akt/mTOR and AMPK activation
- GYY4137, a novel hydrogen sulfide-releasing molecule, likely protects against high glucose-induced cytotoxicity by activation of the AMPK /mTOR signal pathway in H9c2 cells
- Pioglitazone, a PPARγ agonist, attenuates PDGF-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through AMPK -dependent and AMPK -independent inhibit ion of mTOR /p70S6K and ERK signaling
- Negative regulation of mTOR activity by LKB1-AMPK signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Early molecular and behavioral response to lipopolysaccharide in the WAG/Rij rat model of absence epilepsy and depressive-like behavior, involves interplay between AMPK , AKT/mTOR pathways and neuroinflammatory cytokine release
- Anti-Breast cancer Potential of Quercetin via the Akt/AMPK /Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) Signaling Cascade
- Exendin-4 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway activation
- A systems study reveals concurrent activation of AMPK and mTOR by amino acids
- Salmonella Typhimurium disrupts Sirt1/AMPK checkpoint control of mTOR to impair autophagy
- 2-Deoxy-d-glucose cooperates with arsenic trioxide to induce apoptosis in leukemia cells: Involvement of IGF-1R-regulated Akt/mTOR , MEK/ERK and LKB-1/AMPK signaling pathways
- Metformin preconditioning protects Daphnia pulex from lethal hypoxic insult involving AMPK , HIF and mTOR signaling
- Strategies of Eradicating Glioma Cells: A Multi-Scale Mathematical Model with MiR-451-AMPK –mTOR Control
- Phenformin Induces Cell Cycle Change, Apoptosis, and Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition and Regulates the AMPK /mTOR /p70s6k and MAPK/ERK Pathways in Breast cancer Cells
- Sirt3 confers protection against neuronal ischemia by inducing autophagy: Involvement of the AMPK –mTOR pathway
- hepaCAM and p-mTOR Closely Correlate in Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma and hepaCAM Expression inhibit s Proliferation via an AMPK /mTOR Dependent Pathway in Human Bladder cancer Cells
- Hormetic effect of panaxatriol saponins confers neuroprotection in PC12 cells and zebrafish through Pi3k /AKT/mTOR and AMPK /SIRT1/FOXO3 pathways
- Ox-Lp(a) transiently induces HUVEC autophagy via an ROS-dependent PAPR-1-LKB1–AMPK –mTOR pathway
- Liraglutide relieves myocardial damage by promoting autophagy via AMPK –mTOR signaling pathway in zucker diabetic fatty rat
- Hydrogen sulphide exacerbates acute pancreatitis by over‐activating autophagy viaAMPK /mTOR pathway
- Palmitate activates mTOR /p70S6K through AMPK inhibit ion and hypophosphorylation of raptor in skeletal muscle cells: Reversal by oleate is similar to metformin
- 4-Nonylphenol induces autophagy and attenuates mTOR -p70S6K/4EBP1 signaling by modulating AMPK activation in Sertoli cells
- Autophagy Induction by Silibinin Positively Contributes to Its Anti-Metastatic Capacity via AMPK /mTOR Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Alisertib induces apoptosis and autophagy through targeting the AKT/mTOR /AMPK /p38 pathway in leukemic cells
- Sestrin2, as a negative feedback regulator of mTOR , provides neuroprotection by activation AMPK phosphorylation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in rat pups
- Metformin Suppresses Systemic Autoimmunity in Roquinsan/san Mice through inhibit ing B Cell Differentiation into Plasma Cells via Regulation of AMPK /mTOR /STAT3
- Novel mechanism of reducing tumourigenesis: Upregulation of the DNA repair enzyme OGG1 by rapamycin-mediated AMPK activation and mTOR inhibit ion
- 20‐O‐β‐d‐Glucopyranosyl‐20(S)‐Protopanaxadiol Suppresses UV‐Induced MMP‐1 Expression Through AMPK ‐Mediated mTOR inhibit ion as a Downstream of the PKA‐LKB1 Pathway
- Chitosan oligosaccharide suppresses tumor progression in a mouse model of colitis-associated colorectal cancer through AMPK activation and suppression of NF-κB and mTOR signaling
- Role of Energy- and Nutrient-sensing KinasesAMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK ) andMammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) inAdipocyte Differentiation
- Cyanidin-3-O-β-glucoside and protocatechuic acid activate AMPK /mTOR /S6K pathway and improve glucose homeostasis in mice
- Mimulone-Induced Autophagy through p53-Mediated AMPK /mTOR Pathway Increases Caspase-Mediated Apoptotic Cell Death in A549 Human Lung cancer Cells
- G9a inhibit ion Induces Autophagic Cell Death via AMPK /mTOR Pathway in Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma
- Aβ peptide secretion is reduced by Radix Polygalae‑induced autophagy via activation of the AMPK /mTOR pathway
- Down-regulation of HSP60 Suppresses the Proliferation of Glioblastoma Cells via the ROS/AMPK /mTOR Pathway
- Activation of autophagy through calcium-dependentAMPK /mTOR and PKChpathway causes activation of rathepatic stellate cells under hypoxic stress
- Exogenous H2S Protects Against Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Activating Autophagy via the AMPK /mTOR Pathway
- PAS Kinase Is a Nutrient and Energy Sensor in Hypothalamic Areas Required for the Normal Function of AMPK and mTOR /S6K1
- NQO1 Deficiency Leads Enhanced Autophagy in Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Through the AMPK /TSC2/mTOR Signaling Pathway
- The AMPK Agonist PT1 and mTOR inhibit or 3HOI-BA-01 Protect Cardiomyocytes After Ischemia Through Induction of Autophagy
- PARP-1 promotes autophagy via the AMPK /mTOR pathway in CNE-2 human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells following ionizing radiation, while inhibit ion of autophagy contributes to the radiation sensitization of CNE-2 cells
- Chronic Hypoxia-Induced Autophagy Aggravates the Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s Disease through AMPK –mTOR Signaling in the APPSwe/PS1dE9 Mouse Model
- α‐enolase promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis via regulating AMPK /mTOR pathway in colorectal cancer
- Macrophage migration inhibit ory factor promotes cardiac stem cell proliferation and endothelial differentiation through the activation of the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR and AMPK pathways
- AMPK and mTOR : sensors and regulators of immunometabolic changes during Salmonella infection in the chicken
- Polysaccharide from Fuzi Likely Protects Against Starvation-Induced Cytotoxicity in H9c2 Cells by Increasing Autophagy Through Activation of the AMPK /mTOR Pathway
- Augmented β-Cell Function and Mass in Glucocorticoid-Treated Rodents Are Associated with Increased Islet Ir-β/AKT/mTOR and Decreased AMPK /ACC and AS160 Signaling
- Vitamin D3 potentiates the growth inhibit ory effects of metformin in DU145 human prostate cancer cells mediated by AMPK /mTOR signalling pathway
- Liraglutide attenuates the osteoblastic differentiation of MC3T3‑E1 cells by modulating AMPK /mTOR signaling
- Cytoprotective effect of kaempferol against palmitic acid-induced pancreatic β-cell death through modulation of autophagy via AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway
- polyphenol ics from mango (Mangifera indica L.) suppress breast cancer ductal carcinoma in situ proliferation through activation of AMPK pathway and suppression of mTOR in athymic nude mice
- The antidepressant effects of ɑ-tocopherol are related to activation of autophagy via the AMPK /mTOR pathway
- CSC-3436 switched tamoxifen-induced autophagy to apoptosis through the inhibit ion of AMPK /mTOR pathway
- Methylation-induced silencing of miR-34a enhances chemoresistance by directly upregulating ATG4B-induced autophagy through AMPK /mTOR pathway in prostate cancer
- Se‐Allylselenocysteine induces autophagy by modulating the AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway and epigenetic regulation of PCDH17 in human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells
- Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor alleviated 6-OHDA-induced cell damage via ROS-AMPK /mTOR mediated autophagic inhibit ion
- Myocardial Ischemic Postconditioning Promotes Autophagy against Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via the Activation of the nNOS/AMPK /mTOR Pathway
- Local intra-articular injection of resveratrol delays cartilage degeneration in C57BL/6 mice by inducing autophagy via AMPK /mTOR pathway
- Long-term caloric restriction in ApoE-deficient mice results in neuroprotection via Fgf21-induced AMPK /mTOR pathway
- Resveratrol down-regulates a glutamate-induced tissue plasminogen activator via Erk and AMPK /mTOR pathways in rat primary cortical neurons
- Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) Promotes Autophagy-Dependent Survival via Influencing the Balance of mTOR –AMPK Pathways upon Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
- Shengmai injection attenuates the cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induced autophagy via modulation of the AMPK , mTOR and JNK pathways
- Role of nutraceutical SIRT1 modulators in AMPK and mTOR pathway: Evidence of a synergistic effect
- Isoflurane Preconditioning Alleviated Murine Liver Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury by Restoring AMPK /mTOR -Mediated Autophagy
- Anti-Tumor Activity of Yuanhuacine by Regulating AMPK /mTOR Signaling Pathway and Actin Cytoskeleton Organization in Non-Small Cell Lung cancer Cells
- SH2 domain-containing inositol 5-phosphatase (SHIP2) inhibit ion ameliorates high glucose-induced de-novo lipogenesis and VLDL production through regulating AMPK /mTOR /SREBP1 pathway and ROS production in HepG2 cells
- β‐asarone inhibit ed cell growth and promoted autophagy via P53/Bcl‐2/Bclin‐1 and P53/AMPK /mTOR pathways in Human Glioma U251 cells
- Tris (1, 3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate induces apoptosis and autophagy in SH-SY5Y cells: Involvement of ROS-mediated AMPK /mTOR /ULK1 pathways
- Neferine reduces cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing autophagy via the AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway
- Acute stimulation of glucose influx upon mitoenergetic dysfunction requires LKB1, AMPK , Sirt2 and mTOR –RAPTOR
- SR4 Uncouples Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation, Modulates AMP-dependent Kinase (AMPK )-Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR ) Signaling, and inhibit s Proliferation of HepG2 Hepatocarcinoma Cells
- Eugenol Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis by Down-Regulating SREBP1 Gene Expression via AMPK –mTOR -p70S6K Signaling Pathway
- Silencing Nrf2 impairs glioma cell proliferation via AMPK -activated mTOR inhibit ion
- Suppression of c-Myc induces apoptosis via an AMPK /mTOR -dependent pathway by 4-O-methyl-ascochlorin in leukemia cells
- Functional Effects of a Pathogenic Mutation in Cereblon (CRBN) on the Regulation of Protein Synthesis via the AMPK –mTOR Cascade
- Hydrogen peroxide inhibit s mTOR signaling by activation of AMPK α leading to apoptosis of neuronal cells
- The endotoxemia cardiac dysfunction is attenuated by AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway regulating autophagy
- Pleurotus nebrodensis polysaccharide(PN50G) evokes A549 cell apoptosis by the ROS/AMPK /Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway to suppress tumor growth
- Akt/AMPK /mTOR pathway was involved in the autophagy induced by vitamin E succinate in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells
- 2-Arylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid amides (ATCAA) target dual pathways in cancer cells: 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK )/mTOR and Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathways
- Berberine regulates proliferation, collagen synthesis and cytokine secretion of cardiac fibroblasts via AMPK –mTOR -p70S6K signaling pathway
- Netrin-1 Improves Functional Recovery through Autophagy Regulation by Activating the AMPK /mTOR Signaling Pathway in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury
- Irbesartan ameliorates hyperlipidemia and liver steatosis in type 2 diabetic db/db mice via stimulating PPAR-γ, AMPK /Akt/mTOR signaling and autophagy
- Rhein inhibit s Autophagy in Rat Renal Tubular Cells by Regulation of AMPK /mTOR Signaling
- Cucurbitacin E ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in vivo and in vitro through activation of AMPK and blocking mTOR -dependent signaling pathway
- Global Liver Proteome Analysis Using iTRAQ Reveals AMPK –mTOR –Autophagy Signaling Is Altered by Intrauterine Growth restriction in Newborn Piglets
- A unique amidoanthraquinone derivative displays antiproliferative activity against human hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer s through activation of LKB1-AMPK –mTOR signaling pathway
- The mTOR /Pi3k and MAPK pathways converge on eIF4B to control its phosphorylation and activity
- Targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway: Effective combinations and clinical considerations
- Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway in angiogenesis
- Targeting the Pi3k –AKT–mTOR pathway: progress, pitfalls, and promises
- Targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway – Beyond Rapalogs
- Regulation of Dendritic Morphogenesis by Ras–Pi3k –Akt–mTOR and Ras–MAPK Signaling Pathways
- Overcoming acquired resistance to anticancer therapy: focus on the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway
- De novo somatic mutations in components of the Pi3k -AKT3-mTOR pathway cause hemimegalencephaly
- Contributions of the Raf/MEK/ERK, Pi3k /PTEN/Akt/mTOR and Jak/STAT pathways to leukemia
- Strategies for co-targeting the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway in NSCLC
- insulin -like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) Inversely Regulates Atrophy-induced Genes via the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (Pi3k /Akt/mTOR ) Pathway
- The role of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration
- Restraining Pi3k : mTOR signalling goes back to the membrane
- Role of the Pi3k /AKT and mTOR signaling pathways in acute myeloid leukemia
- Involvement of Pi3k /PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in invasion and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma: Association with MMP‐9
- The Pi3k -Akt-mTOR pathway in initiation and progression of thyroid tumors
- The Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway in innate immune cells: emerging therapeutic applications
- Activation of the Pi3k /mTOR pathway by BCR-ABL contributes to increased production of reactive oxygen species
- Pharmacogenomic profiling of the Pi3k /PTEN-AKT-mTOR pathway in common human tumors
- The TORrid affairs of viruses: effects of mammalian DNA viruses on the Pi3k –Akt–mTOR signalling pathway
- The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the Pi3k /AKT signalling pathways: role in cancer pathogenesis and implications for therapeutic approaches
- Pi3k /Akt/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways inhibit ors as anticancer agents: Structural and pharmacological perspectives
- Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and targeted therapy for glioblastoma
- PDGFRs are critical for Pi3k /Akt activation and negatively regulated by mTOR
- Curcumin, a dietary component, has anticancer, chemosensitization, and radiosensitization effects by down-regulating the MDM2 oncogene through the PI3K/mTOR/ETS2 pathway.
- Targeting the translational apparatus to improve leukemia therapy: roles of the Pi3k /PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway
- Complementary genomic approaches highlight the Pi3k /mTOR pathway as a common vulnerability in osteosarcoma
- Targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Transformation by v-Src: Ras-MAPK and Pi3k –mTOR Mediate Parallel Pathways
- inhibit ion of Pi3k /mTOR pathways in glioblastoma and implications for combination therapy with temozolomide
- Targeting survival cascades induced by activation of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK, Pi3k /PTEN/Akt/mTOR and Jak/STAT pathways for effective leukemia therapy
- Pi3k -FRAP/mTOR pathway is critical for hepatocyte proliferation whereas MEK/ERK supports both proliferation and survival
- The Pi3k -Akt-mTOR pathway regulates Aβ oligomer induced neuronal cell cycle events
- Aberrant STAT5 and Pi3k /mTOR pathway signaling occurs in human CRLF2-rearranged B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Status of Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway inhibit ors in Lymphoma
- Pi3k /AKT signaling pathway and cancer : an updated review
- Resveratrol downregulates Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in human U251 glioma cells
- Activation of the Pi3k -Akt-mTOR signaling pathway promotes necrotic cell death via suppression of autophagy
- β-Caryophyllene oxide inhibit s growth and induces apoptosis through the suppression of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR /S6K1 pathways and ROS-mediated MAPKs activation
- Emerging roles of the p38 MAPK and Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathways in oncogene-induced senescence
- Therapeutic resistance resulting from mutations in Raf/MEK/ERK and Pi3k /PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways
- Crosstalk Between the Pi3k /mTOR and MEK/ERK Pathways Involved in the Maintenance of Self‐Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma Stem‐Like Cells
- Combined targeting of MEK and Pi3k /mTOR effector pathways is necessary to effectively inhibit NRAS mutant melanoma in vitro and in vivo
- Management of Metabolic Effects Associated With Anticancer Agents Targeting the Pi3k -Akt-mTOR Pathway
- PI-103 and Sorafenib inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation by Blocking Ras/Raf/MAPK and Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathways
- Dual targeting of the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway as an antitumor strategy in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
- Evolving Strategies for Overcoming Resistance to HER2-Directed Therapy: Targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway
- Activation of the N-Ras–Pi3k –Akt-mTOR Pathway by Hepatitis C Virus: Control of Cell Survival and Viral Replication
- Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway inhibit ors in the therapy of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
- Dual inhibition of the PI3K/mTOR pathway increases tumor radiosensitivity by normalizing tumor vasculature.
- Targeting the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
- Leptin regulates proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal carcinoma through Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signalling pathway
- Preclinical Rationale for Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway inhibit ors as Therapy for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor inhibit or-Resistant Non–Small-Cell Lung cancer
- Targeting the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in glioblastoma: novel therapeutic agents and advances in understanding
- Synergistic effects between auristatin-based antibody drug conjugates and inhibit ors of the Pi3k -AKT mTOR pathway
- Activation of the Pi3k /mTOR /AKT Pathway and Survival in Solid Tumors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- inhibit ion of the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway in Solid Tumors
- Targeting the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway: Biomarkers of Success and Tribulation
- Pyrazino[2,3-b]pyrazine mTOR kinase inhibit ors for oncology indications and diseases associated with the mTOR /Pi3k /Akt pathway
- Advanced glycation endproducts trigger autophagy in cadiomyocyte Via RAGE/Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathway
- Roles of Pi3k /AKT/GSK3/mTOR Pathway in Cell Signaling of Mental Illnesses
- Pi3k ing the Lock: Targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Neuroblastoma
- Suppression of Feedback Loops Mediated by Pi3k /mTOR Induces Multiple Overactivation of Compensatory Pathways: An Unintended Consequence Leading to Drug Resistance
- Dysregulation of the IGF-I/Pi3k /AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in autism spectrum disorders
- The Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Pathway as Therapeutic Target in Neuroblastoma
- Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in airway smooth muscle: rationale and promise.
- Targeting the RTK-Pi3k –mTOR Axis in Malignant Glioma: Overcoming Resistance
- Evidence for Down-Regulation of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (Pi3k /Akt/mTOR )-Dependent Translation Regulatory Signaling Pathways in Ames Dwarf Mice
- 9-Aminoacridine-based anticancer drugs target the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR , NF-κB and p53 pathways
- Molecular neuro-oncology and development of targeted therapeutic strategies for brain tumors. Part 2: Pi3k /Akt/PTEN, mTOR , SHH/PTCH and angiogenesis
- AKTivation of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by KSHV
- Autophagy suppression promotes apoptotic cell death in response to inhibit ion of the Pi3k —mTOR pathway in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- IGF‐1‐stimulated protein synthesis in oligodendrocyte progenitors requires Pi3k /mTOR /Akt and MEK/ERK pathways
- Arenobufagin, a natural bufadienolide from toad venom, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inhibit ion of Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway
- Loss of Tsc1/Tsc2 activates mTOR and disrupts Pi3k -Akt signaling through downregulation of PDGFR
- Activation of RAF/MEK/ERK and Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathways in pituitary adenomas and their effects on downstream effectors
- Dual blockade of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR (AZD8055) and RAS/MEK/ERK (AZD6244) pathways synergistically inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo
- Potential therapeutic targets for chordoma: Pi3k /AKT/TSC1/TSC2/mTOR pathway
- The Pi3k /AKT/mTOR interactive pathway
- The critical role of IL-15–Pi3k –mTOR pathway in natural killer cell effector functions
- Targeting the Pi3k /mTOR pathway in pediatric hematologic malignancies
- Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin (Pi3k -Akt-mTOR ) signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer
- Caffeine induces apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via Pi3k /Akt/mTOR /p70S6K inhibit ion
- Silica nanoparticles induce autophagy and endothelial dysfunction via the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Activation of the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway correlates with tumour progression and reduced survival in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder
- Increased activation of Pi3k /AKT signaling pathway is associated with cholangiocarcinoma metastasis and Pi3k /mTOR inhibit ion presents a possible therapeutic strategy
- The Role of Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Signaling in Gastric Carcinoma
- IL-22 induced cell proliferation is regulated by Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling cascade
- Neuroprotective effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediated by autophagy through the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway
- Therapeutic Priority of the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway in Small Cell Lung cancer s as Revealed by a Comprehensive Genomic Analysis
- Targeting the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its therapeutic potential
- PF-04691502, a Potent and Selective Oral inhibit or of Pi3k and mTOR Kinases with Antitumor Activity
- SMAD-Pi3k -Akt-mTOR Pathway Mediates BMP-7 Polarization of Monocytes into M2 Macrophages
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) protects against methylglyoxal-induced PC12 cell apoptosis through the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR /GCLc/redox signaling pathway
- Selective inhibit ion of Pi3k /Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway Regulates Autophagy of Macrophage and Vulnerability of Atherosclerotic Plaque
- Increased AKT S473 phosphorylation after mTOR C1 inhibit ion is rictor dependent and does not predict tumor cell response to Pi3k /mTOR inhibit ion
- HBx induces HepG-2 cells autophagy through Pi3k /Akt–mTOR pathway
- Targeting Pi3k /AKT/mTOR network for treatment of leukemia
- Characterization of the Activity of the Pi3k /mTOR inhibit or XL765 (SAR245409) in Tumor Models with Diverse Genetic Alterations Affecting the Pi3k Pathway
- Antitumor efficacy of PKI-587, a highly potent dual PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor.
- Ablation of Pi3k blocks BCR-ABL leukemogenesis in mice, and a dual Pi3k /mTOR inhibit or prevents expansion of human BCR-ABL+ leukemia cells
- The Pi3k /Akt and mTOR /P70S6K Signaling Pathways in Human Uveal Melanoma Cells: Interaction with B-Raf/ERK
- Mutations and Deregulation of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and Pi3k /PTEN/Akt/mTOR Cascades Which Alter Therapy Response
- Activation of Pi3k /mTOR pathway occurs in most adult low-grade gliomas and predicts patient survival
- Clinical potential of novel therapeutic targets in breast cancer : CDK4/6, Src, JAK/STAT, PARP, HDAC, and Pi3k /AKT/mTOR pathways
- Multipoint targeting of the Pi3k /mTOR pathway in mesothelioma
- Differential Effects of Selective inhibit ors Targeting the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Vertical inhibit ion of the Pi3k /Akt/mTOR pathway for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Downregulation of Pi3k /Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in curcumin-induced autophagy in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice
- Intranasally delivered siRNA targeting Pi3k /Akt/mTOR inflammatory pathways protects from aspergillosis
- Thyroid Hormone Stimulates Protein Synthesis in the Cardiomyocyte by Activating the Akt-mTOR and p70S6K Pathways
- inhibit ion of Notch Signaling Promotes the Adipogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Autophagy Activation and PTEN-Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway
- A Pan-cancer Proteogenomic Atlas of Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Pathway Alterations
- Pi3k /AKT/mTOR and sonic hedgehog pathways cooperate together to inhibit human pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics and tumor growth
- Identification of a Role for the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Innate Immune Cells
- Targeting the Pi3k /AKT/mTOR signaling network in acute myelogenous leukemia
- Pi3k -Akt-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in polycystic ovarian syndrome, uterine leiomyomas and endometriosis: an update
- Synergistic inhibit ion of ovarian cancer cell growth by combining selective Pi3k /mTOR and RAS/ERK pathway inhibit ors
- Matrix IGF-1 maintains bone mass by activation of mTOR in mesenchymal stem cells
- Regulation of survivin expression by IGF-1/mTOR signaling