
PEEL & SPICE (Combo Pack)
July 1, 2019
HELICO (Helicobacter Pylori Destroyer)
November 8, 2019AUTOPHAGY ACTIVATOR
$275.00
The Most Powerful Science Based Autophagy Activating Formula on the Planet!
MEGA APPETITE SUPPRESSANT! Read the reviews!
The ULTIMATE fasting companion.
100g bag = 300 1/8 tsp servings.
2-deoxy-d-glucose (2-DG) • 8-Prenylnaringenin • Albatrellus confluens • Alisol B isolated from Alisma orientale • Allicin • Amorphophallus konjac tubor • Anthocyanin extract from black soybean (Glycine max L.) • Apigenin • Apios americana Medik flowers extract • Areca nut • Artemisia vulgaris (mugwort) • Azuki bean (Vigna angularis) extract • Bacopa monnieri • Benzoin gum (Styrax benzoin) • Berberine • Betanin‐Enriched Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) • Bitter Melon Extract Saponins30% • Brunfelsia grandiflora • Butea monosperma (Lam.) flowers • Buxus sempervirens • Carnosic acid (CA), a polyphenolic diterpene isolated from Rosemary (Rosemarinus officinalis) • Carnosol • Catechin • Celastrol (tripterine) isolated from the root extracts of Tripterygium wilfordii (Thunder god vine) • Celastrus orbiculatus • Cepharanthine (CEP) a biscoclaurine alkaloid extracted from Stephania cepharantha • Chaihu (Radix bupleuri), • Chebulagic acid from Terminalia chebula • Chuan xiong (Rhizoma chuanxiong) • Cichorium intybus Linn. Extract • Clionamine B Isolated from Cliona celata • convallatoxin isolated from Antiaris toxicaria, • Cordycepin • Corynoxine B , isolated from Uncaria rhynchophylla (Miq.) Jacks (Gouteng in Chinese), • Cucurbita moschata, variety “long of Naples,” • Curcumin • Dandelion root • Dihydromyricetin (Ampelopsin) • Dimethyl cardamonin isolated from Syzygium samarangense • Dioscin • Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) • Donglingcao (Rabdosia rubesens), • EGb 761 from Ginkgo biloba extract • Emblica officinalis extract • Evodiamine, an alkaloid isolated from Evodia rutaecarpa • Fenugreek • Fisetin • Fragaria vesca leaves • Fucoidan • Fucoxanthin from Laminaria japonica • Galangin • Ganoderma lucidum • Genistein • Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) • Gingerol • Ginsenoside 20 (S)-Rg3 • Glucosamine • Glutathione • Gynura formosana Kitam. leaves • Hibiscus sabdariffa Leaf • Honokiol from Magnolia officinalis • Hou po (Cortex magnoliae officinalis) • Hu Zhang (Rhizoma polygoni cuspidati), • Huaier extract • Isorhamnetin from sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) • Isorhynchophylline (IsoRhy) from Uncaria rhynchophylla • Kaempferol • Luteolin • Matrine • Mung bean (Vigna Radiata) • Muscadine grape skin extract • Myrtillin • Naringin • oblongifolin C from Garcinia yunnanensis Hu • Old Man’s Beard (Usnea barbata) • Oleanolic acid • Onjisaponin B derived from Radix Polygalae • Oridonin • Paclitaxel from pacific yew tree • Panax ginseng • Parthenolide from Feverfew • Phellinus Linteus Extract • Pimenta dioica berries (Allspice) • Piperine • Piperlongumine (PL), from fruit of Long pepper (Piper longum) • Pluchea indica root extract • Plumbagin from Plumbago zeylanica L, Juglans regia, J. cinerea, and J. nigra • Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua • Quercetin • Resveratrol • Rhodiola rosea • Rottlerin from Mallotus philippinensis • Safflower extract • Salidroside • Sarsaparilla (Smilax glabra rhizome) extract • Saussurea lappa extract • Schisandrin A. (Schisandra chinensis fructus) • Silibinin • Tanshinone IIA from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, • Theobroma cacao L • Triptolide (TPL) from Tripterygium wilfordii, • Ursolic acid • Vitamin D3 • Vitamin K2 (MK4) • Vitexin • Wogonin from Scutellaria baicalensis
Click on studies below to learn more:
2-deoxy-d-glucose (2-DG)
- The wonders of 2‐deoxy‐d‐glucose
- 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Treatment of Endothelial Cells Induces autophagy by Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Activation of the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase
- Mitofusin 2-Deficiency Suppresses Cell Proliferation through Disturbance of autophagy
- 2-Deoxy-d-glucose enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells through downregulating JNK-mediated cytoprotective autophagy
- Synergy of 2-deoxy-d-glucose combined with berberine in inducing the lysosome/autophagy and transglutaminase activation-facilitated apoptosis
- Glycolysis inhibition by 2-deoxy-d-glucose reverts the metastatic phenotype in vitro and in vivo
- Synergistic increase in efficacy of a combination of 2-deoxy-d-glucose and cisplatin in normoxia and hypoxia: switch from autophagy to apoptosis
- 2‐deoxy‐D‐glucose augments photodynamic therapy induced mitochondrial caspase‐independent apoptosis and energy‐mediated autophagy
- Therapeutic starvation and autophagy in prostate cancer: A new paradigm for targeting metabolism in cancer therapy
- Differential effects of the glycolysis inhibitor 2‐deoxy‐D‐glucose on the activity of pro‐apoptotic agents in metastatic melanoma cells, and induction of a cytoprotective autophagic response
- Melatonin-Mediated Intracellular Insulin during 2-Deoxy-d-glucose Treatment Is Reduced through autophagy and EDC3 Protein in Insulinoma INS-1E Cells
- 2-Deoxy-d-glucose Suppresses the In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy of Erlotinib in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
- Glucose starvation-mediated inhibition of salinomycin induced autophagy amplifies cancer cell specific cell death
- FF when combined with 2-DG lowers ATP levels and inhibits autophagy
- 2-Deoxy-D-glucose targeting of glucose metabolism in cancer cells as a potential therapy
- Glucosamine induces autophagy via an mtor-independent pathway
- Chronic ingestion of 2-deoxy-d-glucose induces cardiac vacuolization and increases mortality in rats
- Deconvoluting the role of reactive oxygen species and autophagy in human diseases
- Hexokinase-II Positively Regulates Glucose Starvation-Induced autophagy through TORC1 Inhibition
- Inhibition of autophagy by 3‑MA enhances endoplasmic reticulum stress‑induced apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- 2-DG led to a higher expression of Beclin-1, a crucial component of the autophagy pathway
- Glycolysis inhibitor 2-deoxy-D-glucose suppresses carcinogen-induced rat hepatocarcinogenesis by restricting cancer cell metabolism
- Glycolytic inhibitor 2-deoxy-d-glucose suppresses cell proliferation and enhances methylprednisolone sensitivity in non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells through down-regulation of HIF-1α and c-MYC
- autophagy induced by 2-deoxy-D-glucose suppresses intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in A/J mouse macrophages
- The combination of tephrosin with 2-deoxy-D-glucose enhances the cytotoxicity via accelerating ATP depletion and blunting autophagy in human cancer cells
- Abstract 1044: A combination of cisplatin and 2-deoxy-d-glucose results in synergistic cell death in both normoxia and hypoxia by the attenuation of autophagy
- Silencing of Elongation Factor-2 Kinase Potentiates the Effect of 2-Deoxy-d-Glucose against Human Glioma Cells through Blunting of autophagy
- autophagy and reversed 2‐DG‐mediated suppression
- Adipokinetic hormone-induced lipolysis in the fat body of an insect, Manduca sexta: synthesis of sn-1, 2-diacylglycerols.
- The differential effects of these stresses on the rise in glycerol as an index of lipolysis implies that the sympathetic circuitry was par- tially disabled vis-a-vis the response to 2-DG,
- It is concluded that 2-DG-induced thermogenesis and lipolysis are primarily dependent on P-adrenergic stimulation
- In conclusion, unlike the vertebrate system in which lipolysis is regulated solely by the cAMP system, in the insect fat body, both cAMP and calcium are relevant messengers in the stimulation of sn-1,2-DG production.
- hyperphagia and in the day-time a low rate of glucose utilization, lipolysis and hypophagia, it might be suspected that 2-DG
- These data therefore support a defect in glucose sensing as a possible initiator of obesity and type 2 diabetes … 50 For instance, glucagon secretion can be induced by the direct injection of 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG)
- in as much as mice deficient in either protein did not develop obesity (Flier, 2004 … chain fatty acid has been found to inhibit food intake (Obici et al., 2002), whereas central administration of 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG
- 2–DG-lnduced eating and that serotoninergic and dopaminerglc anorectic drugs modulate the eating responses of rats to cerebral glucoprivatlon induced by insulin or by 2–DG differently suggesting that glucose dysmetabollsm in obesity
- Early response evaluation of therapy with AP23573 (an mtor inhibitor) in sarcoma using [18F]2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) scan
- Intrinsically lower AKT, mtor and HIF activity correlates with increased sensitivity to 2-deoxy-D-glucose under hypoxia in lung cancer cell lines
- Abstract 4081: Sensitivity of gastric cancer cell lines against 2-deoxy-D-glucose is independent of PI3K/mtor inhibition
- The Relevance of mtor and Hypoxia Inducible Factor to 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Toxicity in Lung Cancer Cell Lines Under Hypoxia
- Inhibition of mtor increases cytotoxicity of 2-deoxy-D-glucose in small cell lung cancer under hypoxia
- Abstract 1422: Dietary 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) reduces TLR-4 induced acute inflammation and prevents chronic inflammation driven carcinogenesis
- Contribution of oxidative stress to radiosensitization by a combination of 2-DG and 6-AN in human cancer cell line
8-PRENYLNARINGENIN (FROM HOPS EXTRACT)
- Flavonoid-induced autophagy in hormone sensitive breast cancer cells
- Treatment of PC‐3 and DU145 prostate cancer cells by prenylflavonoids from hop (Humulus lupulus L.) induces a caspase‐independent form of cell death
- Prenylated chalcones and flavonoids for the prevention and treatment of cancer
- Effects of natural prenylated flavones in the phenotypical ER (+) MCF-7 and ER (−) MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells
- 6- and 8-Prenylnaringenin, Novel Natural Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Found in Hops, Exert Antitumor Activity on Melanoma Cells
- Versatile antitumor potential of isoxanthohumol: Enhancement of paclitaxel activity in vivo
- New Insights into the Benefits of Polyphenols in Chronic Diseases
- Dietary supplementation with shiikuwasha extract attenuates dexamethasone-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in aged rats
- Pharmaceutical composition
- Flavones Inhibit LPS-Induced Atrogin-1/MAFbx Expression in Mouse C2C12 Skeletal Myotubes
- Quercetin and related polyphenols: new insights and implications for their bioactivity and bioavailability
- Natural Estrogen Receptor Modulators and Their Heterologous Biosynthesis
- The hop-derived prenylflavonoid isoxanthohumol inhibits the formation of lung metastasis in B16-F10 murine melanoma model
- Several epidemiologic studies suggest that a polyphenol-enriched diet is an important strategy to prevent obesity and related chronic diseases, namely, T2DM. Both xanthohumol (XN) and 8-prenylnaringenin
- 8-prenylnaringenin from hop) [10, 12, 13 … The prolonged lack of estrogen can cause cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, os- teoarthritis, degenerative disc disease, obesity,
- Effect of xanthohumol and 8‐prenylnaringenin on MCF‐7 breast cancer cells oxidative stress and mitochondrial complexes expression
- Xanthohumol and 8-prenylnaringenin reduce type 2 diabetes–associated oxidative stress by downregulating galectin-3
- Grifolin induces autophagic cell death by inhibiting the Akt/mtor/S6K pathway in human ovarian cancer cells
- The role of targeting kinase activity by natural products in cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy (Review)
- Can cancer therapy be achieved by bridging apoptosis and autophagy: A method based on microRNA-dependent gene therapy and phytochemical targets
- Neoalbaconol induces cell death through necroptosis by regulating RIPK-dependent autocrine TNFα and ROS production
- Inactivation of Ras and Changes of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Contribute to Oridonin-Induced autophagy in A431 Cells
- Neoalbaconol induces energy depletion and multiple cell death in cancer cells by targeting PDK1-PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway
- Recent progress in fungus-derived bioactive agents for targeting of signaling machinery in cancer cells
- Elaborating the Role of Natural Products-Induced autophagy in Cancer Treatment: Achievements and Artifacts in the State of the Art
- Natural products as modulator of autophagy with potential clinical prospects
- Biosynthesis of Antroquinonol and 4-Acetylantroquinonol B via a Polyketide Pathway Using Orsellinic Acid as a Ring Precursor in Antrodia cinnamomea
- Relevance of necroptosis in cancer
- LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT COMPOUNDS WITH ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF MUSHROOM ORIGIN
- Grifolic acid induces mitochondrial membrane potential loss and cell death of RAW264.7 macrophages
- Targeting Cancer Cell Death with Small Molecule Agents for Potential Therapeutics
- Chinese Herbs Interfering with Cancer Reprogramming Metabolism
- Natural Compounds Regulate Glycolysis in Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment
- Roles of PI3‐K/Akt pathways in nanoparticle realgar powders‐induced apoptosis in U937 cells
- Expression and Characterization of Protein Latcripin-3, an Antioxidant and Antitumor Molecule from Lentinula edodesC91-3
- Evaluating DAPK as a therapeutic target
- NA selectively inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells.
- Albatrellus ovinus (sheep … Several other activities have been reported including hypoglycaemic effect [14], effect against obesity
Alisol B isolated (from Alisma orientale)
- Alisol A 24-Acetate and Alisol B 23-Acetate Induced autophagy Mediates Apoptosis and Nephrotoxicity in Human Renal Proximal Tubular Cells
- Alisol B 23-acetate induces autophagic-dependent apoptosis in human colon cancer cells via ROS generation and JNK activation
- Alisol A 24-acetate ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting oxidative stress and stimulating autophagy through the AMPK/mtor pathway
- Alisol B 23-acetate-induced HepG2 hepatoma cell death through mtor signaling-initiated G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis: A quantitative proteomic study
- Alisol B, a Novel Inhibitor of the Sarcoplasmic/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ ATPase Pump, Induces autophagy, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Apoptosis
- Potential Agents for Cancer and obesity Treatment with Herbal Medicines from the Green Garden 1071 cological studies has been conducted using this compound [30,56]. Interestingly, alisol B
- NAFLD has been associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma [6 … Ten potential compounds, that is, gallic acid, chrysophanol, rhein, emodin, physcion, alisol C monoacetate, alisol B
- Alisol B 23-acetate (AB23A) is a natural triterpenoid isolated from Rhizoma alismatis, which is a medicinal plant that has … the gene expression of CPT1α, ACADS and PPARα, which are involved in fatty acid β-oxidation (B). AB23A also increased the lipolysis
- Alisol B 23‑acetate inhibits the viability and induces apoptosis of non‑small cell lung cancer cells via PI3K/AKT/mtor signal pathway
- Allicin attenuates pathological cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting autophagy via activation of PI3K/Akt/mtor and MAPK/ERK/mtor signaling pathways
- Allicin ameliorates obesity comorbid depressive-like behaviors: involvement of the oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, autophagy, insulin resistance and NOX/Nrf2 imbalance in mice
- Therefore the in vivo effects of tolbutamide and insulin on lipolysis and lipid levels may not be similar. Such a difference is also seen in the effect of allicin
- The aim of the research was to study the mechanism of intermolecular interaction of allicin and lecithin with pancreatic lipase, and developing the composition, contributing to the inactivation process of lipolysis,
- behavioral modifications for the treatment of obesity and likely with more success than caloric restriction alone. Based in part on its spectrum of activity in other cell types, we tested ajoene, a stable derivative of allicin
- Our data suggest that allicin potentially prevents obesity and associated metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes mellitus by enhancing the expression of brown adipocyte-specific genes
- Allicin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis
- Allicin Alleviates inflammation of Trinitrobenzenesulfonic Acid-Induced Rats and Suppresses P38 and JNK Pathways in Caco-2 Cells
- Allicin Attenuates inflammation and Suppresses HLA-B27 Protein Expression in Ankylosing Spondylitis Mice
- Attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in hypercholesterolemic rabbits by allicin
- Diet Supplementation with Allicin Protects against Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice by Improving Anti-inflammation and Antioxidative Functions
- Comparative Study of Alliin and Allicin Inhibit Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Induced inflammation
- Allicin Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress
- The immunomodulatory effects of the garlic organosulfur compounds allicin and Z-ajoene in an in vitro murine model of LPS-induced inflammation
- The liver-protective effects of allicin against alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver inflammation.
- Allicin Protects PC12 Cells Against 6-OHDA-Induced oxidative stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction via Regulating Mitochondrial Dynamics
- Allicin prevents H2O2-induced apoptosis of HUVECs by inhibiting an oxidative stress pathway
- Allicin prevents oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced endothelial cell injury by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress pathway
- Allicin inhibits oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis by promoting PI3K/AKT and CREB/ERK signaling in osteoblast cells
- Yap1p, the central regulator of the S. cerevisiae oxidative stress response, is activated by allicin, a natural oxidant and defence substance of garlic
- Protective effect of allicin on high glucose/hypoxia-induced aortic endothelial cells via reduction of oxidative stress
- In situ allicin generation using targeted alliinase delivery for inhibition of MIA PaCa-2 cells via epigenetic changes, oxidative stress and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKI) expression
- Allicin ameliorates cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice via Suppressing oxidative stress by Blocking JNK Signaling Pathways
- Protective effect of allicin against oxidative stress and hepatocyte autophagy in iron-overloaded rats
- Suppression of gastric cancer by extract from the tuber of amorphophallus konjac via induction of apoptosis and autophagy
- Amorphophallus koniac Koch (Araceae), obesity, lipid and glucose metabolism alterations.
- Amorphophallus konjac … KGM has recently been marketed in capsule form, as a drink mix and in food products (Brown, 2000, Talbott, 2003) and has been touted for its potential in the treatment of obesity
- obesity has reached alarming levels in the United States … in the colon,* Glucomannan is a water-soluble, fermentable dietary fiber extracted from the tuber or root ofthe elephant yam, also known as konjac {Amorphophallus
- Therefore using natural products that contain glucomannan to reduce obesity and LDL-C is good choise. Glucomannan in the global market derived from Amorphophallus konjac.
- Amorphophallus Konjac … When stored body fat is broken down and used, lipase enzymes hydrolyze triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids during the breakdown of fat, called lipolysis
The tuber of amorphophallus konjac (TuAK) is an antitumor herb used in traditional Chinese medicine. The present study investigated the inhibitory effect of TuAK against gastric cancer and the underlying mechanisms associated with two programmed cell death pathways, apoptosis and autophagy. TuAK was extracted by organic solvents including ethanol and ligarine. The extract of TuAK, shortened as TuAKe, significantly inhibited the growth of cultured gastric cancer cell lines SGC-7901 and AGS, with IC50 of 35-45 µg/ml. TuAKe could increase cell apoptosis and induce cell cycle arrest. For the apoptosis-associated proteins, expressions of survivin and Bcl-2 were decreased by treatment of TuAKe, and the expression of Bax and caspase-9 was increased. Furthermore, TuAKe could promote autophagy, and the antitumor efficacy of TuAKe was significantly hampered by targeted suppression of autophagy, suggesting that autophagy contributed to TuAKe-induced cell death. Furthermore, patients with gastric cancer who received TuAK-based medicinal decoction achieved improved scores in assessment of life quality compared with those without TuAK treatment. This study demonstrated the antitumor activity of TuAKe against gastric cancer, and is the first report to show that the underlying mechanism is associated with induction of autophagy. Our data provided support of the clinical use of amorphophallus konjac-based medication in combination with classical chemotherapy to achieve optimized outcome for gastric cancer.
Anthocyanin extract (from black soybean Glycine max L.)
- [Study on Mulberry Anthocyanins Induced autophagy and Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Cell autophagy].
- Anthocyanins Regulate NAFLD by Promoting autophagy Pathway
- Mulberry anthocyanins improves thyroid cancer progression mainly by inducing apoptosis and autophagy cell death
- Mulberry Anthocyanins Induce Leukemia WEHI-3 Cells Apoptosis, autophagy, Differentiation and prolong leukemic mice survival.
- MdATG18a overexpression improves tolerance to nitrogen deficiency and regulates anthocyanin accumulation through increased autophagy in transgenic apple
- Protective effect of anthocyanin on alcohol-induced liver fibrosis is due to the regulation on AMPK/mtor/autophagy pathway and energy status
- Protective Effect of Purple Tomato Anthocyanidin on Chromium(VI)-Induced autophagy in LMH Cells by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
- autophagy is required for tolerance of drought and salt stress in plants
- Apoptosis and rotator cuff tears: scientificevidence from basic science to clinical findings
- We investigated the effects of anthocyanins on cell growth, differentiation, and lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells to test our hypothesis that anthocyanins could reduce adipose tissue mass by acting directly on adipocytes.
- These observation provides the first evidence that anthocyanin directly inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes during hyperglycemia, suggesting that this could be a potential mechanism involved in the insulin-sensitizing properties of anthocyanins
- it is possible that the effects of anthocyanins on TG accumulation may not only be achieved by the down-regulation of lipogenic transcription factors, but also by regulating lipolysis pathway(s)
- Effects of Anthocyanin-rich Extract from Black Rice on Rats with High Fat Diets-induced obesity
- Raspberry anthocyanin consumption prevents diet-induced obesity by alleviating oxidative stress and modulating hepatic lipid metabolism
- The main beneficial effect of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa) on obesity is not only related to its anthocyanin content
- Anthocyanin-rich Black Elderberry Extract improves Inflammatory Markers and Insulin Resistance in a High-Fat Diet-Induced obesity Model of Mice
- Dietary anthocyanin prevents obesity and ameliorates hyperglycemia in mice: PO0790
- Vision preservation during retinal inflammation by anthocyanin-rich bilberry extract: cellular and molecular mechanism
- Anthocyanin-rich fractions from red raspberries attenuate inflammation in both RAW264.7 macrophages and a mouse model of colitis
- Mulberry and cherry anthocyanin consumption prevents oxidative stress and inflammation in diet‐induced obese mice
- Inhibitory effect of anthocyanin-rich black soybean testa (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) on the inflammation-induced adipogenesis in a DIO mouse model
- Signatures of anthocyanin metabolites identified in humans inhibit biomarkers of vascular inflammation in human endothelial cells
- Anthocyanin-rich Riceberry bran extract attenuates gentamicin-induced hepatotoxicity by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats
- Anthocyanin-Rich Extract from Red Chinese Cabbage Alleviates Vascular inflammation in Endothelial Cells and Apo E−/− Mice
- Cyanidin 3-Rutinoside, an Anthocyanin Pigment of Schisandra chinensis Baill, Inhibits Allergic inflammation
- Elongator mediates ABA responses, oxidative stress resistance and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis
- A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating the Efficacy of an Anthocyanin–Maqui Berry Extract (Delphinol®) on oxidative stress Biomarkers
- An anthocyanin-rich strawberry extract protects against oxidative stress damage and improves mitochondrial functionality in human dermal fibroblasts exposed to an oxidizing agent
- Anthocyanin‐rich red cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) extract attenuates cardiac and hepatic oxidative stress in rats fed an atherogenic diet
- Overexpression of R2R3-MYB gene leads to accumulation of anthocyanin and enhanced resistance to chilling and oxidative stress
- Anthocyanin-Rich Juice Lowers Serum Cholesterol, leptin, and Resistin and Improves Plasma Fatty Acid Composition in Fischer Rats
Apigenin (From Celery Extract)
- Role of Apigenin in Cancer Prevention via the Induction of Apoptosis and autophagy
- Apigenin Alleviates Endotoxin-Induced Myocardial Toxicity by Modulating inflammation, oxidative stress, and autophagy
- Apigenin induces autophagic cell death in human papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells
- Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- Oral Efficacy of Apigenin against Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Involvement of Reactive Oxygen Species and autophagy as a Mechanism of Action
- Inhibition of autophagy ameliorates atherogenic inflammation by augmenting apigenin-induced macrophage apoptosis
- Apigenin potentiates the antitumor activity of 5-FU on solid Ehrlich carcinoma: Crosstalk between apoptotic and JNK-mediated autophagic cell death platforms
- α-Mangostin and apigenin induced the necrotic death of BT474 breast cancer cells with autophagy and inflammation
- Apigenin restores impairment of autophagy and downregulation of unfolded protein response regulatory proteins in keratinocytes exposed to ultraviolet B radiation
- Apigenin Combined With Gefitinib Blocks autophagy Flux and Induces Apoptotic Cell Death Through Inhibition of HIF-1α, c-Myc, p-EGFR, and Glucose Metabolism in EGFR L858R+T790M-Mutated H1975 Cells
- The flavonoid compound apigenin prevents colonic inflammation and motor dysfunctions associated with high fat diet-induced obesity
- Apigenin Ameliorates the obesity‐Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy by Attenuating Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Muscle of obese Mice
- Activation of PPARγ by a Natural Flavonoid Modulator, Apigenin Ameliorates obesity-Related inflammation Via Regulation of Macrophage Polarization
- Several in vitro and in vivo studies have reported the anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic and anti-obesity effects of the flavonoid apigenin.
- Background and purpose Apigenin can exert beneficial actions in the prevention of obesity. However, its putative action on obesity-associated bowel motor dysfunctions is unknown.
- Apigenin Attenuates Adriamycin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/mtor Pathway
- Apigenin reduces the Toll-like receptor-4-dependent activation of NF-κB by suppressing the Akt, mtor, JNK, and p38-MAPK
- Apigenin inhibits proliferation and migratory properties of Barrett’s esophageal adenocarcinoma cells by targeting PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway
- The antidepressant effects of apigenin are associated with the promotion of autophagy via the mtor/AMPK/ULK1 pathway
- Effect of parsley (Petroselinum crispum) intake on urinary apigenin excretion, blood antioxidant enzymes and biomarkers for oxidative stress in human subjects
- Protective effect of apigenin against oxidative stress-induced damage in osteoblastic cells
- Inhibition of glutamine utilization sensitizes lung cancer cells to apigenin-induced apoptosis resulting from metabolic and oxidative stress
- Protective role of apigenin on rotenone induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Suppression of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress mediated apoptosis
- Apigenin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Apigenin attenuates dopamine-induced apoptosis in melanocytes via oxidative stress-related p38, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and Akt signaling
- Apigenin protects against alcohol-induced liver injury in mice by regulating hepatic CYP2E1-mediated oxidative stress and PPARα-mediated lipogenic gene expression
- Effect on oxidative stress, glucose uptake level and lipid droplet content by Apigenin 7, 4′-dimethyl ether isolated from Piper longum L
- Topical Apigenin Alleviates Cutaneous inflammation in Murine Models
- Apigenin Protects Endothelial Cells from Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced inflammation by Decreasing Caspase-3 Activation and Modulating Mitochondrial Function
- Flavonoid apigenin modified gene expression associated with inflammation and cancer and induced apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells through inhibition of GSK‐3β/NF‐κB signaling cascade
- Apigenin Attenuates inflammation in Experimentally Induced Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Lung Injury
- Apigenin-7-O-β-d-glucuronide inhibits LPS-induced inflammation through the inactivation of AP-1 and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages and protects mice against endotoxin shock
- Apigenin attenuates hippocampal oxidative events, inflammation and pathological alterations in rats fed high fat, fructose diet
- Anti-inflammation and anti-fibrosis with PEGylated, apigenin loaded PLGA nanoparticles in chronic pancreatitis disease
- Apigenin inhibits colonic inflammation and tumorigenesis by suppressing STAT3-NF-κB signaling
- Apigenin Retards Atherogenesis by Promoting ABCA1-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux and Suppressing inflammation
- Apigenin C-glycosides of Microcos paniculata protects lipopolysaccharide induced apoptosis and inflammation in acute lung injury through TLR4 signaling pathway
- Apigenin affects leptin/leptin receptor pathway and induces cell apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cell line
- Counteracting effects of apigenin and leptin on lung adenocarcinoma cells.
- leptin and Apigenin: Antagonists in the Apoptotic Pathway of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Line
Apios americana Medik flowers extract
- Apios americana Medik flowers extract protects PC12 cells against H2O2 induced neurotoxicity via regulating autophagy
- Apios americana Medikus tuber polysaccharide exerts anti-inflammatory effects by activating autophagy
- Apios americana Medik flowers polysaccharide (AFP-2) attenuates H2O2 induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells
- Effects of C-Glycosides from Apios americana against oxidative stress during Hyperglycemia through Regulating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2
- Anti-Visceral obesity Effect of Apios americana Medikus in Diet-Induced obese Mice
- Apios americana Medik (hereinafter Apios) has been reported to treat diseases, including cancer, hypertension, obesity, and diabetes
- Apios could inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells and alleviate obesity, hypertension and diabetes
- There is some evidence that Apios may cure chronic constipation and exert positive effects on hypertension, disorders before and after childbirth, obesity, and diabetes.
- Apios americana Medik extract alleviates lung inflammation in influenza virus H1N1-and endotoxin-induced acute lung injury
- Effects of C-Glycosides from Apios americana Leaves against oxidative stress during Hyperglycemia through Regulating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2
- autophagy Induced by Areca Nut Extract Contributes to Decreasing Cisplatin Toxicity in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells: Roles of Reactive Oxygen Species/AMPK Signaling
- Mechanistic and compositional studies of the autophagy-inducing areca nut ingredient
- Impacts of autophagy-Inducing Ingredient of Areca Nut on Tumor Cells
- autophagy induction by a natural ingredient of areca nut
- autophagy induction by the 30–100 kDa fraction of areca nut in both normal and malignant cells through reactive oxygen species
- Arecoline and the 30–100 kDa fraction of areca nut extract differentially regulate mtor and respectively induce apoptosis and autophagy: a pilot study
- autophagy Induced by Areca Nut Extract Contributes to Decreasing Cisplatin Toxicity in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells: Roles of Reactive Oxygen Species/AMPK Signaling
- Molecular and cellular cues of diet‐associated oral carcinogenesis—with an emphasis on areca‐nut‐induced oral cancer development
- Long‐term stimulation of areca nut components results in increased chemoresistance through elevated autophagic activity
- Impacts of autophagy-Inducing Ingredient of Areca Nut on Tumor Cells
- Areca Nut Extract Induces Pyknotic Necrosis in Serum-Starved Oral Cells via Increasing Reactive Oxygen Species and Inhibiting GSK3β: An Implication for Cytopathic Effects in Betel Quid Chewers
- Ionizing radiation induces autophagy in human oral squamous cell carcinoma.
- autophagy mediates oral submucous fibrosis
- Role of autophagy in head and neck cancer and therapeutic resistance
- autophagy and its implication in human oral diseases
- Areca nut extract upregulates vimentin by activating PI3K/AKT signaling in oral carcinoma
- autophagy and Apoptosis Play Opposing Roles in Overall Survival of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Tetrandrine induces cell death in SAS human oral cancer cells through caspase activation-dependent apoptosis and LC3-I and LC3-II activation-dependent autophagy
- Ultrastructural alterations in liver of mice exposed chronically and transgenerationally to aqueous extract of betel nut: Implications in betel nut‐induced carcinogenesis
- Clathrin‐mediated endocytosis is required for ANE 30‐100K‐induced autophagy
- Chapter 16 – Erufosine Induces autophagy and Apoptosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Role of the Akt–mtor Signaling Pathway
- Thiamine Deficiency and Neurodegeneration: the Interplay Among oxidative stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and autophagy
- Betel nut (Areca catechu) consumption and induction glucose intolerance in adult CD1 mice and their F1 and F2 offspring … Betel nut chewing is strongly associated with general and central obesity in Chinese male middle-aged adults
- It is also used in socio-religious practices, in ayurvedic medicines against leucoderma, leprosy, cough, fits, worms anaemia and obesity. Areca tannins from areca nut are found to have inhibitory activities on reverse transcriptase enzyme
- Areca nut chewing is the fourth most popular substance abuse habit in the world [4]. Previous studies have found that chewing areca nut is associated with obesity, metabolic syndrome, hypertension (HTN),
- The present invention provides a lipolysis stimulator and a slimming agent, containing as an active ingredient any form of a plant or an extract thereof, the plant being selected from among common juniper, togenashi, rosehip, areca.
- Prevalence of type II diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia and metabolic syndromes are more common in areca nut chewers as its metabolite, arecoline, inhibits adipogenic differentiation, induces lipolysis
- Areca nut affecting metabolic processes is that arecoline may inhibit the differentiation of adipose tissue, induce adenylyl-cyclase-dependent lipolysis
- Roles of keratinocyte inflammation in oral cancer: regulating the prostaglandin E 2 , interleukin-6 and TNF-α production of oral epithelial cells by areca nut extract and arecoline
- Areca-nut extract modulates antigen-specific immunity and augments inflammation in ovalbumin-sensitized mice
- Involvement of the mitochondrion-dependent pathway and oxidative stress in the apoptosis of murine splenocytes induced by areca nut extract
- Areca nut extracts increased the expression of cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E2 and interleukin-1α in human immune cells via oxidative stress
- Role of tumor necrosis factor-α, leptin, and white blood cell count in betel nut chewing–related metabolic derangements
- Herbal extract of Artemisia vulgaris (mugwort) induces antitumor effects in HCT-15 human colon cancer cells via autophagy induction, cell migration suppression and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential.
- Therapeutic efficacy of Artemisia absinthium against Hymenolepis nana: in vitro and in vivo studies in comparison with the anthelmintic praziquantel
- The Extracts of Artemisia absinthium L. Suppress the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through Induction of Apoptosis via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitochondrial-Dependent Pathway
- iTRAQ-Based Proteomics Analysis of autophagy-Mediated Responses against MeJA in Laticifers of Euphorbia kansui L.
- Discovery of anticancer drugs from antimalarial natural products: a MEDLINE literature review
- Inhibitory Effect of Herbal Remedy PERVIVO and Anti-Inflammatory Drug Sulindac on L-1 Sarcoma Tumor Growth and Tumor Angiogenesis in Balb/c Mice
- PROMISING BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF SESQUITERPENE LACTONES
- SIRT2 Exacerbates MG132-induced Protein Accumulation and Cytotoxicity by Inhibition of autophagy Turnover
- Accumulation of Indolyl-3-Acetic and Abscisic Acids by “Hairy” Roots of Artemisia vulgaris
- Antilipogenic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Ethanol Extracts from Two Variants of Artemisia in obese Diabetic Mice
- Antioxidant and apoptosis modulating effects of Artemisia Vulgaris leaf extracts on in vitro systems subjected to oxidative stress
- Immunotherapy Of Mugwort Pollen Extract Decreases Airway Hyperresponsiveness And Lung inflammation In A Recombinant Art V1-induced Rat Model Of Allergy
- 126 Creation of a Humanized Model for Respiratory Allergy Using a Human Mugwort-specificT-Cell Receptor and HLA-DR1
Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei koidzumi)
- Soluble fraction of A. keiskei (AK) extracts and its …
LC3B-I, LC3B-II, and SQSTM1/p62 were gradually reduced as evidence of autophagic flux - Ashitaba (Angelica Keiskei) Exudate Prevents Increases in Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Induced by Obesity in Tsumura Suzuki Obese Diabetic Mice
- Daily Supplementation with Fresh Angelica keiskei Juice Alleviates High‐Fat Diet‐Induced Obesity in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota Composition
- Antidiabetic Activities of Chalcones Isolated from a Japanese Herb, Angelica keiskei
- [Effects of angelica keiskei chalcone on expression of glucose transporter proteins in liver and skeletal muscle cells of type 2 diabetic rats].
- Phytonutrient and anti-diabetic functional properties of flavonoid-rich ethanol extract from Angelica Keiskei leaves
- Effects of Angelica Keiskei Chalcone on Insulin Resistance of SkeletalMuscle Cells of Type 2 Diabetic Rats
- Anti – diabetic Activities of Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) : Induction of Adipocyte Differentiation and Enhancement of Glucose Uptake in Adipocyte
Azuki bean (Vigna angularis) extract
- Azuki bean (Vigna angularis) extract reduces oxidative stress and stimulates autophagy in the kidneys of streptozotocin-induced early diabetic rats
- Saponins and Flavonoids from Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis L.) Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced obesity in ICR Mice
- Suppression of obesity by Black Adzuki Beans (Vigna angularis) in High-fat Diet Fed obese Mouse Model
- Effects of azuki beans on oxidative stress, hypertriacylglycerolaemia, hypertension, obesity, and diabetes
- Polyphenol-enriched azuki bean (Vina angularis) extract reduces the oxidative stress and prevents DNA oxidation in the hearts of streptozotocin-induced early diabetic rats
- Studies on the changes of oxidative stress and autophagy in the hearts of streptozotocin-induced early diabetes rats, andthe improvement effects by azuki bean (Vigna angularis) extract [an abstract of dissertation and a summary ofdissertation review
- Bacopa monnieri‐Induced Protective autophagy Inhibits Benzo[a]pyrene‐Mediated Apoptosis
- The Purified Extract from the Medicinal Plant Bacopa monnieri, Bacopaside II, Inhibits Growth of Colon Cancer Cells In Vitro by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
- cPKCγ-Modulated autophagy in Neurons Alleviates Ischemic Injury in Brain of Mice with Ischemic Stroke Through Akt-mtor Pathway
- Bacopa monnieri-induced protective autophagy inhibits benzo[a]pyrene-mediated apoptosis
- Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi) induced autophagy Inhibit Benzo[a]pyrene mediated cytotoxicity
- Leonurine ameliorates cognitive dysfunction via antagonizing excitotoxic glutamate insults and inhibiting autophagy
- Phytochemicals Bridging autophagy Induction and Alpha-Synuclein Degradation in Parkinsonism
- Plant Extracts Stimulate the autophagy-lysosomal Protein Clearance Pathway and Improve Brain Synapse Markers in an Explant Model of Age-related Protein Accumulation Stress (FS05-04-19)
- Pharmaceutical composition and drug effect of synthetic Bacopa monnieri L.health promoting agentfrom the perspective of resistance fatigue
- The Aquaporin 1 Inhibitor Bacopaside II Reduces Endothelial Cell Migration and Tubulogenesis and Induces Apoptosis
- Virtual Screening of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Type 4 Inhibiting Potential of Chosen Flavonoids
- In vitro cytotoxicity studies of silver nanoparticles with activated folic acid on cancer cell lines.
- Bacopa monnieri as an Antioxidant Therapy to Reduce oxidative stress in the Aging Brain
- Renoprotective effect of Bacopa monnieri via inhibition of advanced glycation end products and oxidative stress in STZ-nicotinamide-induced diabetic nephropathy
- Alterations in Hippocampal oxidative stress, Expression of AMPA Receptor GluR2 Subunit and Associated Spatial Memory Loss by Bacopa monnieri Extract (CDRI-08) in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Mice
- Pretreatment with Bacopa monnieri extract offsets 3-nitropropionic acid induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunctions in the striatum of prepubertal mouse brain
- Neuromodulatory role of Bacopa monnieri on oxidative stress induced by postnatal exposure to decabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE -209) in neonate and young female mice
- Role of Bacopa monnieri in the temporal regulation of oxidative stress in clock mutant (cryb) of Drosophila melanogaster
- Microbial interference mitigates Meloidogyne incognita mediated oxidative stress and augments bacoside content in Bacopa monnieri L.
- Extracts of Bacopa monnieri (L) Pennell Down-Regulate the Expression of Leukotriene C4 Synthase mRNA in HL-60 Cells and Suppress OVAInduced inflammation in BALB/c Mice
benzoin gum (Styrax benzoin) ( From Benzoin Tree Bark )
- Antibacterial, anti-biofilm and anticancer potentials of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using benzoin gum (Styrax benzoin) extract
- Oleanolic Acid Alters Multiple Cell Signaling Pathways: Implication in Cancer Prevention and Therapy
- Styrax benzoin D. (SB) on Brain Physiological Activities Monitored in Real-time
- Benzoin-like compounds (Figure [1]) have showed high activity towards inhibiting the 11βHSD1 receptor related to diseases such as diabetes, obesity
Berberine ( From Berberis vulgaris )
- Berberine alleviates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting excessive autophagy in cardiomyocytes
- Berberine alleviates ox-LDL induced inflammatory factors by up-regulation of autophagy via AMPK/mtor signaling pathway
- Berberine enhances the AMPK activation and autophagy and mitigates high glucose-induced apoptosis of mouse podocytes
- Berberine-sonodynamic therapy induces autophagy and lipid unloading in macrophage
- Berberine induces autophagy in glioblastoma by targeting the AMPK/mtor/ULK1-pathway
- Berberine attenuates hepatic steatosis and enhances energy expenditure in mice by inducing autophagy and fibroblast growth factor 21
- Berberine protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury after orthotopic liver transplantation via activating Sirt1/FoxO3α induced autophagy
- Pharmacologic preconditioning with berberine attenuating ischemia-induced apoptosis and promoting autophagy in neuron
- Berberine inhibits palmitate-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation by triggering autophagy in macrophages: A new mechanism linking berberine to insulin resistance improvement
- Berberine inhibits Smad and non-Smad signaling cascades and enhances autophagy against pulmonary fibrosis
- Berberine reduces adipogenic and inflammatory molecules 603 adipocyte reducing effects are caused by lipolysis
- This result is quite consistent with the previous report that berberine could exhibit significant lipolysis effects in Hep G2 cells
- TG is the main component of very low-density lipoprotein and increased extracellular TG suggested insulin-mediated inhibition of lipolysis was attenuated. We also observed that berberine reduced extracellular TG accumulation after the stimulation of palmitate
- However, we previously found that berberine decreased insulin secretion and lipolysis via cAMP/ protein kinase A (PKA) pathway independent of AMPK activation in pancreatic β-cells and adipocytes
- Structural Changes of Gut Microbiota during Berberine-Mediated Prevention of obesity and Insulin Resistance in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats
- Modulation of gut microbiota by berberine and metformin during the treatment of high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats
- Effects and Action Mechanisms of Berberine and Rhizoma coptidis on Gut Microbes and obesity in High-Fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6J Mice
- Berberine Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Suppresses Liver and Adipose Tissue inflammation in Mice with Diet-induced obesity
- Berberine protects against diet-induced obesity through regulating metabolic endotoxemia and gut hormone levels
- Berberine attenuates cAMP-induced lipolysis via reducing the inhibition of phosphodiesterase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- ERK-dependent mTOR pathway is involved in berberine-induced autophagy in hepatic steatosis.
- Berberine decelerates glucose metabolism via suppression of mtor‑dependent HIF‑1α protein synthesis in colon cancer cells
- Berberine attenuates apoptosis in rat retinal Müller cells stimulated with high glucose via enhancing autophagy and the AMPK/mtor signaling
- Protection of berberine on intestinal mucosa following autologous orthotropic liver transplantation and its correlationship with p-AMPK activation and p-mtor inactivation
- GW24-e1352 Berberine mitigated cardiac hypoxiareoxygenation injury by Suppressed Autophagy and Reduced Cell Death via inhibition of the activation of AMPK-mtor signalling pathway in rat H9c2 cells
- Berberine preconditioning protects against hepatic cold ischemia reperfusion injury through the modulation of PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway
- Berberine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced extracelluar matrix accumulation and inflammation in rat mesangial cells: Involvement of NF-κB signaling pathway
- Berberine exerts nephroprotective effect against cisplatin-induced kidney damage through inhibition of oxidative/nitrosative stress, inflammation, autophagy and apoptosis
- Berberine ameliorates inflammation in patients with acute coronary syndrome following percutaneous coronary intervention
- Berberine inhibits dyslipidemia in C57BL/6 mice with lipopolysaccharide induced inflammation
- Berberine Hydrochloride Prevents Postsurgery Intestinal Adhesion and inflammation in Rats
- Berberine Protects against Neuronal Damage via Suppression of Glia-Mediated inflammation in Traumatic Brain Injury
- Berberine ameliorates experimental diabetes-induced renal inflammation and fibronectin by inhibiting the activation of RhoA/ROCK signaling
- Relative Inhibitory Activity of Berberine-Type Alkaloids against 12-ο-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-Induced inflammation in Mice
- Ameliorative effect of berberine against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction
- Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Pentaherbs Formula, Berberine, Gallic Acid and Chlorogenic Acid in Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin inflammation
- Berberine improves endothelial function by reducing endothelial microparticles-mediated oxidative stress in humans
- Berberine inhibits aldose reductase and oxidative stress in rat mesangial cells cultured under high glucose
- Berberine Ameliorate oxidative stress and Astrogliosis in the Hippocampus of STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Berberine Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Reducing oxidative stress and inflammation Response: Role of Silent Information Regulator 1
- Effects of Berberine on Amelioration of Hyperglycemia and oxidative stress in High Glucose and High Fat Diet-Induced Diabetic Hamsters In Vivo
- Berberine ameliorates methotrexate-induced liver injury by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and PPARγ, and suppressing oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats
- Resolution of Liver Fibrosis by Isoquinoline Alkaloid Berberine in CCl4-Intoxicated Mice Is Mediated by Suppression of oxidative stress and Upregulation of MMP-2 Expression
- Berberine exerts an anticonvulsant effect and ameliorates memory impairment and oxidative stress in a pilocarpine-induced epilepsy model in the rat
- The inhibition of inflammatory molecule expression on 3T3-L1 adipocytes by berberine is not mediated by leptin signaling
Betanin‐Enriched Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.)
- Abstract 10893: Dietary Nitrate Supplementation With Beetroot Juice Enhances Cardiac autophagy Markers AMBRA-1 (Activating Molecule in Beclin-1-regulated autophagy) and ATG-5 (autophagy-related Gene 5): Protective Role Against Doxorubicin Cardiotoxicity
- Betanin‐Enriched Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) Extract Induces Apoptosis and Autophagic Cell Death in MCF‐7 Cells
- POTENTIAL APPLICATION OF BEETROOT IN THERAPY OF obesity
- Betanin attenuates oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction in kidney of paraquat-treated rat
- Betanin, isolated from fruits of Opuntia elatior Mill attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic rats through regulating oxidative stress and TGF-β pathway
- Betanin ameliorates isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial infarction through iNOS, inflammation, oxidative stress-myeloperoxidase/low-density lipoprotein in rat
- Short-Term Betanin Intake Reduces oxidative stress in Wistar Rats
- Protective Effects of Betanin against oxidative stress in a Peripheral Artery Vasospasm Model in Rat
- Bitter melon extract inhibits breast cancer growth in preclinical model by inducing autophagic cell death
- Methanolic Extracts of Bitter Melon Inhibit Colon Cancer Stem Cells by Affecting Energy Homeostasis and autophagy
- Bitter melon juice targets molecular mechanisms underlying gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer cells
- Bitter melon: a panacea for inflammation and cancer
- Cucurbitane Triterpenoid from Momordica charantia Induces Apoptosis and autophagy in Breast Cancer Cells, in Part, through Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Activation
- Altered White Adipose Tissue Protein Profile in C57BL/6J Mice Displaying Delipidative, Inflammatory, and Browning Characteristics after Bitter Melon Seed Oil Treatment
- Roles of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α in Bitter Melon Seed Oil-Corrected Lipid Disorders and Conversion of α-Eleostearic Acid into Rumenic Acid in C57BL/6J Mice
- BG-4, a novel anticancer peptide from bitter gourd (Momordica charantia), promotes apoptosis in human colon cancer cells
- Bitter Melon as a Therapy for Diabetes, inflammation, and Cancer: a Panacea?
- Bitter gourd (Momordica charantia) as a rich source of bioactive components to combat cancer naturally: Are we on the right track to fully unlock its potential as inhibitor of deregulated signaling pathways
- Bitter Melon Powder Protects against obesity-associatedFatty Liver Disease by Improving Colonic Microenvironment in Rats with High-fat Diet-induced obesity
- Increased lipolysis in primary human adipocytes, with a concomitant reduction in PPARγ, SREBP-1c, perilipin, and resistin genes expression. These studies are critical as they lay the foundation to identify molecular targets and anti-obesity effects of bitter melon
- Beneficial Role of Bitter Melon Supplementation in obesity and Related Complications in Metabolic Syndrome
- Momordica charantia (Bitter Melon) Reduces obesity-Associated Macrophage and Mast Cell Infiltration as well as Inflammatory Cytokine Expression in Adipose Tissues
- Bitter Melon Powder Protects against obesity-associatedFatty Liver Disease by Improving Colonic Microenvironment in Rats with High-fat Diet-induced obesity
- Anti-obesity effect of bitter melon (Momordica charantia).
- Momordica charantia (Bitter Melon) Improves Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disturbance through Reducing obesity-associated inflammation in Mice
- The Mechanism of Bitter Melon Power Preventing obesity-related inflammation
- Response of gut microbiota and inflammatory status to bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) in high fat diet induced obese rats
- Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia) Reduces Adiposity, Lowers Serum Insulin and Normalizes Glucose Tolerance in Rats Fed a High Fat Diet
- Bitter melon seed oil may reduce the adiposity through the hypothalamus mtor signaling in mice fed a high fat diet
- Strawberry, loquat, mulberry, and bitter melon juices exhibit prophylactic effects on LPS-induced inflammation using murine peritoneal macrophages
- Bitter melon: a panacea for inflammation and cancer
- Wild bitter melon (Momordica charantia Linn. var. abbreviata Ser.) extract and its bioactive components suppress Propionibacterium acnes-induced inflammation
- Inhibitory effects of wild bitter melon leaf extract on Propionibacterium acnes-induced skin inflammation in mice and cytokine production in vitro
- Bitter Melon as a Therapy for Diabetes, inflammation, and Cancer: a Panacea?
- Wild Bitter Melon Leaf Extract Inhibits Porphyromonas gingivalis-Induced inflammation: Identification of Active Compounds through Bioassay-Guided Isolation
- Bitter melon (Momordica charantia) attenuates atherosclerosis in apo-E knock-out mice possibly through reducing triglyceride and anti-inflammation
- Bitter Melon Improves Glycemic Control and inflammation in Adipose Tissue of Obese and Diabetic Rats
- Organ inflammation and oxidative damages in fructose-fed adult offspring born of fructose-fed dams: modulation by maternal bitter melon supplementation (1033.6)
- Regulation of Sphingosine Kinase 1 and Adipose inflammation by Momordica charantia (Bitter Melon) in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice
- Supplementation of Bitter Melon to Rats Fed a High-Fructose Diet During Gestation and Lactation Ameliorates Fructose-Induced Dyslipidemia and Hepatic oxidative stress in Male Offspring
- Supplementation of Bitter Melon to Rats Fed a High-Fructose Diet During Gestation and Lactation Ameliorates Fructose-Induced Dyslipidemia and Hepatic oxidative stress in Male Offspring
- The Butanol Fraction of Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia) Scavenges Free Radicals and Attenuates oxidative stress
- Testicular oxidative stress in Sprague-Dawley rats treated with bitter melon (<i>Momordica charantia</i>): the effect of antioxidant supplementation
- Fresh Bitter Melon Fruit (Momordica charantia) Attenuated oxidative stress, Fibrosis and Renal Injury in Carbon Tetrachloride Treated Rats
- Maternal bitter melon supplementation reduces the risk for metabolic defects later in life: effects on lipidhandling, oxidative stress and inflammation in offspring born to damsfed a high fructose diet
- Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia) Protects from oxidative stress-Induced Premature Senescence in WI-38 Human Lung Fibroblast Cell
- The Effect of Bitter Melon Extract (Momordica charantia)in Inhibition of NFkB Activation in leptin treated HUVECS
- The Effect of Brunfelsia grandiflora Ethanol Extract on the Induction of autophagy in Human Lung Fibroblasts
- Inhibition of Cell Proliferation and Induction of Apoptosis by Ethanolic Extract of Lespedeza cuneata G. Don in Human Colorectal Cancer HT-29 cells
Butea monosperma (Lam.) flowers
- A standardized extract of Butea monosperma (Lam.) flowers suppresses the IL-1β-induced expression of IL-6 and matrix-metalloproteases by activating autophagy in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes
- Indian medicinal plant butea monosperma flower extract and its bioactive constituent butein activates autophagy in human oa chondrocytes under pathological conditions
- BST106 protects against cartilage damage by inhibition of apoptosis and enhancement of autophagy in osteoarthritic rats
- Butein Activates autophagy Through AMPK/TSC2/ULK1/mtor Pathway to Inhibit IL-6 Expression in IL-1β Stimulated Human Chondrocytes
- Knockdown of SGK1 alleviates the IL‐1β‐induced chondrocyte anabolic and catabolic imbalance by activating FoxO1‐mediated autophagy in human chondrocytes
- Deregulation of PI3K/Akt/mtor Signaling Pathways by Isoflavones and its Implication in Cancer Treatment
- Anti-obese activity of Butea monosperma (Lam) bark extract in experimentally induced obese rats
- Evaluation of n-butanolic fractions of butea monosperma flowers on dexamethasone induced hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in mice
- (Butea monosperma) Butea has antifungal, antimicrobial, anti inflammatory, anticonvulsive, anti esterogenic, anti fertility, anti … anticonvulsant, sedative, muscle relaxant, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, hepato protective, antimicrobial, antiulcer and lipolytic
- The plant is known for antioxidant,[5] anti-obesity,[6] anticancer, and chemoprotective[7 … free radical scavenging, anti-oxidative and proapoptotic properties in the flower extracts of Butea monosperma
- Anti-obese activity of Butea monosperma (Lam) bark extract in experimentally induced obese rats
- Butea monosperma and Syzygium cumini are used to treat kidney-stones problem and Trigonella foenum-graceum is used as anti-obesity
- Anti-obese activity of Butea monosperma (Lam) bark extract in experimentally induced obese rats
- Proanthocyanidins (CLPr) reduced blood glucose levels in obese diabetic mice … and antioxidant attributes of ethanolic extracts of Butea monosperma
- Protective effect of a Butea monosperma (Lam.) Taub. flowers extract against skin inflammation: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and matrix metalloproteinases inhibitory activities
- Effect of Butea monosperma leaf extracts on cyclophosphamide induced clastogenicity and oxidative stress in mice
- Acetonic Extract of Buxus sempervirens Induces Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis and autophagy in Breast Cancer Cells
- Investigation of the laxative, spasmolytic and prokinetic properties of aqueous methanol extract of Buxus sempervirens Linn (Buxaceae)
- Buxus sempervirens L. Improves Lipid Profile in Diabetic Rats … to insulin resistance, since the same effect on HDL catabolism is observed also in obese
- Reversal of obesity by targeted … Kupchan and coworkers isolated the first B-ring homosteroid, buxenine G, from Buxus sempervirens and elucidated its structure in 1966
Carnosic acid (CA), a polyphenolic diterpene (from Rosemary)
- Carnosic acid protects starvation-induced SH-SY5Y cell death through Erk1/2 and Akt pathways, autophagy, and FoxO3a
- Carnosic Acid Attenuates 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells by Inducing autophagy Through an Enhanced Interaction of Parkin and Beclin1
- Carnosic Acid Prevents Beta-Amyloid-Induced Injury in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells via the Induction of autophagy
- Carnosic acid potentiates the anticancer effect of temozolomide by inducing apoptosis and autophagy in glioma
- The protective role of carnosic acid in ischemic/reperfusion injury through regulation of autophagy under T2DM
- Carvedilol (CAR) combined with carnosic acid (CAA) attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by suppressing excessive oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy
- Carnosic acid induces autophagic cell death through inhibition of the Akt/mtor pathway in human hepatoma cells
- Cooperative antitumor activities of carnosic acid and Trastuzumab in ERBB2+ breast cancer cells
- Relevance of carnosic acid to the treatment of several health disorders: Molecular targets and mechanisms
- Rosmarinic acid potentiates carnosic acid induced apoptosis in lung fibroblasts
- Carnosic acid slows photoreceptor degeneration in the Pde6brd10 mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa
- Compounds with potential health benefits but poorly absorbed, oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and carnosic acid (CA), have been added to the nanoemulsions before lipolysis
- Carnosic acid prevents obesity and hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice
- Carnosic Acid as a Major Bioactive Component in Rosemary Extract Ameliorates High-Fat-Diet-Induced obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Mice
- Carnosic acid attenuates obesity‐induced glucose intolerance and hepatic fat accumulation by modulating genes of lipid metabolism in C57BL/6J‐ob/ob mice
- Rosemary extract enriched in carnosic acid shows anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects on in vitro and in vivo models
- Abstract: P1422 CARNOSIC ACID & URSOLIC ACID (ORIGANUM MAJORANA L.) PREVENT ATHEROSCLEROSIS CAUSED BY obesity: SUPPRESSION OF leptin-INDUCED PROLIFERATION IN VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS
- Prevention of 4-hydroxynonenal-induced lipolytic activation by carnosic acid is related to the induction of glutathione S-transferase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- Carnosic acid induces autophagic cell death through inhibition of the Akt/mtor pathway in human hepatoma cells
- The mechanisms of carnosic acid attenuates tumor necrosis factor‐α‐mediated inflammation and insulin resistance in 3T3‐L1 adipocytes
- Upregulation of Akt/NF-κB-regulated inflammation and Akt/Bad-related apoptosis signaling pathway involved in hepatic carcinoma process: suppression by carnosic acid nanoparticle
- Carnosic acid (CA) attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in db/db mice via inflammation suppression by regulating ROS-dependent p38 pathway
- Protective effect of rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid against streptozotocin-induced oxidation, glycation, inflammation and microbiota imbalance in diabetic rats
- Carnosic acid inhibits inflammation response and joint destruction on osteoclasts, fibroblast‐like synoviocytes, and collagen‐induced arthritis rats
- Carnosic acid alleviates brain injury through NF‑κB‑regulated inflammation and Caspase‑3‑associated apoptosis in high fat‑induced mouse models
- Effects of supercritical fluid extract of rosemary leaf and carnosic acid in inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.
- Activated Glutathione Metabolism Participates in Protective Effects of Carnosic Acid against oxidative stress in Neuronal
- oxidative stress induced by ochratoxin A in LLC-PK1 cell line and the chemoprotective effects of carnosic acid
- Carnosic Acid, a Natural Diterpene, Attenuates Arsenic-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Reducing oxidative stress, MAPK Activation, and Apoptotic Cell Death Pathway
- Study of Carnosic acid, Genistein, Quercetin , Taurine, and Melatonin Modulation of AP-1 Gene Regulation in the Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Under oxidative stress
- Carnosic acid slows photoreceptor degeneration in Pde6rd10 mice bycontrolling oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Abstract: P1422 CARNOSIC ACID & URSOLIC ACID (ORIGANUM MAJORANA L.) PREVENT ATHEROSCLEROSIS CAUSED BY OBESITY: SUPPRESSION OF leptin-INDUCED PROLIFERATION IN VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS
(Rosemarinus officinalis) Carnosol
- Carnosol-Induced ROS Inhibits Cell Viability of Human Osteosarcoma by Apoptosis and autophagy
- Carnosol Induces ROS-Mediated Beclin1-Independent autophagy and Apoptosis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
- P0174 Anti-metastatic and anti-tumour growth effects of carnosol on breast cancer through autophagy and apoptosis
- Mechanistic insight into carnosol-mediated pharmacological effects: Recent trends and advancements
- Anti-Carcinogenic Effects of Carnosol-An Updated Review
- Carnosol, a Natural Polyphenol, Inhibits Migration, Metastasis, and Tumor Growth of Breast Cancer via a ROS-Dependent Proteasome Degradation of STAT3
- Anti-Metastatic and Anti-Tumor growth effects ofcarnosol on breast cancer
- Carnosic Acid and Carnosol Induced Apoptosis through EP4 Signaling in Human Colon Cancer HCT116 Cells
- Phytochemicals, withaferin A and carnosol, overcome pancreatic cancer stem cells as c-Met inhibitors
- The Dietary Components Carnosic Acid and Carnosol as Neuroprotective Agents: a Mechanistic View
- Protective effects of carnosol against oxidative stress induced brain damage by chronic stress in rats
- CARNOSOL ALLEVIATES inflammation AND BACTERIAL TRANSLOCATION IN A RAT MODEL OF INTESTINAL ISCHEMIA-REPERFUSION INJURY
Catechin (From Green Tea Extract)
- Green Tea Catechin Prevents Hypoxia/Reperfusion-Evoked oxidative stress-Regulated autophagy-Activated Apoptosis and Cell Death in Microglial Cells
- Achievable Central Nervous System Concentrations of the Green Tea Catechin EGCG Induce Stress in Glioblastoma Cells in Vitro
- Green tea extract induces protective autophagy in A549 non-small lung cancer cell line
- Effects of green tea catechin- induced lipolysis on cytosol glycerol content in differenti- ated 3T3-L1 cells
- Furthermore, procyanidins (oligomers of catechins) exhibited lipolytic effects in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, although the monomers had no effect upon lipolysis
- Dietary catechin and Spirulina elevated ascorbate levels, increased carnitine synthesis and consequently promoted lipolysis activity in red sea bream
- Modulation of obesity by a green tea catechin
- A Catechin‐rich Beverage Improves obesity and Blood Glucose Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
- Reduction of diet-induced obesity by a combination of tea-catechin intake and regular swimming
- Beneficial Effects of Tea and the Green Tea Catechin Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
- Catechin-Rich Grape Seed Extract Supplementation Attenuates Diet-Induced obesity in C57BL/6J Mice
- Effects of green tea catechin‐induced lipolysis on cytosol glycerol content in differentiated 3T3‐L1 cells
- Green tea catechins enhance norepinephrine-induced lipolysis via a protein kinase A-dependent pathway in adipocytes
- Pro-apoptotic effect of Epigallo-catechin-3-gallate on B lymphocytes through regulating BAFF/PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling in rats with collagen-induced arthritis
- Catechin and quercetin attenuate adipose inflammation in fructose‐fed rats and 3T3‐L1 adipocytes
- Different effects of catechin on angiogenesis and inflammation depending on VEGF levels
- Modulatory effects of catechin hydrate against genotoxicity, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis induced by benzo(a)pyrene in mice
- Protective Effects of Catechin against Monosodium Urate-Induced inflammation through the Modulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
- Catechin Attenuates Coronary Heart Disease in a Rat Model by Inhibiting inflammation
- Against NF-κB/thymic stromal lymphopoietin signaling pathway, catechin alleviates the inflammation in allergic rhinitis
- Catechin modulates inflammation in TNBS induced colitis. (P6238)
- Modulation effect of catechin in angiogenesis and inflammation
- Catechin remits the inflammation in allergic asthma mice by suppressing NF-κB-TSLP signal pathway
- Catechin protects against oxidative stress and inflammatory-mediated cardiotoxicity in adriamycin-treated rats
- Protective effect of quercetin, EGCG, catechin and betaine against oxidative stress induced by ethanol in vitro
- The role of the mitochondrial oxidative stress in the cytotoxic effects of the green tea catechin, (–)‐epigallocatechin‐3‐gallate, in oral cells
- Effect of the Intake of Resveratrol, Resveratrol Phosphate, and Catechin-Rich Grape Seed Extract on Markers of oxidative stress and Gene Expression in Adult Obese Subjects
- (+)-Catechin protects dermal fibroblasts against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis
- (+)-Catechin, an Ingredient of Green Tea, Protects Murine Microglia From oxidative stress-Induced DNA Damage and Cell Cycle Arrest
- Effect of Catechin on Blood leptin Level in C57BL/6 Mice Fed High-fat Diet
- Effect of Catechin on 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes and Mature Adipocytes in leptin Metabolic Pathway
Celastrol (tripterine) (from the root extracts of Tripterygium wilfordii)
- Celastrol-Induced Nur77 Interaction with TRAF2 Alleviates inflammation by Promoting Mitochondrial Ubiquitination and autophagy
- Celastrol induces apoptosis and autophagy via the ROS/JNK signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells: an in vitro and in vivo study
- autophagy induction by celastrol augments protection against bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis in rats: Role of adaptor protein p62/ SQSTM1
- Celastrol Induces autophagy by Targeting AR/miR-101 in Prostate Cancer Cells
- Downregulation of miR-17-92a cluster promotes autophagy induction in response to celastrol treatment in prostate cancer cells
- Celastrol ameliorates experimental colitis in IL-10 deficient mice via the up-regulation of autophagy
- Abstract 455: Enhanced autophagy by Celastrol Supplementation Profoundly Increases Angiotensin II-induced Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation in Male and Female Mice
- Celastrol alleviates angiotensin II‑mediated vascular smooth muscle cell senescence via induction of autophagy
- Celastrol mediates autophagy and apoptosis via the ROS/JNK and Akt/mtor signaling pathways in glioma cells
- Celastrol protects human retinal pigment epithelial cells against hydrogen peroxide mediated oxidative stress, autophagy, and apoptosis through sirtuin 3 signal pathway
- Paraptosis accompanied by autophagy and apoptosis was induced by celastrol, a natural compound with influence on proteasome, ER stress and Hsp90
- Celastrol inhibits gastric cancer growth by induction of apoptosis and autophagy
- Celastrol protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells from rotenone-induced injury through induction of autophagy
- Celastrol-Induced Nur77 Interaction with TRAF2 Alleviates inflammation by Promoting Mitochondrial Ubiquitination and autophagy
- Inhibition of autophagy Strengthens Celastrol-Induced Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo Models
- autophagy induction by celastrol augments protection against bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis in rats: Role of adaptor protein p62/ SQSTM1
- Celastrol alleviates angiotensin II‑mediated vascular smooth muscle cell senescence via induction of autophagy
- Release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum and its subsequent influx into mitochondria trigger celastrol-induced paraptosis in cancer cells
- Autophagic degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor in gefitinib-resistant lung cancer by celastrol
- Celastrol targets proteostasis and acts synergistically with a heat-shock protein 90 inhibitor to kill human glioblastoma cells
- Celastrol Stimulates Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Activity in Tumor Cells by Initiating the ROS/Akt/p70S6K Signaling Pathway and Enhancing Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Protein Synthesis
- Molecular targets of celastrol in cancer: Recent trends and advancements
- Celastrol ameliorates inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- Celastrol induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting ER-stress/UPR
- autophagy flux inhibition mediated by celastrol sensitized lung cancer cells to TRAIL‑induced apoptosis via regulation of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and reactive oxygen species
- Celastrol and Its Role in Controlling Chronic Diseases
- Application of white adipose tissue browning irritant to preparation of obesity resisting medicine use of tripterine (celastrol) which is capable of promoting lipolysis, inhibiting fat synthesis,
- Cascade regulation of PPARγ2 and C/EBPα signaling pathways by celastrol impairs adipocyte differentiation and stimulates lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- Treatment of obesity with Celastrol
- Celastrol Protects against obesity and Metabolic Dysfunction through Activation of a HSF1-PGC1α Transcriptional Axis
- Celastrol suppresses obesity process via increasing antioxidant capacity and improving lipid metabolism
- Celastrol identified as a leptin sensitizer and potential novel treatment for obesity
- The leptin sensitizer celastrol reduces age‐associated obesity and modulates behavioral rhythms
- Celastrol prevents cadmium‐induced neuronal cell death via targeting JNK and PTEN‐Akt/mtor network
- Celastrol inhibits the HIF-1α pathway by inhibition of mtor/p70S6K/eIF4E and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in human hepatoma cells
- Celastrol induces cell cycle arrest by MicroRNA-21-mtor-mediated inhibition p27 protein degradation in gastric cancer
- Celastrol Attenuates Cadmium‐Induced Neuronal Apoptosis via Inhibiting Ca2+‐CaMKII‐Dependent Akt/mtor Pathway
- Celastrol Modulates Lipid Synthesis via PI3K/Akt/mtor Signaling Axis to finalize Cell Death Response in Prostate Cancer Cells
- miR-33a-5p enhances the sensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma cells to celastrol by regulating mtor signaling
- Celastrol induces ubiquitin-dependent degradation of mtor in breast cancer cells
- Celastrol prevents cadmium-induced neuronal cell death by blocking mitochondrial ROS inactivation of AMPK and activation of mtor pathway
- Celastrol Prevents Atherosclerosis via Inhibiting LOX-1 and oxidative stress
- Anticancer effect of celastrol on human triple negative breast cancer: Possible involvement of oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis and PI3K/Akt pathways
- Celastrol ameliorates murine colitis via modulating oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines and intestinal homeostasis
- Celastrol attenuates oxidative stress in the skeletal muscle of diabetic rats by regulating the AMPK-PGC1α-SIRT3 signaling pathway
- Celastrol reduces IL-1β induced matrix catabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo
- Celastrol, a Chinese herbal compound, controls autoimmune inflammation by altering the balance of pathogenic and regulatory T cells in the target organ
- Celastrol ameliorates inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- Celastrol aggravates LPS-induced inflammation and injuries of liver and kidney in mice
- Inhibition of inflammation with celastrol fails to improve muscle function in dysferlin-deficient A/J mice
- Celastrol inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in orbital fibroblasts through the suppression of NF-κB activity
- Celastrol modulates inflammation through inhibition of the catalytic activity of mediators of arachidonic acid pathway: Secretory phospholipase A2 group IIA, 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2
- Targeting Mast Cells and Basophils with Anti-FcεRIα Fab-Conjugated Celastrol-Loaded Micelles Suppresses Allergic inflammation
- Celastrol attenuates incision-induced inflammation and pain associated with inhibition of the NF-κB signalling pathway via SARM
- inflammation-Targeted Delivery of Celastrol via Neutrophil Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles in the Management of Acute Pancreatitis
- Celastrol Alleviates Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease by Inhibiting Cellular inflammation Induced by Cigarette Smoke via the Ednrb/Kng1 Signaling Pathway
- Celastrol identified as a leptin sensitizer and potential novel treatment for obesity
- The leptin sensitizer celastrol reduces age‐associated obesity and modulates behavioral rhythms
- SUN-096 Hypothalamic ATP Has a Crucial Role in the Pathogenesis of leptin Resistance: A Potential Mechanism for the Amelioration of leptin Resistance by Celastrol and Withaferin A
- leptin sensitizer celastrol, glial calcineurin and hypothalamic glutathione peroxidase 7 – novel entities in weight control and glucose homeostasis
Celastrol (FROm Thunder god vine)
- Paraptosis accompanied by autophagy and apoptosis was induced by celastrol, a natural compound with influence on proteasome, ER stress and Hsp90
- Celastrol protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells from rotenone-induced injury through induction of autophagy
- Inhibition of Autophagy Strengthens Celastrol-Induced Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo Models
- Autophagic degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor in gefitinib-resistant lung cancer by celastrol
- Release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum and its subsequent influx into mitochondria trigger celastrol-induced paraptosis in cancer cells
- Celastrol targets proteostasis and acts synergistically with a heat-shock protein 90 inhibitor to kill human glioblastoma cells
- Celastrol Stimulates Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Activity in Tumor Cells by Initiating the ROS/Akt/p70S6K Signaling Pathway and Enhancing Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Protein Synthesis
- Autophagy flux inhibition mediated by celastrol sensitized lung cancer cells to TRAIL‑induced apoptosis via regulation of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and reactive oxygen species
- Celastrol from ‘Thunder God Vine’ Protects SH-SY5Y Cells Through the Preservation of Mitochondrial Function and Inhibition of p38 MAPK in a Rotenone Model of Parkinson’s Disease
- celastrol administration and leptin, in obese mice with genetically disrupted leptin signalling
- Natural product celastrol suppressed macrophage M1 polarization against inflammation in diet-induced obese mice via regulating Nrf2/HO-1, MAP kinase and NF-κB pathways
- celastrol has been demonstrated to show effects that control obesity in several mice models
- celastrol in inflammatory diseases, namely, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, inflammatory bowel diseases, osteoarthritis and allergy, as well as in cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and other diseases, such as diabetes, obesity
- celastrol on leptin resistance, and further studies are needed to clarify whether celastrol can be used in humans to combat obesity
- Celastrol was recently identified as a potential novel treatment for obesity
- celastrol inhibits high fat diet-induced obesity
- Celastrol suppresses obesity process via increasing antioxidant capacity
- use of tripterine (celastrol) which is capable of promoting lipolysis
- Celastrol increased adipocyte differentiation and lipolysis by regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma 2
- Celastrus orbiculatus extract triggers apoptosis and autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mtor inhibition in human colorectal cancer cells
- A New Sesquiterpene Ester from Celastrus orbiculatus Reversing Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Cells
- Cytotoxic constituents from Celastrus paniculatus induce apoptosis and autophagy in breast cancer cells
- Antiinflammatory Constituents of Celastrus orbiculatus Inhibit the NF-κB Activation and NO Production
- Interplay between apoptosis and autophagy in colorectal cancer
- Celastrus Orbiculatus Extract Suppresses Migration and Invasion of Gastric Cancer by Inhibiting Prohibitin and c-Raf/ERK Signaling Pathway
- Celastrus orbiculatus extracts induce apoptosis in mtor-overexpressed human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells
- Celastrus orbiculatus Extracts Inhibit Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth by Targeting mtor Signaling Pathways
- lipogenic and lipolytic enzymes in rats fed with methanolic seed extract (50%) of Celastrus paniculatus
- Celastrus orbiculatus extracts induce apoptosis in mtor-overexpressed human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells
- Celastrus Orbiculatus Extracts Inhibit the Metastasis through Attenuating PI3K/Akt/mtor Signaling Pathway in Human Gastric Cance.
- Celastrus orbiculatus Extracts Inhibit Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth by Targeting mtor Signaling Pathways
- Celastrus orbiculatus extracts induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human esophageal squamous carcinoma ECA-109 cells in vitro via the PI3K/AKT/mtor signaling pathway
- Effects of Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb.Extract on the Overexpression of mtor in Human HepG2 Cells
Cepharanthine (CEP) a biscoclaurine alkaloid (from extracted Stephania)
- Cepharanthine Induces autophagy, Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer Cells
- Cepharanthine hydrochloride degrades polyglutamine-expanded androgen receptor proteins through an autophagy pathway in neuron cells
- Identification of a novel autophagic inhibitor cepharanthine to enhance the anti-cancer property of dacomitinib in non-small cell lung cancer
- cepharanthine (1.5mM), tetrandrine (1.5mM) or isotetrandrine (1.5mM), shifted the insulin-re- sponse curve of isoproterenol-induced lipolysis
- alkaloids such as liensinine, isoliensinine, dauricine and cepharanthine induced AMPK … Autophagy is hence correlated to the degree of obesity,
- Tetrandrine and cepharanthine induce apoptosis through caspase cascade regulation, cell cycle arrest, MAPK activation and PI3K/Akt/mtor signal modification in glucocorticoid resistant human leukemia Jurkat T cells
- Biscoclaurine alkaloid cepharanthine protects DNA in TK6 lymphoblastoid cells from constitutive oxidative damage
- Cepharanthine Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects Via NF-κB Inhibition in a LPS-Induced Rat Model of Systemic inflammation
- Inhibitory effect of cepharanthine and its related compounds on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced inflammation and inhibition of tumor promotion by cepharanthine in two-stage carcinogenesis in mice
- Cepharanthine exerts anti-inflammatory effects via NF-κB inhibition in a LPS-induced rat model of systemic inflammation
- Cepharanthine prevents atherosclerosis by attenuation of vascular inflammation and Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cell proliferation and migration
cepharantha Chaihu (Radix bupleuri),
- Effect of Chaihu Shugan Powder-Contained Serum on Glutamate-Induced autophagy of Interstitial Cells of Cajal in the Rat Gastric Antrum
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography Determination and Optimization of the Extraction Process for the Total Alkaloids from Traditional Herb Stephania cepharantha Hayata
- Cepharanthine Induces autophagy, Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer Cells
- Cepharanthine hydrochloride degrades polyglutamine-expanded androgen receptor proteins through an autophagy pathway in neuron cells
- Radix Bupleuri is the saikosaponin a (SSNa) … that SSNa is a novel therapeutic agent against that can be used against obesity‑associated inflammation
- Vinegar-Baked Radix Bupleuri Regulates Lipid Disorders via a Pathway Dependent on Peroxisome-Proliferator-Activated Receptor-in High-Fat-Diet-Induced obese Rats
- Radix Bupleuri regulates lipid disorders via a pathway dependent on peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in high-fat-diet-induced obese rats
- Radix Bupleuri (thorowax root … resistance is shared by several disorders, including hypertension, diabetes, obesity,
- Radix Bupleuri, fresh ginger … In the clinical trial, fluoxetine was reported to improve insulin-mediated glucose disposal in obese patients,
- Radix Bupleuri extracts (RBE) on growth, lipid deposition and metabolism and … than in those fed RBE0 diets, while dietary supplementation with 200–800 mg/kg RBE diets up-regulated lipolysis-related genes
Chebulagic acid (from Terminalia chebula)
- Neuroprotective Effect of Chebulagic Acid via autophagy Induction in SH-SY5Y Cells
- Recent advances in autophagy-based neuroprotection
- Preventive effect of Terminalia bellirica on obesity and metabolic disorders in spontaneously obese type 2 diabetic model mice
- Chebulagic acid (CA), the major constituent of Terminalia chebula and Phyllanthus emblica, is a benzopyran tannin com pound with various kinds of … Enhanced susceptibility to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine neurotoxicity in high-fat diet induced obesity
- Anti-hyperglycemic effect of chebulagic acid from the fruits of Terminalia chebula Retz … Preventive effect of Terminalia bellirica on obesity
- Chebulagic acid, ellagic and … Prevention effect of Terminalia bellirica on obesity
- These results clearly indicate that chebulagic acid can be used as an auxiliary in the treatment of obese associated comorbidities and in the control of type 2 diabetes.
- chebulagic Acid in HT22 and SH-SY5Y Cells … in inflammation and related diseases ㆍHepatic sulfur amino acid metabolism in obese and diabetic
- chebulagic acid increased the ACTH—induced lipolysis in fat
- Chebulagic acid (CA) attenuates LPS-induced inflammation by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages
- Chebulagic acid reduces inflammation and regulates enteric glial cells in mouse models of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis
Chuan xiong (Rhizoma chuanxiong)
- Chuan xiong (Rhizoma chuanxiong) modulates cancers, neurodegeneration and cardiovascular disease via autophagy.
- Puerariae Lobatae Radix with chuanxiong Rhizoma for treatment of cerebral ischemic stroke by remodeling gut microbiota to regulate the brain–gut barriers
- Antioxidative Activity of the Extract from Rhizoma Chuanxiong in Vitro
Cichorium intybus Linn. Extract
- This study demonstrates the hepatic protective effect of Cichorium intybus L. and active compounds in Cichorium intybus L. The active compounds ameliorate liver injury by acting on Akt-1 and caspase-1, which are related to apoptosis or autophagy.
- Treatment with EAEC-PDT reduced xenograft tumor size. Further evaluation suggested that activation of the PERK pathway mediates these effects, as the apoptotic rate and autophagy flux increased markedly after EAEC-PDT. EAEC, a natural photosensitizer extracted from Cichorium, displays potential utility in PDT of CRC by targeting the PERK pathway.
- (Cichorium intybus) and nettle … may be considered as the net result of the balance among dietary absorbed fat, fat synthesis (lipogenesis) and fat catabolism via β-oxidation (lipolysis)
- Cichorium intybus group (CI … So, if the fat intake and excreted is equal, decreased body fat accumulation could be due to lipolysis or decreased fatty
- (Cichorium intybus L.) is a medicinal and edible herb that belongs to the Compositae Cichorium family … Polysaccharides promote TG lipolysis
- Cichorium intybus L. (chicory … 9]. This effect may be due to a decrease in the activity of cholesterol biosynthesis enzymes or decreasing the rate of lipolysis
- Ameliorating effect of chicory (Cichorium intybus L.)-supplemented diet against nitrosamine precursors-induced liver injury and oxidative stress in male rats
- Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) Root Extract Regulates the Oxidative Status and Antioxidant Gene Transcripts in CCl4-Induced Hepatotoxicity
- Effects of Cichorium Intybus Linn on Blood Glucose, Lipid Constituents and Selected oxidative stress Parameters in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Prevention of oxidative stress-Induced Apoptosis of C2C12 Myoblasts by a Cichorium intybus Root Extract
- Phenolic compounds, oxidative enzymes and their relationship with discoloration in endive (Cichorium intybus L.).
- Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) Root Extract Regulates the Oxidative Status and Antioxidant Gene Transcripts in CCl4-Induced Hepatotoxicity
- P-302 – Cichorium intybus attenuates streptozotocin induced diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammatory response in rats
- Mechanistic evaluation of AMPK/SIRT1/FXR signaling axis, inflammation, and redox status in thioacetamide‐induced liver cirrhosis: The role of Cichorium intybus linn (chicory)‐supplemented diet
Clionamine B ( from Cliona celata )
- Synthesis, activity and molecular target identification of clionamine B analogues : autophagy stimulating
- Synthesis of Clionamine B, an autophagy Stimulating Aminosteroid Isolated from the Sponge Cliona celata
- Highly Efficient and Scalable Synthesis of Clionamine D
- Clionamine B, an Autophagy Stimulating Aminosteroid Isolated
from the Sponge Cliona celata. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B … GP-BAR1 is a promising pharmacological target for the treatment of steatohepatitis, type 2 diabetes, and obesity
Convallatoxin ( from Antiaris toxicaria )
- Convallatoxin, a Dual Inducer of Autophagy and Apoptosis, Inhibits Angiogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo
- Inhibition of cell proliferation, invasion and migration by the cardenolides digitoxigenin monodigitoxoside and convallatoxin in human lung cancer cell line
- Cytotoxic effects of the cardenolide convallatoxin and its Na,K-ATPase regulation
- Antitumor effects of naturally occurring cardiac glycosides convallatoxin and peruvoside on human ER+ and triple-negative breast cancers
- Molecular mechanisms of anti-oxidant and anti-aging effects induced by convallatoxin in Caenorhabditis elegans
- Plant-derived cardiac glycosides: Role in heart ailments and cancer management
- obesity and Cardiovascular Disease … CMV protein synthesis has also been shown to decrease in cells treated with the cardiac glycoside convallatoxin
Cordycepin ( From Cordyceps Sinensis )
- Cordycepin activates autophagy through AMPK phosphorylation to reduce abnormalities in Machado–Joseph disease models
- Cordycepin induces autophagy-mediated c-FLIPL degradation and leads to apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Cordycepin induces apoptotic cell death of human brain cancer through the modulation of autophagy
- Cordycepin stimulates autophagy in macrophages and prevents atherosclerotic plaque formation in ApoE-/- mice
- Cordycepin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH and BE(2)-M17 cells
- Cordycepin alleviates hepatic lipid accumulation by inducing protective autophagy via PKA/mtor pathway
- [Effect of cordycepin on apoptosis and autophagy of tongue cancer cells in vitro and the molecular mechanism].
- AMPK has therefore been proposed as a major
therapeu- tic target for obesity and obesity-linked metabolic disor- ders such as hyperlipidemia (7). Cordycepin, also known as 3′-deoxyadenosine, - Cordycepin, by blocking both adipogenesis
and lipid accumulation, may have potential as a therapeutic agent for effective treatment of obesity and obesity‐related disorders. - Cordycepin regulates body weight by inhibiting lipid droplet formation, promoting lipolysis and recruiting beige adipocytes
- In this study, we explored the molecular mechanism of the anti-obesity effect of cordycepin.
- Lipolytic effect of novel extracts from mulberry (Morus alba) leaves fermented with Cordyceps militaris in the primary adipocytes derived from SD rats
- Drug effects on the fine structure of Trypanosoma rhodesiense: Puromycin and its aminonucleoside, Cordycepin and Nucleocidin
- Cordycepin, by blocking both adipogenesis
and lipid accumulation, may have potential as a therapeutic agent for effective treatment of obesity and obesity‐related disorders. - Cordycepin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by the suppression of NF-κB through Akt and p38 inhibition in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells
- Cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) Down-Regulates the Proinflammatory Cytokines in inflammation-Induced Osteoporosis Model
- Cordycepin ameliorates skin inflammation in a DNFB-challenged murine model of atopic dermatitis
- the polyadenylation inhibitor cordycepin reduces pain, inflammation and joint pathology in rodent models of osteoarthritis
- The cordycepin derivative IMM-H007 improves endothelial dysfunction by suppressing vascular inflammation and promoting AMPK-dependent eNOS activation in high-fat diet-fed ApoE knockout mice
- Cordycepin Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated inflammation in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
- Effect of Manganese oxidative stress on Contents of Cordycepin and Adenosine in Mycelia of Cordyceps militaris
- Cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) attenuates age-related oxidative stress and ameliorates antioxidant capacity in rats
- Cordycepin prevents oxidative stress-induced inhibition of osteogenesis
- Cordycepin inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress
- Protective effects of cordycepin on the histopathological changes and oxidative stress induced by hepatic ischemia/reperfusion in rats
Corynoxine B (Cory B), ( from Uncaria rhynchophylla (Miq.) Jacks (Gouteng in Chinese) )
- Corynoxine B ameliorates HMGB1-dependent autophagy dysfunction during manganese exposure in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells
- B1 is involved in autophagy inhibition caused by SNCA/a-synuclein overexpression: a process modulated by the natural autophagy inducer corynoxine B.
- HMGB1 is involved in autophagy inhibition caused by SNCA/α-synuclein overexpression
- Corynoxine, a Natural autophagy Enhancer, Promotes the Clearance of Alpha-Synuclein via Akt/mtor Pathway
- Corynoxine isomers decrease levels of amyloid-β peptide and amyloid-β precursor protein by promoting autophagy and lysosome biogenesis
Cucurbita Moschata
- autophagy flux modulation by a carotenoid-enriched extract from the pumpkin Cucurbita moschata on human chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell line
- A water-soluble extract from Cucurbita moschata shows anti-obesity effects by controlling lipid metabolism in a high fat diet-induced obesity mouse model
- Corrigendum to “A water-soluble extract from Cucurbita moschata shows anti-obesity effects by controlling lipid metabolism in a high fat diet-induced obesity mouse model”
- Cucurbita maxima fruit …the C. pepo esterases may have a considerable potential in the lipolysis
- (Cucurbita pepo L.) var … They were identified by co migration of commercial standards. The triacylglycerol (TAG) spots and their lipolysis
- Ameliorative effects of squash (Cucurbita moschata Duchesne ex Poiret) leaf extracts on oxidative stress
- Cytoprotective Effects of Pumpkin (Cucurbita Moschata) Fruit Extract against oxidative stress and Carbonyl Stress
- Phytochemical Composition And Oxidative Stability Of Cold-Pressed Butternut Squash (Cucurbita Moschata) And Pumpkin (Cucurbita Pepo L.) Seed Oils
Curcumin ( From Tumeric Extract )
- Curcumin-Loaded Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles-Induced autophagy for Reducing Glioma Cell Migration and Invasion
- autophagy inhibition improves the efficacy of curcumin/temozolomide combination therapy in glioblastomas
- Curcumin regulates proliferation, autophagy, and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by affecting PI3K and P53 signaling
- Curcumin: A naturally occurring autophagy modulator
- Curcumin induces autophagy, inhibits proliferation and invasion by downregulating AKT/mtor signaling pathway in human melanoma cells
- Curcumin Suppresses Proliferation and Migration of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells through autophagy-Dependent Akt Degradation
- Curcumin targets the TFEB-lysosome pathway for induction of autophagy
- Curcumin hormesis mediates a cross-talk between autophagy and cell death
- Curcumin inhibits autophagy and apoptosis in hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced myocytes
- Role of autophagy on Heavy Metal-Induced Renal Damage and the Protective Effects of Curcumin in autophagy and Kidney Preservation
- Autophagic and apoptotic mechanisms of curcumin-induced death in K562 cells
- Curcumin alleviates isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through inhibition of autophagy and activation of mtor
- Antagonism between curcumin and the topoisomerase II inhibitor etoposide
- Curcumin as an ROS Scavenger in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Curcumin alleviates neuronal apoptosis and cerebral mitochondrial dysfunction in septic mice
- Is Chronic Curcumin Supplementation Neuroprotective Against Ischemia for Antioxidant Activity, Neurological Deficit, or Neuronal Apoptosis in an Experimental Stroke Model?
- The Polyphenolic Compound Curcumin Conjugation with an Alkyne Moiety in the Process of autophagy
- Curcumin‐induced autophagy and nucleophagy in Sp
- Targeting inflammation-Induced obesity and Metabolic Diseases by Curcumin and Other Nutraceuticals
- curcumin-treated adipocytes contained a greater number of small lipid … provide a greater surface area for the actions of water-soluble lipolytic
- Finally, a recent report has demonstrated that curcumin prevents the lipolytic effects
- In this study, we used curcumin as a model lipophilic component that could be incorporated into functional food products
- Curcumin inhibits lipolysis via suppression of ER stress in adipose tissue and prevents hepatic insulin resistance
- Curcumin attenuates lipolysis stimulated by tumor necrosis factor-α or isoproterenol in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- New mechanisms and the anti-inflammatory role of curcumin in obesity and obesity-related metabolic diseases
- Curcumin and obesity: evidence and mechanisms
- Curcumin and obesity
- Curcumin Prevents High Fat Diet Induced Insulin Resistance and obesity via Attenuating Lipogenesis in Liver and Inflammatory Pathway in Adipocytes
- Curcumin molecular targets in obesity and obesity-related cancers
- Roles of the Akt/mtor/p70S6K and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways in Curcumin-Induced Autophagy
- Curcumin Inhibits Proliferation of Colorectal Carcinoma by Modulating Akt/mtor Signaling
- Curcumin Ameliorates the Neurodegenerative Pathology in A53T α-synuclein Cell Model of Parkinson’s Disease Through the Downregulation of mtor/p70S6K Signaling and the Recovery of Macroautophagy
- Curcumin disrupts uterine leiomyosarcoma cells through AKT-mtor pathway inhibition
- Tetrahydrocurcumin, a major metabolite of curcumin, induced autophagic cell death through coordinative modulation of PI3K/Akt‐mtor and MAPK signaling pathways in human leukemia HL‐60 cells
- Curcumin inhibited HGF-induced EMT and angiogenesis through regulating c-Met dependent PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathways in lung cancer
- Curcumin inhibits cancer-associated fibroblast-driven prostate cancer invasion through MAOA/mtor/HIF-1α signaling
- Transient Metals Enhance Cytotoxicity of Curcumin: Potential Involvement of the NF-κB and mtor Signaling Pathways
- Curcumin sensitizes glioblastoma to temozolomide by simultaneously generating ROS and disrupting AKT/mtor signaling
- A novel curcumin analog binds to and activates TFEB in vitro and in vivo independent of mtor inhibition
- Curcumin attenuates gentamicin-induced renal oxidative damage in rats
- Curcumin and Especially Tetrahydrocurcumin Ameliorate oxidative stress-Induced Renal Injury in Mice
- Chemical Studies on Antioxidant Mechanism of Curcumin: Analysis of Oxidative Coupling Products from Curcumin and Linoleate
- Curcumin Activates Defensive Genes and Protects Neurons Against oxidative stress
- Protective Effects of Curcumin against Oxidative Damage on Skin Cells In Vitro: Its Implication for Wound Healing
- Effect of Curcumin on inflammation and oxidative stress in Cisplatin-Induced Experimental Nephrotoxicity
- Curcumin suppresses AGEs induced apoptosis in tubular epithelial cells via protective autophagy
- Curcumin, a diferuloylmethane, attenuates cyclosporine-induced renal dysfunction and oxidative stress in rat kidneys
- Curcumin protected PC12 cells against beta-amyloid-induced toxicity through the inhibition of oxidative damage and tau hyperphosphorylation
- Curcumin induces autophagy to protect vascular endothelial cell survival from oxidative stress damage
- Curcumin, inflammation, ageing and age-related diseases
- Biodegradable microspheres of curcumin for treatment of inflammation.
- The beneficial role of curcumin on inflammation, diabetes and neurodegenerative disease: A recent update
- Curcumin effects on inflammation and performance recovery following eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage
- Curcumin attenuates inflammation through inhibition of TLR-4 receptor in experimental colitis
- Inhibition by curcumin of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic hyperplasia, inflammation, cellular gene products and cell-cycle-related proteins in rats
- Modulation Of Inflammatory Mediators By Ibuprofen And Curcumin Treatment During Chronic inflammation In Rat
- Curcumin attenuates ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation by regulating nitric oxide
- Curcumin ameliorates renal failure in 5/6 nephrectomized rats: role of inflammation
- Synergistic chondroprotective effects of curcumin and resveratrol in human articular chondrocytes: inhibition of IL-1β-induced NF-κB-mediated inflammation and apoptosis
- Curcumin Eliminates leptin’s Effects on Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via Interrupting leptin Signaling
- Inhibition of leptin and leptin Receptor Gene Expression by Silibinin-Curcumin Combination
- Curcumin Protects Hepatic Stellate Cells against leptin-Induced Activation in Vitro by Accumulating Intracellular Lipids
- Curcumin prevents leptin raising glucose levels in hepatic stellate cells by blocking translocation of glucose transporter‐4 and increasing glucokinase
- Curcumin eliminates the effect of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) on the divergent regulation of gene expression of receptors of AGEs by interrupting leptin signaling
- Curcumin prevents leptin-induced tight junction dysfunction in intestinal Caco-2 BBe cells
- Curcumin inhibits leptin gene expression and secretion in breast cancer cells by estrogen receptors
- [The study of insulin resistance and leptin resistance on the model of simplicity obesity rats by curcumin].
- Therapeutic effect of curcumin on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats and its influence on the expression of leptin in liver
- Evaluation of serum cancer antigen 125, resistin, leptin, homocysteine, and total antioxidant capacity in rat model of endometriosis treated with Curcumin
- Effect of Phytosomal Curcumin on Circulating Levels of Adiponectin and leptin in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.
- Effect of Curcumin Supplement on Pulmonary Functions, Total and Differential White Blood Cell Count, Serum Level of leptin and Body Mass Index in a Sample of Iraqi Patients with Chronic Bronchial Asthma
- 7 Food additives sodium sulfite, sodium benzoate and curcumin inhibit leptin release in murine adipocytes in vitro
- Preparation and Evaluation of effect Magnetic Nanoparticles Modified with Biodegradable Copolymer PCL-PEG containing Curcumin – Silibinin on leptin Gene Experession in Lung Cancer
Dihydromyricetin (Ampelopsin) ( From Vine Tea Extract )
- Dihydromyricetin improves skeletal muscle insulin resistance by inducing autophagy via the AMPK signaling pathway
- Dihydromyricetin improves skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity by inducing autophagy via the AMPK-PGC-1α-Sirt3 signaling pathway
- Dihydromyricetin promotes autophagy and apoptosis through ROS-STAT3 signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Dihydromyricetin and Salvianolic acid B inhibit alpha-synuclein aggregation and enhance chaperone-mediated autophagy
- Dihydromyricetin protects against liver ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis via activation of FOXO3a-mediated autophagy
- Dihydromyricetin modulates p62 and autophagy crosstalk with the Keap-1/Nrf2 pathway to alleviate ethanol-induced hepatic injury
- Dihydromyricetin induces apoptosis and cytoprotective autophagy through ROS-NF-κB signalling in human melanoma cells
- Dihydromyricetin inhibits PC12 cell injury induced by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium by up-regulating autophagy activity
- Dihydromyricetin improves skeletal muscle insulin resistance by inducing autophagy via the AMPK signaling pathway
- Dihydromyricetin induces autophagy in HepG2 cells involved in inhibition of mtor and regulating its upstream pathways
- Dihydromyricetin protects against liver ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis via activation of FOXO3a-mediated autophagy
- Dihydromyricetin modulates p62 and autophagy crosstalk with the Keap-1/Nrf2 pathway to alleviate ethanol-induced hepatic injury
- Dihydromyricetin Protects against Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice
- The Versatile Effects of Dihydromyricetin in Health
- Dihydromyricetin Enhances the Chemo-Sensitivity of Nedaplatin via Regulation of the p53/Bcl-2 Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
- Determination of dihydromyricetin in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study
- Dihydromyricetin protects against lipopolysaccharide‑induced cardiomyocyte injury through the toll‑like receptor‑4/nuclear factor‑κB pathway
- The in vitro assays detected action of dihydromyricetin on adipogenesis, lipolysis and lipogenesis
- “Dihydromyricetin prevents obesity-induced slow-twitch-fiber reduction partially via FLCN/FNIP1/AMPK pathway,”
- Dihydromyricetin improves glucose and lipid metabolism and exerts anti-inflammatory effects in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial
- Dihydromyricetin[A];[C];2006 … on Seral Lipids in High Fat and Sugar Diet-induced obese
- Dihydromyricetin induces autophagy in HepG2 cells involved in inhibition of mtor and regulating its upstream pathways
- Ampelopsin suppresses breast carcinogenesis by inhibiting the mtor signalling pathway
- Dihydromyricetin ameliorates the oxidative stress response induced by methylglyoxal via the AMPK/GLUT4 signaling pathway in PC12 cells
- Dihydromyricetin ameliorates oleic acid-induced lipid accumulation in L02 and HepG2 cells by inhibiting lipogenesis and oxidative stress
- Dihydromyricetin attenuated Ang II induced cardiac fibroblasts proliferation related to inhibitory of oxidative stress
- Protection of oxidative stress induced apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells by dihydromyricetin through down-regulation of caspase activation and up-regulation of BcL-2
- Dihydromyricetin Attenuates Myocardial Hypertrophy Induced by Transverse Aortic Constriction via oxidative stress Inhibition and SIRT3 Pathway Enhancement
- Dihydromyricetin improves type 2 diabetes-induced cognitive impairment via suppressing oxidative stress and enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated neuroprotection in mice
- Dihydromyricetin Inhibits Lead-Induced Cognitive Impairments and inflammation by the Adenosine 5′-Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Mice
- Dihydromyricetin attenuates inflammation through TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway
- Dihydromyricetin Inhibits inflammation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes through Regulation of Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling in Rats with Collagen-Induced Arthritis
dimethyl cardamonin (from Syzygium samarangense)
- Induction of autophagy by dimethyl cardamonin is associated with proliferative arrest in human colorectal carcinoma HCT116 and LOVO cells
- Autophagy induced by cardamonin is associated with mtorC1 inhibition in SKOV3 cells
- Cardamonin Inhibits Metastasis of Lewis Lung Carcinoma Cells by Decreasing mtor Activity
- mtor inhibition of cardamonin on antiproliferation of A549 cells is involved in a FKBP12 independent fashion
- Cardamonin Inhibits Angiogenesis by mtor Downregulation in SKOV3 Cells
- [Antiproliferation of cardamonin associated with mRNA expression of mtor, Raptor and Rictor].
- Discovery of a highly active anticancer analogue of cardamonin that acts as an inducer of caspase-dependent apoptosis and modulator of the mtor pathway
- Anti-inflammatory Effects of Cardamonin in Ovarian Cancer Cells Are Mediated via mtor Suppression
- Cardamonin attenuates lung carcinoma and promotes autophagy via targeting p53 and regulating mtor.
- Glycolysis inhibition via mtor suppression is a key step in cardamonin-induced autophagy in SKOV3 cells
- Cardamonin inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by suppressing the PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway
- Semi-synthesis of novel cardamonin analogues and identification of a highly active Cu(II)-cardamonin complex that inhibits migration and induces apoptosis via inhibition of mtor expression
- Cardamonin Attenuates Tamoxifen Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats through Modulation of Inflammatory Mediators, oxidative stress and Apoptosis
- Pre-treatment with cardamonin protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: Impact on NOX-1, inflammation and apoptosis
- Cardamonin attenuates chronic inflammation and tumorigenesis in colon
- Cardamonin Alleviates Pressure Overload-induced Cardiac Remodeling and Dysfunction Through Inhibition of oxidative stress
- Apoptotic cell death via oxidative stress mediated caspase-dependent mechanism in Jurkat T cells by cardamonin and its transition metal Cu (II) and Fe (II) complexes
Dioscin (CAS 19057-60-4) (From Wild Yam Root Extract)
- Dioscin Alleviates Crystalline Silica-Induced Pulmonary inflammation and Fibrosis through Promoting Alveolar Macrophage autophagy
- Corrigendum to(autophagy Inhibition Enhances ApoptosisInduced by Dioscin in Huh7 Cells)
- Potent effects of dioscin against hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating TP53‐induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR)‐mediated apoptosis, autophagy, and DNA damage
- Erratum to: Dioscin-induced autophagy mitigates cell apoptosis through modulation of PI3K/Akt and ERK and JNK signaling pathways in human lung cancer cell lines
- Dioscin strengthens the efficiency of adriamycin in MCF-7 and MCF-7/ADR cells through autophagy induction: More than just down-regulation of MDR1
- Dioscin enhances osteoblastic cell differentiation and proliferation by inhibiting cell autophagy via the ASPP2/NF-κβ pathway
- Dioscin-induced autophagy mitigates cell apoptosis through modulation of PI3K/Akt and ERK and JNK signaling pathways in human lung cancer cell lines
- Diosgenin induces ROS-dependent autophagy and cytotoxicity via mtor signaling pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
- autophagy Inhibition Enhances Apoptosis Induced by Dioscin in Huh7 Cells
- Diosgenin‑induced autophagy and apoptosis in a human prostate cancer cell line
- Dioscin induces caspase-independent apoptosis through activation of apoptosis-inducing factor in breast cancer cells
- Diosgenin Glucoside Protects against Spinal Cord Injury by Regulating autophagy and Alleviating Apoptosis
- Diosgenin: Recent Highlights on Pharmacology and Analytical Methodology
- Dioscin, Human pleura[ fluid (HPF) INTRODUCTION Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) is lipolytic enzyme that specifically hydrolyzes the sn-2 position of glyceropho- spholipid.
- dioscin exerts a protective effect against NAFLD … fed mice prevented fat accumulation in epididymal tissues by stimulating lipolysis and ameliorating
- dioscin and its aglycone, diosgenin, showed inhibitory potential against fat absorption(12 …Besides, the observed reduction in intracellular lipolytic activity of cultured 3T3-L1 adipocytes may reduce the levels
- Dioscin ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy through inhibition of the MAPK and Akt/GSK3β/mtor pathways
- Dioscin induces cancer cell apoptosis through elevated oxidative stress mediated by downregulation of peroxiredoxins
- Protective effects of dioscin against doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity via adjusting FXR-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation
- Dioscin Prevents the Mitochondrial Apoptosis and Attenuates oxidative stress in Cardiac H9c2 Cells
- Protective Effects of Dioscin against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Dioscin Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats Through Inhibition of Oxidative-Nitrative Stress, inflammation and Apoptosis
- Protective effects of dioscin against fructose-induced renal damage via adjusting Sirt3-mediated oxidative stress, fibrosis, lipid metabolism and inflammation
- Dioscin alleviates dimethylnitrosamine-induced acute liver injury through regulating apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation
- Potent effects of dioscin against thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis through attenuating oxidative stress in turn inhibiting inflammation, TGF-β/Smad and MAPK signaling pathways
- Dioscin Protects ANIT-Induced Intrahepatic Cholestasis Through Regulating Transporters, Apoptosis and oxidative stress
- Dioscin: A diverse acting natural compound with therapeutic potential in metabolic diseases, cancer, inflammation and infections
- Dioscin inhibits ischemic stroke‑induced inflammation through inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NF‑κB signaling pathway in a rat model
- Dioscin protects against coronary heart disease by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation via Sirt1/Nrf2 and p38 MAPK pathways
- Dioscin relieves endotoxemia induced acute neuro-inflammation and protect neurogenesis via improving 5-HT metabolism
- Dioscin ameliorates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via adjusting miR-351-5p/MAPK13-mediated inflammation and apoptosis
- Corrigendum to “Protective effects of dioscin agains doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity via adjusting FXR-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation” [Toxicology 378 (2017) 53-64].
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) ( From Algae )
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) promotes immunogenic apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cells, induces autophagy and inhibits STAT3 in both tumor and dendritic cells
- Docosahexaenoic acid enhances M2 macrophage polarization via the p38 signaling pathway and autophagy
- Docosahexaenoic Acid Attenuated Experimental Chronic Colitis in Interleukin 10–Deficient Mice by Enhancing autophagy Through Inhibition of the mtor Pathway
- Docosahexaenoic acid, an omega-3 fatty acid, induces autophagy in human breast cancer cells: role of oxidative stress-induced growth inhibitor 1
- Docosahexaenoic acid induces autophagy through p53/AMPK/mtor signaling and promotes apoptosis in human cancer cells harboring wild-type p53
- Docosahexaenoic Acid Induces Cell Death in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Repressing mtor via AMPK Activation and PI3K/Akt Inhibition
- Docosahexaenoic acid-induced apoptosis is mediated by activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in human cancer cells
- Different fatty acids inhibit apoB100 secretion by different pathways: unique roles for ER stress, ceramide, and autophagy
- Docosahexaenoic acid prevents palmitate-induced activation of proteolytic systems in C2C12 myotubes
- Omega‐3 PUFA ethanolamides DHEA and EPEA induce autophagy through PPARγ activation in MCF‐7 breast cancer cells
- Induction of oxiapoptophagy on 158N murine oligodendrocytes treated by 7-ketocholesterol-, 7β-hydroxycholesterol-, or 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol: Protective effects of α-tocopherol and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; C22:6 n-3)
- Microarray analysis of anti-cancer effects of docosahexaenoic acid on human colon cancer model in nude mice
- AKT/mtor signaling pathway is involved in salvianolic acid B-induced autophagy and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- DHA regulates lipogenesis and lipolysis genes in mice adipose and liver
- In vitro examination of DHA-edible micro algae: 1. Effect on rumen lipolysis and biohydrogenation of linoleic and linolenic acids
- The effects of dietary EPA and DHA fortification on lipolysis activity and physiological function in juvenile black sea bream Acanthopagrus schlegeli (Bleeker)
- The Effect of Insulin, TNFα and DHA on the Proliferation, Differentiation and lipolysis of Preadipocytes Isolated from Large Yellow Croaker (Pseudosciaena Crocea R.)
- EPA and DHA influenced differently the MRNA expression levels of some lipolysis-related factors in subcutaneous and visceral rabbit ADSCs in vitro
- Prevention and Reversal of obesity and Glucose Intolerance in Mice by DHA Derivatives
- The Role of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) in the Control of obesity and Metabolic Derangements in Breast Cancer
- Effect of DHA supplementation in a very low-calorie ketogenic diet in the treatment of obesity: a randomized clinical trial
- Frontline Science: A reduction in DHA‐derived mediators in male obesity contributes toward defects in select B cell subsets and circulating antibody
- Long-term dietary EPA or DHA supplementation do not ameliorate obesity but improve glucose homeostasis via gut-adipose axis in already obese mice
- Abstract 2867: Docosahexaenoic acid induces autophagy through p53/AMPK/mtor signaling in human cancer cells
- Abstract 4654: Docosahexaenoic acid induces autophagy through reactive oxygen species /mtor pathway in p53 mutant cancer
- 139 Docosahexaenoic Acid-induced Autophagy is Related to Inhibition of mtor by Reactive Oxygen Species in P53 Mutant Cancer Cells
- Abstract 2274: Docosahexaenoic acid-induced cell death may be related to inhibition of mtor through AMPK activation and PI3K/Akt inhibition in human non-small cell lung cancer cells
- 138 Inhibition of mtor Through AMPK Activation and PI3K/Akt Inhibition is Important to Docosahexaenoic Acid-induced Cell Death in Human Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells
- 1034 POSTER Docosahexaenoic Acid Induces Autophagy Through p53/AMPK/mtor Signaling in Human Cancer Cells Harboring Wild-type p53
- EPA and DHA reduce LPS-induced inflammation responses in HK-2 cells: Evidence for a PPAR-γ–dependent mechanism
- DHA Supplementation Decreases Serum C-Reactive Protein and Other Markers of inflammation in Hypertriglyceridemic Men
- Dietary Olive Oil Supplemented with Fish Oil, Rich in EPA and DHA (n-3) Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Attenuates Colonic inflammation in Rats with DSS-Induced Colitis
- DHA- and EPA-derived resolvins, protectins, and maresins in airway inflammation
- The influence of EPA and DHA on markers of inflammation in 3T3-L1 cells at different stages of cellular maturation
- Administration of DHA Reduces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Associated inflammation and Alters Microglial or Macrophage Activation in Traumatic Brain Injury
- A randomized, crossover, head-to-head comparison of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid supplementation to reduce inflammation markers in men and women: the Comparing EPA to DHA (ComparED) Study
- DHA at nutritional doses restores insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle by preventing lipotoxicity and inflammation
- Healthy effect of different proportions of marine ω-3 PUFAs EPA and DHA supplementation in Wistar rats: Lipidomic biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) has neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress in retinal ganglion cells
- DHA-induced stress response in human colon cancer cells – Focus on oxidative stress and autophagy
- The marine n-3 PUFA DHA evokes cytoprotection against oxidative stress and protein misfolding by inducing autophagy and NFE2L2 in human retinal pigment epithelial cells
- Effects of dietary DHA and α-tocopherol on bone development, early mineralisation and oxidative stress in Sparus aurata (Linnaeus, 1758) larvae
- Selenium inclusion decreases oxidative stress indicators and muscle injuries in sea bass larvae fed high-DHA microdiets
- Vitamin C Enhances Vitamin E Status and Reduces oxidative stress Indicators in Sea Bass Larvae Fed High DHA Microdiets
- PUFA and oxidative stress. Differential modulation of the cell response by DHA
- Membrane Lipid Modification by Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Promotes the Formation of α-Synuclein Inclusion Bodies Immunopositive for SUMO-1 in Oligodendroglial Cells After oxidative stress
- Tumor and non-tumor tissues differential oxidative stress response to supplemental DHA and chemotherapy in rats
- Increased Uncoupling Protein2 mRNA in White Adipose Tissue, and Decrease in leptin, Visceral Fat, Blood Glucose, and Cholesterol in KK-AyMice Fed with Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acids in Addition to Linolenic Acid
- leptin and phospholipid-esterified docosahexaenoic acid concentrations in plasma of women: observations during pregnancy and lactation
- A possible role for ghrelin, leptin, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and docosahexaenoic acid in reducing the quality of life of coeliac disease patients following a gluten-free diet
Donglingcao (From Rabdosia rubesens)
- Donglingcao (Rabdosia rubesens) modulates cancers, neurodegeneration and cardiovascular disease via autophagy.
- Donglingcao (Rabdosia rubesens … is frequently lost in patients enduring metabolic syndromes such as obesity
EGb 761 (from Ginkgo biloba extract)
- Ginkgo biloba Extract EGb 761 and Its Specific Components Elicit Protective Protein Clearance Through the autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway in Tau-Transgenic Mice and Cultured Neurons
- Long-term treatment with Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 improves symptoms and pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
- The Ginkgo biloba Extract EGb 761 Modulates Proteasome Activity and Polyglutamine Protein Aggregation
- EGb761 improves the cognitive function of elderly db/db−/− diabetic mice by regulating the beclin-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways
- Role of EGB 761 as a Possible Aromatase Inhibitor for Breast Cancer Therapy
- EGB 761 Reduces Tumor Growth in Postmenopausal Xenograft Models Implanted MCF-7 AROM Breast Cancer Cells
- Influence of Standardized Extract Ginkgo biloba EGb761® Towards Quality of Life Indicators in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
- EGb 761 (5) may counteract this process … of the glu- cose- and fatty acid metabolism in diabetes leading to high levels of free fatty acids in the blood and to in-creasing synthesis of triglicerides accompanied by in- hibition of lipolysis
- EGb 761 may prevent LDL lipoperoxidation in both lipolytic and hydrophylic phases and may be useful in the prevention of atherosclerosis
- EGb 761 has a broad spectrum of beneficial effects in several disease states, but the primary interest of this laboratory is to … the insulin resistance syndrome (also called syndrome X). The insulin resistance syndrome includes metabolic defects such as obesity,
- adipogenesis involved in obesity (Naaz et al., 2002). Therefore, the present results suggest that the potency of EGb 761 on the ER-mediated reproductive actions
- Ginkgo biloba exocarp extracts induces autophagy in Lewis lung cancer cells involving AMPK / mtor / p70S6k signaling pathway
- Ginkgo Biloba Leaf Extract Attenuates Atherosclerosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic ApoE-/- Mice by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress via Restoration of Autophagy through the mtor Signaling Pathway
- Central and Local Administration of Gingko Biloba Extract EGb 761® Inhibits Thermal Hyperalgesia and inflammation in the Rat Carrageenan Model
- Ginkgo biloba (EGb 761): An anti-dementia drug with inflammation inhibiting and cardiovascular effects
- Central and local administration of Gingko biloba extract EGb 761® inhibits thermal hyperalgesia and inflammation in the rat carrageenan model
- Ginkgo biloba Extract (EGb 761) Pretreatment Limits Free Radical oxidative stress in Patients Undergoing Coronary Bypass Surgery
- Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) attenuates lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats: Roles of oxidative stress and nitric oxide
- Effect of the antioxidant action of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) on aging and oxidative stress
- Ginkgo biloba leaves extract (EGb 761) attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and NF-κB-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 pathway
- Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) attenuates oxidative stress induction in erythrocytes of sickle cell disease patients
- The Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) on parameters of oxidative stress in different regions of aging rat brains after acute hypoxia
- Suppressive effect ofGinkgo bilobaextract (EGb 761) on topsin induced ovarian toxicity and oxidative stress in albino rats
- Antioxidant effect of EGb 761 on aging and oxidative stress
- Emblica officinalis Extract Induces Autophagy and Inhibits Human Ovarian Cancer Cell Proliferation, Angiogenesis, Growth of Mouse Xenograft Tumors
- Emblica officinalis Gaertn. Attentuates N-Nitrosodiethylamine-Induced Apoptosis, Autophagy, and inflammation in Rat Livers
- (Emblica officinalis Gartn.) is … as an antidiabetic and anti- atherogenic adipokine.37 Serum adiponectin levels are de- creased under the conditions of obesity,
- Emblica officinalis Non-obese type 2 diabetes β-Cell function Antioxidant Ellagic acid Insulin secretion.
- (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.), at 10 … High-fructose diets have been used in animal models to induce the metabolic syndrome, including abdominal obesity
- Anti-obesity effects of Emblica officinalis (Amla) are associated with inhibition of nuclear transcription factor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ)
- Emblica officinalis – Anti-obesity activity
- Emblica officinalis in non-diabetic control and diabetic rats … These may be due to inhibition of lipolysis in adipose tissue by insulin sensitizing or insulin mimetic effect of polyphenolic fraction
- Emblica officinalis (family: Euphorbiaceae), also known as Indian gooseberry or amla … A) High-fat-fed animals showed decreased hepatic lipolytic enzyme ie CPT
- Emblica officinalis in our study hypothesizes that a possible inhibition of lipolysis in adipose tissue due to insulin sensitizing or insulin mimetic effect of polyphenolic compound
- Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) prevents dyslipidaemia and oxidative stress in the ageing process
- Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) Extracts Reduce oxidative stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Emblica officinalis causes myocardial adaptation and protects against oxidative stress in ischemic‐reperfusion injury in rats
- Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) Attenuates Age-Related Renal Dysfunction by oxidative stress
- Supplementation of Emblica Officinalis (Amla) Extract Reduces oxidative stress in Uremic Patients
- Studies on effects of Emblica officinalis (Amla) on oxidative stress and cholinergic function in scopolamine induced amnesia in mice.
- A Pilot clinical study to evaluate the effect of Emblica officinalis extract (Amlamax™) on markers of systemic inflammation and dyslipidemia
- Emblica officinalis Gaertn. Attentuates N-Nitrosodiethylamine-Induced Apoptosis, Autophagy, and inflammation in Rat Livers
- Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Emblica officinalis in Rodent Models of Acute and Chronic inflammation: Involvement of Possible Mechanisms
- Protective effect of Emblica-officinalis in arsenic induced biochemical alteration and inflammation in mice
- Rutin rich Emblica officinalis Geart. fruit extract ameliorates inflammation in the pancreas of rats subjected to alcohol and cerulein administration
- Amelioration of Aluminum Maltolate-Induced inflammation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis by Tannoid Principles of Emblica officinalis in Neuronal Cellular Model
Evodiamine, an alkaloid ( from Evodia rutaecarpa )
- Corrigendum to “Evodiamine, a plant alkaloid, induces calcium/JNK-mediated autophagy and calcium/mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells”
- WZY‑321, a novel evodiamine analog, inhibits glioma cell growth in an autophagy‑associated manner
- oxidative stress and autophagy in cardiac disease, neurological disorders, aging and cancer
- Reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide regulate mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and autophagy in evodiamine-treated human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells
- Evodiamine, a plant alkaloid, induces calcium/JNK-mediated autophagy and calcium/mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells
- A Drug Screening Method Based on the autophagy Pathway and Studies of the Mechanism of Evodiamine against Influenza A Virus
- Evodiamine Induces Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid-1-Mediated Protective autophagy in U87-MG Astrocytes
- Anti-Proliferative Effects of Evodiamine in Human Lung Cancer Cells
- The effects of evodiamine on autophagy in human colon adenocarcinoma Lovo cells
- Evodiamine Induces Cell Growth Arrest, Apoptosis and Suppresses Tumorigenesis in Human Urothelial Cell Carcinoma Cells
- Evodiamine and Its Role in Chronic Diseases
- Reported a capsaicin‐like anti‐obese activity of evodiamine
- Evodiamine Improves Diet-Induced obesity in a Uncoupling Protein-1-Independent Manner: Involvement of Antiadipogenic Mechanism and Extracellularly Regulated Kinase/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling
- Inhibitory effect of evodiamine alone and in combination with rosiglitazone on in vitro adipocyte differentiation and in vivo obesity related to diabetes
- Dietary supplementation with evodiamine prevents obesity and improves insulin resistance in ageing mice
- Capsaicin-Like Anti-obese Activities of Evodiamine from Fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa, a Vanilloid Receptor Agonist
- Effect of evodiamine on the mRNA expression of lipolytic enzymes Given the results described above,
- Long-term effects of evodiamine on expressions of lipogenesis and lipolysis genes in mouse adipose and liver tissues
- Evodiamine had on hemodynamics, energy expenditure, and markers … Epinephrine strongly enhances the rate of glycogenolysis and of lipolysis and appearance of free fatty acids
- Evodiamine from fruits of … alba) is provided for increasing individual’s natural adipose lipolytic metabolism via adipose metabolism by way of lipolysis or lipolytic metabolism.
- Evodiamine, and hordenine, all of which have been shown to play a role in enhancing lipolysis and increasing ener- gy expenditure
- Evodiamine Induces Apoptosis and Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Human Bladder Cancer Cells through mtor/S6K1-Mediated Downregulation of Mcl-1
- [Effect of evodiamine in inducing apoptosis of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells through mtor signal pathway].
- The molecular mechanism of apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells induced by evodiamine inhibition mtor signal pathway
- Evodiamine Inhibits Zymosan-Induced inflammation In Vitro and In Vivo: Inactivation of NF-κB by Inhibiting IκBα Phosphorylation
- Protective Effects of Evodiamine against LPS-Induced Acute Kidney Injury through Regulation of ROS-NF-κB-Mediated inflammation
- Evodiamine ameliorates paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain by inhibiting inflammation and maintaining mitochondrial anti-oxidant functions
- Inhibitory effects of evodiamine on zymosan-induced inflammation: inactivation of NF-κB by inhibiting IκBα phosphorylation
- Nitric oxide activated by p38 and NF-κB facilitates apoptosis and cell cycle arrest under oxidative stress in evodiamine-treated human melanoma A375-S2 cells
- Evodiamine inhibits PDGF‑BB‑induced proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells through the suppression of cell cycle progression and oxidative stress
- The Effect of Evodiamine Against Intestinal Tissue Injury Induced By Mesenteric Ischemia-Reperfusion: Role of oxidative stress
- Fenugreek extract as an inducer of cellular death via autophagy in human T lymphoma Jurkat cells
- Fenugreek alkaloids have also been shown to stimulate the hepatic lipogenic enzymes . During [43] diabetes, lipogenesis is decreased while lipolysis
- Fenugreek may be due, at least in part, to intestinal glucosidase inhibition … Measurement of adrenaline-induced lipolysis
- Hypolipidemic Effect of Fenugreek Seeds Is Mediated Through Inhibition of Fat Accumulation and Upregulation of LDL Receptor.
- Fenugreek hypolipidemic action may be an outcome of the achievement of normal glucose level which may reduce degradation of already accumulated lipids and inhibit lipolysis
- Effects of fenugreek seeds on adipogenesis and lipolysis in normal and diabetic rats.
- 4-Hydroxyisoleucine from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum): Effects on Insulin Resistance Associated with obesity
- Efficacy of Fenugreek-based bionanocomposite on renal dysfunction and endogenous intoxication in high-calorie diet-induced obesity rat model—comparative study
- Low molecular weight galactomannans-based standardized fenugreek seed extract ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice via modulation of FASn, IL-6, leptin, and TRIP-Br2†
- Treatment Effects of Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) Seed Powder against High Calorie Diet Indused obesity in Rats
- Protein based product from fenugreek seeds that regulates dyslipidemia and obesity, and a process for the preparation thereof
- Supplementation of Fenugreek Leaves Reduces oxidative stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Effect of trigonelline and ethanol extract of Iraqi Fenugreek seeds on oxidative stress in alloxan diabetic rabbits
- A Mechanism-based Pharmacological Evaluation of Efficacy of Trigonella foenum graecum (Fenugreek) Seeds in Regulation of Dyslipidemia and oxidative stress in Hyperlipidemic Rats
- Amelioration of oxidative stress by dietary fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) seeds is potentiated by onion (Allium cepa L.) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Effect of Aqueous Extract of Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) On Selected Biochemical and oxidative stress Biomarkers in Rats Intoxicated with Carbon Tetrachloride
- Alleviation of oxidative stress-mediated nephropathy by dietary fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seeds and onion (Allium cepa) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Diosgenin present in fenugreek improves glucose metabolism by promoting adipocyte differentiation and inhibiting inflammation in adipose tissues
- Does fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seed improve inflammation, and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? A parallel group randomized clinical trial
- Dietary Fenugreek Attenuates Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis: Role of inflammation
- Mol Nutr Food Res: Diosgenin present in fenugreek improves glucose metabolism by promoting adipocyte differentiation and inhibiting inflammation in adipose tissues
- Fenugreek alleviates airway eosinophilic inflammation of allergic asthma in OVA-induced mouse model
- Fenugreek, A Potent Hypoglycaemic Herb Can Cause Central Hypothyroidism Via leptin – A Threat To Diabetes Phytotherapy
- Low molecular weight galactomannans-based standardized fenugreek seed extract ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice via modulation of FASn, IL-6, leptin, and TRIP-Br2
fisetin (From Cotinus Coggygria Extract)
- Fisetin induces autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress- and mitochondrial stress-dependent pathways
- Crosstalk between Fisetin-induced Apoptosis and autophagy in Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Fisetin regulates obesity by targeting mtorC1
- Fisetin at low concentration that does not affect Akt/mtorC1 signaling inhibited adipocyte differentiation, which does not compromise the fisetin’s potential of anti-obesity
- Fisetin regulates obesity by targeting mtorC1 signaling
- Potentiation of β-adrenoceptor agonist-mediated lipolysis by quercetin and fisetin in isolated rat adipocytes
- Another possible mechanism by which fisetin may regulate obesity pathogenesis is by reducing hepatic lipogenesis
- fisetin act synergistically with epinephrine on β-adrenergic receptor (4), while genistein inhibits … Hormonal short-term modulation of lipolysis is mainly driven by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A
- Fisetin has also been reported as a potent inhibitor of the human P-form phenolsulfonyl transferase, which reflects its role as chemo-preventive agent in carcinogenesis induced by sulfation [12]. It increases lipolysis
- Fisetin shows a dose- and time-dependent increase in lipolysis,
- fisetin exhibited the most effective lipolysis
- Fisetin modulates adipogenesis and lipolysis in steatotic hepatocytes
- Fisetin inhibits human melanoma cell growth through direct binding to p70S6K and mtor: Findings from 3-D melanoma skin equivalents and computational modeling
- Fisetin inhibits laryngeal carcinoma through regulation of AKT/NF-κB/mtor and ERK1/2 signaling pathways
- Fisetin Suppresses Lipid Accumulation in Mouse Adipocytic 3T3-L1 Cells by Repressing GLUT4-Mediated Glucose Uptake through Inhibition of mtor-C/EBPα Signaling
- Promising tumor inhibiting potentials of Fisetin through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- Anti‑cancer effects of fisetin on mammary carcinoma cells via regulation of the PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Flavonol-rich RVHxR from Rhus verniciflua Stokes and its major compound fisetin inhibits inflammation-related cytokines and angiogenic factor in rheumatoid arthritic fibroblast-like synovial cells and in vivo models
- Fisetin, a bioactive flavonol, attenuates allergic airway inflammation through negative regulation of NF-κB
- Fisetin Enhances Behavioral Performances and Attenuates Reactive Gliosis and inflammation During Aluminum Chloride-Induced Neurotoxicity
- Fisetin Inhibits UVB‐induced Cutaneous inflammation and Activation of PI3K/AKT/NFκB Signaling Pathways in SKH‐1 Hairless Mice
- Fisetin inhibits high-glucose-induced vascular inflammation in vitro and in vivo
- Fisetin-treatment alleviates airway inflammation through inhbition of MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Fisetin ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy
- Fisetin Regulates Nrf2 Expression and the inflammation-Related Signaling Pathway to Prevent UVB-Induced Skin Damage in Hairless Mice
- Activated TNF-α/RIPK3 signaling is involved in prolonged high fat diet-stimulated hepatic inflammation and lipid accumulation: inhibition by dietary fisetin intervention
- Abstract 216: The Effect of Fisetin on Lipopolysccharide-induced inflammation and MMP Activity in Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages
- Fisetin, a tetra hydroxy flavone recuperates antioxidant status and protects hepatocellular ultrastructure from hyperglycemia mediated oxidative stress in streptozotocin induced experimental diabetes in rats
- Fisetin averts oxidative stress in pancreatic tissues of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Fisetin protects liver from binge alcohol-induced toxicity by mechanisms including inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and oxidative stress
- Fisetin alleviates oxidative stress after traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE pathway
- Fisetin Confers Cardioprotection against Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Mitochondrial oxidative stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Inhibiting Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β Activity
- Fisetin inhibits cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing oxidative stress
Fucoidan ( From Seaweed Extract )
- Protective effect of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus on liver fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smad pathway-mediated inhibition of extracellular matrix and autophagy
- Real-time tracking of the autophagy process in living cells using plasmonically enhanced Raman spectroscopy of fucoidan-coated gold nanoparticles
- Effect of fucoidan on autophagy, migration and invasion of U266 cells
- fucoidan can be useful for the prevention or treatment of obesity
- Fucoidan administration reduced circulating lipopolysaccharide and ameliorated systematic inflammation in HFD-induced obese mice
- The present study was undertaken to investigate the potential effects of fucoidan on obesity through an in vitro study by determining the effects of fucoidan on preadipocyte differentiation into adipocytes
- Fucoidan Prevents High‐Fat Diet‐Induced obesity in Animals by Suppression of Fat Accumulation
- Effect of Fucoidan Administration on Insulin Secretion and Insulin Resistance in Overweight or obese Adults
- Lipolytic regulation. Here, we examined the biological response of fucoidan on the protein level of lipolysis pathway
- fucoidan inhibited the fat accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via regulation of lipolysis
- Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide derived from brown seaweeds, has been shown to reduce blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity in mice. We investigated the effects of fucoidan on lipid accumulation, lipolysis
- Fucoidan inhibits leukocyte recruitment in a model peritonial inflammation in rat and blocks interaction of P‐selectin with its carbohydrate ligand
- Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide from brown algae, against myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats via regulating the inflammation response
- Fucoidan from the sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida suppresses adipocyte differentiation by inhibition of inflammation-related cytokines in 3T3-L1 cells
- Different Suppressive Effects of Fucoidan and Lentinan on IL-8 mRNA Expression in in Vitro Gut inflammation
- Low molecular weight fucoidan from the sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida suppresses inflammation by promoting the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases and oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells
- Fucoidan inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and during the acute response in vivo
- Low molecular weight fucoidan ameliorates the inflammation and glomerular filtration function of diabetic nephropathy
- Attenuation of inflammation by marine algae Turbinaria ornata in cotton pellet induced granuloma mediated by fucoidan like sulphated polysaccharide
- Fucoidan from Acaudina molpadioides protects pancreatic islet against cell apoptosis via inhibition of inflammation in type 2 diabetic mice
- Fucoidan attenuates atherosclerosis in LDLR-/- mice through inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress
- Suppression by Fucoidan of Liver Fibrogenesis via the TGF-β/Smad Pathway in Protecting against oxidative stress
- Fucoidan protects mesenchymal stem cells against oxidative stress and enhances vascular regeneration in a murine hindlimb ischemia model
- Fucoidan ameliorates steatohepatitis and insulin resistance by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in experimental non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan Alleviates Cardiac Dysfunction in Diabetic Goto-Kakizaki Rats by Reducing oxidative stress and Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis
- Fucoidan protects ARPE-19 cells from oxidative stress via normalization of reactive oxygen species generation through the Ca2+-dependent ERK signaling pathway
- Fucoidan reduces oxidative stress by regulating the gene expression of HO‑1 and SOD‑1 through the Nrf2/ERK signaling pathway in HaCaT cells
- Fucoidan-Vitamin C complex suppresses tumor invasion through the basement membrane, with scarce injuries to normal or tumor cells, via decreases in oxidative stress and matrix metalloproteinases
Fucoxanthin (from Laminaria japonica)
- Fucoxanthin provides neuroprotection in models of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE and Nrf2-autophagy pathways
- Fucoxanthin, the constituent of Laminaria japonica, triggers AMPK-mediated cytoprotection and autophagy in hepatocytes under oxidative stress
- Effects of fucoxanthin on autophagy and apoptosis in SGC‐7901cells and the mechanism
- Study on the Mechanism of autophagy of HeLa Cells in Human Cervical Cancer Induced by Fucoxanthin
- Anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects of fucoxanthin on diet-induced obesity conditions in a murine model
- Anti-obesity Activity of the Marine Carotenoid Fucoxanthin
- Nutraceutical Effects of Fucoxanthin for obesity and Diabetes Therapy: A Review
- Petalonia binghamiae Extract and Its Constituent Fucoxanthin Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced obesity by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase
- We next examined whether fucoxanthin stimulated lipolysis in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes by measuring levels of glycerol in culture supernatants.
- These data indicate that fucoxanthin suppresses lipid accumulation and reduces lipolysis; lipolytic enzyme activity was also inhibited in the NAC positive control group
- The effect of fucoxanthin on lipolysis-related protein
- Fucoxanthin-supplemented group with a high-fat diet; FCH, 0.167 mg/kg/bw fucoxanthin-supplemented group
- Fucoxanthin Activates Apoptosis via Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mtor Pathway and Suppresses Invasion and Migration by Restriction of p38-MMP-2/9 Pathway in Human Glioblastoma Cells
- Fucoxanthin restrains oxidative stress induced by retinol deficiency through modulation of Na+K+-ATPase and antioxidant enzyme activities in rats
- Neuroprotective effects of fucoxanthin and its derivative fucoxanthinol from the phaeophyte Undaria pinnatifida attenuate oxidative stress in hippocampal neurons
- The protective effect of fucoxanthin isolated from Ishige okamurae on oxidative stress induced by high glucose in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and zebrafish model
- Assessment of therapeutic effects of Fucoxanthin by attenuates the inflammation in ovalbumin induced asthma in experimental animal model
- Undaria pinnatifidaand Fucoxanthin AmeliorateLipogenesis and Markers of Both inflammation andCardiovascular Dysfunction in an Animal Model ofDiet-Induced Obesity
- Protective Effects of Fucoxanthin against Alcoholic Liver Injury by Activation of Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Defense and Inhibition of TLR4-Mediated inflammation
- Down‐Regulation of Hepatic Stearoyl‐CoA Desaturase‐1 Expression by Fucoxanthin via leptin Signaling in Diabetic/Obese KK‐Ay Mice
galangin ( From Galangal Root Extract )
- Galangin Induces autophagy via Deacetylation of LC3 by SIRT1 in HepG2 Cells
- Galangin decreases p‑tau, Aβ42 and β‑secretase levels, and suppresses autophagy in okadaic acid‑induced PC12 cells via an Akt/GSK3β/mtor signaling‑dependent mechanism
- Galangin Induces autophagy through Upregulation of p53 in HepG2 Cells
- Galangin suppresses HepG2 cell proliferation by activating the TGF-β receptor/Smad pathway
- Galangin inhibits proliferation of HepG2 cells by activating AMPK via increasing the AMP/TAN ratio in a LKB1-independent manner
- Ethanolic Extract of Algerian Propolis and Galangin Decreased Murine Melanoma T
- Anti-inflammatory effects of galangin on lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages via ERK and NF-κB pathway regulation
- Galangin sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis through down-regulation of anti-apoptotic proteins in renal carcinoma Caki cells
- Synergistic anti-cancer effects of galangin and berberine through apoptosis induction and proliferation inhibition in oesophageal carcinoma cells
- Protection by Naringin and Some Other Flavonoids of Hepatocytic autophagy and Endocytosis against Inhibition by Okadaic Acid
- Cytoprotective effect of flavonoid‐induced autophagy on bisphosphonate mediated cell death in osteoblast
- Galangin Induces Apoptosis in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells Through Mitochondrial Pathway and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Inhibition
- Algerian ethanolic extract of Propolis and galangin decreased melanoma tumour progression in C57BL6 mice
- Galangin Inhibits Thrombin-Induced MMP-9 Expression in SK-N-SH Cells via Protein Kinase-Dependent NF-κB Phosphorylation
- This mechanism is believed to be active in preventing obesity, although the activity of galangin in animal models was not investigated
- Anti-obesity effects of galangin, a pancreatic lipase inhibitor in cafeteria diet fed female rats
- Galangin and primers for RT-PCR analysis were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich Pvt … that TGF-β1 gene expression is elevated in the adipose tissue from genetically obese mice
- Anti-obesity effects of galangin
- Galangin induced antitumor effects in human kidney tumor cells mediated via mitochondrial mediated apoptosis, inhibition of cell migration and invasion and targeting PI3K/ AKT/mtor signalling pathway.
- Galangin attenuates mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation
- Galangin Abrogates Ovalbumin-Induced Airway inflammation via Negative Regulation of NF-B
- Galangin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death in mice through inhibition of ERK and NF-kappaB signaling
- Galangin ameliorates cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in vivo by modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation through interplay of MAPK signaling cascade
- Galangin Activates Nrf2 Signaling and Attenuates Oxidative Damage, inflammation, and Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity
- D31 NOVEL MECHANISMS OF ALLERGY AND AIRWAY inflammation: Galangin Attenuates Airway Remodeling By Inhibiting Tgf-[Beta]1-Mediated Ros Generation And Mapk/akt Phosphorylation In Asthma
- Galangin Suppresses Renal inflammation via the Inhibition of NF-κB, PI3K/AKT and NLRP3 in Uric Acid Treated NRK-52E Tubular Epithelial Cells
- A Ribonuclease Isolated from Wild Ganoderma Lucidum Suppressed autophagy and Triggered Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells
- Methanolic Extract of Ganoderma lucidum Induces autophagy of AGS Human Gastric Tumor Cells
- Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides Prevent Palmitic Acid-Evoked Apoptosis and autophagy in Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cell Line via Restoration of Mitochondrial Function and Regulation of MAPK and AMPK/Akt/mtor Signaling Pathway
- Triterpenes From Ganoderma Lucidum Induce autophagy in Colon Cancer Through the Inhibition of p38 Mitogen-Activated Kinase (p38 MAPK)
- Anti-cancer properties of triterpenoids isolated from Ganoderma lucidum – a review
- A methanolic extract of Ganoderma lucidum fruiting body inhibits the growth of a gastric cancer cell line and affects cellular autophagy and cell cycle
- Biologic Activity of Spores and Dried Powder from Ganoderma lucidum for the Inhibition of Highly Invasive Human Breast and Prostate Cancer Cells
- Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi) Inhibits Cancer Cell Growth and Expression of Key Molecules in Inflammatory Breast Cancer
- Active lipids of Ganoderma lucidum spores-induced apoptosis in human leukemia THP-1 cells via MAPK and PI3K pathways
- GMI, an Immunomodulatory Protein from Ganoderma microsporum, Potentiates Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis via autophagy in Lung Cancer Cells
- Total triterpenoids from Ganoderma Lucidum suppresses prostate cancer cell growth by inducing growth arrest and apoptosis
- GMI, an immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma microsporum, induces autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoid extract induces apoptosis in human colon carcinoma cells (Caco-2)
- A supercritical-CO2 extract of Ganoderma lucidum spores inhibits cholangiocarcinoma cell migration by reversing the epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides Reduce Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Interleukin-1β Expression in Cultured Smooth Muscle Cells and in Thoracic Aortas in Mice
- Studying Ganoderma lucidum as a source of molecular inducers of autophagy
- Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota
- Anti-obesity Effect Of Mushroom (Ganoderma Lucidum) On Experimentally Induced obese Rats
- Method to prepare Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides possessing anti-obesity properties
- Sporoderm-broken spores of Ganoderma lucidum water extract (BSGLWE) inhibits high-fat diet induced obesity through regulating gut microbiota in mice
- The Effects of Ganoderma Lucidum Pharmacopuncture and Moxibustion (Wang-tteum) on Abdominal obesity: Case Report
- The Mechanism of Ganoderma lucidum Specific microRNA glu-miR-01Regulation of Target Genes on PI3K/AKT/mtor Signaling Pathway
- Inhibition of oxidative stress-induced invasiveness of cancer cells by Ganoderma lucidum is mediated through the suppression of interleukin-8 secretion
- Ganoderma Lucidum Polysaccharide Accelerates Refractory Wound Healing by Inhibition of Mitochondrial oxidative stress in Type 1 Diabetes
- Suppression of proliferation and oxidative stress by extracts of Ganoderma lucidum in the ovarian cancer cell line OVCAR-3
- Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide peptide prevents renal ischemia reperfusion injury via counteracting oxidative stress
- Ganoderma lucidum protects liver mitochondrial oxidative stress and improves the activity of electron transport chain in carbon tetrachloride intoxicated rats
- Laccase isozymes from Ganoderma lucidum MDU-7: Isolation, characterization, catalytic properties and differential role during oxidative stress
- Neuroprotective effects of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides against oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis
- Effects of Selenium-Enriched Protein from Ganoderma lucidum on the Levels of IL-1β and TNF-α, oxidative stress, and NF-κB Activation in Ovalbumin-Induced Asthmatic Mice
- Effectiveness of Dp2 nasal therapy for Dp2- induced airwayinflammation in mice: using oral Ganoderma lucidum as animmunomodulator
- Ganoderma lucidum beta 1,3/1,6 glucan as an immunomodulator in inflammation induced by a high-cholesterol diet
- Ganoderma lucidum repress injury of ethanol-induced steatohepatitis via anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation and reducing hepatic lipid in C57BL/6J mice
- Le Ganoderma lucidum: accompagnement cancérologique, lutte antivirale, lutte contre l’inflammation ou contre le syndrome métabolique
- LBPS 01–05 GANODERMA LUCIDUM POLYSACCHARIDE PEPTIDES AS ANTIOXIDANT, ANTI-inflammation, ANTI-HYPERTENSION AND ANTI-LIPID IN HIGH-RISK PATIENTS OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS
- A Study on the Controlling Effect of Ganoderma lucidum Mycelium Extract on the Respiratory System inflammation of the Mice
- Ganoderma lucidum suppresses colon carcinogenesis and inflammation
- PS 02-02 Effect Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharide Peptides as Anti-hypertension, Anti-lipid, Anti-oxidant, Anti-inflammation in High Risk Patients of Atherosclerosis
- A study on the controlling effect of Ganoderma lucidum mycelium extract on the respiratory system inflammation of the mice
Genistein (From Genista Extract)
- autophagy plays a role in genistein inhibiting proliferation of cervical cancer cells
- Genistein-induced LKB1–AMPK activation inhibits senescence of VSMC through autophagy induction
- Correction of Huntington’s Disease Phenotype by Genistein-Induced autophagy in the Cellular Model
- A High Concentration of Genistein Induces Cell Death in Human Uterine Leiomyoma Cells by autophagy
- Genistein and Myd88 Activate autophagy in High Glucose-Induced Renal Podocytes In Vitro
- autophagy-dependent mechanism of genistein-mediated elimination of behavioral and biochemical defects in the rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease
- Genistein protects against rat hippocampus amyloid-β1-42 neurotoxicity through p-mtor-dependent autophagy
- Genistein protects against ox-LDL-induced senescence through enhancing SIRT1/LKB1/AMPK-mediated autophagy flux in HUVECs
- L11 A novel approach for treatment of huntington’s disease by genistein-mediated stimulation of autophagy
- [Role of PPAR-γ-regulated autophagy in genistein-induced inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation].
- Genistein affects lipogenesis and lipolysis in isolated rat adipocytes
- Genistein and daidzein repress adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue‐derived mesenchymal stem cells via Wnt/β‐catenin signalling or lipolysis
- Genistein inhibits adipogenesis and increases lipolysis in primary human adipocytes
- Maternal Genistein Alters Coat Color and Protects Avy Mouse Offspring from obesity by Modifying the Fetal Epigenome
- Genistein: A promising therapeutic agent for obesity and diabetes treatment
- Hepatic Gene Expression Profiles Are Altered by Genistein Supplementation in Mice with Diet-Induced obesity
- Effect of Genistein with Carnitine Administration on Lipid Parameters and obesity in C57Bl/6J Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
- Impact of estradiol, ER subtype specific agonists and genistein on energy homeostasis in a rat model of nutrition induced obesity
- Genistein Exposure During the Early Postnatal Period Favors the Development of obesity in Female, But Not Male Rats
- Modulation of Adipocyte Differentiation and Proadipogenic Gene Expression by Sulforaphane, Genistein, and Docosahexaenoic Acid as a First Step to Counteract obesity
- Sensitization of Cervical Cancer Cells to Cisplatin by Genistein: The Role of NF B and Akt/mtor Signaling Pathways
- Novasoy and genistein inhibit endometrial cancer cell proliferation through disruption of the AKT/mtor and MAPK signaling pathways
- Genistein protects against rat hippocampus amyloid-β1-42 neurotoxicity through p-mtor-dependent autophagy
- Genistein and Gut inflammation: Role of Nitric Oxide
- Estradiol or genistein prevent Alzheimer’s disease-associated inflammation correlating with an increase PPARγ expression in cultured astrocytes
- Genistein attenuates retinal inflammation associated with diabetes by targeting of microglial activation
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitor, genistein, reduces renal inflammation and injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
- Oral treatment with genistein reduces the expression of molecular and biochemical markers of inflammation in a rat model of chronic TNBS-induced colitis
- Genistein inhibits TNF-α-induced endothelial inflammation through the protein kinase pathway A and improves vascular inflammation in C57BL/6 mice
- Genistein modulates NF-κB-associated renal inflammation, fibrosis and podocyte abnormalities in fructose-fed rats
- Genistein ameliorates cardiac inflammation and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats
- Genistein Prevents Hyperglycemia-Induced Monocyte Adhesion to Human Aortic Endothelial Cells through Preservation of the cAMP Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates Vascular inflammation in Obese Diabetic Mice
- Soy isoflavones (daidzein & genistein) inhibit 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced cutaneous inflammation via modulation of COX-2 and NF-κB in Swiss albino mice
- Genistein attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal damage following transient global cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus
- The Soy Isoflavone, Genistein, Protects Human Cortical Neuronal Cells from oxidative stress
- Suppressive Effects of Genistein on oxidative stress and NFκB Activation in RAW 264.7 Macrophages
- Genistein protects prostate cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA damage and induces expression of genes involved in the defence against oxidative stress
- Genistein reduced the neural apoptosis in the brain of ovariectomised rats by modulating mitochondrial oxidative stress
- Dietary genistein and equol (4′, 7 isoflavandiol) reduce oxidative stress and protect rats against focal cerebral ischemia
- Activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and PPARγ plays a role in the genistein-mediated attenuation of oxidative stress-induced endothelial cell injury
- Genistein modulates oxidative stress in breast cancer cell lines according to ERα/ERβ ratio: Effects on mitochondrial functionality, sirtuins, uncoupling protein 2 and antioxidant enzymes
- Genistein induces apoptosis and autophagy in human breast MCF-7 cells by modulating the expression of proapoptotic factors and oxidative stress enzymes
- Genistein restricts leptin secretion from rat adipocytes
- Genistein induces adipogenesis but inhibits leptin induction in human synovial fibroblasts
- Genistein stimulates fatty acid oxidation in a leptin receptor-independent manner through the JAK2-mediated phosphorylation and activation of AMPK in skeletal muscle
- Effects of estradiol, estrogen receptor subtype-selective agonists and genistein on glucose metabolism in leptin resistant female Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats
- Effect of the genistein metabolite on leptin secretion in murine adipocytes in vitro
- Genistein suppresses leptin‐induced proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells and neointima formation
- Genistein Precipitated Hypothyroidism, Altered leptin and C-Reactive Protein Synthesis in Pregnant Rats
- The effect of resistance training and genistein on leptin and lipid profile of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Hypothyroidism, altered leptin and c-reactive protein synthesis characterised pregnancy exposed to genistein
- Genistein stimulates fatty acid oxidation in a leptin receptor-independent manner through the JAK2-mediated phosphorylation and activation of AMPK in skeletal muscle
- Impact of estradiol, estrogen receptor subtype specific agonists and genistein on food intake, body weight, and glucose metabolism in leptin resistant ovariectomized Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Genistein Combined with Exercise Improves Lipid Profiles and leptin Levels in C57BL/6J Mice Fed a High Fat Diet
ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe)
- Zerumbone, a ginger sesquiterpene, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human hormone-refractory prostate cancers through tubulin binding and crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial insult
- Genetic and Histopathological Responses to Cadmium Toxicity in Rabbit’s Kidney and Liver: Protection by Ginger (Zingiber officinale)
- Ginger was reported that it could stimulate the lipolysis activity
- Zingiber officinale, has shown therapeutic role in health management since … reported to be effective in enhancing basal lipolysis
- Beneficial effects of Zingiber officinale on goldthioglucose induced obesity
- Beneficial effects of ginger Zingiber officinale Roscoe on obesity and metabolic syndrome: a review.
- Mioga (Zingiber mioga Rosc.) Extract Prevents 3T3-L1 Differentiation into Adipocytes and obesity in Mice
- A systematic review of the anti‐obesity and weight lowering effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) and its mechanisms of action
- Effect of Zingiber officinale Supplementation on obesity Management with Respect to the Uncoupling Protein 1 ‐3826A>G and ß3‐adrenergic Receptor Trp64Arg Polymorphism
- Ginger (Zingiber officinale) has been used as a medicinal spice for a long time.21, 22 It … zingerone at the concentration of 1000 μM increases basal lipolysis
- Mechanism of Chemoprevention against Colon Cancer Cells Using Combined Gelam Honey and Ginger Extract via mTOR and Wnt/β-catenin Pathways.
- Influence of dietary ginger (Zingiber officinales Rosc) on oxidative stress induced by malathion in rats
- Modulatory effects of garlic, ginger, turmeric and their mixture on hyperglycaemia, dyslipidaemia and oxidative stress in streptozotocin–nicotinamide diabetic rats
- 6-Shogaol (Alkanone from Ginger) Induces Apoptotic Cell Death of Human Hepatoma p53 Mutant Mahlavu Subline via an oxidative stress-Mediated Caspase-Dependent Mechanism
- Ginger Pharmacopuncture Improves Cognitive Impairment and oxidative stress Following Cerebral Ischemia
- Effects of Cinnamon, Cardamom, Saffron, and Ginger Consumption on Markers of Glycemic Control, Lipid Profile, oxidative stress, and inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Effect of Ginger and Cinnamon Intake on oxidative stress and Exercise Performance and Body Composition in Iranian Female Athletes
- Inhibitory effects of [6]-gingerol, a major pungent principle of ginger, on phorbol ester-induced inflammation, epidermal ornithine decarboxylase activity and skin tumor promotion in ICR mice
- Ginger, micro-inflammation and kidney disease
- Ginger prevents Th2-mediated immune responses in a mouse model of airway inflammation
- Influence of Ginger and Cinnamon Intake on inflammation and Muscle Soreness Endued by Exercise in Iranian Female Athletes
- Dried Ginger (Zingiber officinalis) Inhibits inflammation in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mouse Model
- Protective effects of ginger‐turmeric rhizomes mixture on joint inflammation, atherogenesis, kidney dysfunction and other complications in a rat model of human rheumatoid arthritis
- inflammation reducing action of synergistic mixtures of bisabolol and ginger extracts
- Effects of ginger on serum glucose, advanced glycation end products, and inflammation in peritoneal dialysis patients
- Standardized ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract reduces bacterial load and suppresses acute and chronic inflammation in Mongolian gerbils infected with cagA+ Helicobacter pylori
- Effects of clove and fermented ginger on blood glucose, leptin, insulin and insulin receptor levels in high fat diet- induced type 2 diabetic rabbits
- Effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) supplementation on nutritional status and circulating level of some adipocytokines in obese women with regard to genetic polymorphism of leptin, adiponectin, UCP-1 and beta 3 adrenergic receptors
Gingerol (From Zingiber Officinale)
- 6-Gingerol induces autophagy to protect HUVECs survival from apoptosis
- autophagy-dependent apoptosis is triggered by a semi-synthetic [6]-gingerol analogue in triple negative breast cancer cells
- Inhibition of the autophagy flux by gingerol enhances TRAIL-induced tumor cell death
- A Bioactive Constituent of Ginger, 6‐Shogaol, Prevents Adipogenesis and Stimulates lipolysis in 3T3‐L1 Adipocytes
- Anti‐obesity action of gingerol: effect on lipid profile, insulin, leptin, amylase and lipase in male obese rats induced by a high‐fat diet
- Synergistic effect of quercetin and 6-gingerol treatment in streptozotocin induced type 2 diabetic rats and poloxamer P-407 induced hyperlipidemia
- Ameliorative potential of gingerol: Promising modulation of inflammatory factors and lipid marker enzymes expressions in HFD induced obesity in rats
- 6-Gingerol Inhibits Lipid Accumulation and obesity-Induced Inflammatory Responses In 3T3-L1 adipocytes and RAW264.7 Macrophages.
- Mechanisms for antidiabetic effect of gingerol in cultured cells and obese diabetic model mice
- 6-Gingerol Suppresses Adipocyte-Derived Mediators of inflammation In Vitro and in High-Fat Diet-Induced obese Zebra Fish
- A study on 6-gingerol attenuate vascular smooth muscle cells senescence through inhibition of mtor pathway molecular
- 6-Gingerol Protects against Nutritional Steatohepatitis by Regulating Key Genes Related to inflammation and Lipid Metabolism
- [6]-Gingerol dampens hepatic steatosis and inflammation in experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- 6-Gingerol Protects Heart by Suppressing Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Induced inflammation via the PI3K/Akt-Dependent Mechanism in Rats
- 6-Gingerol mitigates nutritional steatohepatitis through regulating key genes related to oxidative stress, inflammation and fibrogenesis
- The Natural Product 6-Gingerol Inhibits inflammation-Associated Osteoclast Differentiation via Reduction of Prostaglandin E2 Levels
- Corrigendum to(6-Gingerol Protects Heart by SuppressingMyocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Induced inflammation viathe PI3K/Akt-Dependent Mechanism in Rats)
- Chapter 24 – The Phenolic Gingerols and Gingerol-Derived Shogaols: Features and Properties Related to the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer and Chronic inflammation
- 6-gingerol ameliorates gentamicin induced renal cortex oxidative stress and apoptosis in adult male albino rats
- Zingiber officinale and 6-gingerol alleviate liver and kidney dysfunctions and oxidative stress induced by mercuric chloride in male rats: A protective approach
- 6-gingerol ameliorates age-related hepatic steatosis: Association with regulating lipogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
- Anti‐obesity action of gingerol: effect on lipid profile, insulin, leptin, amylase and lipase in male obese rats induced by a high‐fat diet
Ginsenoside 20 (S)-Rg3 ( From Ginseng Root Extact )
- Ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 induced autophagy to inhibit migration and invasion of ovarian cancer
- 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 Induce the Apoptosis and autophagy in U937 and K562 Cells
- Stereoisomer-Specific Anticancer Activities of Ginsenoside Rg3 and Rh2 in HepG2 Cells: Disparity in Cytotoxicity and autophagy-Inducing Effects Due to 20(S)-Epimers
- Inhibition of autophagy potentiates anticancer property of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 by promoting mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells
- 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 sensitizes human non-small cell lung cancer cells to icotinib through inhibition of autophagy
- 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 is a novel inhibitor of autophagy and sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to doxorubicin
- The Ginsenoside 20-O-β-D-Glucopyranosyl-20(S)-Protopanaxadiol Induces autophagy and Apoptosis in Human Melanoma via AMPK/JNK Phosphorylation
- Ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 induced autophagy to inhibit migration and invasion of ovarian cancer
- Ginsenoside Rg5 Inhibits Succinate-Associated lipolysis in Adipose Tissue and Prevents Muscle Insulin Resistance
- Ginsenoside Rb_1 facilitates adipocyte differentiation and inhibits lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- Ginsenoside Rb1 Induces Beta 3 Adrenergic Receptor-dependent lipolysis and Thermogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and db/db Mice
- Anti-obesity effects of ginsenoside Rh2 are associated with the activation of AMPK signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocyte
- Ginsenoside Rh1 Ameliorates High Fat Diet-Induced obesity in Mice by Inhibiting Adipocyte Differentiation
- Ginsenoside F2 possesses anti-obesity activity via binding with PPARγ and inhibiting adipocyte differentiation in the 3T3-L1 cell line
- Ginsenoside Rg1 inhibits dietary-induced obesity and improves obesity-related glucose metabolic disorders
- Anti-obesity Effects of Ginsenoside Rd via AMPK and PPAR Gamma
- Ginsenoside Rg5: Rk1 Exerts an Anti-obesity Effect on 3T3-L1 Cell Line by the Downregulation of PPARγ and CEBPα
- Saponin from sea cucumber exhibited more significant effects than ginsenoside on ameliorating high fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice
- Stereoisomer-specific ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 reverses replicative senescence of human diploid fibroblasts via Akt-mtor-Sirtuin signaling
- 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 displays efficacy against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia through the PI3K/Akt/mtor signal pathway
- Central Inflammation and leptin Resistance Are Attenuated by Ginsenoside Rb1 Treatment in Obese Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
- Ginsenoside Rb1 improves leptin sensitivity in the prefrontal cortex in obese mice
- Ginsenoside Rb1 exerts antidiabetic action on C2C12 muscle cells by leptin receptor signaling pathway
Glucosamine ( From Crab and Shrimp SHells )
- Glucosamine Activates autophagy In Vitro and In Vivo
- Glucosamine induces autophagy via an mtor-independent pathway
- Glucosamine protects nucleus pulposus cells and induces autophagy via the mtor‐dependent pathway
- Glucosamine promotes osteoblast proliferation by modulating autophagy via the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway
- Glucosamine extends the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via autophagy induction
- Glucosamine-Induced autophagy through AMPK–mtor Pathway Attenuates Lipofuscin-Like Autofluorescence in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells In Vitro
- Glucosamine regulates autophagy in vitro and in vivo
- O-LINKED N-ACETYL GLUCOSAMINE (O-GLCNAC) REGULATES autophagy AND APOPTOSIS IN CARDIOMYOCYTES: A DOUBLE-EDGED SWORD IN INTERMITTENT HYPOXIA-INDUCED CARDIAC REMODELING
- Glucosamine induces autophagic cell death through the stimulation of ER stress in human glioma cancer cells
- Glucosamine protects nucleus pulposus cells and induces autophagy via the mtor‐dependent pathway
- autophagy in osteoarthritis
- autophagy and cartilage homeostasis mechanisms in joint health, aging and OA
- Post-translational protein modification by O-linked N-acetyl-glucosamine: Its role in mediating the adverse effects of diabetes on the heart
- Effects of Lipofectamine 2000/siRNA Complexes on autophagy in Hepatoma Cells
- Beneficial reward-to-risk action of glucosamine during pathogenesis of osteoarthritis
- Molecular mechanisms of anticancer effects of Glucosamine
- autophagy Modulation for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy
- Glucosamine: an ingredient with skin and other benefits
- Cytotoxic Effects of d-Glucosamine on the Ultrastructures of Normal and Neoplastic Tissues in Vivo
- Anti-obese Effect of Glucosamine and Chitosan Oligosaccharide in High-Fat Diet-Induced obese Rats
- glucosamine (glucosamine-6-phosphate, PGlc) was synthesized using methanesulfonic acid, phosphorus … genes and proteins associated with adipogenesis and lipolysis
- glucosamine and inositol monophosphate, whereas the insulin effects on 3-0-methylglucose, cyclic AMP and lipolysis were unaffected
- Glucosamine induces insulin … identification of phosphorylation sites and effects on the phosphorylation by lipolytic hormones
- Anti-obesity effect of sulfated glucosamine by AMPK signal pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- Glucosamine Enhances Body Weight Gain and Reduces Insulin Response in Mice Fed Chow Diet but Mitigates obesity, Insulin Resistance and Impaired Glucose Tolerance in Mice High-Fat Diet
- Anti-obesity effect of EGCG and glucosamine-6-phosphate through decreased expression of genes related to adipogenesis and cell cycle arrest in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- Oral Glucosamine for 6 Weeks at Standard Doses Does Not Cause or Worsen Insulin Resistance or Endothelial Dysfunction in Lean or obese Subjects
- Anti-obese Effect of Glucosamine and Chitosan Oligosaccharide in High-Fat Diet-Induced obese Rats
- Increased number of subjects with elevated levels of blood glucose (HbA1c) after prolonged glucosamine usage among overweight and obese women
- An analysis of high glucose and glucosamine-induced gene expression and oxidative stress in renal mesangial cells
- Influence of glucosamine sulphate on oxidative stress in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes: effects on HO-1, p22Phox and iNOS expression
- Comparison of effect of chitin, chitosan, chitosan oligosaccharide and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine on growth performance, antioxidant defenses and oxidative stress status of Penaeus monodon
- Protective Effects of Glucosamine on Oxidative-Stress and Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Retinal Injury
- Randomized Trial of Glucosamine and Chondroitin Supplementation on inflammation and oxidative stress Biomarkers and Plasma Proteomics Profiles in Healthy Humans
- Augmented O-GlcNAc signaling via glucosamine attenuates oxidative stress and apoptosis following contrast-induced acute kidney injury in rats
- Evaluation of antigenotoxic effects of Glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine on human peripheral lymphocytes exposed to oxidative stress
- Combined effect of celecoxib and glucosamine sulfate on inflammatory factors and oxidative stress indicators in patients with knee osteoarthritis
- Inflammatory and oxidative stress in the Airway Epithelium Are Mediated Through O-Linked N-Acetyl-Glucosamine Modification and Regulated by FGF23
- Effects of Chondroitin and Glucosamine Sulfate in a Dietary Bar Formulation on inflammation, Interleukin-1β, Matrix Metalloprotease-9, and Cartilage Damage in Arthritis
- Joint inflammation increases glucosamine levels attained in synovial fluid following oral administration of glucosamine hydrochloride
- Glucosamine attenuates cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation by inhibiting ROS-sensitive inflammatory signaling
- Attenuation of LPS-Induced Lung inflammation by Glucosamine in Rats
- Effect of a high dose of glucosamine on systemic and tissue inflammation in an experimental model of atherosclerosis aggravated by chronic arthritis
- Fullerenols and glucosamine fullerenes reduce infarct volume and cerebral inflammation after ischemic stroke in normotensive and hypertensive rats
- Effects of dietary supplementation of glucosamine sulfate on intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of experimental colitis
- Glucosamine and egg for reducing inflammation
- Associations Between Glucosamine and Chondroitin Supplement Use and Biomarkers of Systemic inflammation
- Effects of glucosamine sulfate and exercise therapy on serum leptin levels in patients with knee osteoarthritis: preliminary results of randomized controlled clinical trial
- Glucosamine attenuates increases of intraabdominal fat, serum leptin levels, and insulin resistance induced by a high-fat diet in rats
- Effect of oral glucosamine sulfate on serum leptin levels in human subjects
Glutathione (From Glutamic Acid, Cysteine and Glycine)
- Glutathione participates in the modulation of starvation-induced autophagy in carcinoma cells
- Lysosomal thiol reductase negatively regulates autophagy by altering glutathione synthesis and oxidation
- Glutathione transferase mu 2 protects glioblastoma cells against aminochrome toxicity by preventing autophagy and lysosome dysfunction
- Intracellular Glutathione Regulates Sesquiterpene Lactone-induced Conversion of autophagy to Apoptosis in Human Leukemia HL60 Cells
- Glutathione Depletion Induces Spermatogonial Cell autophagy
- Parkin deficiency increases the resistance of midbrain neurons and glia to mild proteasome inhibition: the role of autophagy and glutathione homeostasis
- A bacterial metabolite induces glutathione-tractable proteostatic damage, proteasomal disturbances, and PINK1-dependent autophagy in C. elegans
- Glutathione-S-transferase omega 1 (GSTO1-1) acts as mediator of signaling pathways involved in aflatoxin B1-induced apoptosis–autophagy crosstalk in macrophages
- Ascorbic acid prevents acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice by ameliorating glutathione recovery and autophagy
- Glutathione depletion induces ferroptosis, autophagy, and premature cell senescence in retinal pigment epithelial cells
- Glutathione participates in the modulation of starvation-induced autophagy in carcinoma cells
- Lysosomal thiol reductase negatively regulates autophagy by altering glutathione synthesis and oxidation
- Glutathione transferase mu 2 protects glioblastoma cells against aminochrome toxicity by preventing autophagy and lysosome dysfunction
- Sodium nitroprusside induces autophagic cell death in glutathione-depleted osteoblasts
- Glutathione Participates in the Regulation of Mitophagy in Yeast
- Ascorbate induces autophagy in pancreatic cancer
- Chirality of Glutathione Surface Coating Affects the Cytotoxicity of Quantum Dots
- Glutathione in Cancer Cell Death
- Glutathione: new roles in redox signaling for an old antioxidant
- Glutathione Efflux and Cell Death
- Cystatin SN inhibits auranofin-induced cell death by autophagic induction and ROS regulation via glutathione reductase activity in colorectal cancer
- Glutathione peroxidase activity is neuroprotective in models of Huntington’s disease
- Cellular glutathione peroxidase in human brain: cellular distribution, and its potential role in the degradation of Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies
- Effect of Alloxan on Spontaneous lipolysis and Glutathione System in Isolated Rat Adipocytes
- Effect of insulin, the glutathione system, and superoxide anion radical in modulation of lipolysis in adipocytes of rats with experimental diabetes
- Development of insulin resistance and obesity in mice overexpressing cellular glutathione peroxidase
- Glutathione-S-Transferase M1, obesity, Statins, and Autonomic Effects of Particles
- Glutathione S-Transferase Polymorphisms, Passive Smoking, obesity, and Heart Rate Variability in Nonsmokers
- Cytochrome P450-dependent mixed-function oxidase and glutathione S-transferase activities in spontaneous obesity-diabetes
- Glutathione Depletion Prevents Diet‐Induced obesity and Enhances Insulin Sensitivity
- Hepatic Expression of Adiponectin Receptors Increases with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Progression in Morbid obesity in Correlation with Glutathione Peroxidase 1
- Serum Selenium and Glutathione Peroxidase in Patients with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Mutant Type Glutathione S-transferase Theta 1 Gene Homologue to mtor in Myelodysplastic Syndrome: Possible Clinical Application of Rapamycin
- P663 Cardiac energy dependence on glucose increases metabolites related to glutathione and activates metabolic genes controlled by mtor.
- Systemic L-buthionine-S-R-sulfoximine administration modulates glutathione homeostasis via NGF/TrkA and mtor signaling in the cerebellum
- Glutathione, Stress Responses, and Redox Signaling in Lung inflammation
- Regulation of redox glutathione levels and gene transcription in lung inflammation: therapeutic approaches
- Environmental toxicity, redox signaling and lung inflammation: The role of glutathione
- High-dose oral N-acetylcysteine, a glutathione prodrug, modulates inflammation in cystic fibrosis
- Role of Se-dependent glutathione peroxidases in gastrointestinal inflammation and cancer
- Role of glutathione in immunity and inflammation in the lung
- Regulation of glutathione in inflammation and chronic lung diseases
- Glutathione Redox Regulates Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Airway inflammation in Mice
- Protein-Deficient Pigs Cannot Maintain Reduced Glutathione Homeostasis When Subjected to the Stress of inflammation
- Polymorphisms at the glutathione S‐transferase, GSTP1 locus: a novel mechanism for susceptibility and development of atopic airway inflammation
- Glutathione, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration
- Glutathione and glutathione-dependent enzymes represent a co-ordinately regulated defence against oxidative stress
- Importance of SE-glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and CU/ZN-SOD for cell survival against oxidative stress
- Plasma glutathione and glutathione disulfide in the rat: regulation and response to oxidative stress.
- Neurodegenerative disorders in humans: the role of glutathione in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal death
- Tissue glutathione, nutrition, and oxidative stress
- Glutathione Depletion Due to Copper-Induced Phytochelatin Synthesis Causes oxidative stress in Silene cucubalus
- Glutathione depletion and oxidative stress
- Renal antioxidant enzymes and glutathione redox status in leptin-induced hypertension
- Wound tissue malondialdehyde and glutathione levels in leptin treated healthy and diabetic rats.
- [Effects of glutathione on oxidative stress, leptin and adiponectin in patients with obstructive sleep apnea complicated with metabolic syndrome].
- leptin sensitizer celastrol, glial calcineurin and hypothalamic glutathione peroxidase 7 – novel entities in weight control and glucose homeostasis
Grifolin, a secondary metabolic product isolated from the mushroom Albatrellus confluence
- Grifolin induces autophagic cell death by inhibiting the Akt/mtor/S6K pathway in human ovarian cancer cells
- Grifolin, a potent antitumour natural product upregulates death-associated protein kinase 1 DAPK1 via p53 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- Grifolin, a potent antitumour natural product inhibits the growth and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro
Gynura formosana Kitam. leaves
- The Ethyl Acetate Extract of Gynura formosana Kitam. Leaves Inhibited Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation via Induction of autophagy
- Differential induction of apoptosis and autophagy by pyrrolizidine alkaloid clivorine in human hepatoma Huh-7.5 cells and its toxic implication
- First record of Phytophthora drechsleri on Gynura formosana
- Antioxidant Capacity, Cytotoxicity, and Acute Oral Toxicity of Gynura bicolor
- Gynura procumbens modulates the microtubules integrity and enhances distinct mechanism on doxorubicin and 5-flurouracil-induced breast cancer cell death
- Effects of light quality on growth, secondary metabolites, and oxidative stress tolerance of Gynura bicolor.
- Gynura divaricata ameliorates hepatic insulin resistance by modulating insulin signalling, maintaining glycolipid homeostasis and reducing inflammation in type 2 diabetic mice
- Hibiscus sabdariffa Leaf Polyphenolic Extract Induces Human Melanoma Cell Death, Apoptosis, and autophagy
- Delphinidin-rich extracts of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. trigger mitochondria-derived autophagy and necrosis through reactive oxygen species in human breast cancer cells
- Autophagic effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa leaf polyphenols and epicatechin gallate (ECG) against oxidized LDL-induced injury of human endothelial cells
- Hibiscus sabdariffa extract inhibits obesity and fat accumulation, and improves liver steatosis in humans
- Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa extract on high fat diet–induced obesity and liver damage in hamsters
- Potential use of dietary fibre from Hibiscus sabdariffa and Agave tequilana in obesity management
- Multi-Targeted Molecular Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa Polyphenols: An Opportunity for a Global Approach to obesity
- Postweaning Consumption of Aqueous Extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa May Predispose Rats to Obesity
- Antidiabetic properties of Hibiscus rosa sinensis L. leaf extract fractions on non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse
- Hibiscus sabdariffa L. aqueous extract attenuates hepatic steatosis through down-regulation of PPAR-γ and SREBP-1c in diet-induced obese mice
- Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa Calices on Dyslipidemia in obese Adolescents: A Triple-masked Randomized Controlled Trial
- Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa Supplementation on Renal Function and Lipidic Profile in obese Rats
- Effect of different fractions of Hibiscus rosa sinensis leaf extract on islets of Langerhans and antioxidant activity in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse
- Polyphenols Extracted from Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Inhibited Lipopolysaccharide-Induced inflammation by Improving Antioxidative Conditions and Regulating Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression
- Anti-inflammatory Activity of Methanolic Extract ofHibiscus sabdariffaon CarrageenanInduced inflammation in Wistar Rat
- Exploring the effect and mechanism of Hibiscus sabdariffa on urinary tract infection and experimental renal inflammation
- Aqueous extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. decelerates acetaminophen‐induced acute liver damage by reducing cell death and oxidative stress in mouse experimental models
- The protective effect of aqueous extracts of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L. UKMR-2) against red blood cell membrane oxidative stress in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes
- Anthocyanin – Rich Red Dye of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Calyx Modulates Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in Rats
- Hibiscus sabdariffa ethanolic extract protects against dyslipidemia and oxidative stress induced by chronic cholesterol administration in rabbits.
- The Effect of Green Tea and Sour Tea (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) Supplementation on oxidative stress and Muscle Damage in Athletes
- Infusion of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Modulates oxidative stress in Patients with Marfan Syndrome
- Efficacy of Hibiscus sabdariffa and Telfairia occidentalis in the attenuation of CCl4-mediated oxidative stress
- Evaluation of the effects of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) on oxidative stress and serum levels of lipids, insulin and hs-CRP in adult patients with metabolic syndrome: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial
- Modulation of oxidative stress in Fatty Liver of Rat with Metabolic Syndrome by Hibiscus Sabdariffa
- oxidative stress Attenuation in Hiv/Aids Patients on Antiretroviral Drugs by Calyx Juice of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn (Malvaceae)
- Anthocyanin–Rich Red Dye of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Calyx Modulates CdCl2- Induced Hypochromic Microcytic Anaemia and oxidative stress in Rat Red Blood Cells
honokiol (from Magnolia officinalis)
- Honokiol‑induced apoptosis and autophagy in glioblastoma multiforme cells
- Honokiol activates reactive oxygen species‐mediated cytoprotective autophagy in human prostate cancer cells
- Honokiol induces autophagy of neuroblastoma cells through activating the PI3K/Akt/mtor and endoplasmic reticular stress/ERK1/2 signaling pathways and suppressing cell migration
- Magnolol and honokiol exert a synergistic anti-tumor effect through autophagy and apoptosis in human glioblastomas
- Honokiol exhibits enhanced antitumor effects with chloroquine by inducing cell death and inhibiting autophagy in human non-small cell lung cancer cell
- Honokiol Induces Apoptosis, G1 Arrest, and autophagy in KRAS Mutant Lung Cancer Cells
- Honokiol induces apoptosis and autophagy via the ROS/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo
- Liposomal honokiol induced lysosomal degradation of Hsp90 client proteins and protective autophagy in both gefitinib-sensitive and gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cells
- Data analyses of honokiol-induced autophagy of human glioma cells in vitro and in vivo
- Improved effects of honokiol on temozolomide-induced autophagy and apoptosis of drug-sensitive and -tolerant glioma cells
- Honokiol‑induced apoptosis and autophagy in glioblastoma multiforme cells
- Honokiol, a Multifunctional Antiangiogenic and Antitumor Agent
- Honokiol induces autophagy of neuroblastoma cells through activating the PI3K/Akt/mtor and endoplasmic reticular stress/ERK1/2 signaling pathways and suppressing cell migration
- Honokiol induces autophagic cell death in malignant glioma through reactive oxygen species-mediated regulation of the p53/PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway
- Honokiol inhibits melanoma stem cells by targeting notch signaling
- Honokiol triggers the activation of the LKB1–AMPK signaling pathway, thereby leading to the induction of lipolysis
- We next evaluated the effect of honokiol on lipolysis by Western blotting and confirmed enhanced expression of p-HSL and p-PLIN
- Honokiol (molecular weight: 266.33; 99.8% purity)36 was provided by Jack Arbiser’s Laboratory, Department of Dermatology, Emory University Medical School … In vitro studies show that solar radiation produces TNF‐α, IL‐1α, IL‐11, and IL‐6, inducing lipolysis and decreasing
- honokiol in an effective amount to increase lipolysis in mature adipocytes
- Honokiol, magnolol, and a combination of both compounds improve glucose metabolism in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
- Growth Inhibitory Activity of Honokiol through Cell-cycle Arrest, Apoptosis and Suppression of Akt/mtor Signaling in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
- Honokiol induces autophagic cell death in malignant glioma through reactive oxygen species-mediated regulation of the p53/PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway
- Honokiol Inhibits Vascular Vessel Formation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial Cells via the Suppression of PECAM and MAPK/mtor Signaling Pathway
- Honokiol induces autophagy and apoptosis of osteosarcoma through PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway
- mtor signaling pathway is inhibited downstream of the cyclophilin D-mediated mitochondrial permeability transition in honokiol-triggered regulated necrosis
- Honokiol induces apoptosis and suppresses migration and invasion of ovarian carcinoma cells via AMPK/mtor signaling pathway
- Inhibition of NADPH oxidase-related oxidative stress-triggered signaling by honokiol suppresses high glucose-induced human endothelial cell apoptosis
- Protective action of honokiol, administered orally, against oxidative stress in brain of mice challenged with NMDA
- Honokiol protects rat hearts against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation
- Honokiol protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via the suppression of oxidative stress, iNOS, inflammation and STAT3 in rats
- Honokiol Reduces oxidative stress, c-jun-NH2-Termial Kinase Phosphorylation and Protects against Glycochenodeoxycholic Acid-Induced Apoptosis in Primary Cultured Rat Hepatocytes
- Honokiol Alleviates oxidative stress-Induced Neurotoxicity via Activation of Nrf2
- Honokiol Ameliorates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Type 1 Diabetic Rats by Reducing oxidative stress and Apoptosis through Activating the SIRT1-Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
- Long‐term supplementation of honokiol and magnolol ameliorates body fat accumulation, insulin resistance, and adipose inflammation in high‐fat fed mice
- Honokiol Downregulates Kruppel-Like Factor 4 Expression, Attenuates inflammation, and Reduces Histopathology After Spinal Cord Injury in Rats
- Honokiol inhibits ultraviolet radiation-induced immunosuppression through inhibition of ultraviolet-induced inflammation and DNA hypermethylation in mouse skin
- Honokiol Attenuates Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury via the Inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Honokiol protects skin cells against inflammation, collagenolysis, apoptosis, and senescence caused by cigarette smoke damage
- Honokiol improved chondrogenesis and suppressed inflammation in human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells via blocking nuclear factor-κB pathway
- Oral administration of honokiol attenuates airway inflammation in asthmatic mouse model.
- Effects of Honokiol on airway inflammation in asthmatic mice exposed to PM2.5 and its mechanism
- Administration of synergistic amounts of modified citrus pectin and honokiol to treat inflammation and anti-oxidant needs
- Effects of particulate matter (PM 2.5) exposure on airway inflammation in asthmatic mice and intervention effect of Honokiol
- Honokiol abrogates leptin-induced tumor progression by inhibiting Wnt1-MTA1-β-catenin signaling axis in a microRNA-34a dependent manner
- Honokiol activates LKB1-miR-34a axis and antagonizes the oncogenic actions of leptin in breast cancer
Hou po (Cortex magnoliae officinalis)
- Autophagy triggered by magnolol derivative negatively regulates angiogenesis
- Magnolol-lnduced H460 cells deathvia autophagy but not apoptosis
- Tiron and trolox potentiate the autophagic cell death induced by magnolol analog Ery5 by activation of Bax in HL-60 cells
- Magnolol derivative 002C-3 protects brain against ischemia–reperfusion injury via inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy
- Magnolol, a natural compound, induces apoptosis of SGC-7901 human gastric adenocarcinoma cells via the mitochondrial and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways
Hu Zhang (Rhizoma polygoni cuspidati)
Huaier extract (From Auricularia on Sophora Japonica)
- Huaier extract synergizes with tamoxifen to induce autophagy and apoptosis in ER-positive breast cancer cells
- Huaier suppresses proliferative and metastatic potential of prostate cancer PC3 cells via downregulation of Lamin B1 and induction of autophagy
- [Huaier aqueous extract inhibits proliferation of human hepatoma SK-HEP-1 cells through up-regulation of autophagy].
- Huaier Extract Induces Autophagic Cell Death by Inhibiting the mtor/S6K Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells
- Huaier extract synergizes with tamoxifen to induce autophagy and apoptosis in ER-positive breast cancer cells
- Huaier Extract Inhibits Breast Cancer Progression Through a LncRNA-H19/MiR-675-5p Pathway
- Huaier aqueous extract protects against dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- Huaier polysaccharide induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through p38 MAPK
- Huaier extract restrains the proliferative potential of endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells through increased ATM by suppressing miR-203
- Huaier extract enhances the treatment efficacy of paclitaxel in breast cancer cells via the NF-κB/IκBα pathway
- Huaier aqueous extract inhibits cervical cancer cell proliferation via JNK/p38 pathway
- A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Study on the Curative Effect of Huaier on Mild-to-Moderate Psoriasis and an Experimental Study on the Proliferation of Hacat Cells
- A polysaccharide from Huaier ameliorates cisplatin nephrotoxicity by decreasing oxidative stress and apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling
Isorhamnetin (from sea buckthorn / Hippophae rhamnoides L.)
- Autophagy inhibition enhances isorhamnetin‑induced mitochondria‑dependent apoptosis in non‑small cell lung cancer cells
- Isorhamnetin: A hepatoprotective flavonoid inhibits apoptosis and autophagy via P38/PPAR-α pathway in mice
- Isorhamnetin Inhibits Liver Fibrosis by Reducing autophagy and Inhibiting Extracellular Matrix Formation via the TGF-β1/Smad3 and TGF-β1/p38 MAPK Pathways
- Antiviral Effect of Methylated Flavonol Isorhamnetin against Influenza
- 7-O-geranylquercetin-induced autophagy contributes to apoptosis via ROS generation in human non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Isorhamnetin‐3‐O‐Glucuronide Suppresses JNK and p38 Activation and Increases Heme‐Oxygenase‐1 in Lipopolysaccharide‐Challenged RAW264.7 Cells
- FRI0531 THE ARTICULAR PROTECTION EFFECT OF ISORHAMNETIN IN THE RATS OF MONOSODIUM IODOACETATE-INDUCED OSTEOARTHRITIS
- Water Dropwort, Hyperoside and Isorhamnetin, Regulates the Inflammasome Activation
- Induction of HO-1 by Isorhamnetin Inhibits COX-2 Expression in Response to inflammation
- Isorhamnetin glycoside isolated from Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) MilI induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells through mitochondrial damage
- isorhamnetin may be beneficial to obesity and steatosis prevention
- The effect of isorhamnetin glycosides extracted from Opuntia ficus-indica in a mouse model of diet induced obesity
- Dietary Isorhamnetin Reduces obesity-induced Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Fed a High-fat Diet
- Isorhamnetin (ISOR), known as 3-O-methylquercetin (Figure 1a), a metabolite of quercetin, is a … Dietary quercetin, ameliorated high fat diet-induced obesity
- Isorhamnetin revealed that isorhamnetin suppresses the … In vivo studies to observe the effects of SL extract on obesity
- lipolysis and the … inhibitors of adipose differentiation have been identified, including isorhamnetin
- Isorhamnetin reduced the mRNA levels of C/EBP α and … expression may impair the barrier function of the protein, thereby leading to enhanced lipolysis
- Isorhamnetin-3-O … hepatic lipid metabolism is controlled by a balance between lipogenesis and lipolysis processes
- Isorhamnetin (ISOR), known as 3-O-methylquercetin (Figure 1a), a metabolite of quercetin, is a naturally occurring flavonoid in … essential for maintaining metabolic homeostasis in white adipose tissue because, they are involved in adipogenesis, lipogenesis, lipolysis
- Isorhamnetin-3-O … Studies found H. fulva plant extract to be a novel lipolysis-promoting material that sensitized the lipolytic response
- Isorhamnetin suppresses colon cancer cell growth through the PI3K‑Akt‑mtor pathway
- O-methylated flavonol isorhamnetin prevents acute inflammation through blocking of NF-κB activation
- The Antioxidant Effects of Isorhamnetin Contribute to Inhibit COX-2 Expression in Response to inflammation: A Potential Role of HO-1
- Protective effects of isorhamnetin on apoptosis and inflammation in TNF-α-induced HUVECs injury
- Induction of HO-1 by Isorhamnetin Inhibits COX-2 Expression in Response to inflammation
- Isorhamnetin protects against oxidative stress by activating Nrf2 and inducing the expression of its target genes
- AMPK activation by isorhamnetin protects hepatocytes against oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
- Isorhamnetin-3-glucoside alleviates oxidative stress and opacification in selenite cataract in vitro
- Isorhamnetin attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad signaling and relieving oxidative stress
- Isorhamnetin attenuates collagen-induced arthritis via modulating cytokines and oxidative stress in mice
- The cytoprotective effect of isorhamnetin against oxidative stress is mediated by the upregulation of the Nrf2-dependent HO-1 expression in C2C12 myoblasts through scavenging reactive oxygen species and ERK inactivation.
- Protective effect of isorhamnetin on H9 C2 cell line against oxidative stress
- Isorhamnetin protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injure by attenuating apoptosis and oxidative stress in H9c2 cardiomyocytes
- O-Methylated Flavonoid Isorhamnetin Protects against oxidative stress via Activation of Nrf2 and Target Gene Expression
- Dietary component isorhamnetin is a PPARγ antagonist and ameliorates metabolic disorders induced by diet or leptin deficiency
Isorhynchophylline (IsoRhy) (from Uncaria rhynchophylla)
- Isorhynchophylline, a natural alkaloid, promotes the degradation of alpha-synuclein in neuronal cells via inducing autophagy
- Isorhynchophylline, a natural alkaloid, promotes the degradation of α-synuclein in neuronal cells via inducing autophagy. autophagy 2012; 8:98–108
- Isorhynchophylline: A plant alkaloid with therapeutic potential for cardiovascular and central nervous system diseases
- Isorhynchophylline, a natural alkaloid, promotes the degradation of α-synuclein in neuronal cells via inducing autophagy
- Aberrant autophagy and Parkinsonism: Does Correction Rescue from Disease Progression?
- Isorhynchophylline improves learning and memory impairments induced by D-galactose in mice
- Isorhynchophylline Attenuates MPP+-Induced Apoptosis Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress- and Mitochondria-Dependent Pathways in PC12 Cells: Involvement of Antioxidant Activity
- Isorhynchophylline Treatment Improves the Amyloid-β-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Rats via Inhibition of Neuronal Apoptosis and Tau Protein Hyperphosphorylation
- Stereoselective in vitro metabolism of rhynchophylline and isorhynchophylline epimers of Uncaria rhynchophylla in rat liver microsomes
- Isorhynchophylline, a Potent Plant Alkaloid, Induces Apoptotic and Anti-Metastatic Effects in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through the Modulation of Diverse Cell Signaling Cascades
kaempferol (From Sophora Japonica Extract)
- Neuroprotection of kaempferol by autophagy in models of rotenone-mediated acute toxicity: possible implications for Parkinson’s disease
- Carcinoma cells activate AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent autophagy as survival response to kaempferol-mediated energetic impairment
- Kaempferol induces autophagy through AMPK and AKT signaling molecules and causes G2/M arrest via downregulation of CDK1/cyclin B in SK-HEP-1 human hepatic cancer cells
- The role of kaempferol-induced autophagy on differentiation and mineralization of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells
- Cytoprotective effect of kaempferol against palmitic acid-induced pancreatic β-cell death through modulation of autophagy via AMPK/mtor signaling pathway
- Kaempferol alleviates ox-LDL-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of autophagy via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway in human endothelial cells
- Kaempferol induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell death via endoplasmic reticulum stress-CHOP-autophagy signaling pathway
- Kaempferol suppresses proliferation but increases apoptosis and autophagy by up-regulating microRNA-340 in human lung cancer cells
- The Effects of Kaempferol-Inhibited autophagy on Osteoclast Formation
- Kaempferol suppresses human gastric cancer SNU-216 cell proliferation, promotes cell autophagy, but has no influence on cell apoptosis
- Neuroprotection of kaempferol by autophagy in models of rotenone-mediated acute toxicity: possible implications for Parkinson’s disease
- Kaempferol induces autophagic cell deathvia IRE1-JNK-CHOP pathway and inhibitionof G9a in gastric cancer cells
- A review of the dietary flavonoid, kaempferol on human health and cancer chemoprevention
- Kaempferol induces autophagic cell death of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via activating AMPK signaling
- Succinate-induced neuronal mitochondrial fission and hexokinase II malfunction in ischemic stroke: Therapeutical effects of kaempferol
- Kaempferol Reduces Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression by Down-Regulating ERK1/2 and the Activator Protein-1 Signaling Pathways in Oral Cancer Cells
- kaempferol has antioxidative [17], antimicrobial [15], anti-inflammatory [18], lipolytic [19]
- Anti-obesity effects of kaempferol by inhibiting adipogenesis and increasing lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells
- Kaempferol Prevents obesity through Inhibiting Adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 Cells
- effect of kaempferol on lipolysis, it is unlikely that kaempferol increases lipolysis
- kaempferol only inhibits the early stage. Regarding mature adipocytes, the three compounds reduce TG accumulation by activating, at least in part, lipolysis,
- kaempferol increased lipolysis and restored chronic high fatty acid-impaired glucose uptake
- Kaempferol alleviates palmitic acid-induced lipid stores, endoplasmic reticulum stress and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction through AMPK/mtor-mediated lipophagy
- Kaempferol Inhibits Angiogenesis by Suppressing HIF-1α and VEGFR2 Activation via ERK/p38 MAPK and PI3K/Akt/mtor Signaling Pathways in Endothelial Cells
- A Novel C-Glucosides of Kaempferol Isolated From the Steam-Bark of Ulmus Walli
- Kaempferol Inhibits Angiogenesis through the Suppression of HIF-1α and VEGFR2 Expression via ERK/p38 MAPK-Dependent and PI3K/AKT/mtor Signaling Pathways in Endothelial Cells.
- Effects of Phenol-Depleted and Phenol-Rich Diets on Blood Markers of oxidative stress, and Urinary Excretion of Quercetin and Kaempferol in Healthy Volunteers
- Protective and detrimental effects of kaempferol in rat H4IIE cells: Implication of oxidative stress and apoptosis
- Kaempferol Derivatives Prevent oxidative stress–Induced Cell Death in a DJ-1–Dependent Manner
- Effects of Parsley (Petroselinum crispum) and its Flavonol Constituents, Kaempferol and Quercetin, on Serum Uric Acid Levels, Biomarkers of oxidative stress and Liver Xanthine Oxidoreductase Aactivity inOxonate-Induced Hyperuricemic Rats
- Kaempferol Attenuates Cardiac Hypertrophy via Regulation of ASK1/MAPK Signaling Pathway and oxidative stress
- Kaempferol attenuates hyperglycemia-induced cardiac injuries by inhibiting inflammatory responses and oxidative stress
- Kaempferol protects against propacetamol-induced acute liver injury through CYP2E1 inactivation, UGT1A1 activation, and attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in mice
- Kaempferol and inflammation: From chemistry to medicine
- Kaempferol Suppresses Eosionphil Infiltration and Airway inflammation in Airway Epithelial Cells and in Mice with Allergic Asthma
- Quercetin and kaempferol suppress immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic inflammation in RBL-2H3 and Caco-2 cells
- Kaempferol Alleviates the Interleukin-1β-Induced inflammation in Rat Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes via Suppression of NF-κB
- Blockade of Airway inflammation by Kaempferol via Disturbing Tyk-STAT Signaling in Airway Epithelial Cells and in Asthmatic Mice
- Inhibitory effects of kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside on ovalbumin-induced lung inflammation in a mouse model of allergic asthma
- Enzymatic Synthesis of a Novel Kaempferol-3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-α-d-glucopyranoside Using Cyclodextrin Glucanotransferase and Its Inhibitory Effects on Aldose Reductase, inflammation, and oxidative stress
- Anti-inflammatory effects of Kaempferol on Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation
- Kaempferol inhibits chemokine expression and attenuates airway inflammation by suppressing STAT/JAK and NF-kB activity in human airway epithelial cells
luteolin (Peanut Shell Extract)
- autophagy Inhibitor Chloroquine Enhanced the Cell Death Inducing Effect of the Flavonoid Luteolin in Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
- Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis and non-canonical autophagy by luteolin in NCI-H460 lung carcinoma cells
- Posttraumatic administration of luteolin protects mice from traumatic brain injury: Implication of autophagy and inflammation
- Luteolin alleviates post‐infarction cardiac dysfunction by up‐regulating autophagy through Mst1 inhibition
- Anti-tumor activities of luteolin and silibinin in glioblastoma cells: overexpression of miR-7-1-3p augmented luteolin and silibinin to inhibit autophagy and induce apoptosis in glioblastoma in vivo
- Luteolin Attenuates Foam Cell Formation and Apoptosis in Ox-LDL-Stimulated Macrophages by Enhancing autophagy
- Luteolin Promotes Cell Apoptosis by Inducing autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- The Association of Palmitoylethanolamide with Luteolin Decreases Neuroinflammation and Stimulates autophagy in Parkinson’s Disease Model
- The Association of Palmitoylethanolamide with Luteolin Decreases autophagy in Spinal Cord Injury
- Luteolin decreases the UVA‑induced autophagy of human skin fibroblasts by scavenging ROS
- Anti-tumor activities of luteolin and silibinin in glioblastoma cells: overexpression of miR-7-1-3p augmented luteolin and silibinin to inhibit autophagy and induce apoptosis in glioblastoma in vivo
- Molecular targets of luteolin in cancer
- The flavonoid luteolin enhances doxorubicin-induced autophagy in human osteosarcoma U2OS cells
- Luteolin promotes the sensitivity of cisplatin in ovarian cancer by decreasing PRPA1-medicated autophagy.
- Luteolin: A Flavonoid that Has Multiple Cardio-Protective Effects and Its Molecular Mechanisms
- Luteolin and Apigenin Attenuate 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal-Mediated Cell Death through Modulation of UPR, Nrf2-ARE and MAPK Pathways in PC12 Cells
- Protective effects of luteolin-7-O-glucoside against starvation-induced injury through upregulation of autophagy in H9c2 Cells
- Caspase Activation and Extracellular Signal‐Regulated Kinase/Akt Inhibition Were Involved in Luteolin‐Induced Apoptosis in Lewis Lung Carcinoma Cells
- Luteolin Induces Apoptosis and autophagy in Mouse Macrophage ANA-1 Cells via the Bcl-2 Pathway
- RECENT UPDATES ON NEUROPHARMACOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF LUTEOLIN
- Luteolin-induced apoptosis through activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress sensors in pheochromocytoma cells
- Luteolin exerts an anticancer effect on NCI-H460 human non-small cell lung cancer cells through the induction of Sirt1-mediated apoptosis
- luteolin suppressed adipogenic and lipogenic genes in the cells, while lipolytic genes
- Luteolin can maintain fasting blood glucose in normal levels and thus prevent lipolysis.
- Luteolin protects against high fat diet-induced cognitive deficits in obesity mice
- Brain “fog,” inflammation and obesity: key aspects of neuropsychiatric disorders improved by luteolin
- Luteolin Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance Through the Interplay Between the Liver and Adipose Tissue in Mice with Diet-Induced obesity
- Low‐dose diet supplement of a natural flavonoid, luteolin, ameliorates diet‐induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice
- Luteolin reduces obesity-associated insulin resistance in mice by activating AMPKα1 signalling in adipose tissue macrophages
- Luteolin Prevents Cardiometabolic Alterations and Vascular Dysfunction in Mice With HFD-Induced obesity
- Luteolin-Enriched Artichoke Leaf Extract Alleviates the Metabolic Syndrome in Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced obesity
- Modulating effect of luteolin on ethanol and cerulein induced inflammation— In silico and in vivo studies using rat model of pancreatitis
- Combination of curcumin and Luteolin synergistically inhibits TNF-α-induced vascular inflammation in human vascular cells and mice
- Investigating the Effect of Luteolin on Interleukin-1β and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in inflammation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in Male Rats
- Luteolin Ameliorates Gut inflammation by Inhibition of NF-?B Activation in in vivo and in vitro inflammation Models
- Effects of luteolin on inflammation and immune function
- [The inhibitory effect of luteolin on inflammation in LPS-induced microglia].
- Quercetin, luteolin and epigallocatechin gallate alleviate TXNIP and NLRP3-mediated inflammation and apoptosis with regulation of AMPK in endothelial cells
- Brain “fog,” inflammation and obesity: key aspects of neuropsychiatric disorders improved by luteolin
- Luteolin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice through inhibition of platinum accumulation, inflammation and apoptosis in the kidney
- LUTEOLIN REDUCES CARDIAC DYSFUNCTIONS AND MITOCHONDRIAL oxidative stress IN STREPTOZOTOCIN-INDUCED DIABETIC RATS
- Luteolin Ameliorates Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by oxidative stress
- Luteolin extracted from Platycodon grandiflorum protects retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative stress-induced caspase-3 dependent apoptosis
- LUTEOLIN HAS THERAPEUTIC POTENTIAL THROUGH THE REGULATION OF oxidative stress IN CASTRATION-RESISTANT PROSTATE CANCER: MP84-17
- Flavonoids as protective agents against oxidative stress induced by gentamicin in systemic circulation. Potent protective activity and microbial synergism of luteolin
- Fisetin and luteolin protect human retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death and regulate inflammation
- Luteolin attenuate the d-galactose-induced renal damage by attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Luteolin rescues pentylenetetrazole-induced cognitive impairment in epileptic rats by reducing oxidative stress and activating PKA/CREB/BDNF signaling
Matrine (From Sophora Flavescens Extract)
- Antitumor effect of matrine in human hepatoma G2 cells by inducing apoptosis and autophagy
- Matrine, a novel autophagy inhibitor, blocks trafficking and the proteolytic activation of lysosomal proteases
- JNK-Bcl-2/Bcl-xL-Bax/Bak Pathway Mediates the Crosstalk between Matrine-Induced autophagy and Apoptosis via Interplay with Beclin 1
- Matrine induces Akt/mtor signalling inhibition‐mediated autophagy and apoptosis in acute myeloid leukaemia cells
- Matrine-induced autophagy regulated by p53 through AMP-activated protein kinase in human hepatoma cells
- autophagy is involved in anticancer effects of matrine on SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cells
- Matrine‑induced autophagy counteracts cell apoptosis via the ERK signaling pathway in osteosarcoma cells
- Involvement of β‑catenin in matrine‑induced autophagy and apoptosis in WB‑F344 cells
- Matrine suppresses KRAS‐driven pancreatic cancer growth by inhibiting autophagy‐mediated energy metabolism
- [Matrine inhibits proliferation and promotes autophagy and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by deactivating PI3K/AKT/mtor pathway].
- Blocking Autophagic Flux Enhances Matrine-Induced Apoptosis in Human Hepatoma Cells
- Protective role of autophagy in matrine‑induced gastric cancer cell death
- JNK-Bcl-2/Bcl-xL-Bax/Bak Pathway Mediates the Crosstalk between Matrine-Induced autophagy and Apoptosis via Interplay with Beclin 1
- Matrine induces Akt/mtor signalling inhibition‐mediated autophagy and apoptosis in acute myeloid leukaemia cells
- Matrine induces programmed cell death and regulates expression of relevant genes based on PCR array analysis in C6 glioma cells
- Matrine‑induced autophagy counteracts cell apoptosis via the ERK signaling pathway in osteosarcoma cells
- Involvement of β‑catenin in matrine‑induced autophagy and apoptosis in WB‑F344 cells
- Autophagic death induced by matrine in BEL-7402 cells
- Anticancer Advances of Matrine and Its Derivatives
- Potentiation of resveratrol-induced apoptosis by matrine in human hepatoma HepG2 cells
- Effect of matrine on transforming growth factor β1 and hepatocyte growth factor in rat liver fibrosis model
- Synthesis and biological evaluation of matrine derivatives containing benzo-α-pyrone structure as potent anti-lung cancer agents
- Anti-tumor effect of matrine combined with cisplatin on rat models of cervical cancer
- The effect of matrine on adriamycin-induced podocyte injury and the function of mtor signaling pathway
- Matrine Exerts Antidepressant-Like Effects on Mice: Role of the Hippocampal PI3K/Akt/mtor Signaling
- Matrine induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway
- [Matrine inhibits proliferation and promotes autophagy and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by deactivating PI3K/AKT/mtor pathway].
- Matrine Protects Against MCD-Induced Development of NASH via Upregulating HSP72 and Downregulating mtor in a Manner Distinctive From Metformin
- Matrine improves skeletal muscle atrophy by inhibiting E3 ubiquitin ligases and activating the Akt/mtor/FoxO3α signaling pathway in C2C12 myotubes and mice
- Impact of matrine on inflammation related factors in rat intestinal microvascular endothelial cells
- Matrine attenuates allergic airway inflammation and eosinophil infiltration by suppressing eotaxin and Th2 cytokine production in asthmatic mice
- Matrine protects neuro-axon from CNS inflammation-induced injury
- Prevention of ocular inflammation by matrine, prednisolone, and cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase inhibitors.
- Matrine suppresses airway inflammation by downregulating SOCS3 expression via inhibition of NF-κB signaling in airway epithelial cells and asthmatic mice
- [Effect of matrine on NO and ADMA metabolism pathways in serum and tissues of mice with lipopolysaccharide-induced intestine tissue inflammation].
- [Effects of matrine on airway inflammation and early airway remodeling in asthmatic mice].
- The Matrine Derivate MASM Prolongs Survival, Attenuates inflammation, and Reduces Organ Injury in Murine Established Lethal Sepsis
- Matrine reduces cigarette smoke-induced airway neutrophilic inflammation by enhancing neutrophil apoptosis.
- Neuroprotective effects of matrine on scopolamine-induced amnesia via inhibition of AChE/BuChE and oxidative stress
- Matrine attenuates oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via maintaining AMPKα/UCP2 pathway
- Matrine Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Aging-Related Behavior in Mice via Inhibition of Cellular Senescence and oxidative stress
- Cotyledon cells of Vigna mungo seedlings use at least two distinct autophagic machineries for degradation of starch granules and cellular components
- Connections between dictyosomes, ER and GERL in cotyledons of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.)
- Chemistry and technology of green gram (Vigna radiata [L.] Wilczek)
- Protein bodies of mung bean cotyledons as autophagic organelles
- Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cotyledon Senescence During Early Seedling Stage of Mung Bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]
- Involvement of carboxypeptidase in the degradation of the mung bean (Vigna radiata) trypsin inhibitor during germination and early seedling growth
- Relationship between loss of desiccation tolerance and programmed cell death (PCD) in mung bean (Vigna radiata) seeds
- Ameliorative effect of melatonin on meristematic cells of chilled and re-warmed Vigna radiata roots
- The first possibility is that MBT may activate AMPK-induced lipolysis. AMPK is a critical regulator of leptin-induced fatty acid metabolism and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. 12–14 Even though vitexin in mung bean extracts increased AMPK protein expression
- Effects of Mung-Bean and Black-Bean ethanol extracts on inflammation related to obesity in the high fat induced obesity model
- Mung Bean-Derived Protein Protects Against Neurodegeneration and Memory Impairment in Animal Model of Menopause with obesity
- Physiological Effects of Mung Bean Starch RS-3 on the obesity Index and Adipose Cell Profile of Sprague-Dawley Rats
- lipolytic activity of the mung bean lipase
- Mung bean protein hydrolysates … hypocaloric diets: effects on weight loss and mitochondrial oxidation in obese
- mung bean protein (MPI) suppresses hepatic lipogenesis in rodent models and reduces fasting plasma glucose and insulin levels in obese adults.
- mung bean hulls have high potential as a new feedstock for xylitol production. In addressing the current concerns of obesity
- mung bean coat (MBC … db/db Mice are leptin receptor-deficient and are considered to be an animal model of type 2 diabetes because mice are obese,
- mung bean can be quite beneficial for planning the diets of diabetic, obese and patients
- Arsenic-induced root growth inhibition in mung bean (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.) is due to oxidative stress resulting from enhanced lipid peroxidation
- Changes in oxidative stress defense system in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) cultivars grown with and without mineral nutrients and irradiated by supplemental ultraviolet-B
- Cadmium causes oxidative stress in mung bean by affecting the antioxidant enzyme system and ascorbate-glutathione cycle metabolism
- Mobile phone radiation inhibits Vigna radiata (mung bean) root growth by inducing oxidative stress
- oxidative stress and antioxidant defense mechanism in mung bean seedlings after lead and cadmium treatments
- Caffeic acid inhibits in vitro rooting in mung bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] hypocotyls by inducing oxidative stress
- Dimethoate modifies enhanced UV-B effects on growth, photosynthesis and oxidative stress in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) seedlings: Implication of salicylic acid
- Protective role of mannitol against the oxidative stress induced by H2O2 in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.): Changes in antioxidant defense systems
- Dietary Mung Bean Protein Reduces Hepatic Steatosis, Fibrosis, and inflammation in Male Mice with Diet-Induced, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Fermented composition of mung bean hulls, method for forming thereof, and anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation composition using the same
- Muscadine Grape Skin Extract Induces an Unfolded Protein Response-Mediated autophagy in Prostate Cancer Cells: A TMT-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis
- Attenuation of obesity by tocotrienol and application of muscadine grape seed oil as its food based delivery system
- muscadine grapes … rice bran oil and may offer an alternative solution to attenuate high fat diet-mediated obesity
- Muscadine Grape (Vitis rotundifolia) and Wine Phytochemicals Prevented obesity-Associated Metabolic Complications in C57BL/6J Mice
- Nutraceutical Values of Muscadine against obesity and Metabolic Complications in-vivo
- Correction to Muscadine Grape (Vitis rotundifolia) and Wine Phytochemicals Prevented obesity Associated Metabolic Complications in C57BL/6J Mice
- Attenuation of obesity by tocotrienol and application of muscadine grape seed oil as its food based delivery system
- Muscadine Juice, Wine and Dealcoholized wine 125 … Thus under normal conditions, insulin suppresses glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver, and inhibits lipolysis
- muscadine or peppervine … increase heart rate, release energy from glucose and glycogen, increase muscle readiness and induce lipolysis
- muscadine extracts being more effective … The spoilage microorganisms including yeasts and moulds and lipolytic
- muscadine or peppervine …Zucker rats are known to have reduced response to stimulators of lipolysis,
- muscadine grape poly … are maintained in abdominally obese men through a reduction in lipolytic
- Muscadine Grape Extract Prevents Proliferation of HER2 Positive Breast Cancer Cells in Association with a Decrease in Phosphorylation of AKT and mtor
- Polyphenolics from Açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) and Red Muscadine Grape (Vitis rotundifolia) Protect Human Umbilical Vascular Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) from Glucose- and Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced inflammation and Target MicroRNA-126
- Topical Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Vitis rotundifolia (Muscadine Grape) Extracts in the Tetradecanoylphorbol Acetate Model of Ear inflammation
- Muscadine grape seed oil as a novel source of tocotrienols to reduce adipogenesis and adipocyte inflammation
- Muscadine grape pomace in the treatment of intestinal inflammation
- Muscadine Grape (Vitis rotundifolia) or Wine Phytochemicals Reduce Intestinal inflammation in Mice with Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis
- Muscadine Skin Nutraceutical Extract Is Highly Anti-Inflammatory In The TPA Model Of Topical inflammation
- Muscadine Grape (Vitis rotundifolia) or Wine Supplement Alleviates Intestinal inflammation in a Chronic Colitis Mice Model
- Identification and Characterization of Tocotrienols in Muscadine Grape Seed Oil and their Inhibitory Effects on Adipogenesis and inflammation
- Ocular endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation is attenuated by supplementation with muscadine grape polyphenols in vitro and in vivo (1045.2)
- Abstract P3052: A Muscadine Grape Extract Improves Hypertension-Induced Aortic Damage in Conjunction With a Reduction in Fibrosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation
- Abstract P2007: Muscadine Grape Extract Prevents Cardiac Cell Cytotoxicity Due to oxidative stress by Enhancing Mitochondrial Function
- Muscadine Grape Extract Improves Exercise Capacity and Reduces oxidative stress in Aging Transgenic (mRen2)27 Hypertensive Female Rats
Myrtillin (From Commiphora Myrrha Extract)
- Myrrh induces apoptosis and autophagy and enhances the activity of cisplatin in vitro.
- Polyphenol content influences the course of obesity disease, Aqueous extract … myrtillus L. Ericaceae, Lowering blood glucose levels (active component: myrtillin
- Most important of these is reduction of obesity by low calorie diets … The extract was given the name myrtillin (Myrtomel Squibb)
- myrtillin, soon discredited because of their … As with insulin, these drugs might find misapplication in the obese
- Myrtillin, Glucosone etc., etc. 7. Use of insulin in non -diabetic conditions … From these figures Joslin concludes that diab- etes is largely a penalty of obesity
Naringin (From Grapefruit Extract)
- Protection by Naringin and Some Other Flavonoids of Hepatocytic autophagy and Endocytosis against Inhibition by Okadaic Acid
- Naringin induces autophagy-mediated growth inhibition by downregulating the PI3K/Akt/mtor cascade via activation of MAPK pathways in AGS cancer cells
- Naringin protects against cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity through modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and DNA damage
- Naringin-sensitive protein phosphorylation pathways in the regulation of hepatocytic autophagy
- Therapeutic Potential of Naringin for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Involvement of autophagy Against oxidative stress-Induced Apoptosis in Nucleus Pulposus Cells
- Naringin Attenuates Autophagic Stress and Neuroinflammation in Kainic Acid-Treated Hippocampus In Vivo
- Naringin supplementation lowers plasma lipids and enhances erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in hypercholesterolemic subjects
- Naringin in Ganshuang Granule suppresses activation of hepatic stellate cells for anti‐fibrosis effect by inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin
- Therapeutic effects of silymarin and naringin on methotrexate‐induced nephrotoxicity in rats: Biochemical evaluation of anti‐inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and antiautophagic properties
- Naringin attenuates granule cell dispersion in the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy
- Okadaic acid-induced, naringin-sensitive phosphorylation of glycine N-methyltransferase in isolated rat hepatocytes
- A spectroscopic study of the interaction of the antioxidant naringin with bovine serum albumin
- Naringin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibiting Peroxynitrite-Mediated Mitophagy Activation
- Natural dietary compound naringin prevents azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate-induced chronic colorectal inflammation and carcinogenesis in mice
- naringin in acute … food consisting of Salacia Reticula has shown a significant lipolytic effect
- Naringin Improves Diet-Induced Cardiovascular Dysfunction and obesity in High Carbohydrate, High Fat Diet-Fed Rats
- Naringin Improves Neuronal Insulin Signaling, Brain Mitochondrial Function, and Cognitive Function in High-Fat Diet-Induced obese Mice
- Naringin Activates AMPK Resulting in Altered Expression of SREBPs, PCSK9, and LDLR To Reduce Body Weight in obese C57BL/6J Mice
- Combination effect naringin and pravastatin in lipid profile and glucose in obese rats
- Naringin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced damage in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via attenuation of inflammation, apoptosis and MAPK pathways
- [Research progress on Drynaria fortunei naringin on inflammation and bone activity].
- Protective effect of naringin against ankylosing spondylitis via ossification, inflammation and oxidative stress in mice
- Naringin regulates cholesterol homeostasis and inhibits inflammation via modulating NF-κB and ERK signaling pathways in vitro
- Natural dietary compound naringin prevents azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate-induced chronic colorectal inflammation and carcinogenesis in mice
- Naringin at a nutritional dose modulates expression of genes related to lipid metabolism and inflammation in liver of mice fed a high-fat diet
- Naringin protects acrolein-induced pulmonary injuries through modulating apoptotic signaling and inflammation signaling pathways in mice
- Naringin As Natural Fruit Product And Bitter Taste Agonist Induces Relaxation Of Airway SmoothMuscle Cells Via Intracellular Calcium Signaling
- P18. Treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures/defect in rats by naringin/hydroxyapatite/silk fibroin composite scaffolds in regulation of osteogenic differentiation, angiogenesis and inflammation
- Protective Effects of Rutin and Naringin in Testicular Ischemia-Reperfusion Induced oxidative stress in Rats
- Naringin Reduces Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis by Relieving oxidative stress
- Preconditioning L6 Muscle Cells with Naringin Ameliorates oxidative stress and Increases Glucose Uptake
- Naringin ameliorates cognitive deficits via oxidative stress, proinflammatory factors and the PPARγ signaling pathway in a type 2 diabetic rat model
- Naringin alleviates early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage by reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting apoptosis
- Naringin Reverses Hepatocyte Apoptosis and oxidative stress Associated with HIV-1 Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors-Induced Metabolic Complications
- Inhibition of the leptin-induced activation of the p38 MAPK pathway contributes to the protective effects of naringin against high glucose-induced injury in H9c2
Old Man’s Beard (Usnea barbata)
- Usnic Acid Induces Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, and Autophagy in Gastric Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo
- The Role of Autophagy in Usnic Acid-Induced Toxicity in Hepatic Cells
- The role of usnic acid-induced apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma
- 869 The lichen compound usnic acid disturbs mitochondrial function and induces autophagy in cancer cells
- Usnea barbata toxicity INTRODUCTION …Subsequently, 2,4- dinitrophenol was formulated into an anti-obesity drug
Oleanolic acid (From Olive Leaf Extract)
- Oleanolic acid induces protective autophagy in cancer cells through the JNK and mtor pathways
- Methyl 3-hydroxyimino-11-oxoolean-12-en-28-oate (HIMOXOL), a synthetic oleanolic acid derivative, induces both apoptosis and autophagy in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
- Oleanolic acid inhibits proliferation and invasiveness of Kras-transformed cells via autophagy
- SZC015, a synthetic oleanolic acid derivative, induces both apoptosis and autophagy in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- SZC017, a novel oleanolic acid derivative, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human breast cancer cells
- The dual induction of apoptosis and autophagy by SZC014, a synthetic oleanolic acid derivative, in gastric cancer cells via NF-κB pathway
- AMPK activation-dependent autophagy compromises oleanolic acid-induced cytotoxicity in human bladder cancer cells
- Induction of autophagy by an oleanolic acid derivative, SZC017, promotes ROS‐dependent apoptosis through Akt and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in human lung cancer cells
- Oleanolic acid but not ursolic acid induces cell death in HepG2 cells under starvation-induced autophagy
- Alleviation of Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Oleanolic Acid Pretreating via Reducing HMGB1 Release and Inhibiting Apoptosis and autophagy
- Oleanolic acid induces protective autophagy in cancer cells through the JNK and mtor pathways
- Oleanolic acid induced autophagic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via PI3K/Akt/mtor and ROS-dependent pathway
- Oleanolic acid induces autophagic death in human gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
- Oleanolic acid suppresses the proliferation of lung carcinoma cells by miR-122/Cyclin G1/MEF2D axis
- Oleanolic Acid Alters Multiple Cell Signaling Pathways: Implication in Cancer Prevention and Therapy
- Oleanolic acid suppresses the proliferation of human bladder cancer by Akt/mtor/S6K and ERK1/2 signaling
- Synthesis and proapoptotic activity of oleanolic acid derived amides
- ERK inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to oleanolic acid-induced apoptosis through ERK/Nrf2/ROS pathway
- Oleanolic acid induces mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis and G0/G1 phase arrest in gallbladder cancer cells
- 3-O-[N-(p-fluorobenzenesulfonyl)-carbamoyl]-oleanolic acid, a semisynthetic analog of oleanolic acid, induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells
- Caveolin-1 plays a key role in the oleanolic acid-induced apoptosis of HL-60 cells
- Oleanolic acid, a natural triterpenoid improves blood glucose tolerance in normal mice and ameliorates visceral obesity in mice fed a high-fat diet
- Oleanolic acid improves diet-induced obesity by modulating fat preference and inflammation in mice
- The therapeutic effects of an oleanolic acid derivative in diet induced obesity
- 2030-P: BS-016, a Novel Oleanolic Acid Derivative, Exerts Antidiabetic and Anti-obesity Effects in Preclinical Studies
- Pomace Olive Oil Enriched In Oleanolic Acid Improves Diet-Induced obesity And Exerts Protective Effects In Vascular Dysfunction And Metabolic Parameters
- [Oleanolic acid-stimulated lipolysis in primary adipocytes and its mechanisms].
- Inhibition of mtor signaling by oleanolic acid contributes to its anti‐tumor activity in osteosarcoma cells†
- Oleanolic acid suppresses the proliferation of human bladder cancer by Akt/mtor/S6K and ERK1/2 signaling
- Oleanolic acid induced autophagic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via PI3K/Akt/mtor and ROS-dependent pathway
- Protosappanin‐A and oleanolic acid protect injured podocytes from apoptosis through inhibition of AKT‐mtor signaling
- Inhibition of mtor signaling by oleanolic acid contribute to its anti-tumor activity in osteosarcoma cells
- Oleanolic acid and N-acetylcysteine ameliorate diabetic nephropathy through reduction of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in a type 2 diabetic rat model
- Identification of a novel oxidative stress induced cell death by Sorafenib and oleanolic acid in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- Protective effects of oleanolic acid on oxidative stress and the expression of cytokines and collagen by the AKT/NF‑κB pathway in silicotic rats
- Oleanolic acid protects against oxidative stress‑induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury by activating AKT/eNOS signaling
- Oleanolic acid controls oxidative stress and expression of the anti-inflammatory protein netrin-1 to protect against autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- Effect of Oleanolic Acid on Complement in Adjuvant‐ and Carrageenan‐induced inflammation in Rats
- Anti-inflammatory Effects of Oleanolic Acid on LPS-Induced inflammation In Vitro and In Vivo
- Antioxidant inflammation modulators: oleanolic acid derivatives with saturation in the C-ring
- Antioxidant inflammation modulators: C-17 homologated oleanolic acid derivatives
- Antioxidant inflammation modulators: novel derivatives of oleanolic acid
- Antioxidant inflammation modulators: oleanolic acid derivatives with amino and other modifications at C-17
- Oleanolic acid suppresses ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation and Th2-mediated allergic asthma by modulating the transcription factors T-bet, GATA-3, RORγt and Foxp3 in asthmatic mice
Onjisaponin B derived (from Radix Polygalae)
Ophiopogonin B (OP-B) (From Radix Ophiopogon Japonicus)
- Ophiopogonin B-induced autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer cells via inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
- Ophiopogonin B induces apoptosis, mitotic catastrophe and autophagy in A549 cells
- [Molecular mechanism of ophiopogonin B induced cellular autophagy of human cervical cancer HeLa cells].
- Ophiopogonin B sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis through activation of autophagy flux and downregulates cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein
- Ophiopogonin B induces the autophagy and apoptosis of colon cancer cells by activating JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway
Oridonin (From Rabdosia Rubescens Extract)
- autophagy Preceded Apoptosis in Oridonin-Treated Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells
- Oridonin Induced autophagy in Human Cervical Carcinoma HeLa Cells Through Ras, JNK, and P38 Regulation
- Augmentation of Oridonin-Induced Apoptosis Observed With Reduced autophagy
- Molecular mechanisms of oridonin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells
- autophagy inhibits reactive oxygen species‐mediated apoptosis via activating p38‐nuclear factor‐kappa B survival pathways in oridonin‐treated murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells
- Apoptosis-suppressing and autophagy-promoting effects of calpain on oridonin-induced L929 cell death
- Oridonin Up-regulates Expression of P21 and Induces autophagy and Apoptosis in Human Prostate Cancer Cells
- Reactive oxygen species contribute to oridonin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells
- NF-κb facilitates oridonin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in HT1080 cells through a p53-mediated pathway
- Involvement of PKC signal pathways in oridonin-induced autophagy in HeLa cells: A protective mechanism against apoptosis
- Oridonin: An active diterpenoid targeting cell cycle arrest, apoptotic and autophagic pathways for cancer therapeutics
- autophagy counteracts apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cells exposed to oridonin in vitro via regulating intracellular ROS and SIRT1
- Oridonin phosphate-induced autophagy effectively enhances cell apoptosis of human breast cancer cells
- Inactivation of Ras and Changes of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Contribute to Oridonin-Induced autophagy in A431 Cells
- Inhibition of c‐Met promoted apoptosis, autophagy and loss of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential in oridonin‐induced A549 lung cancer cells
- autophagy enhanced phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by oridonin-treated human histocytic lymphoma U937 cells
- Oridonin: targeting programmed cell death pathways as an anti‐tumour agent
- Study on the autophagy of Prostate Cancer PC‐3 Cells Induced by Oridonin
- Oridonin induces autophagy via inhibition of glucose metabolism in p53-mutated colorectal cancer cells
- Nitric oxide augments oridonin-induced efferocytosis by human histocytic lymphoma U937 cells via autophagy and the NF-κB-COX-2-IL-1β pathway
- Synergistic anticancer effects of combined γ-tocotrienol and oridonin treatment is associated with the induction of autophagy
- Hydroxyl Radical (·OH) Played a Pivotal Role in Oridonin-Induced Apoptosis and autophagy in Human Epidermoid Carcinoma A431 Cells
- Recent advances in the molecular basis of anti-neoplastic mechanisms of oridonin
- Oridonin induces apoptosis and autophagy in murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells partly via NO-ERK-p53 positive-feedback loop signaling pathway
- Molecular Insight in the Multifunctional Effects of Oridonin
- Oridonin induces apoptosis in gastric cancer through Apaf-1, cytochrome c and caspase-3 signaling pathway
- [Mechanism of downregulation of apoptosis by autophagy induced by oridonin in HeLa cells].
- Downregulation of Cdk1 and CyclinB1 Expression Contributes to Oridonin-induced Cell Cycle Arrest at G2/M Phase and Growth Inhibition in SGC-7901 Gastric Cancer Cells
- Inhibition of caspase-9 by oridonin, a diterpenoid isolated from Rabdosia rubescens, augments apoptosis in human laryngeal cancer cells
- Reactive oxygen species H2O2 and OH, but not O2− promote oridonin-induced phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by human histocytic lymphoma U937 cells
- Oridonin in combination with imatinib exerts synergetic anti-leukemia effect in Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells in vitro by inhibiting activation of LYN/mtor signaling pathway
- Oridonin Suppresses Proliferation of Human Ovarian Cancer Cells via Blockage of mtor Signaling.
- Synergistic effect of oridonin and a PI3K/mtor inhibitor on the non-germinal center B cell-like subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Oridonin‐induced mitochondria‐dependent apoptosis in esophageal cancer cells by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mtor and Ras/Raf pathways
- Oridonin inhibits metastasis of human ovarian cancer cells by suppressing the mtor pathway
- Oridonin Sensitizes Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis via AMPK/Akt/mtor-Dependent Autophagosome Accumulation in A549 Cells
- Inhibition of EGFR signaling augments oridonin-induced apoptosis in human laryngeal cancer cells via enhancing oxidative stress coincident with activation of both the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways
- Effects of Oridonin on growth performance and oxidative stress in broilers challenged with lipopolysaccharide
- The tyrphostin AG1478 augments oridonin-induced A431 cell apoptosis by blockage of JNK MAPK and enhancement of oxidative stress
- Proteomic and functional analyses demonstrate the involvement of oxidative stress in the anticancer activities of oridonin in HepG2 cells
- Oridonin protects LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulating Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress and Nrf2-independent NLRP3 and NF-κB pathways
- Oridonin inhibits vascular inflammation by blocking NF-κB and MAPK activation
- Oridonin inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in human gingival fibroblasts by activating PPARγ
- Oridonin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes by activating PPAR-γ
Paclitaxel (from pacific yew tree)
- autophagy inhibition promotes paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in cancer cells
- The chemotherapeutic agent paclitaxel inhibits autophagy through two distinct mechanisms that regulate apoptosis
- Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in the regulation of paclitaxel-induced cell death in v-Ha-ras-transformed fibroblasts
- autophagy promotes paclitaxel resistance of cervical cancer cells: involvement of Warburg effect activated hypoxia-induced factor 1-α-mediated signaling
- The Stent-Eluting Drugs Sirolimus and Paclitaxel Suppress Healing of the Endothelium by Induction of autophagy
- Re-expression of ARHI (DIRAS3) induces autophagy in breast cancer cells and enhances the inhibitory effect of paclitaxel
- TXNDC17 promotes paclitaxel resistance via inducing autophagy in ovarian cancer
- Autophagy is the dominant type of programmed cell death in breast cancer MCF-7 cells exposed to AGS 115 and EFDAC, new sesquiterpene analogs of paclitaxel.
- Inhibition of autophagy enhances the effects of the AKT inhibitor MK‐2206 when combined with paclitaxel and carboplatin in BRAF wild‐type melanoma
- miR-16 targets Bcl-2 in paclitaxel-resistant lung cancer cells and overexpression of miR-16 along with miR-17 causes unprecedented sensitivity by simultaneously modulating autophagy and apoptosis
- Paclitaxel resistance is associated with switch from apoptotic to autophagic cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Differential Expression of autophagy in Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells Treated with Various Anti-Cancer Drug
- autophagy regulates resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells to paclitaxel
- Blockade of autophagy Aggravates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Improves Paclitaxel Cytotoxicity in Human Cervical Cancer Cells
- Suppression of autophagy enhances preferential toxicity of paclitaxel to folliculin-deficient renal cancer cells
- A novel C,D-spirolactone analogue of paclitaxel: autophagy instead of apoptosis as a previously unknown mechanism of cytotoxic action for taxoids
- autophagy inhibition re-sensitizes pulse stimulation-selected paclitaxel-resistant triple negative breast cancer cells to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis
- Cytoprotective role of autophagy during paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells
- Effect of autophagy inhibition on chemotherapy‑induced apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells
- Glucosylceramide Synthase Protects Glioblastoma Cells Against Autophagic and Apoptotic Death Induced by Temozolomide and Paclitaxel
- autophagy inhibition enhances sensitivity of endometrial carcinoma cells to paclitaxel
- Paclitaxel and the dietary flavonoid fisetin: a synergistic combination that induces mitotic catastrophe and autophagic cell death in A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells
- miR-17-5p Downregulation Contributes to Paclitaxel Resistance of Lung Cancer Cells through Altering Beclin1 Expression
- Effect of autophagy on paclitaxel-induced CaSki cell death.
- Regulation of paclitaxel-induced programmed cell death by autophagic induction: A model for cervical cancer
- Combination of Cl-IB-MECA with paclitaxel is a highly effective cytotoxic therapy causing mtor-dependent autophagy and mitotic catastrophe on human melanoma cells
- Inhibition of REDD1 Sensitizes Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma to Paclitaxel by Inhibiting autophagy
- Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor RAD001 sensitizes endometrial cancer cells to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis via the induction of autophagy
- Sensitization of breast cancer cells to paclitaxel by dichloroacetate through inhibiting autophagy
- Toxicity and Prognosis in Overweight and obese Women With Lung Cancer Receiving Carboplatin-Paclitaxel Doublet Chemotherapy
- 5PSQ-063 More risk of neutropaenia in obese patients treated with paclitaxel?
- Less myelotoxicity in obese patients with weekly paclitaxel in localized breast cáncer
- Safety and pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel and the oral mtor inhibitor everolimus in advanced solid tumours
- Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) by rapamycin increases chemosensitivity of CaSki cells to paclitaxel
- Colocalized Delivery of Rapamycin and Paclitaxel to Tumors Enhances Synergistic Targeting of the PI3K/Akt/mtor Pathway
- Micro RNA 100 sensitizes luminal A breast cancer cells to paclitaxel treatment in part by targeting mtor
- The dual PI3K/mtor inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 enhances nab-paclitaxel antitumor response in experimental gastric cancer
- Significant response after treatment with the mtor inhibitor sirolimus in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in metastatic melanoma patients
- Synergistic inhibition of colon cancer cell growth with nanoemulsion-loaded paclitaxel and PI3K/mtor dual inhibitor BEZ235 through apoptosis
- Differential Healing After Sirolimus, Paclitaxel, and Bare Metal Stent Placement in Combination With Peroxisome Proliferator-Activator Receptor γ Agonists
- A Phase Ib Trial of RAD001, an mtor Inhibitor, with Weekly Cisplatin and Paclitaxel in Patients with HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer.
- Dual PI3K/mtor inhibitor BEZ235 as a promising therapeutic strategy against paclitaxel-resistant gastric cancer via targeting PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway
- Differential Response of Delayed Healing and Persistent inflammation at Sites of Overlapping Sirolimus- or Paclitaxel-Eluting Stents
- Antitumor Effect of Paclitaxel Is Mediated by Inhibition of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Chronic inflammation in the Spontaneous Melanoma Model
- Endothelium-Dependent Vasomotor Dysfunction in Pig Coronary Arteries With Paclitaxel-Eluting Stents Is Associated With inflammation and oxidative stress
- Tumor suppression via paclitaxel-loaded drug carriers that target inflammation marker upregulated in tumor vasculature and macrophages
- Paclitaxel-induced Arterial Wall Toxicity and inflammation: Part 2—Long-term Tissue Response in a Minipig Model
- Paclitaxel-induced Arterial Wall Toxicity and inflammation: Tissue Uptake in Various Dose Densities in a Minipig Model
- Paclitaxel Coating Inhibits inflammation Surrounding Subcutaneously Implanted Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) Hemodialysis Grafts in Rabbit Model
- inflammation of actinic keratoses during paclitaxel chemotherapy
- Paclitaxel Coating Inhibits inflammation Around theSubcutaneously Transplanted Expanded PolytetrafluoroethyleneHemodialysis Graft in Rabbit Model
- Involvement of oxidative stress and caspase activation in paclitaxel-induced apoptosis of primary effusion lymphoma cells
- Paclitaxel combined with inhibitors of glucose and hydroperoxide metabolism enhances breast cancer cell killing via H2O2-mediated oxidative stress
- oxidative stress in the development, maintenance and resolution of paclitaxel-induced painful neuropathy
- oxidative stress induced in rat liver by anticancer drugs doxorubicin, paclitaxel and docetaxel
- Systemic toxicity induced by paclitaxel in vivo is associated with the solvent cremophor EL through oxidative stress-driven mechanisms
- Co-encapsulation of paclitaxel and baicalein in nanoemulsions to overcome multidrug resistance via oxidative stress augmentation and P-glycoprotein inhibition
- Paclitaxel-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Living Rats Is Prevented by Nicorandil via Reduction of oxidative stress
- MiR-4673 Modulates Paclitaxel-Induced oxidative stress and Loss of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential by Targeting 8-Oxoguanine-DNA Glycosylase-1
- Modified Panax ginseng extract regulates autophagy by AMPK signaling in A549 human lung cancer cells
- Increase in apoptotic effect of Panax ginseng by microwave processing in human prostate cancer cells: in vitro and in vivo studies
- Protective effects of Panax ginseng on muscle injury and inflammation after eccentric exercise
- Saponins from stems and leaves of Panax ginseng prevent obesity via regulating thermogenesis, lipogenesis and lipolysis in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice
- Effect of ginsam, a vinegar extract from Panax ginseng, on body weight and glucose homeostasis in an obese insulin-resistant rat model
- Influence of Panax ginseng on obesity and gut microbiota in obese middle-aged Korean women
- Panax ginseng Leaf Extracts Exert Anti-obesity Effects in High-Fat Diet-Induced obese Rats
- Anti-obese Function of Polysaccharides derived from Korean Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) and Development of Functional Food Material in Preventing obesity
- Antiobesity Effects of Panax Ginseng Supercitical Fluid Extract in High-Fat Diet Fed obese Mice
- Anti-obesity Effect of Carbon Dioxide Supercritical Fluid Extracts of Panax Ginseng C. A. Meyer
- Effects of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) on obesity and adipose inflammation in ovariectomized mice
- Anti-obesity effects of protopanaxdiol types of Ginsenosides isolated from the leaves of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) in mice fed with a high-fat diet
- Panax notoginsenoside saponins Rb1 regulates the expressions of Akt/ mtor/PTEN signals in the hippocampus after focal cerebral ischemia in rats
- Effects of Panax notoginseng saponins on severe acute pancreatitis through the regulation of mtor/Akt and caspase-3 signaling pathway by upregulating miR-181b expression in rats
- Panax notoginseng saponins promote liver regeneration through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mtor cell proliferation pathway and upregulation of the AKT/Bad cell survival pathway in mice
- Panax ginseng reduces oxidative stress and restores antioxidant capacity in aged rats
- Implications of red Panax ginseng in oxidative stress associated chronic diseases
- Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer extract counteracts the oxidative stress in rats fed multi-mycotoxins-contaminated diet
- Influence of fluoride on streptozotocin induced diabetic nephrotoxicity in mice: Protective role of Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng) & banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa) on mitochondrial oxidative stress
- Panax ginseng Meyer prevents radiation-induced liver injury via modulation of oxidative stress and apoptosis
- Modulation of Radiation‐Induced Alterations in oxidative stress and Cytokine Expression in Lung Tissue by Panax Ginseng Extract
- Ethyl acetate extract from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer and its main constituents inhibit α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanogenesis by suppressing oxidative stress in B16 mouse melanoma cells
- Effects of Panax ginseng on Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Mediated inflammation: A Mini-Review
- Effects of Panax ginseng Supplementation on Muscle Damage and inflammation after Uphill Treadmill Running in Humans
- Panax ginseng ameliorates airway inflammation in an ovalbumin-sensitized mouse allergic asthma model
- Panax ginseng aqueous extract prevents pneumococcal sepsis in vivo by potentiating cell survival and diminishing inflammation
- Prevention of bone loss by Panax ginseng in a rat model of inflammation-induced bone loss.
- Effects Of Panax Ginseng Supplementation On Muscle Damage And inflammation After Treadmill Running In Humans: 1790Board #323 June 1 3:30 PM – 5:00 PM
- Anti-inflammation Effect of Small Molecule Oligopeptides Prepared from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer in Rats
- Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) Oligopeptides Protect Against Binge Drinking-Induced Liver Damage through Inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation in Rats
- Parthenolide generates reactive oxygen species and autophagy in MDA-MB231 cells. A soluble parthenolide analogue inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in a xenograft model of breast cancer
- Parthenolide induces apoptosis and autophagy through the suppression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in cervical cancer
- Parthenolide-induced apoptosis, autophagy and suppression of proliferation in HepG2 cells.
- Inhibition of AMPK/autophagy Potentiates Parthenolide‐Induced Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells
- Parthenolide induces autophagy via the depletion of 4E-BP1
- Parthenolide suppresses pancreatic cell growth by autophagy-mediated apoptosis
- Parthenolide Inhibits the Proliferation of MDA-T32 Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells in Vitro and in Mouse Tumor Xenografts and Activates autophagy and Apoptosis by Downregulation of the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mtor)/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
- Anti-Proliferiative Effect of Parthenolide on G2/M arrest and autophagy in Huaman Malignant Glioblastoma Cell Lines
- Parthenolide Induces Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Autophagic Cell Death in Human Osteosarcoma Cells
- Cell death in amastigote forms of Leishmania amazonensis induced by parthenolide
- The Synergistic Effect of SAHA and Parthenolide in MDA‐MB231 Breast Cancer Cells
- Parthenolide induces caspase‐independent and AIF‐mediated cell death in human osteosarcoma and melanoma cells
- Targeting Thioredoxin Reductase by Parthenolide Contributes to Inducing Apoptosis of HeLa Cells
- Induction of apoptosis by parthenolide in human oral cancer cell lines and tumor xenografts
- Chapter 9 – Parthenolide and Parthenolide-Like Sesquiterpene Lactones as Multiple Targets Drugs: Current Knowledge and New Developments
- Parthenolide induces superoxide anion production by stimulating EGF receptor in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
- Parthenolide ameliorates Concanavalin A-induced acute hepatitis in mice and modulates the macrophages to an anti-inflammatory state
- The oxygen radicals involved in the toxicity induced by parthenolide in MDA-MB-231 cells
- Abstract 609: Pharmacological Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome by Parthenolide Improves obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance in Diet-Induced obese Mice
- Parthenolide Reverses obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance
- Parthenolide, a feverfew-derived phytochemical, ameliorates obesity and obesity-induced inflammatory responses via the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway
- Pharmaceutical Composition Containing Bay 11-7082, Parthenolide or Dimethylfumarate or a Combination Thereof for the Treatment of obesity or Cardiovascular Diseases
- Novel mtor inhibitory activity of ciclopirox enhances parthenolide antileukemia activity
- Sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide attenuates production of inflammatory mediators by suppressing the Toll-like receptor-4-mediated activation of the Akt, mtor, and NF-κB pathways
- Chemical Genomic Screening Reveals That PI3K/mtor Inhibition Enhances Activity of the Anti-Leukemia Stem Cell Compound Parthenolide.
- Parthenolide Inhibits the Proliferation of MDA-T32 Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells in Vitro and in Mouse Tumor Xenografts and Activates Autophagy and Apoptosis by Downregulation of the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mtor)/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
- Parthenolide attenuates LPS-induced fever, circulating cytokines and markers of brain inflammation in rats
- Sesquiterpene Lactone Parthenolide Ameliorates Bladder inflammation and Bladder Overactivity in Cyclophosphamide Induced Rat Cystitis Model by Inhibiting Nuclear Factor-κB Phosphorylation
- Co-administration of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) congener with parthenolide for treating inflammation
- Mitigation of monocyte inflammation by inhibition of sodium phosphate co-transporter with phosphonoformic acid and parthenolide in diabetic nephropathy uremia
- Systemic parthenolide treatment attenuates LPS-induced fever, circulating cytokines and markers of brain inflammation in rats
- PARTHENOLIDE AMELIORATES BLADDER inflammation AND BLADDER OVERACTIVITY IN CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE-INDUCED CYSTITIS IN RATS BY INHIBITING NF-κB PHOSPHORYLATION
- Sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide amelioratesbladder inflammation and bladder overactivity incyclophosphamide-induced rat cystitis model byinhibiting NF-κB phosphorylation
- oxidative stress-mediated Apoptosis THE ANTICANCER EFFECT OF THE SESQUITERPENE LACTONE PARTHENOLIDE
- Evidence that IL‐6‐type cytokine signaling in cardiomyocytes is inhibited by oxidative stress: Parthenolide targets JAK1 activation by generating ROS
- Parthenolide protects human lens epithelial cells from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via inhibition of activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9
- Parthenolide and DMAPT exert cytotoxic effects on breast cancer stem-like cells by inducing oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and necrosis
- Parthenolide induces a distinct pattern of oxidative stress in cardiac myocytes
- Parthenolide-Induced Cytotoxicity in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts Involves oxidative stress
- Crucial role of oxidative stress in bactericidal effect of parthenolide against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae
- Parthenolide regulates oxidative stress‐induced mitophagy and suppresses apoptosis through p53 signaling pathway in C2C12 myoblasts
- Parthenolide induces caspase-independent cell death in osteosarcoma, melanoma and breast cancer cells through the induction of oxidative stress.
- Phellinus Linteus Extract Induces autophagy and Synergizes With 5-Fluorouracil to Inhibit Breast Cancer Cell Growth
- The ethanolic extract of Phellinus linteus inhibits breast cancer cell growth through autophagy-related cell death
- Phellinus linteus Mycelium Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through Autophagic Regulation
- Activation of P27kip1-cyclin D1/E-CDK2 pathway by polysaccharide from Phellinus linteus leads to S-phase arrest in HT-29 cells
- Anticancer Effect of Phellinus linteus; Potential Clinical Application in Treating Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- A Review: The Bioactivities and Pharmacological Applications of Phellinus linteus
- Evaluation of antidiabetic activity of polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus linteus in non-obese diabetic mouse
- Protective effects of Phellinus linteus extract against Iron overload‐mediated oxidative stress in cultured rat hepatocytes
- Phellinus linteus mushroom protects against tacrine-induced mitochondrial impairment and oxidative stress in HepG2 cells
- Protective Effects of Phellinus linteus and Curry-Added Cooked Mixed Grain Rice Extracts on oxidative stress-Induced LLC-PK1 Cell Damage
- Investigations of antioxidative activity against oxidative stress induced by H2O2 in PC-12 neuronal cells from enzymatic hydrolysates of Phellinus linteus
- An Extract of Phellinus linteus Grown on Germinated Brown Rice Inhibits inflammation Markers in RAW264.7 Macrophages by Suppressing Inflammatory Cytokines, Chemokines, and Mediators and Up-Regulating Antioxidant Activity
- Effects of Fermented Rice Wine by Using Mycelium of Phellinus linteus on the Expression of inflammation-Related Proteins in Human Hepatoma Cells and Rat Liver
- Effects of Traditional Wine by using Mycelium of Phellinus linteus on the Expression of inflammation-Related Proteins in Rat Liver
- Effects of Fermented Traditional Wine by using Mycelium of Phellinus linteus on the Expression of inflammation-Related Proteins in HepG2 cells
- Effects of Fermented Liquor by using Phellinus linteus on the Expression of inflammation-Related Proteins in Human Hepatoma Cell and in Rat Liver
Pimenta dioica berries (Allspice)
- Abstract P3-03-03: Phenolic compounds from pimenta dioica berries (allspice) inhibit breast cancer cell proliferation by autophagy induction
- Abstract 5589: An aqueous extract of Allspice (berries of Pimenta dioica) inhibits breast cancer growth through autophagy by targeting the estrogen receptor
- Polyphenol-rich extract of Pimenta dioica berries (Allspice) kills breast cancer cells by autophagy and delays growth of triple negative breast cancer in athymic mice
- Medicinal Properties of the Jamaican Pepper Plant Pimenta dioica and Allspice
- Abstract 576: Novel compounds from Allspice (Pimenta dioica) inhibit breast cancer growth by autophagy induction
Piperine (From Black Pepper Extract)
- Piperine inhibits the proliferation of human prostate cancer cells via induction of cell cycle arrest and autophagy
- Piperine induces autophagy by enhancing protein phosphotase 2A activity in a rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease model
- Enhancement of paclitaxel and doxorubicin cytotoxicity in breast cancer cell lines in combination with piperine treatment and analysis of expression of autophagy and apoptosis genes
- Cancer Chemoprevention and Piperine: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities
- Piperine Enhances the Efficacy of TRAIL-based Therapy for Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells
- Piperine: Bioactivities and Structural Modifications
- Protection effect of piperine and piperlonguminine from Piper longum L. alkaloids against rotenone-induced neuronal injury
- Chapter 13 – Role of Piperine in Chemoresistance
- Piperine as a Potential Anti-cancer Agent: A Review on Preclinical Studies
- Curcumin–Piperine/Curcumin–Quercetin/Curcumin–Silibinin dual drug-loaded nanoparticulate combination therapy: A novel approach to target and treat multidrug-resistant cancers
- Piperine (PP) enhanced mitomycin-C (MMC) therapy of human cervical cancer through suppressing Bcl-2 signaling pathway via inactivating STAT3/NF-κB
- Combating breast cancer using combination therapy with 3 phytochemicals: Piperine, sulforaphane, and thymoquinone
- Piperine depresses the migration progression via downregulating the Akt/mtor/MMP‑9 signaling pathway in DU145 cells
- Piperine: role in prevention and progression of cancer
- Piperine Suppresses the Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis in HER2-overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells through the Inhibition of FAS Expression
- Piperine attenuates the cancerous activity response in Neuro-2a cell line.
- Potential of piperine in modulation of voltage-gated K+ current and its influences on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
- Piperine inhibits IL-1β-induced IL-6 expression by suppressing p38 MAPK and STAT3 activation in gastric cancer cells
- Piperine Suppresses the Expression of CXCL8 in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated SW480 and HT-29 Cells via Downregulating the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways
- Protective effects of piperine against copper-ascorbate induced toxic injury to goat cardiac mitochondria in vitro
- glucose intolerance, and oxidative stress in high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by combination consisting of “curcumin with piperine
- Effect of piperine in the regulation of obesity-induced dyslipidemia in high-fat diet rats
- Mitigating efficacy of piperine in the physiological derangements of high fat diet induced obesity in Sprague Dawley rats
- Effect of piperine in obesity induced insulin resistance and type-II diabetes mellitus in rats.
- Curcumin and piperine supplementation of obese mice under caloric restriction modulates body fat and interleukin-1β
- The effect of curcumin plus piperine on body weight and fat loss as well as on the plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines in obese mice
- Caloric restriction favorably impacts metabolic and immune/inflammatory profiles in obese mice but curcumin/piperine consumption adds no further benefit
- Piperine depresses the migration progression via downregulating the Akt/mtor/MMP‑9 signaling pathway in DU145 cells
- Piperine Triggers Apoptosis of Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma Through Cell Cycle Arrest and Mitochondrial oxidative stress
- Piperine inhibits aflatoxin B1 production in Aspergillus flavus by modulating fungal oxidative stress response
- Anticonvulsant effect of piperine ameliorates memory impairment, inflammation and oxidative stress in a rat model of pilocarpine-induced epilepsy
- oxidative stress is decreased with short-term Protandim use when piperine is substituted for ashwagandha (LB399)
- Protective effect of piperine in ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury through inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress
- Potential anti-inflammatory action of resveratrol and piperine in adjuvant-induced arthritis: Effect on pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress biomarkers
- Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by piperine during experimental inflammation in rats.
- A Role of Piperine on Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced inflammation—An Experimental Model of Gouty Arthritis
- Effect of piperine on inhibition of FFA induced TLR4 mediated inflammation and amelioration of acetic acid induced ulcerative colitis in mice
- Piperine inhibit inflammation, alveolar bone loss and collagen fibers breakdown in a rat periodontitis model
- Induction of nociceptive stimulus in TMJ region : minimum effective concentration of piperine in normality, local chronic inflammation and chronic stress conditions
- A Role of Piperine on Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced inflammation—An Experimental Model of Gouty Arthritis
- Effect of piperine on inhibition of FFA induced TLR4 mediated inflammation and amelioration of acetic acid induced ulcerative colitis in mice
- Piperine suppresses cerebral ischemia–reperfusion-induced inflammation through the repression of COX-2, NOS-2, and NF-κB in middle cerebral artery occlusion rat model
- Piperine inhibit inflammation, alveolar bone loss and collagen fibers breakdown in a rat periodontitis model
- Quercetin along with piperine prevents cognitive dysfunction, oxidative stress and neuro-inflammation associated with mouse model of chronic unpredictable stress
- Anticonvulsant effect of piperine ameliorates memory impairment, inflammation and oxidative stress in a rat model of pilocarpine-induced epilepsy
Piperlongumine (PL), (from fruit of Long pepper / Piper longum)
- Piperlongumine induces autophagy by targeting p38 signaling
- Piperlongumine promotes autophagy via inhibition of Akt/mtor signalling and mediates cancer cell death
- Piperlongumine induces apoptosis and autophagy in human lung cancer cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway
- Piperlongumine restores the balance of autophagy and apoptosis by increasing BCL2 phosphorylation in rotenone-induced Parkinson disease models
- Piperlongumine induces apoptosis and autophagy in leukemic cells through targeting the PI3K/Akt/mtor and p38 signaling pathways
- Development and mechanism investigation of a new piperlongumine derivative as a potent anti-inflammatory agent
- Piperlongumine induces rapid depletion of the androgen receptor in human prostate cancer cells
- Redox-directed cancer therapeutics: Taurolidine and Piperlongumine as broadly effective antineoplastic agents (Review)
- Historical Spice as a Future Drug: Therapeutic Potential of Piperlongumine
- Piperlongumine induces apoptotic and autophagic death of the primary myeloid leukemia cells from patients via activation of ROS-p38/JNK pathways
- Piperlongumine as a potential activator of AMP-activated protein kinase in HepG2 cells
- Piperlongumine (piplartine) and analogues: Antiproliferative microtubule-destabilising agents
- Piperlongumine and immune cytokine TRAIL synergize to promote tumor death
- JNK signaling pathway is involved in piperlongumine‑mediated apoptosis in human colorectal cancer HCT116 cells
- Piperlongumine induces apoptosis and reduces bortezomib resistance by inhibiting STAT3 in multiple myeloma cells
- Piperlongumine is a novel nuclear export inhibitor with potent anticancer activity
- Piperlongumine reverses doxorubicin resistance through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in K562/A02 human leukemia cells
- Hypoxia potentiates the cytotoxic effect of piperlongumine in pheochromocytoma models
- Transcriptome Analysis of Piperlongumine-Treated Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells Reveals Involvement of oxidative stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathways
- Piperlongumine Inhibits Migration of Glioblastoma Cells via Activation of ROS-Dependent p38 and JNK Signaling Pathways
- Piperlongumine, an alkaloid causes inhibition of PI3 K/Akt/mtor signaling axis to induce caspase-dependent apoptosis in human triple-negative breast cancer cells
- P1 Piperlongumine inhibits growth potential of gastric cancer cells by targeting PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway
- Piperlongumine, a piper alkaloid targets Ras/PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling axis to inhibit tumor cell growth and proliferation in DMH/DSS induced experimental colon cancer
- Piperlongumine reduces ovalbumin‑induced asthma and airway inflammation by regulating nuclear factor‑κB activation
- Transcriptome Analysis of Piperlongumine-Treated Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells Reveals Involvement of oxidative stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathways
- The synergistic effects of oxaliplatin and piperlongumine on colorectal cancer are mediated by oxidative stress
- Hexane fraction of Pluchea indica root extract inhibits proliferation and induces autophagy in human glioblastoma cells
- Simultaneous HPTLC quantification of three caffeoylquinic acids in Pluchea indica leaves and their commercial products in Thailand
- Uji Sitotoksik Ekstrak Etanol Daun dan Akar Beluntas (Pluchea indica (L.)) terhadap Sel Kanker Kolon Widr
- The effect of Indian marsh fleabane (Pluchea indica (L.) Less) dried leaves extract against oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Plumbagin ( from Plumbago zeylanica L, Juglans regia, J. cinerea, and J. nigra )
- Plumbagin induces G2-M arrest and autophagy by inhibiting the AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in breast cancer cells
- Induction of apoptosis and autophagy via sirtuin1- and PI3K/Akt/mtor-mediated pathways by plumbagin in human prostate cancer cells
- Plumbagin induces G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38 MAPK- and PI3K/Akt/mtor-mediated pathways in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells
- Plumbagin induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy and suppresses epithelial to mesenchymal transition involving PI3K/Akt/mtor-mediated pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells
- Plumbagin elicits differential proteomic responses mainly involving cell cycle, apoptosis, autophagy, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition pathways in human prostate cancer PC-3 and DU145 cells
- Plumbagin induces autophagy and apoptosis of SMMC‐7721 cells in vitro and in vivo
- Plumbagin‐induced apoptosis of human breast cancer cells is mediated by inactivation of NF‐κB and Bcl‐2
- Anticancer Properties and Pharmaceutical Applications of Plumbagin: A Review
- Plumbagin attenuates cancer cell growth and osteoclast formation in the bone microenvironment of mice
- Plumbagin and Its Role in Chronic Diseases
- Suppressive Effects of Plumbagin on Invasion and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells via the Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling and Down-regulation of Inflammatory Cytokine Expressions
- Plumbagin Induces Apoptosis in Her2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells through the Mitochondrial-Mediated Pathway
- Plumbagin reduces obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by fructose in rats through regulation of lipid metabolism, inflammation and oxidative stress
- Plumbagin inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt-mtor pathway
- Plumbagin induces RPE cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via p38 MARK and PI3K/AKT/mtor signaling pathways in PVR
- Plumbagin inhibits LPS-induced inflammation through the inactivation of the nuclear factor-kappa B and mitogen activated protein kinase signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells
- Treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with plumbagin alleviates spinal cord injury by affecting oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptotis and the activation of the Nrf2 pathway
- Plumbagin protects liver against fulminant hepatic failure and chronic liver fibrosis via inhibiting inflammation and collagen production
- Plumbagin ameliorates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: Role of high mobility group box 1 in inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis
- Plumbagin inhibits neuronal apoptosis, intimal hyperplasia and also suppresses TNF-α/NF-κB pathway induced inflammation and matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 expression in rat cerebral ischemia
- Plumbagin, a vitamin K3 analogue ameliorate malaria pathogenesis by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation
- oxidative stress via inhibition of the mitochondrial electron transport and Nrf-2-mediated anti-oxidative response regulate the cytotoxic activity of plumbagin
- Plumbagin inhibits amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity regulation of oxidative stress and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 activation
- Abstract 891: Plumbagin and atovaquone inhibit Na+/K+-ATPase through the generation of oxidative stress
- Plumbagin Inhibits leptin-Induced Proliferation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via JAK2-STAT3 Pathway to Protect against Hepatic Fibrosis
- [Effects of plumbagin on expression of TNF-alpha and PDGF-BB in human hepatic stellate cells activated by leptin].
- Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human melanoma A375 cells through a mitochondria-mediated ROS–p38–p53 pathway
- Molecular mechanisms of Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells
- Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces murine fibrosarcoma L929 cell apoptosis and autophagy via blocking Ras–Raf and PI3K–Akt signaling pathways
- Role of reactive oxygen species-mediated MAPK and NF-κB activation in polygonatum cyrtonema lectin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells
- Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin, a potential antineoplastic drug targeting programmed cell death pathways
- Polygonatum odoratum lectin induces apoptosis and autophagy via targeting EGFR-mediated Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Molecular Switch Role of Akt in Polygonatum odoratum Lectin-Induced Apoptosis and autophagy in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cells
- Induction of apoptosis by Polygonatum odoratum lectin and its molecular mechanisms in murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells
- Polygonatum odoratum lectin induces apoptosis and autophagy by regulation of microRNA-1290 and microRNA-15a-3p in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells
- Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces murine fibrosarcoma L929 cell apoptosis via a caspase-dependent pathway as compared to Ophiopogon japonicus lectin
- In vitro plantlet regeneration system from rhizomes and mannose-binding lectin analysis of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua.
- Pharmacological and phytochemical updates of genus Polygonatum
- Polygonatum odoratum lectin promotes BECN1 expression and induces autophagy in malignant melanoma by regulation of miR1290
- Bioinformatics analyses of the mannose-binding lectins from Polygonatum cyrtonema, Ophiopogon japonicus and Liparis noversa with antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing activities
- Chemical Constituents of the Genus Polygonatum and their Role in Medicinal Treatment
- Effect of Polygonatum odoratum extract on human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation and apoptosis
- A REVIEW ON PLANTS OF GENUS POLYGONATUM
- Effects of Polygonatum sibiricum rhizome extract on lipid and energy metabolism in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
- Anti-obesity Effects of Ethanolic Extract of Polygonatum sibiricum Rhizome in High-fat Diet-fed Mice
- Polygonatum stenophyllum improves menopausal obesity via regulation of lipolysis-related enzymes
- Polygonatum odoratum Polysaccharides Modulate Gut Microbiota and Mitigate Experimentally Induced obesity in Rats
- Effects of ethanol extract of Polygonatum sibiricum rhizome on obesity-related genes
- Polygonatum stenophyllum improves menopausal obesity via regulation of lipolysis-related enzymes
Quercetin (Sophora Japonica Extract)
- Quercetin induces protective autophagy in gastric cancer cells: Involvement of Akt-mtor– and hypoxia-induced factor 1α-mediated signaling
- Ameliorative Effect of Quercetin on Neurochemical and Behavioral Deficits in Rotenone Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease: Modulating autophagy (Quercetin on Experimental Parkinson’s Disease)
- Quercetin Induces Mitochondrial Mediated Apoptosis and Protective autophagy in Human Glioblastoma U373MG Cells
- Quercetin mediates preferential degradation of oncogenic Ras and causes autophagy in Ha- RAS -transformed human colon cells
- Quercetin alleviates high glucose-induced Schwann cell damage by autophagy
- Quercetin attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via an activation of AMP-activated protein kinase-regulated autophagy pathway
- MicroRNA-143 enhances chemosensitivity of Quercetin through autophagy inhibition via target GABARAPL1 in gastric cancer cells
- Quercetin induces apoptosis and autophagy in primary effusion lymphoma cells by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mtor and STAT3 signaling pathways
- Quercetin-induced autophagy flux enhances TRAIL-mediated tumor cell death
- Quercetin induces protective autophagy and apoptosis through ER stress via the p-STAT3/Bcl-2 axis in ovarian cancer
- Proteasome inhibition by quercetin triggers macroautophagy and blocks mtor activity
- The critical role of quercetin in autophagy and apoptosis in HeLa cells
- Quercetin nanoparticles induced autophagy and apoptosis through AKT/ERK/Caspase-3 signaling pathway in human neuroglioma cells: In vitro and in vivo
- The effect of quercetin nanoparticle on cervical cancer progression by inducing apoptosis, autophagy and anti-proliferation via JAK2 suppression
- Quercetin attenuates neuronal autophagy and apoptosis in rat traumatic brain injury model via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
- Quercetin prevents hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation and reducing autophagy via the TGF-β1/Smads and PI3K/Akt pathways
- Quercetin-Rich Guava (Psidium guajava) Juice in Combination with Trehalose Reduces autophagy, Apoptosis and Pyroptosis Formation in the Kidney and Pancreas of Type II Diabetic Rats
- Quercetin Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Accumulation in the Liver: Implication for autophagy Regulation
- Inhibition of autophagy induced by quercetin at a late stage enhances cytotoxic effects on glioma cells
- Quercetin induces autophagy via FOXO1-dependent pathways and autophagy suppression enhances quercetin-induced apoptosis in PASMCs in hypoxia
- Quercetin suppresses the mobility of breast cancer by suppressing glycolysis through Akt-mtor pathway mediated autophagy induction
- Apoptosis induction in human glioblastoma multiforme T98G cells upon temozolomide and quercetin treatment
- Resveratrol Potently Counteracts Quercetin Starvation‐Induced autophagy and Sensitizes HepG2 Cancer Cells to Apoptosis
- Quercetin simultaneously induces G0/G1‐phase arrest and caspase‐mediated crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy in human leukemia HL‐60 cells
- Changes of intracellular Ca2+ in quercetin-induced autophagy progression
- Quercetin inhibited cadmium-induced autophagy in the mouse kidney via inhibition of oxidative stress
- Temozolomide, quercetin and cell death in the MOGGCCM astrocytoma cell line
- Mechanisms of Neuroprotection by Quercetin: Counteracting oxidative stress and More
- Quercetin blocks t-AUCB-induced autophagy by Hsp27 and Atg7 inhibition in glioblastoma cells in vitro
- Potentiation of β-adrenoceptor agonist-mediated lipolysis by quercetin and fisetin in isolated rat adipocytes
- Gastrointestinal Fate of Fluid and Gelled Nutraceutical Emulsions: Impact on Proteolysis, lipolysis, and Quercetin Bioaccessibility
- Beneficial Effects of Quercetin on obesity and Diabetes
- Role of quercetin as an alternative for obesity treatment: You are what you eat!
- The inhibitory effects of quercetin on obesity and obesity-induced inflammation by regulation of MAPK signaling
- Quercetin Protects against obesity-Induced Skeletal Muscle inflammation and Atrophy
- Therapeutic Effects of Quercetin on inflammation, obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes
- Quercetin reduces obesity-induced hepatosteatosis by enhancing mitochondrial oxidative metabolism via heme oxygenase-1
- A combination of quercetin and resveratrol reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed rats by modulation of gut microbiota†
- Failure of dietary quercetin to alter the temporal progression of insulin resistance among tissues of C57BL/6J mice during the development of diet-induced obesity
- Quercetin Inhibits Angiogenesis Mediated Human Prostate Tumor Growth by Targeting VEGFR- 2 Regulated AKT/mtor/P70S6K Signaling Pathways
- Concomitant reduction of c-Myc expression and PI3K/AKT/mtor signaling by quercetin induces a strong cytotoxic effect against Burkitt’s lymphoma
- Quercetin suppresses breast cancer stem cells (CD44+/CD24−) by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mtor-signaling pathway
- Synergistic effects of snail and quercetin on renal cell carcinoma Caki-2 by altering AKT/mtor/ERK1/2 signaling pathways
- Quercetin-6-C-β-d-glucopyranoside, natural analog of quercetin exhibits anti-prostate cancer activity by inhibiting Akt-mtor pathway via aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- A novel synthetic derivative of quercetin, 8-trifluoromethyl-3,5,7,3′,4′-O-pentamethyl-quercetin, inhibits bladder cancer growth by targeting the AMPK/mtor signaling pathway
- Quercetin Induces Apoptosis via Regulation of mtor-VASP Signaling Pathway in HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells
- Quercetin‐3‐methyl ether inhibits esophageal carcinogenesis by targeting the AKT/mtor/p70S6K and MAPK pathways
- Involvement of AMPK/mtor/HIF-1α in anticancer control of quercetin in hypoxic MCF-7 cells
- Vanadium quercetin complex attenuates mammary cancer by regulating the P53, Akt/mtor pathway and downregulates cellular proliferation correlated with increased apoptotic events
- Inhibitory effect of quercetin on carrageenan-induced inflammation in rats
- Role of quercetin (a natural herbal compound) in allergy and inflammation.
- Quercetin reduces markers of oxidative stress and inflammation in sarcoidosis
- Chronic quercetin ingestion and exercise-induced oxidative damage and inflammation
- Quercetin Treatment Ameliorates inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Quercetin transiently increases energy expenditure but persistently decreases circulating markers of inflammation in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet
- Quercetin is equally or more effective than resveratrol in attenuating tumor necrosis factor-α–mediated inflammation and insulin resistance in primary human adipocytes
- Quercetin Protects against Diabetes-Induced Exaggerated Vasoconstriction in Rats: Effect on Low Grade inflammation
- Quercetin attenuates inflammation in human macrophages and adipocytes exposed to macrophage-conditioned media
- Quercetin reduced inflammation and increased antioxidant defense in rat adjuvant arthritis
- Quercetin protects human hepatocytes from ethanol-derived oxidative stress by inducing heme oxygenase-1 via the MAPK/Nrf2 pathways
- Quercetin Increases oxidative stress Resistance and Longevity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Quercetin Prevents oxidative stress in Cirrhotic Rats
- Beneficial effects of quercetin on oxidative stress induced by ultraviolet A
- Quercetin suppresses inflammation by reducing ERK1/2 phosphorylation and NF kappa B activation in leptin-induced Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs)
- [Quercetin affects leptin and its receptor in human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells and JAK-STAT pathway].
- Fructose Induced leptin Dysfunction and Improvement by Quercetin and Rutin in Rats
- No effects of quercetin from onion skin extract on serum leptin and adiponectin concentrations in overweight-to-obese patients with (pre-)hypertension: a randomized double-blinded, placebo-controlled crossover trial
- Effect of quercetin on secretion and gene expression of leptin in breast cancer
- QUERCETIN DECREASE leptin GENE EXPRESSION IN BREAST CANCER
- Quercetin sebagai Penghambat Aktivasi NF-κβ dan Penurunan Kadar MCP-1 pada Kultur HUVECs yang Dipapar dengan leptin
- Onjisaponin B Derived from Radix Polygalae Enhances autophagy and Accelerates the Degradation of Mutant α-Synuclein and Huntingtin in PC-12 Cells
- Aβ peptide secretion is reduced by Radix Polygalae‑induced autophagy via activation of the AMPK/mtor pathway
- Radix Polygalae Enhances autophagy and Accelerates the Degradation of Mutant Aggregated Proteins In Vitro
- Identification of novel autophagic Radix Polygalae fraction by cell membrane chromatography and UHPLC-(Q)TOF-MS for degradation of neurodegenerative disease proteins
- 1,3,7-Trihydroxyxanthone, derived from Polygalae Radix, a herbal medicine, stimulates the expression of neurotrophic factors in rat astrocyte primary cultures via cAMP- and ERK-dependent pathways
Radix Scutellariae (RS), ( From dried root of Scutellariae baicalensis Georgi )
- Total flavonoid aglycones extract in Radix Scutellariae induces cross-regulation between autophagy and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells
- Effect of autophagy in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma SCC 25 cells from Scutellariae Radix by ethanol extract
- Heat-Processed Scutellariae Radix Protects Hepatic inflammation through the Amelioration of oxidative stress in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mice
- Effect of Scutellariae radix (Huangqin) on preventing rhinovirus-provoked asthmatic inflammation in cultured human bronchial epithelia
- Research of Effective Components of Scutellariae Radix on Action Targets in inflammation Pathway
- Ethanol-Heated Processed Scutellariae Radix Improve Inflammatory Response through an Inhibitory Effect against oxidative stress in Mice with the Lipopolysaccharide-induced Intestine Injury of Mice
resveratrol (From Polygonum Cuspidatum Extract)
- Spermidine and resveratrol induce autophagy by distinct pathways converging on the acetylproteome
- Caloric restriction and resveratrol promote longevity through the Sirtuin-1-dependent induction of autophagy
- Resveratrol-Activated AMPK/SIRT1/autophagy in Cellular Models of Parkinson’s Disease
- Role of non-canonical Beclin 1-independent autophagy in cell death induced by resveratrol in human breast cancer cells
- autophagy mediates pharmacological lifespan extension by spermidine and resveratrol
- Cardioprotection by resveratrol: a novel mechanism via autophagy involving the mtorC2 pathway
- Inhibition of mammalian S6 kinase by resveratrol suppresses autophagy
- Resveratrol attenuates vascular endothelial inflammation by inducing autophagy through the cAMP signaling pathway
- Resveratrol enhances the therapeutic effect of temozolomide against malignant glioma in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting autophagy
- Resveratrol induces apoptosis via ROS-triggered autophagy in human colon cancer cells
- Dihydroceramide intracellular increase in response to resveratrol treatment mediates autophagy in gastric cancer cells
- Sulfate Metabolites Provide an Intracellular Pool for Resveratrol Generation and Induce autophagy with Senescence
- Resveratrol, a Phytochemical Inducer of Multiple Cell Death Pathways: Apoptosis, autophagy and Mitotic Catastrophe
- Cathepsin L mediates resveratrol-induced autophagy and apoptotic cell death in cervical cancer cells
- Resveratrol Inhibits Breast Cancer Stem-Like Cells and Induces autophagy via Suppressing Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
- autophagy induced by resveratrol prevents human prion protein-mediated neurotoxicity
- Resveratrol induces autophagy by directly inhibiting mtor through ATP competition
- autophagy Interplay with Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Regulation in the Growth Inhibiting Effect of Resveratrol in Glioma Cells
- AMPK– and p62/SQSTM1-dependent autophagy mediate Resveratrol-induced cell death in chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Resveratrol Reverses Remodeling in Hearts with Large, Old Myocardial Infarctions through Enhanced autophagy-Activating AMP Kinase Pathway
- Resveratrol induces cell death in cervical cancer cells through apoptosis and autophagy
- Resveratrol improves hepatic steatosis by inducing autophagy through the cAMP signaling pathway
- Resveratrol-mediated autophagy requires WIPI-1-regulated LC3 lipidation in the absence of induced phagophore formation
- The prosurvival role of autophagy in Resveratrol-induced cytotoxicity in human U251 glioma cells
- Resveratrol-induced apoptosis is enhanced by inhibition of autophagy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Resveratrol Partially Prevents Rotenone-Induced Neurotoxicity in Dopaminergic SH-SY5Y Cells through Induction of Heme Oxygenase-1 Dependent autophagy
- Resveratrol Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Death via Inhibition of p70 S6 Kinase 1-Mediated autophagy
- Resveratrol modulates autophagy and NF-κB activity in a murine model for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Resveratrol Induces Apoptosis and autophagy in T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells by Inhibiting Akt/mtor and Activating p38-MAPK
- Resveratrol, obesity and diabetes
- Resveratrol: Anti-obesity Mechanisms of Action
- Resveratrol Attenuates obesity-Associated Peripheral and Central inflammation and Improves Memory Deficit in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
- Resveratrol and obesity: Can resveratrol relieve metabolic disturbances?
- Effects of resveratrol on gut microbiota and fat storage in a mouse model with high-fat-induced obesity
- Resveratrol regulates lipolysis via adipose triglyceride lipase
- Resveratrol, a naturally occurring diphenolic compound, affects lipogenesis, lipolysis and the antilipolytic action of insulin in isolated rat adipocytes
- Resveratrol directly affects in vitro lipolysis and glucose transport in human fat cells
- Metformin and resveratrol ameliorate muscle insulin resistance through preventing lipolysis and inflammation in hypoxic adipose tissue
- Resveratrol Inhibits mtor Signaling by Promoting the Interaction between mtor and DEPTOR
- At concentrations that inhibit mtor, resveratrol suppresses cellular senescence
- Resveratrol inhibits the mtor mitogenic signaling evoked by oxidized LDL in smooth muscle cells
- Resveratrol activates autophagic cell death in prostate cancer cells via downregulation of STIM1 and the mtor pathway
- mTOR: more targets of resveratrol?
- Resveratrol pre-treatment reduces early inflammatory responses induced by status epilepticus via mtor signaling
- Resveratrol Triggers Protective Autophagy Through the Ceramide/Akt/mtor Pathway in Melanoma B16 Cells
- Resveratrol inhibits mtor signaling by targeting DEPTOR
- Targeting mtor: Evaluating the Therapeutic Potential of Resveratrol for Cancer Treatment
- Resveratrol as a novel treatment for diseases with mtor pathway hyperactivation
- Amelioration of oxidative stress by antioxidants and resveratrol in PC12 cells
- Resveratrol Prevents the Prohypertrophic Effects of oxidative stress on LKB1
- Resveratrol Improves Endothelial Function Role of TNFα and Vascular oxidative stress
- Resveratrol protects primary rat hepatocytes against oxidative stress damage:: Activation of the Nrf2 transcription factor and augmented activities of antioxidant enzymes
- RESVERATROL REDUCES ENDOTHELIAL oxidative stress BY MODULATING THE GENE EXPRESSION OF SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE 1 (SOD1), GLUTATHIONEPEROXIDASE 1 (GPX1) AND NADPH OXIDASE SUBUNIT (NOX4
- Molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress resistance induced by resveratrol: Specific and progressive induction of MnSOD
- Mechanism for the protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative stress-induced neuronal death
- Oxyresveratrol and resveratrol are potent antioxidants and free radical scavengers: effect on nitrosative and oxidative stress derived from microglial cells
- Protective effect of trans-resveratrol against kainic acid-induced seizures and oxidative stress in rats
- A Resveratrol and Polyphenol Preparation Suppresses Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress Response to a High-Fat, High-Carbohydrate Meal
- Regulation of inflammation signalling by resveratrol in human chondrocytes in vitro
- Resveratrol, MicroRNAs, inflammation, and Cancer
- Resveratrol mitigates lipopolysaccharide‐ and Aβ‐mediated microglial inflammation by inhibiting the TLR4/NF‐κB/STAT signaling cascade
- Resveratrol, a polyphenol found in grapes, suppresses oxidative damage and stimulates apoptosis during early colonic inflammation in rats
- The effects of resveratrol, a phytoalexin derived from red wines, on chronic inflammation induced in an experimentally induced colitis model
- Resveratrol attenuates hepatic steatosis in high-fat fed mice by decreasing lipogenesis and inflammation
- Resveratrol Prevents High Fat/Sucrose Diet-Induced Central Arterial Wall inflammation and Stiffening in Nonhuman Primates
- Prevention of Ocular inflammation in Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis with Resveratrol by Inhibiting Oxidative Damage and Nuclear Factor–κB Activation
- Effect of a Low Dose of Dietary Resveratrol on Colon Microbiota, inflammation and Tissue Damage in a DSS-Induced Colitis Rat Model
- The inhibitory effect of resveratrol on leptin secretion from rat adipocytes
- Resveratrol treatment rescues hyperleptinemia and improves hypothalamic leptin signaling programmed by maternal high-fat diet in rats
- Effect of Resveratrol on leptin and Sirtuin 2 Expression in the Kidneys in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats.
- Resveratrol Prevents Hyperleptinemia and Central leptin Resistance in Adult Rats Programmed by Early Weaning
- The effect of leptin and resveratrol on JAK/STAT pathways and Sirt-1 gene expression in the renal tissue of ischemia/reperfusion induced rats.
- Resveratrol increases serum adiponectin level and decreases leptin and insulin level in an experimental model of hypercholesterolemia
- Potential Involvement of Peripheral leptin/STAT3 Signaling in the Effects of Resveratrol and Its Metabolites on Reducing Body Fat Accumulation
- The effects of resveratrol on bone and growth plate cartilage in leptin-deficient mice
- Resveratrol does not affect leptin while it has regulatory effects on liver glycogen levels in exercised and non-exercised rats
- The Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on the Level of Adiponectin and leptin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Resveratrol Treatment Ameliorates leptin Resistance and Adiposity Programed by the Combined Effect of Maternal and Post‐Weaning High‐Fat Diet
- Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside decrease the growth of bladder cancer cell lines via inhibition of the mtor pathway and induction of autophagy
- Rhodiola Rosea Modulates Apoptosis and autophagy in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Tumor Xenograft Model
- Rhodiola Rosea Extract Reduces autophagy In Acute Myeloid Leukemia Transformed From Myelodysplastic Syndromes Tumor Xenograft Model
- Abstract 3799: Rhodiola rosea extracts, salidroside, and metformin decrease the growth of bladder cancer cell lines via inhibition of TSC- mediated translation initiation and induction of autophagy
- Rhodiola rosea Improves Lifespan, Locomotion, and Neurodegeneration in a Drosophila melanogaster Model of Huntington’s Disease
- The use of Griffonia Simplicifolia and Rhodiola Rosea l. in obese women with eating compulsion/A UTILIZACAO DA GRIFFONIA SIMPLICIFOLIA E RHODIOLA ROSEA L. EM MULHERES OBESAS COM COMPULSAO ALIMENTAR
- Evaluation of Rhodiola rosea supplementation on skeletal muscle damage and inflammation in runners following a competitive marathon
- The golden root, Rhodiola rosea, prolongs lifespan but decreases oxidative stress resistance in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Effects of Rhodiola rosea supplementation on mental performance, physical capacity, and oxidative stress biomarkers in healthy men
Rottlerin (from Mallotus philippinensis)
- Rottlerin-induced autophagy leads to the apoptosis in breast cancer stem cells: molecular mechanisms
- Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptosis in prostate cancer stem cells via PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway
- Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic cell death through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway in human pancreatic cancer stem cells
- Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptotic cell death through a PKC-delta-independent pathway in HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells: The protective role of autophagy in apoptosis
- Alternative Pathways of Cancer Cell Death by Rottlerin: Apoptosis versus autophagy
- Phosphorylation-independent mtorC1 inhibition by the autophagy inducer Rottlerin
- Rottlerin-induced autophagy leads to apoptosis in bladder cancer cells
- Rottlerin Reduces cAMP/CREB-Mediated Melanogenesis via Regulation of autophagy
- AB161. Rottlerin-induced autophagy leads to the apoptosis in bladder cancer cells
- Rottlerin induce early autophagy and late apoptosis via PKC-delta independent pathway.
- Rottlerin and Cancer: Novel Evidence and Mechanisms
- Protection of human colon epithelial cells against deoxycholate by rottlerin
- Rottlerin exerts its anti-tumor activity through inhibition of Skp2 in breast cancer cells
- Rottlerin inhibits cell growth and invasion via down-regulation of Cdc20 in glioma cells
- Rottlerin suppresses growth of human pancreatic tumors in nude mice, and pancreatic cancer cells isolated from KrasG12D mice
- Antiproliferative Effect of Rottlerin on Sk-Mel-28 Melanoma Cells
- Rottlerin exhibits anti-cancer effect through inactivation of S phase kinase-associated protein 2 in pancreatic cancer cells
- Rottlerin induces Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and suppresses both Wnt/β-catenin and mtorC1 signaling in prostate and breast cancer cells
- Non-conventional rottlerin anticancer properties
- Inhibitions of mtorC1 and 4EBP-1 are key events orchestrated by Rottlerin in SK-Mel-28 cell killing
- Rottlerin Suppresses Airway Hyperreactivity And inflammation In Mouse Models Of Experimental Asthma
Safflower extract
- Safflower extract inhibiting apoptosis by inducing autophagy in myocardium derived H9C2 cell
- Hypolipidemic effect of safflower yellow and primary mechanism analysis
- Research strategy for the development of conjugated linoleic acid from safflower seed oil as an antiaging material
- Intestinal absorption and lipolysis of safflower oiland other unsaturated vegetable oils in rats
- Comparison of dietary conjugated linoleic acid with safflower oil on body composition in obese postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Genotype and Diet Effects in Lean and obese Zucker Rats Fed Either Safflower or Coconut Oil Diets
- Time-dependent effects of safflower oil to improve glycemia, inflammation and blood lipids in obese, post-menopausal women with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-masked, crossover study
- CLA Does Not Impair Endothelial Function and Decreases Body Weight as Compared with Safflower Oil in Overweight and obese Male Subjects
- Metabolic effects of coconut, safflower, or menhaden oil feeding in lean and obese Zucker rats.
- The Mechanism by Which Safflower Yellow Decreases Body Fat Mass and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in HFD-Induced obese Mice
- Relationship of plasma levels of C-reactive protein and adiponectin and change of lean body mass in obese postmenopausal women supplemented with safflower oil
- The Role of Dietary Safflower Oil in the Management of Glucose Levels in obese Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Prevention of diet-induced obesity by safflower oil: insights at the levels of PPARα, Orexin, and Ghrelin gene expression of adipocytes in mice
- Protective effect of dried safflower petal aqueous extract and its main constituent, carthamus yellow, against lipopolysaccharide‐induced inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages
- A safflower oil based high‐fat/high‐sucrose diet modulates the gut microbiota and liver phospholipid profiles associated with early glucose intolerance in the absence of tissue inflammation
- Protective Effect of Safflower Seed on Cisplatin-Induced Renal Damage in Mice via oxidative stress and Apoptosis-Mediated Pathways
- Biochar alleviates fluoride toxicity and oxidative stress in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) seedlings
- FISH OIL INSTEAD OF SAFFLOWER OIL AS THE DIETARY FAT SOURCE MODIFIES THE oxidative stress RESPONSE TO BORON DEFICIENCY IN RATS
- RESPONSE OF CADMIUM–INDUCED oxidative stress CONTAMINATION AND ITS RELATION TO SOME PHYSIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SAFFLOWER GENOTYPES
- Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) seed attenuates memory impairment induced by scopolamine in mice via regulation of cholinergic dysfunction and oxidative stress
- Inhibitory Effects of Safflower Seed Extract on Memory Impairment and oxidative stress and the Qualitative Analyses of Serotonin and Its Derivatives in the Water Extracts
- Memory Improving Activity of Safflower Seed Extracts against oxidative stress and Cholinergic Dysfunction in Scopolamine-induced Amnesic Mice
- Changes in liver PPARα mRNA expression in response to two levels of high-safflower-oil diets correlate with changes in adiposity and serum leptin in rats and mice
- EFFECTS OF FEEDING HIGH LINOLEATE SAFFLOWER SEEDS PREPARTUM ON leptin CONCENTRATION, WEANING, AND RE-BREEDING PERFORMANCE OF BEEF HEIFERS
- Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside decrease the growth of bladder cancer cell lines via inhibition of the mtor pathway and induction of autophagy
- Salidroside induces apoptosis and autophagy in human colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway
- Inhibiting ROS-TFEB-Dependent autophagy Enhances Salidroside-Induced Apoptosis in Human Chondrosarcoma Cells
- Salidroside pretreatment attenuates apoptosis and autophagy during hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury by inhibiting the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in mice
- Salidroside protects cortical neurons against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity by inhibiting autophagy
- Inhibition of autophagy enhances synergistic effects of Salidroside and anti-tumor agents against colorectal cancer
- Salidroside attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance by upregulating autophagy through the AMPK–mtor-ULK1 pathway
- Salidroside mediates apoptosis and autophagy inhibition in concanavalin A‑induced liver injury
- Salidroside ameliorates autophagy and activation of hepatic stellate cells in mice via NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad3 pathways
- Salidroside induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer SKOV3 and A2780 cells through the p53 signaling pathway
- Salidroside attenuates neuroinflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury through microglia polarization regulation
- Anticancer effect of salidroside reduces viability through autophagy/PI3K/Akt and MMP‑9 signaling pathways in human bladder cancer cells
- Salidroside Promotes Random Skin Flap Survival in Rats by Enhancing Angiogenesis and Inhibiting Apoptosis
- Salidroside prevents skin carcinogenesis induced by DMBA/TPA in a mouse model through suppression of inflammation and promotion of apoptosis
- Salidroside, a scavenger of ROS, enhances the radioprotective effect of Ex-RAD® via a p53-dependent apoptotic pathway
- Osteoprotective effects of salidroside in ovariectomized mice and diabetic mice
- Salidroside mediated stabilization of Bcl -xL prevents mitophagy in CA3 hippocampal neurons during hypoxia
- Salidroside inhibits the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells via suppression of Src‑associated signaling pathway activation and heat shock protein 70 expression
- Salidroside protects renal tubular epithelial cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in vitro
- Salidroside protects hypoxia-induced injury by up-regulation of miR-210 in rat neural stem cells
- Salidroside reduce inflammatory cytokines in atherosclecrosis via suppressing MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway
- Salidroside protects against kainic acid-induced status epilepticus via suppressing oxidative stress
- Salidroside in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats and its induced autophagy reaction
- Salidroside protects against ox-LDL-induced endothelial injury by enhancing autophagy mediated by SIRT1-FoxO1 pathway
- LBD16 and LBD18 acting downstream of ARF7 and ARF19 are involved in adventitious root formation in Arabidopsis
- Salidroside protects SH‑SY5Y from pathogenic α‑synuclein by promoting cell autophagy via mediation of mtor/p70S6K signaling
- GW26-e4765 Vasomotor effect of salidroside on acute exhaustive rat mesenteric artery and its calcium regulation mechanisms
- Protective Effects of Salidroside against Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)-Induced Liver Injury by Initiating Mitochondria to Resist oxidative stress in Mice
- Beneficial Effects of Rhodiola and Salidroside in Diabetes: Potential Role of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase
- Salidroside improves glucose homeostasis in obese mice by repressing inflammation in white adipose tissues and improving leptin sensitivity in hypothalamus
- Salidroside protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in HUVECs via the regulation of REDD1 and mtor activation
- Effects of Salidroside on Cobalt Chloride-Induced Hypoxia Damage and mtor Signaling Repression in PC12 Cells
- Salidroside exerts angiogenic and cytoprotective effects on human bone marrow‐derived endothelial progenitor cells via Akt/mtor/p70S6K and MAPK signalling pathways
- Salidroside alleviates cachexia symptoms in mouse models of cancer cachexia via activating mtor signalling
- Salidroside suppressing LPS‐induced myocardial injury by inhibiting ROS‐mediated PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway in vitro and in vivo
- [Salidroside via ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT/mtor signal pathway induces mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into neural cells].
- Salidroside attenuates beta amyloid-induced cognitive deficits via modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators in rat hippocampus
- Protection by Salidroside against Bone Loss via Inhibition of oxidative stress and Bone-Resorbing Mediators
- Salidroside Improves Homocysteine-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Reducing oxidative stress
- Salidroside promotes erythropoiesis and protects erythroblasts against oxidative stress by up-regulating glutathione peroxidase and thioredoxin
- Salidroside Protects Caenorhabditis elegans Neurons from Polyglutamine-Mediated Toxicity by Reducing oxidative stress
- [Study on effects of salidroside on lipid peroxidation on oxidative stress in rat hepatic stellate cells].
- Salidroside Improves Doxorubicin-induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Suppression of Excessive oxidative stress and Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis
- The cardioprotective effect of salidroside against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation
- Salidroside Regulates Inflammatory Response in Raw 264.7 Macrophages via TLR4/TAK1 and Ameliorates inflammation in Alcohol Binge Drinking-Induced Liver Injury
- Salidroside Attenuates Allergic Airway inflammation Through Negative Regulation of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and p38 Mitogen–Activated Protein Kinase
- The Effect of Synthetic Salidroside on Cytokines and Airway inflammation of Asthma Induced by Diisocyanate (TDI) in Mice by Regulating GATA3/T-bet
- Salidroside Inhibits inflammation Through PI3K/Akt/HIF Signaling After Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Rats
- Salidroside suppresses solar ultraviolet-induced skin inflammation by targeting cyclooxygenase-2
- Anti-inflammatory effect of salidroside on phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate plus A23187-mediated inflammation in HMC-1 cells
- Salidroside Inhibits HMGB1 Acetylation and Release through Upregulation of SirT1 during inflammation
- Skeletal Muscle Atrophy Was Alleviated by Salidroside Through Suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation During Denervation
- Salidroside attenuates interleukin‐1β‐induced inflammation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes
- Salidroside improves glucose homeostasis in obese mice by repressing inflammation in white adipose tissues and improving leptin sensitivity in hypothalamus
Sarsaparilla (From Smilax glabra rhizome extract)
- Sarsaparilla (Smilax Glabra Rhizome) Extract Activates Redox-Dependent ATM/ATR Pathway to Inhibit Cancer Cell Growth by S Phase Arrest, Apoptosis, and autophagy
- Sarsaparilla (Smilax Glabra Rhizome) Extract Inhibits Cancer Cell Growth by S Phase Arrest, Apoptosis, and autophagy via Redox-Dependent ERK1/2 Pathway
- Anticancer effect of Saussurea lappa extract via dual control of apoptosis and autophagy in prostate cancer cells
- A brief review of remedial uses of Saussurealappa
- Anti-obesity Activity of Extract from Saussurea lappa
- Acacetin from Traditionally Used Saussurea involucrata Kar. et Kir. Suppressed Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and Attenuated Lipid Accumulation in obese Mice
- Evaluation of sesquiterpene lactone fraction of Saussurea lappa on transudative, exudative and proliferative phases of inflammation
- Inhibition of TNF-α-Induced inflammation by Sesquiterpene Lactones from Saussurea lappa and Semi-Synthetic Analogues
- Dehydrocostus lactone, a sesquiterpene from Saussurea lappa Clarke, suppresses allergic airway inflammation by binding to dimerized translationally controlled tumor protein
schisandrin A. (FRom Schisandra chinensis fructus)
- Attenuation of cyclosporine A induced nephrotoxicity by schisandrin B through suppression of oxidative stress, apoptosis and autophagy
- Mechanism of Schisandrin A on autophagy and Apoptosis of Hippocampal Neurons in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Rats
- The protective mechanism of schisandrin A in d-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury through activation of autophagy
- Schisandrin B Prevents Doxorubicin Induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Modulation of DNA Damage, oxidative stress and inflammation through Inhibition of MAPK/p53 Signaling
- Comparative Effects of Schisandrin A, B, and C on Acne-Related inflammation
- Schisandrin B ameliorated chondrocytes inflammation and osteoarthritis via suppression of NF-κB and MAPK signal pathways
- Schisandrin A suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in RAW 264.7 macrophages by suppressing the NF-κB, MAPKs and PI3K/Akt pathways and activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling
- Schisandrin A Inhibits the IL-1β-Induced inflammation and Cartilage Degradation via Suppression of MAPK and NF-κB Signal Pathways in Rat Chondrocytes
- Schisandrin B alleviates diabetic nephropathy through suppressing excessive inflammation and oxidative stress
- Schisandrin B Attenuates inflammation in LPS-Induced Sepsis Through miR-17-5p Downregulating TLR4
- Correction to: Schisandrin B Attenuates inflammation in LPS-Induced Sepsis through miR-17-5p Downregulating TLR4.
- Corrigendum to “Schisandrin B alleviates diabetic nephropathy through suppressing excessive inflammation and oxidative stress” Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 508 (2019): 243-249.
- Schisandrin B protects PC12 cells against oxidative stress of neurodegenerative diseases
- Schisandrin B attenuates the inflammatory response, oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by traumatic spinal cord injury via inhibition of p53 signaling in adult rats
- Schisandrin A prevents oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and apoptosis by attenuating ROS generation in C2C12 cells
- Schisandrin B alleviates acute oxidative stress via modulation of the Nrf2/Keap1-mediated antioxidant pathway
Silibinin (From Milk Thistle Extract)
- Silibinin, a natural flavonoid, induces autophagy via ROS-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction and loss of ATP involving BNIP3 in human MCF7 breast cancer cells
- Anti-tumor activities of luteolin and silibinin in glioblastoma cells: overexpression of miR-7-1-3p augmented luteolin and silibinin to inhibit autophagy and induce apoptosis in glioblastoma in vivo
- Mechanism of autophagy induction and role of autophagy in antagonizing mitomycin C-induced cell apoptosis in silibinin treated human melanoma A375-S2 cells
- ERα down-regulation plays a key role in silibinin-induced autophagy and apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells
- In vivo recovery effect of silibinin treatment on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice is associated with the modulations of sirt-1 expression and autophagy in pancreatic β-cell
- autophagy Induction by Silibinin Positively Contributes to Its Anti-Metastatic Capacity via AMPK/mtor Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma
- autophagy induced by silibinin protects human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells from UVB-induced apoptosis
- Silibinin protects murine fibroblast L929 cells from UVB‐induced apoptosis through the simultaneous inhibition of ATM‐p53 pathway and autophagy
- autophagy inhibition enhances silibinin-induced apoptosis by regulating reactive oxygen species production in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells
- Silibinin ameliorates anxiety/depression-like behaviors in amyloid β-treated rats by upregulating BDNF/TrkB pathway and attenuating autophagy in hippocampus
- Silibinin Activated p53 and Induced Autophagic Death in Human Fibrosarcoma HT1080 Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species-p38 and c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Pathways
- Energy deprivation by silibinin in colorectal cancer cells
- Silibinin ameliorates Aβ25-35-induced memory deficits in rats by modulating autophagy and attenuating neuroinflammation as well as oxidative stress
- Silibinin activated ROS–p38–NF-κB positive feedback and induced autophagic death in human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells
- Crosstalk of ROS/RNS and autophagy in silibinin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in vitro
- Dual effects of silibinin treatment on autophagy-regulated dermal apoptosis retardation and epidermal apoptosis up-regulation in UVB-induced skin inflammation
- Silibinin Induced Autophagic and Apoptotic Cell Death in HT1080 Cells Through a Reactive Oxygen Species Pathway
- P53 activation plays a crucial role in silibinin induced ROS generation via PUMA and JNK
- Silibinin triggers apoptotic signaling pathways and autophagic survival response in human colon adenocarcinoma cells and their derived metastatic cells
- p53-mediated autophagy adjustment is involved in the protection of silibinin against murine dermal inflammation and epidermal apoptosis induced by UVB irradiation
- Silibinin induced-autophagic and apoptotic death is associated with an increase in reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in HeLa cells
- Silibinin negatively contributes to primary cilia length via autophagy regulated by histone deacetylase 6 in confluent mouse embryo fibroblast 3T3-L1 cells
- Role of ROS in the protective effect of silibinin on sodium nitroprusside-induced apoptosis in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells
- Inhibitory effects of silibinin on proliferation and lung metastasis of human high metastasis cell line of salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma via autophagy induction
- Silibinin inhibits VEGF secretion and age‐related macular degeneration in a hypoxia‐dependent manner through the PI‐3 kinase/Akt/mtor pathway
- Silibinin to improve cancer therapeutic, as an apoptotic inducer, autophagy modulator, cell cycle inhibitor, and microRNAs regulator
- ERβ up-regulation was involved in silibinin-induced growth inhibition of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells
- Silibinin: a potential old drug for cancer therapy
- An Overview of Ultraviolet B Radiation-Induced Skin Cancer Chemoprevention by Silibinin
- Nitric oxide (•NO) generation but not ROS plays a major role in silibinin-induced autophagic and apoptotic death in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells
- Silibinin Reduces the Impact of obesity on Invasive Liver Cancer
- Beneficial effects of silibinin against the progression of metabolic syndrome, increased oxidative stress, and liver steatosis in Psammomys obesus, a relevant animal model of human obesity and diabetes
- The Efficacy of Silibinin to Reduce the Impact of obesity on Invasive Prostate Cancer
- Silibinin Differentially Decreases the Aggressive Cancer Phenotype in an In Vitro Model of obesity and Prostate Cancer
- Effect of silibinin on endothelial dysfunction and ADMA levels in obese diabetic mice
- 1276 SILIBININ IMPROVES HEPATIC AND MYOCARDIAL INJURY IN obese DIABETIC MICE
- Supplementation of Silibinin Improves Adiposity, Dyslipidemia and Hepatic Fibrosis in High-fat Diet-Induced obese C57BL/6J Mice
- Silibinin suppresses the maintenance of colorectal cancer stem‐like cells by inhibiting PP2A/AKT/mtor pathways
- Silibinin induces apoptosis through inhibition of the mtor-GLI1-BCL2 pathway in renal cell carcinoma
- Silibinin Induced Human Glioblastoma Cell Apoptosis Concomitant with Autophagy through Simultaneous Inhibition of mtor and YAP
- SILIBININ INDUCE APOPTOSIS IN BREAST CANCER MCF7 CELLS THROUGH DOWN REGULATION OF PI3K/AKT/mtor PATHWAY
- Differential In Vitro Effects of Intravenous versus Oral Formulations of Silibinin on the HCV Life Cycle and inflammation
- Potent inhibitory effect of silibinin from milk thistle on skin inflammation stimuli by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
- Combinations of indole-3-carbinol and silibinin suppress inflammation-driven mouse lung tumorigenesis by modulating critical cell cycle regulators
- Silibinin Inhibits Neutrophilic inflammation and Mucus Secretion Induced by Cigarette Smoke via Suppression of ERK‐SP1 Pathway
- Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Silibinin in Animal Models of Chronic inflammation
- Silibinin inhibits inflammation and apoptosis in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy
- Silibinin Ameliorates O-GlcNAcylation and inflammation in a Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Inhibitory Effects of Silibinin on inflammation via Attenuation of HO-1 in Murine Macrophage Cell
- Silibinin Inhibits Neutrophilic inflammation and Mucus Secretion Induced by Cigarette Smoke via Suppression of ERKâSP1 Pathway [2016]
- Silibinin protects H9c2 cardiac cells from oxidative stress and inhibits phenylephrine-induced hypertrophy: potential mechanisms
- Silibinin mitigates zidovudine-induced hepatocellular degenerative changes, oxidative stress and hyperlipidaemia in rats
- Silibinin induced the apoptosis of Hep-2 cells via oxidative stress and down-regulating survivin expression
- Assessment of oxidative stress in leukocytes and granulocyte function following oral administration of a silibinin-phosphatidylcholine complex in cats
- Silibinin attenuates methotrexate-induced pulmonary injury by targeting oxidative stress
- Protective role of silibinin in cadmium induced changes of acetylcholinesterase, ATPases and oxidative stress in brain of albino wistar rats
- Silibinin ameliorates hyperglycaemia, hyperlipidemia and prevent oxidative stress in streptozotocin induced diabetes in Sprague Dawley rats.
- Inhibition of leptin and leptin Receptor Gene Expression by Silibinin-Curcumin Combination
- Inhibition of leptin gene expression and secretion by silibinin: possible role of estrogen receptors
- POSTER PRESENTATIONS: P-59: INHIBITORY EFFECT OF SILIBININ ON VARIATION OF leptin GENE EXPRESSION IN THE T47D BREAST CANCER CELL LINE
- INHIBITION OF leptin GENE EXPRESSION AND SECRETION BY SILIBININ: POSSIBLE ROLE OF ESTROGEN RECEPTORS
- Silibinin decrease the expression and secretion of leptin in T47D
- Preparation and Evaluation of effect Magnetic Nanoparticles Modified with Biodegradable Copolymer PCL-PEG containing Curcumin – Silibinin on leptin Gene Experession in Lung Cancer
Sophoraflavanone G (from Sophora flavescens)
- Sophoraflavanone G Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukemia Cells and Blocks MAPK Activation
- Sophoraflavanone G from Sophora alopecuroides inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells by targeting PI3K/Akt, JAK/STAT and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways
- Protective effect of Sophoraflavanone G on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced inflammation in diabetic rats
- Sophoraflavanone G fromSophora alopecuroidesinhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells by targeting PI3K/Akt, JAK/STAT and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways
Tanshinone IIA (from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge)
- The interplay between autophagy and apoptosis induced by tanshinone IIA in prostate cancer cells
- Tanshinone IIA Affects autophagy and Apoptosis of Glioma Cells by Inhibiting Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway
- Tanshinone IIA sensitizes oral squamous cell carcinoma to radiation due to an enhanced autophagy
- Crosstalk between Beclin-1-dependent autophagy and caspase‑dependent apoptosis induced by tanshinone IIA in human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells
- Tanshinone IIA Protects Hippocampal Neuronal Cells from Reactive Oxygen Species Through Changes in autophagy and Activation of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Protein Kinas B, and Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Pathways
- Tanshinone IIA induces cell death via Beclin‐1‐dependent autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC‐9 cell line
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates Aβ25–35‐induced spatial memory impairment via upregulating receptors for activated C kinase1 and inhibiting autophagy in hippocampus
- Tanshinone IIA protects against heart failure post-myocardial infarction via AMPKs/mtor-dependent autophagy pathway
- Tanshinone IIA activates autophagy to reduce liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by MEK/ERK/mtor pathway
- HGK-sestrin 2 signaling-mediated autophagy contributes to antitumor efficacy of Tanshinone IIA in human osteosarcoma cells
- Tanshinone IIA sodium sulfonate facilitates endocytic HMGB1 uptake
- Total Tanshinones-Induced Apoptosis and autophagy Via Reactive Oxygen Species in Lung Cancer 95D Cells
- Sensitivity of apoptosis-resistant colon cancer cells to tanshinones is mediated by autophagic cell death and p53-independent cytotoxicity
- Tanshinone IIA from Salvia miltiorrhiza BUNGE inhibits human aortic smooth muscle cell migration and MMP‐9 activity through AKT signaling pathway
- Novel Microemulsion of Tanshinone IIA, Isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, Exerts Anticancer Activity Through Inducing Apoptosis in Hepatoma Cells
- Tanshinone IIA potentiates the efficacy of 5-FU in Colo205 colon cancer cells in vivo through downregulation of P-gp and LC3-II
- Tanshinone I induces apoptosis and pro-survival autophagy in gastric cancers
- Protective effects of tanshinone IIA sodium sulfonate on ischemia-reperfusion-induced myocardial injury in rats
- A promising “TRAIL” of tanshinones for cancer therapy
- The antitumor natural product tanshinone IIA inhibits protein kinase C and acts synergistically with 17-AAG
- Mechanisms of Tanshinone II a inhibits malignant melanoma development through blocking autophagy signal transduction in A375 cell
- Protective effect of tanshinone IIA against cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats through inhibiting the Cys-C/Wnt signaling pathway
- Tanshinone IIA enhances chemosensitivity of colon cancer cells by suppressing nuclear factor-κB
- Tanshinone IIA decreases the protein expression of EGFR, and IGFR blocking the PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway in gastric carcinoma AGS cells both in vitro and in vivo
- Atheroprotective Effects and Molecular Targets of Tanshinones Derived From Herbal Medicine Danshen
- The Role of Tanshinone IIA in the Treatment of obesity through Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Antagonism
- obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Treatment with Tanshinone Derivatives Which Increase Metabolic
- Tanshinone IIA Inhibits HIF-1α and VEGF Expression in Breast Cancer Cells via mtor/p70S6K/RPS6/4E-BP1 Signaling Pathway
- Regulation of the cell cycle and PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway by tanshinone I in human breast cancer cell lines
- Tanshinone IIA protects against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by activating the PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway
- Nutlin-3 plus tanshinone IIA exhibits synergetic anti-leukemia effect with imatinib by reactivating p53 and inhibiting the AKT/mtor pathway in Ph+ ALL
- Tanshinone IIA can inhibit MiaPaCa‑2 human pancreatic cancer cells by dual blockade of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mtor pathways
- Abstract 2131: Tanshinone IIA can decrease growth factor receptors expression and dural-block both Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and Ras/PI3K/Akt/mtor pathways to inhibit human breast cancer BT-20 cells
- The combination of Nutlin-3 and Tanshinone IIA promotes synergistic cytotoxicity in acute leukemic cells expressing wild-type p53 by co-regulating MDM2-P53 and the AKT/mtor pathway
- GW29-e0760 Tanshinone IIA protects H9c2 cells from reactive oxygen species through inhabiting excessive autophagy via activation of PI3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway
- Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Protects Cardiomyocytes Against oxidative stress-mediated Apoptosis Through Inhibiting JNK Activation
- Tanshinone II A attenuates atherosclerotic calcification in rat model by inhibition of oxidative stress
- Amelioration of atherosclerosis by tanshinone IIA in hyperlipidemic rabbits through attenuation of oxidative stress
- Protective effects of tanshinone IIA on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress, HMGB1 expression, and inflammatory reaction
- Hydrogen peroxide-mediated oxidative stress and collagen synthesis in cardiac fibroblasts: Blockade by tanshinone IIA
- Study of Anti-Myocardial Cell oxidative stress Action and Effect of Tanshinone IIA on Prohibitin Expression
- Effects of tanshinone IIA on fibrosis in a rat model of cirrhosis through heme oxygenase-1, inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis
- Tanshinone II Aattenuates renal damage in STZ-induced diabetic rats via inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation
- Tanshinone IIA inhibits myocardial remodeling induced by pressure overload via suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation: Possible role of silent information regulator 1
- Tanshinone I Activates the Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Response and Protects Against As(III)-Induced Lung inflammation In Vitro and In Vivo
- Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate ameliorates ischemia-induced myocardial inflammation and lipid accumulation in Beagle dogs through NLRP3 inflammasome
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates renal fibrosis and inflammation via altering expression of TGF-β/Smad and NF-κB signaling pathway in 5/6 nephrectomized rats
- Tanshinone IIA therapeutically reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis in mice
- Establishment of an interleukin‑1β‑induced inflammation‑activated endothelial cell‑smooth muscle cell‑mononuclear cell co‑culture model and evaluation of the anti‑inflammatory effects of tanshinone IIA on atherosclerosis
- Tanshinone IIA Sodium sulfonate regulates antioxidant system, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis by downregulation of CLIC1
- Effect of Tanshinone IIA intrathecal injections on pain and spinal inflammation in mice with bone tumors
- Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via suppressing nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- Tanshinone IIA Attenuates Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Experimental Rats via Inhibiting inflammation
- Tanshinone IIA decreases the levels of inflammation induced by Aβ1–42 in brain tissues of Alzheimer’s disease model rats
-
- Protective Activity of Theobroma cacao L. Phenolic Extract on AML12 and MLP29 Liver Cells by Preventing Apoptosis and Inducing autophagy
- Proteomic response of Moniliophthora perniciosaexposed to pathogenesis-related protein-10 from Theobroma cacao
- Photosynthetic, antioxidative, molecular and ultrastructural responses of young cacao plants to Cd toxicity in the soil
- Clovamide and phenolics from cocoa beans (Theobroma cacao L.) inhibit lipid peroxidation in liposomal systems
- Carbon source-induced changes in the physiology of the cacao pathogen Moniliophthora perniciosa (Basidiomycetes) affect mycelial morphology and secretion of necrosis-inducing proteins
- Anti-obesity effect of cocoa proteins (Theobroma cacao L.) variety “Criollo” and the expression of genes related to the dysfunction of white adipose tissue in high-fat diet-induced obese rats
- Modulation of obesity-Related inflammation by Cocoa (Theobroma Cacao L. Sterculiaceae)
- DIETARY COCOA (THEOBROMA CACAO) SUPPLEMENTATION IMPROVES obesity-RELATED FATTY LIVER DISEASE IN MICE
- Anti-Diabetic and Anti-obesity Activities of Cocoa (Theobroma cacao) via Physiological Enzyme Inhibition
- Anti-obesity effect of cocoa proteins (Theobroma cacao L.) variety “Criollo” and the expression of genes related to the dysfunction of white adipose tissue in high-fat diet-induced obese rats
- Photosynthesis, chloroplast ultrastructure, chemical composition and oxidative stress in Theobroma cacao hybrids with the lethal gene Luteus-Pa mutant
- Cocoa bean (Theobroma cacao L.) phenolic extracts as PTP1B inhibitors, hepatic HepG2 and pancreatic β-TC3 cell cytoprotective agents and their influence on oxidative stress in rats
- Short-term capacities of ethanolicTheobroma cacaobean extract to ameliorate oxidative stress, hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia in alloxan-induced diabetic rats
Triptolide (TPL) (from Tripterygium wilfordii)
- autophagy Upregulation and Apoptosis Downregulation in DAHP and Triptolide Treated Cerebral Ischemia
- Triptolide-mediated cell death in neuroblastoma occurs by both apoptosis and autophagy pathways and results in inhibition of nuclear factor–kappa B activity
- Triptolide induces protective autophagy through activation of the CaMKKβ-AMPK signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells
- autophagy plays an important role in triptolide-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes
- Triptolide Inhibited Cytotoxicity of Differentiated PC12 Cells Induced by Amyloid-Beta25–35 via the autophagy Pathway
- Triptolide Promotes the Clearance of α-Synuclein by Enhancing autophagy in Neuronal Cells
- Triptolide induced cell death through apoptosis and autophagy in murine leukemia WEHI‐3 cells in vitro and promoting immune responses in WEHI‐3 generated leukemia mice in vivo
- Triptolide Restores autophagy to Alleviate Diabetic Renal Fibrosis through the miR-141-3p/PTEN/Akt/mtor Pathway
- Anti-tumor effects of triptolide on angiogenesis and cell apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells by inducing autophagy via repressing Wnt/β-Catenin signaling
- Effect of triptolide on human colorectal cancer HCT116 cell proliferation, autophagy and apoptosis
- Triptolide Induces Cell Death in Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Apoptotic and Autophagic Pathways
- Toxicity of triptolide and the molecular mechanisms involved
- Triptolide induces lysosomal-mediated programmed cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Triptolide induces autophagy and apoptosis through ERK activation in human breast cancer MCF‑7 cells
- Triptolide abrogates growth of colon cancer and induces cell cycle arrest by inhibiting transcriptional activation of E2F
- Triptolide, A Potential autophagy Modulator
- Triptolide induces protective autophagy and apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells by downregulating Akt/mtor activation
- Effect of the Natural Product Triptolide on Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies
- Mechanism of Action of the Anti-cancer Agent, Triptolide
- Sorafenib and triptolide as combination therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Inhibition of Tumor Cellular Proteasome Activity by Triptolide Extracted from the Chinese Medicinal Plant ‘Thunder God Vine’
- Triptolide enhances the tumoricidal activity of TRAIL against renal cell carcinoma
- Triptolide inhibits the inflammatory activities of neutrophils to ameliorate chronic arthritis
- Triptolide inhibits the migration and invasion of human prostate cancer cells via Caveolin-1/CD147/MMPs pathway
- Effect of triptolide on focal adhesion kinase and survival in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- Combined Effects of Curcumin and Triptolide on an Ovarian Cancer Cell Line
- Primary and liver metastasis-derived cell lines from KRasG12D; Trp53R172H; Pdx-1 Cre animals undergo apoptosis in response to triptolide
- Triptolide: A new star for treating human malignancies
- Does triptolide induce lysosomal-mediated apoptosis in human breast cancer cells?
- autophagy Involved in Hepatic Injury Induced by Triptolide
- Neuroprotective effects of DAHP and Triptolide in focal cerebral ischemia via apoptosis inhibition and PI3K/Akt/mtor pathway activation
- Synergistic cytotoxicity of BIIB021 with triptolide through suppression of PI3K/Akt/mtor and NF-κB signal pathways in thyroid carcinoma cells
- Triptolide Suppresses Glomerular Mesangial Cell Proliferation in Diabetic Nephropathy Is Associated with Inhibition of PDK1/Akt/mtor Pathway
- Antitumor effect of triptolide in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma by inhibiting cell viability, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition via regulating the PI3K/AKT/mtor pathway
- Triptolide Induces Glioma Cell Autophagy and Apoptosis via Upregulating the ROS/JNK and Downregulating the Akt/mtor Signaling Pathways
- Triptolide, an Extracted Phytomedicine Attenuates Glomerularsclerosis in Diabetic
- Role of oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and ERK activation in triptolide-induced apoptosis
- Triptolide attenuate the oxidative stress induced by LPS/D‐GalN in mice
- Triptolide attenuated injury via inhibiting oxidative stress in Amyloid-Beta25–35-treated differentiated PC12 cells
- [Monoside antagonizes triptolide-induced hepatocyte apoptosis via the anti-oxidative stress pathway].
- [Triptolide induces oxidative stress and apoptosis and activates PIK3/Akt signaling pathway in TM4 sertoli cells].
- Protective Effect of Vitamin C on Triptolide-induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in Mice through mitigation of oxidative stress.
- Triptriolide antagonizes triptolide-induced nephrocyte apoptosis via inhibiting oxidative stress in vitro and in vivo
- 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid exhibit protective effect against triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity:role in oxidative stress,inflammation and apoptosis
- Triptolide, a diterpenoid triepoxide, suppresses inflammation and cartilage destruction in collagen-induced arthritis mice
- Triptolide protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-mediated damage induced by lipopolysaccharide intranigral injection
- Triptolide, a Chinese herbal extract, protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-mediated damage through inhibition of microglial activation
- Triptolide promotes spinal cord repair by inhibiting astrogliosis and inflammation
- Identification of triptolide, a natural diterpenoid compound, as an inhibitor of lung inflammation
- Triptolide-Assisted Phosphorylation of p53 Suppresses inflammation-Induced NF-κB Survival Pathways in Cancer Cells
- Mycophenolate mofetil and triptolide alleviating airway inflammation in asthmatic model mice partly by inhibiting bone marrow eosinophilopoiesis
- Interleukin 6 inhibition by triptolide prevents inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis
- Effectiveness of Triptolide-Coated Stent on Decreasing inflammation and Attenuation of Intimal Hyperplasia in a Pig After Coronary Angioplasty
- Effects of Triptolide on inflammation and Immune Function
Ursolic acid (From Loquat Leaf Extract)
- autophagy inhibition enhances ursolic acid-induced apoptosis in PC3 cells
- Ursolic acid promotes cancer cell death by inducing Atg5‐dependent autophagy
- Ursolic acid induces cell death and modulates autophagy through JNK pathway in apoptosis-resistant colorectal cancer cells
- Ursolic acid induces autophagy in U87MG cells via ROS-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress
- autophagy-dependent EIF2AK3 activation compromises ursolic acid-induced apoptosis through upregulation of MCL1 in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
- Ursolic Acid Attenuates Diabetic Mesangial Cell Injury through the Up-Regulation of autophagy via miRNA-21/PTEN/Akt/mtor Suppression
- Ursolic acid improves lipid and glucose metabolism in high‐fat‐fed C57BL/6J mice by activating peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor alpha and hepatic autophagy
- Ursolic acid-mediated changes in glycolytic pathway promote cytotoxic autophagy and apoptosis in phenotypically different breast cancer cells
- Ursolic acid enhances macrophage autophagy and attenuates atherogenesis
- Ursolic acid protects hepatocytes against lipotoxicity through activating autophagy via an AMPK pathway
- Ursolic acid inhibits breast cancer growth by inhibiting proliferation, inducing autophagy and apoptosis, and suppressing inflammatory responses via the PI3K/AKT and NF‑κB signaling pathways in vitro
- SIRT1/Atg5/autophagy are involved in the antiatherosclerosis effects of ursolic acid
- Ursolic acid triggers nonprogrammed death (necrosis) in human glioblastoma multiforme DBTRG‐05MG cells through MPT pore opening and ATP decline
- Ursolic acid inhibits the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of novel A-ring cleaved ursolic acid derivatives in human non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Ursolic Acid—A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid with a Wide Spectrum of Pharmacological Activities
- Combined Use of Zoledronic Acid Augments Ursolic Acid-Induced Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cells through Enhanced oxidative stress and autophagy
- Ursolic Acid Induces Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells via the PI3K/Akt/mtor Pathway
- Ursolic Acid Activates Intracellular Killing Effect of MacrophagesDuring Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection
- Ursolic acid, a potential anticancer compound for breast cancer therapy
- Ursolic acid improves podocyte injury caused by high glucose
- Ursolic acid in health and disease
- Ursolic acid attenuates temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma cells by downregulating O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) expression
- Activation of AMP‐activated Protein Kinase and Phosphorylation of Glycogen Synthase Kinase3 β Mediate Ursolic Acid Induced Apoptosis in HepG2 Liver Cancer Cells
- A phase I pharmacokinetic study of ursolic acid nanoliposomes in healthy volunteers and patients with advanced solid tumors
- Ursolic acid stimulates lipolysis in primary‐cultured rat adipocytes
- Effects of ursolic acid on glucose metabolism, the polyol pathway and dyslipidemia in non-obese type 2 diabetic mice
- Ursolic acid prevents augmented peripheral inflammation and inflammatory hyperalgesia in high-fat diet-induced obese rats by restoring downregulated spinal PPARα
- Ursolic Acid Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis, Fibrosis, and Insulin Resistance by Modulating the Circadian Rhythm Pathway in Diet-Induced obese Mice
- S1833 Ursolic Acid Ameliorates Dietary Steatohepatitis in obese Diabetic Kk-aY Mice
- [P8-168] Effect of Ursolic Acid on Immune Response and Pancreatic ß-Cell Function in Non-obese Type 2 Diabetic Mice
- Beneficial Effect of Ursolic Acid on Lipid Metabolism via Altered Plasma and Hepatic Lipid Profile Levels and Hepatic Transcriptional Response in Diet-Induced obese Mice
- Amelioration of obesity and Glucose Intolerance in High-Fat-Fed C57BL/6 Mice by Anthocyanins and Ursolic Acid in Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas)
- Ursolic Acid Increases Skeletal Muscle and Brown Fat and Decreases Diet-Induced obesity, Glucose Intolerance and Fatty Liver Disease
- Ursolic Acid and Chronic Disease: An Overview of UA’s Effects On Prevention and Treatment of obesity and Cancer
- Ursolic Acid Inhibits Leucine-Stimulated mtorC1 Signaling by Suppressing mtor Localization to Lysosome
- The combination of ursolic acid and leucine potentiates the differentiation of C2C12 murine myoblasts through the mtor signaling pathway
- A comparison of the effects of ursolic acid and l-leucine supplementation on IGF-1 receptor and AKT-mtor signaling in response to resistance exercise in trained men
- Ursolic Acid Attenuates High Glucose-Mediated Mesangial Cell Injury by Inhibiting the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mtor) Signaling Pathway
- Ursolic acid attenuates diabetic mesangial cell injury by up-regulating autophagy via suppressing miRNA21-PTEN-Akt-mtor pathway
- Inhibitory effects of ursolic acid from Bushen Yijing Formula on TGF-β1-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell fibrosis via AKT/mtor signaling and Snail gene
- A comparison of the effects of ursolic acid and L-leucine supplementation on markers of muscle protein synthesis via Akt-mtor signaling response to resistance exercise.
- Ursolic acid attenuates oxidative stress in nigrostriatal tissue and improves neurobehavioral activity in MPTP-induced Parkinsonian mouse model
- Influence of oxidative stress on the antibacterial activity of betulin, betulinic acid and ursolic acid
- A bioinformatic and mechanistic study elicits the antifibrotic effect of ursolic acid through the attenuation of oxidative stress with the involvement of ERK, PI3K/Akt, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in human hepatic stellate cells and rat liver
- Oral supplementation with ursolic acid ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury in a mouse model by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammatory responses
- Effects of ursolic acid on oxidative stress and apoptosis in focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats
- Suppression of Tumor Promoterinduced inflammation of Mouse Ear by Ursolic Acid and 4, 4-Dimethylcholestane Derivatives
- Ursolic acid ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats
- Ursolic Acid, a Natural Nutraceutical Agent, Targets Caspase3 and Alleviates inflammation‐Associated Downstream Signal Transduction
- Effect of Ursolic Acid on Metabolic Syndrome, Insulin Sensitivity, and inflammation
- Ursolic acid improves diabetic nephropathy via suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation in streptozotocin-induced rats
- Renoprotective effects of ursolic acid on ischemia/reperfusion‑induced acute kidney injury through oxidative stress, inflammation and the inhibition of STAT3 and NF‑κB activities
- Ursolic Acid Ameliorates inflammation in Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury Possibly via High Mobility Group Box 1/Toll-Like Receptor 4/NFκB Pathway
- Ursolic acid alleviates inflammation and against diabetes‑induced nephropathy through TLR4‑mediated inflammatory pathway
- Ursolic acid, a potential PPARγ agonist, suppresses Ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness
- Ursolic acid suppresses leptin-induced cell proliferation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells
- Abstract: P1422 CARNOSIC ACID & URSOLIC ACID (ORIGANUM MAJORANA L.) PREVENT ATHEROSCLEROSIS CAUSED BY OBESITY: SUPPRESSION OF leptin-INDUCED PROLIFERATION IN VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS
- Effect of ursolic acid on leptin-induced JAK2-STAT3 activation and reactive oxygen species generation in hepatic stellate cells
vitamin D3 (From 7-Dehydrocholesterol)
- Vitamin D3 Induces autophagy in Human Monocytes/Macrophages via Cathelicidin
- Vitamin D3 Induces autophagy of Human Myeloid Leukemia Cells
- Hormonally Active Vitamin D3 (1α,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol) Triggers autophagy in Human Macrophages That Inhibits HIV-1 Infection
- Dual functions of autophagy in the response of breast tumor cells to radiation
- Potentiation of radiation sensitivity in breast tumor cells by the vitamin D3 analogue, EB 1089, through promotion of autophagy and interference with proliferative recovery
- Vitamin D3 supplementation alleviates rotavirus infection in pigs and IPEC-J2 cells via regulating the autophagy signaling pathway
- autophagy induced by vitamin D3 inhibits the proliferation of human bladder cancer cells
- Abstract 2663: Dual cytoprotective and cytotoxic functions of autophagy in the response ofbreast tumor cells to radiation and in radiosensitization by vitamin D3
- Relation of obesity with serum 25 hydroxy vitamin D3 levels in type 2 diabetic patients
- Vitamin D3 supplementation and body composition in persons with obesity and type 2 diabetes in the UAE: A randomized controlled double-blinded clinical trial
- Vitamin D3: A Role in Dopamine Circuit Regulation, Diet-Induced obesity, and Drug Consumption1,2,3
- 25OH-Vitamin D3 Levels in obesity and Metabolic Syndrome—Unaltered in Young and not Correlated to Carotid IMT in All Ages
| Size | 25g, 50g, 100g |
|---|
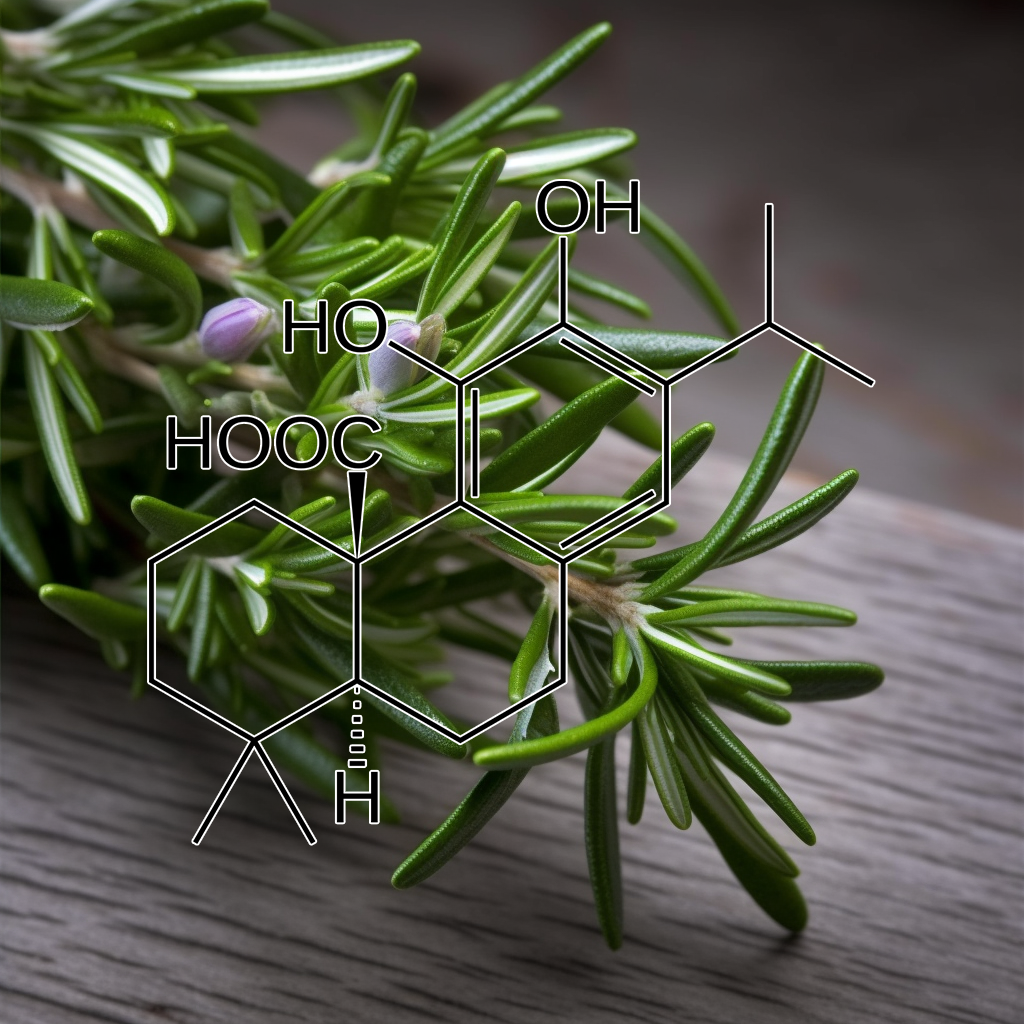
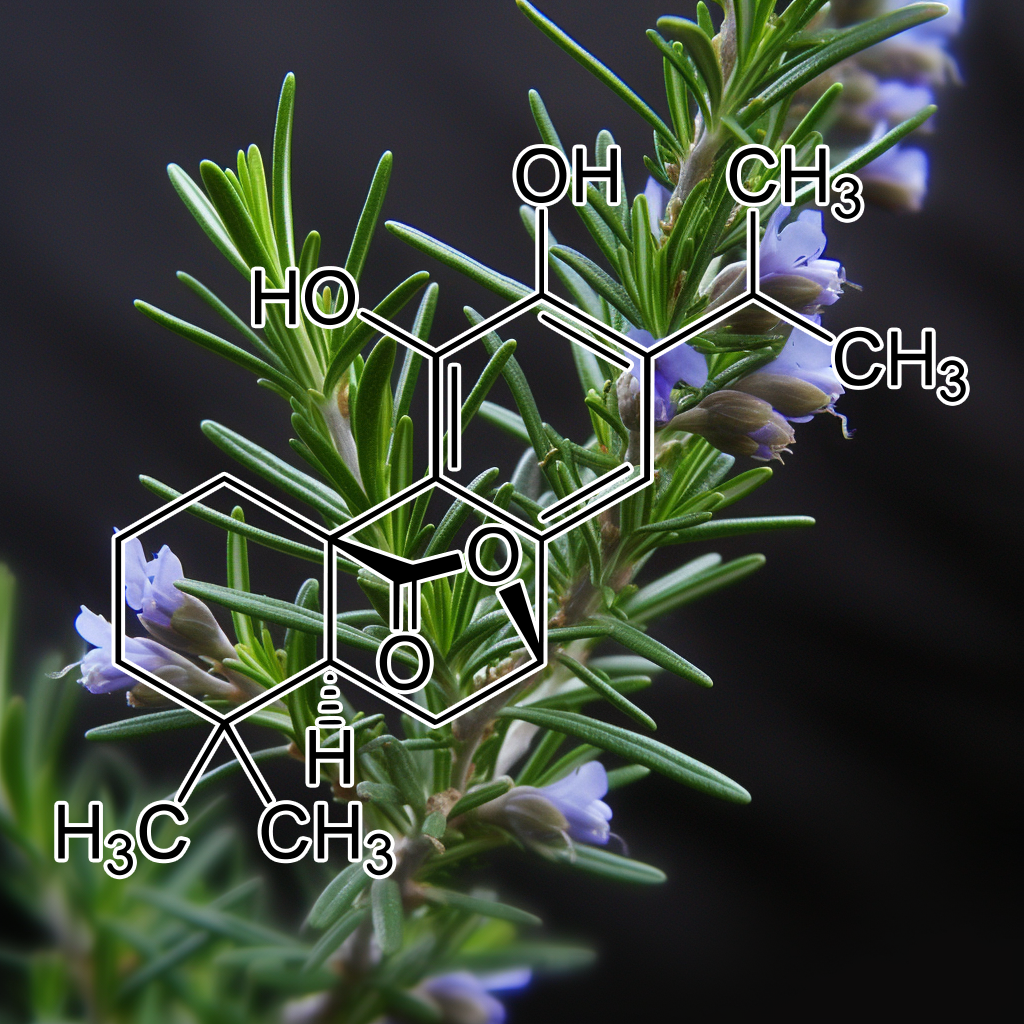
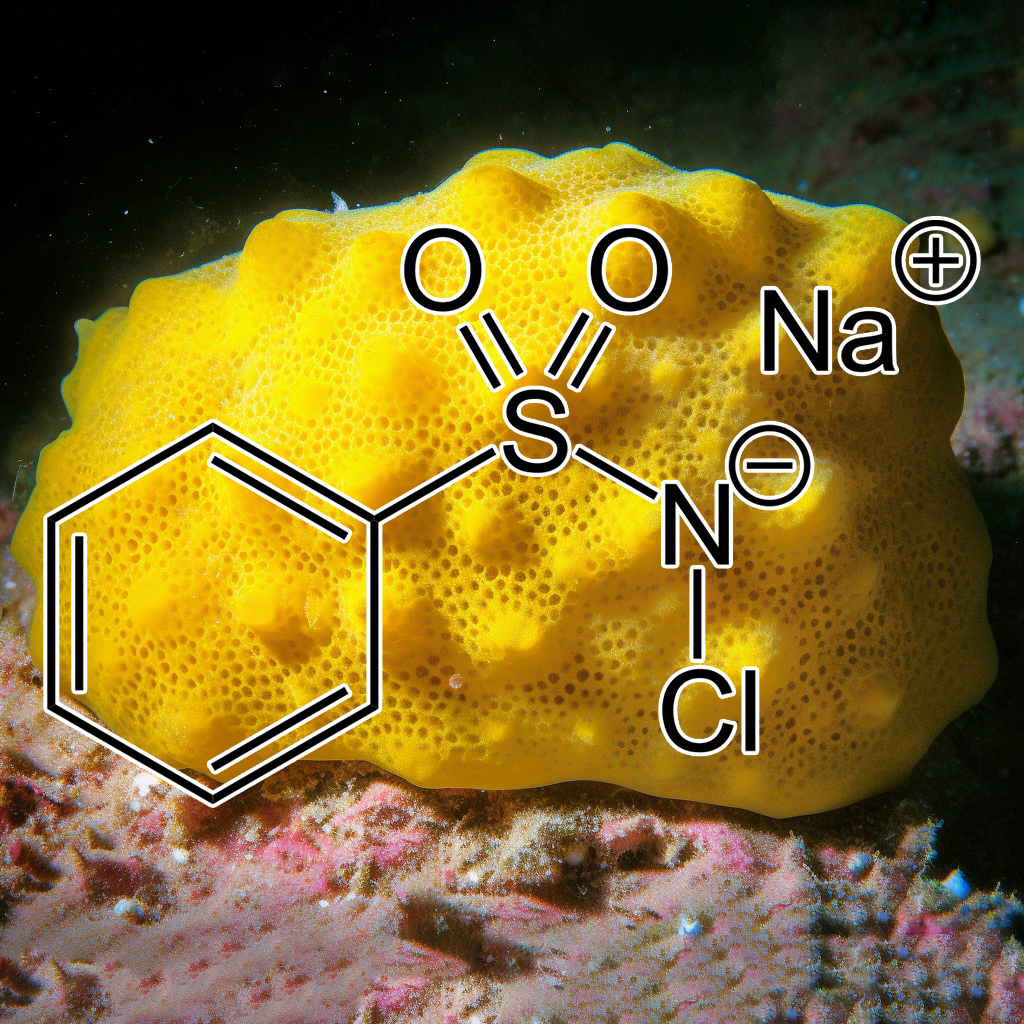
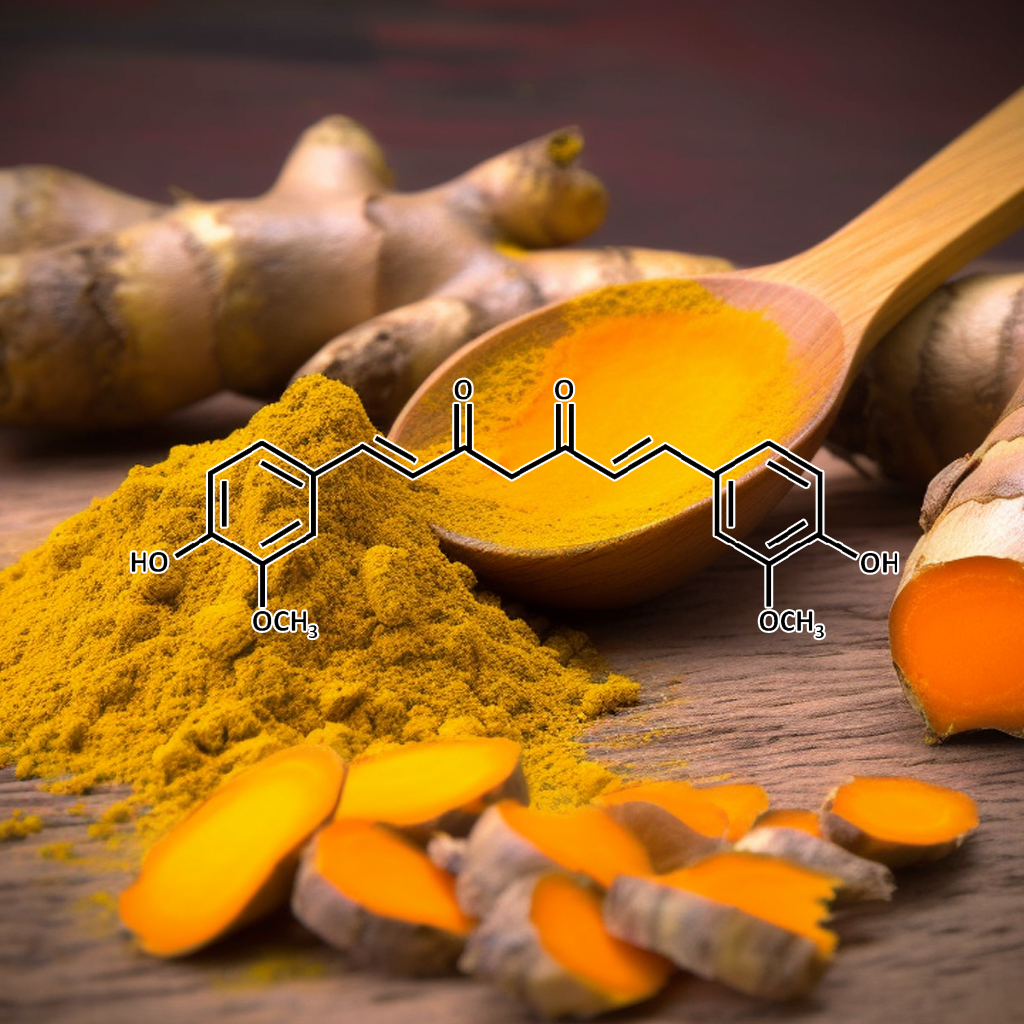
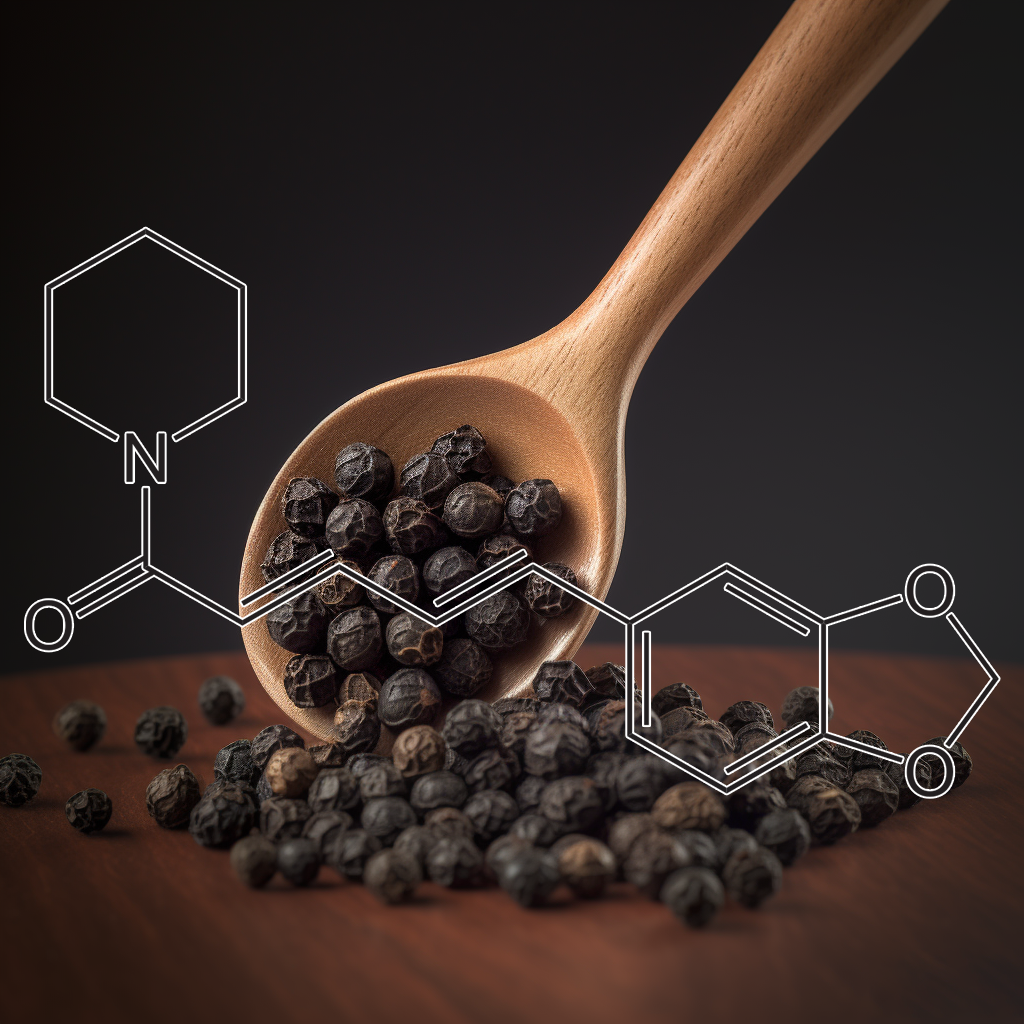
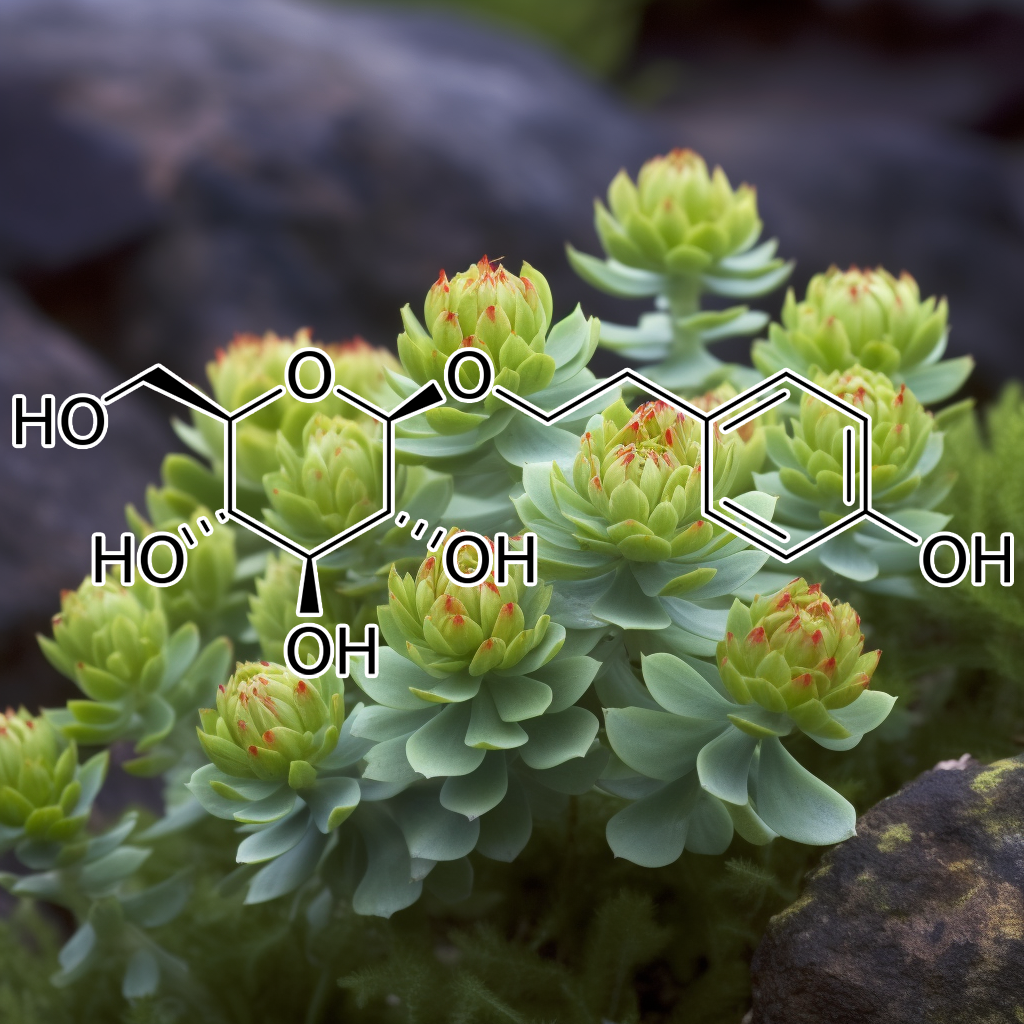




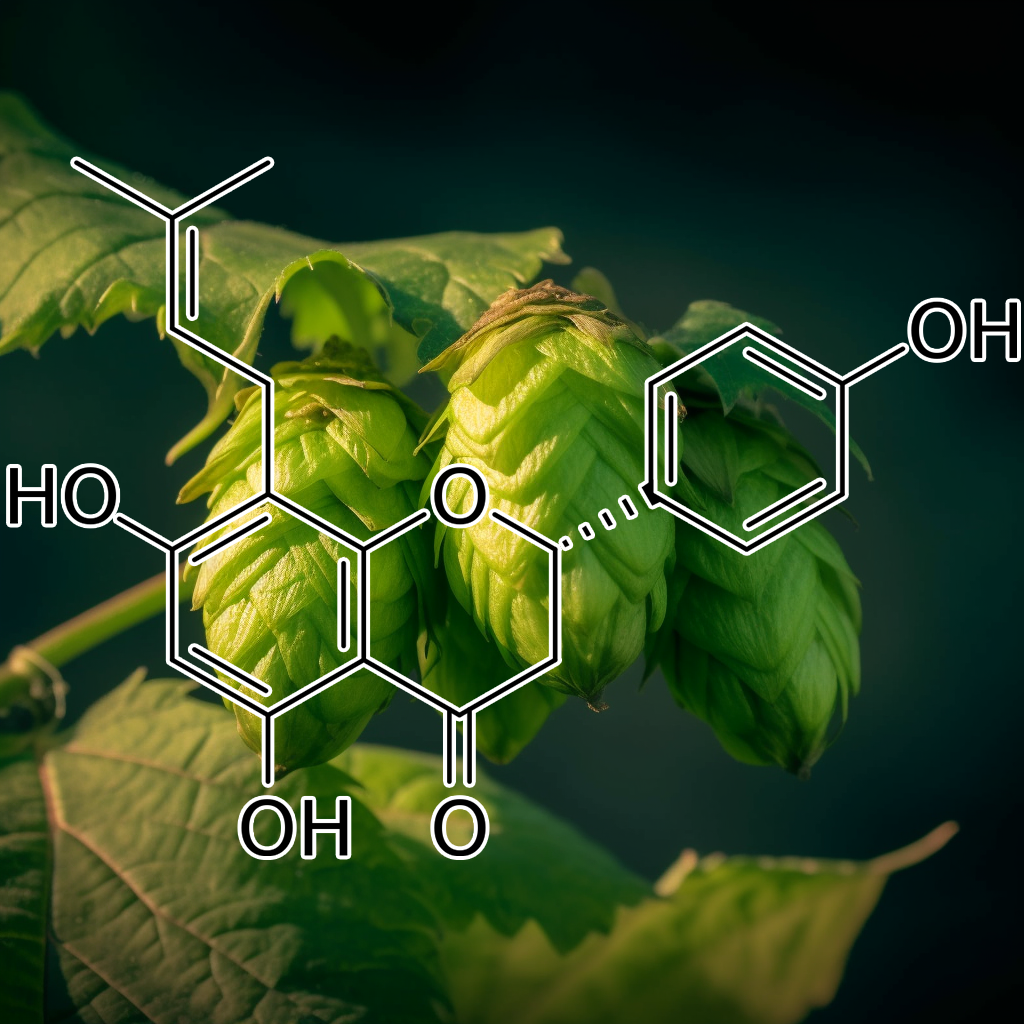

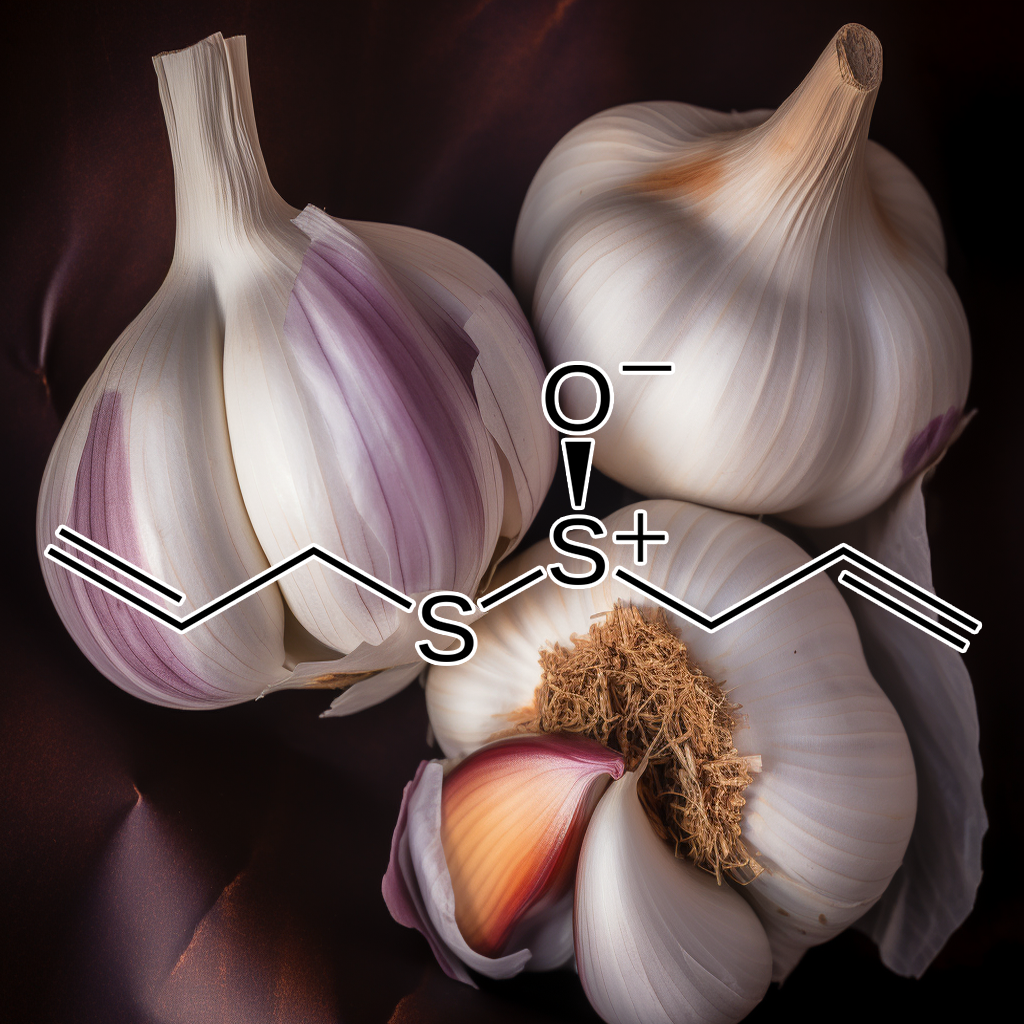









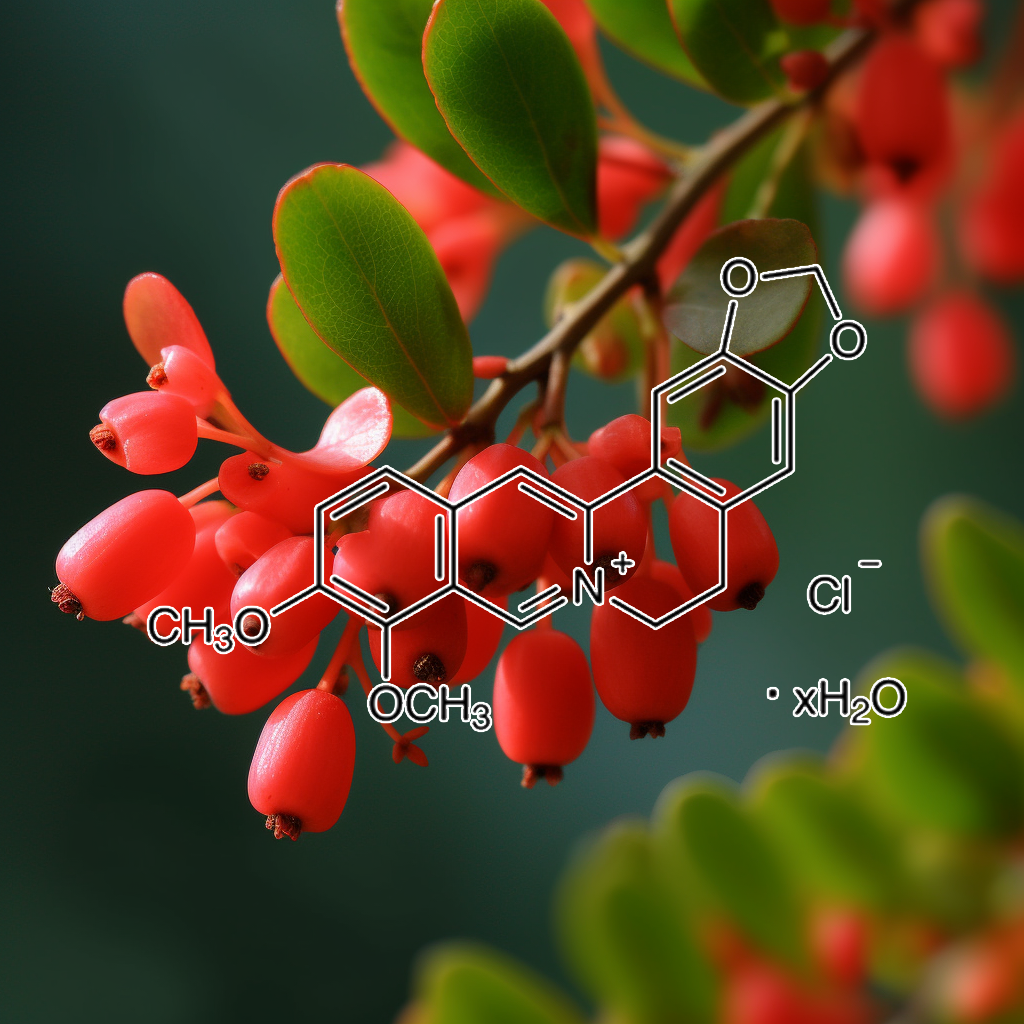
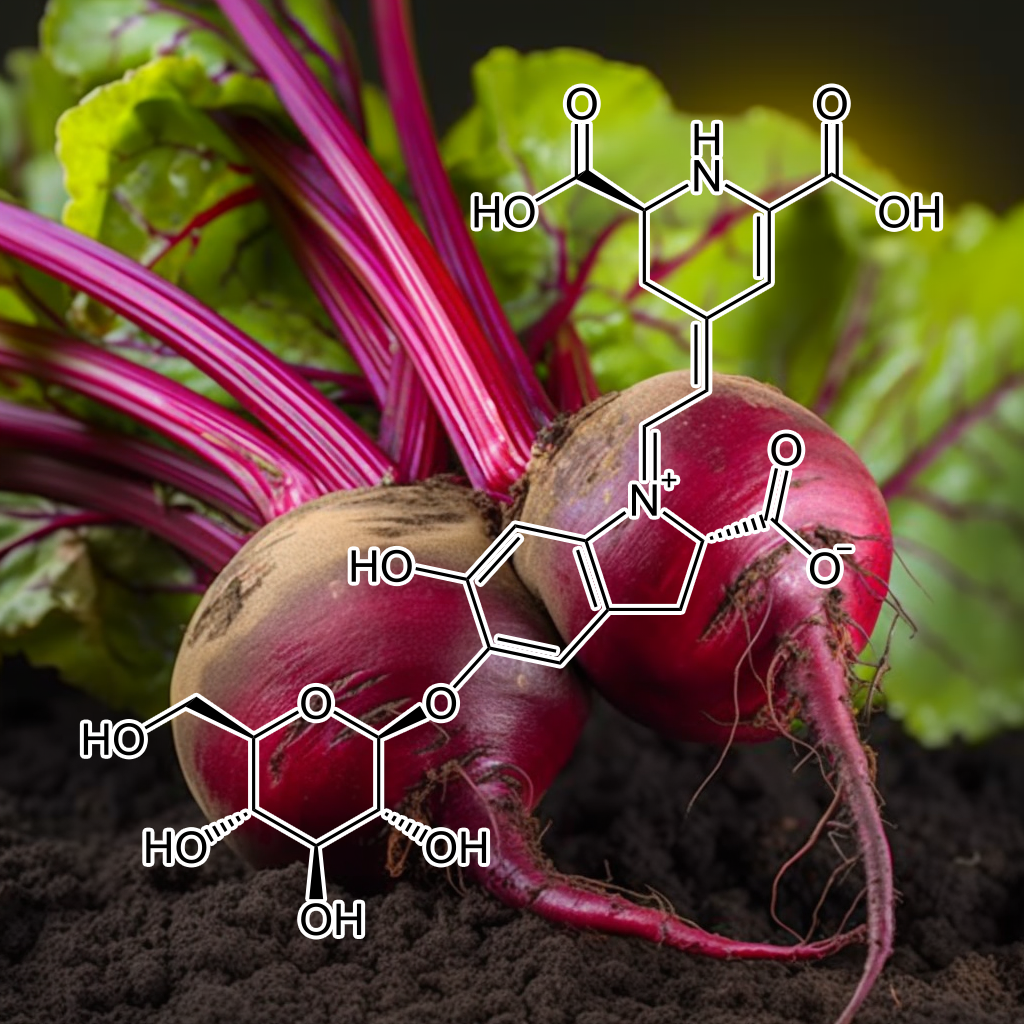






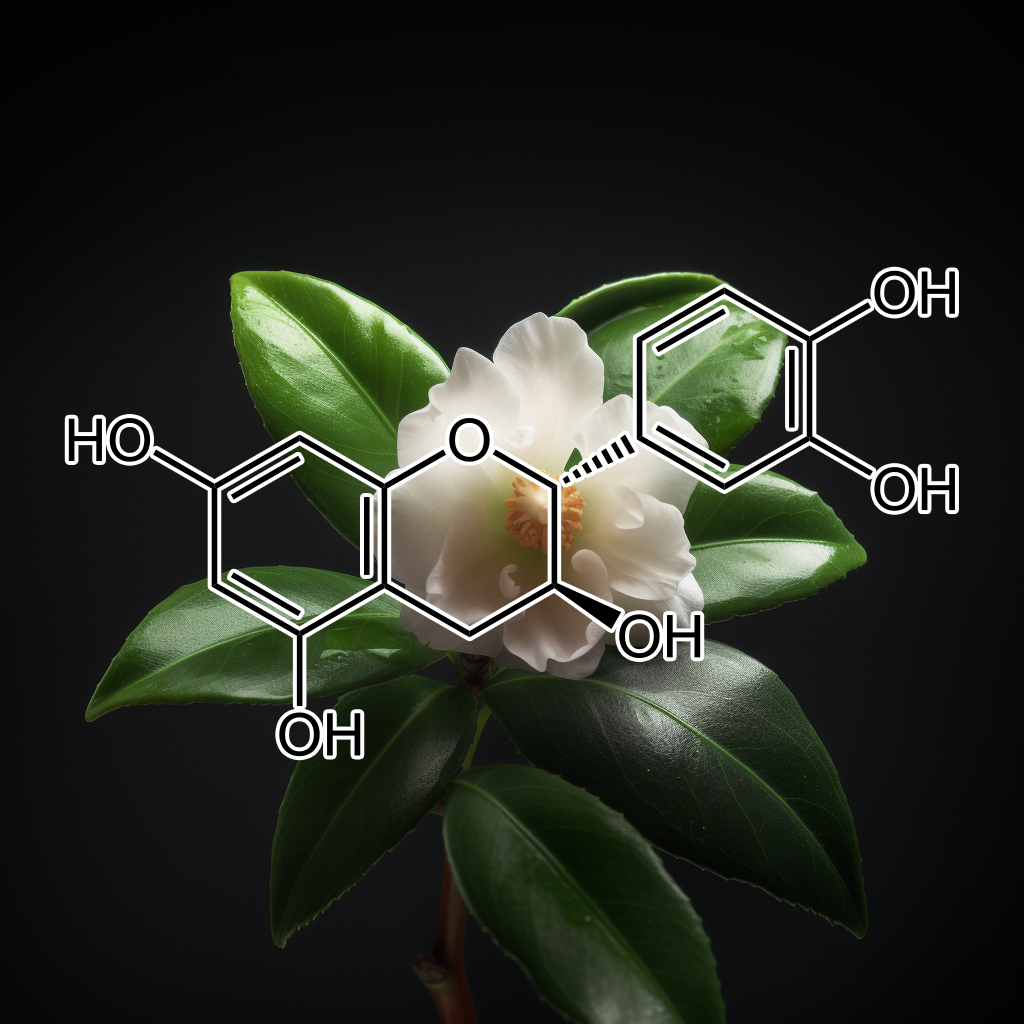
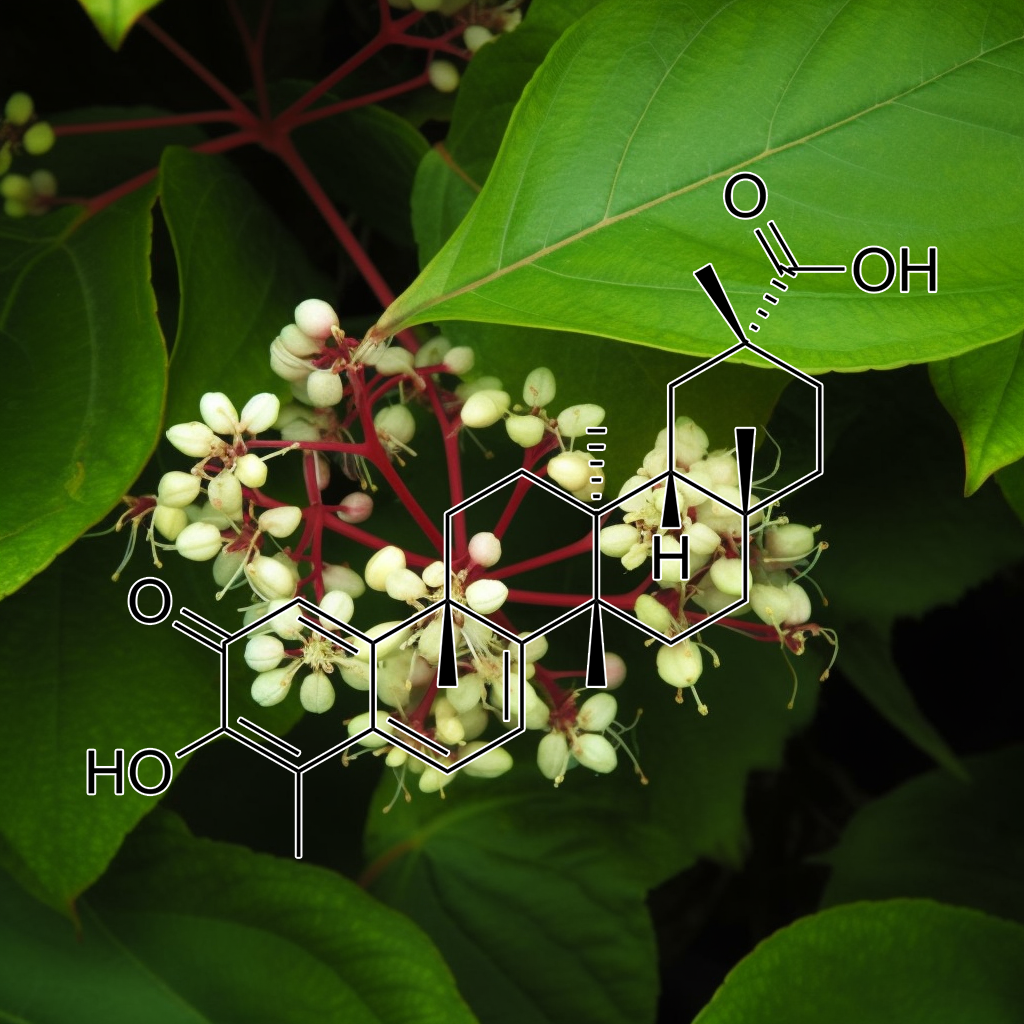
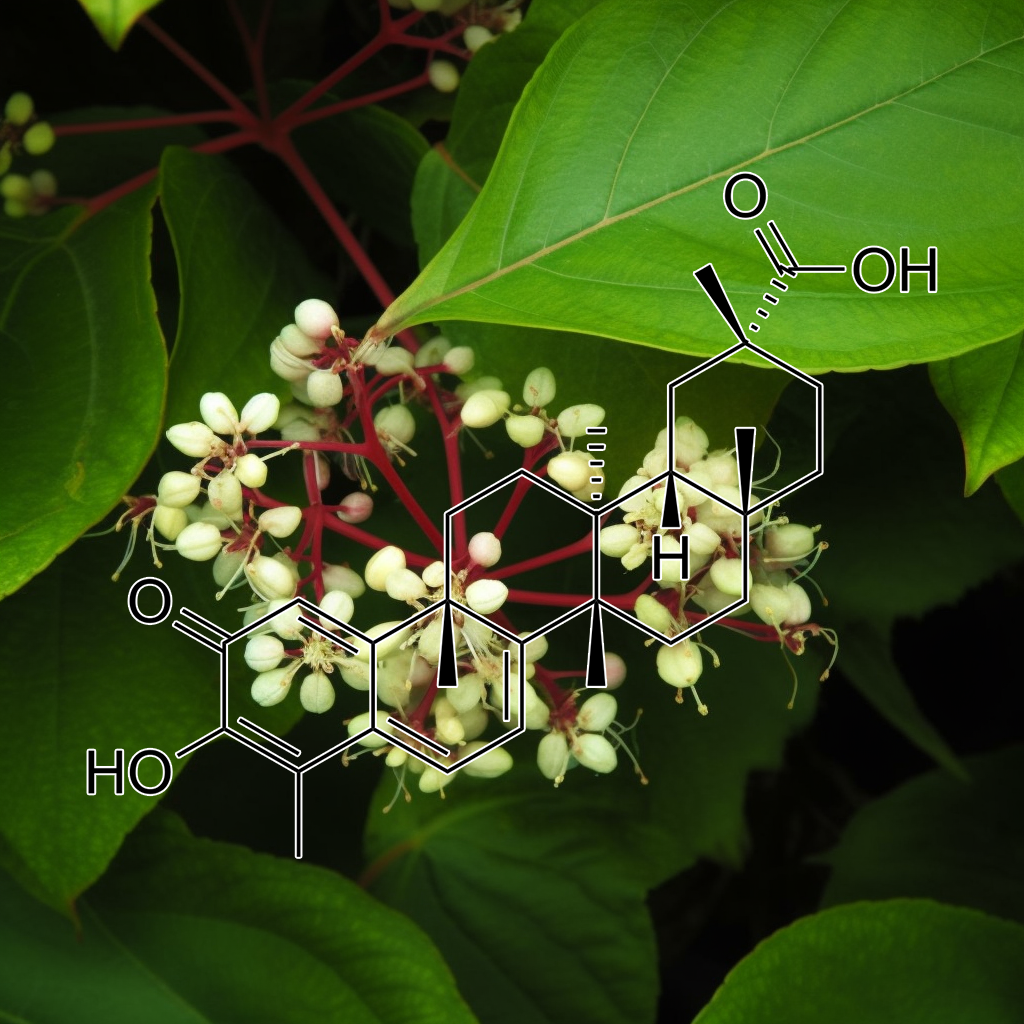





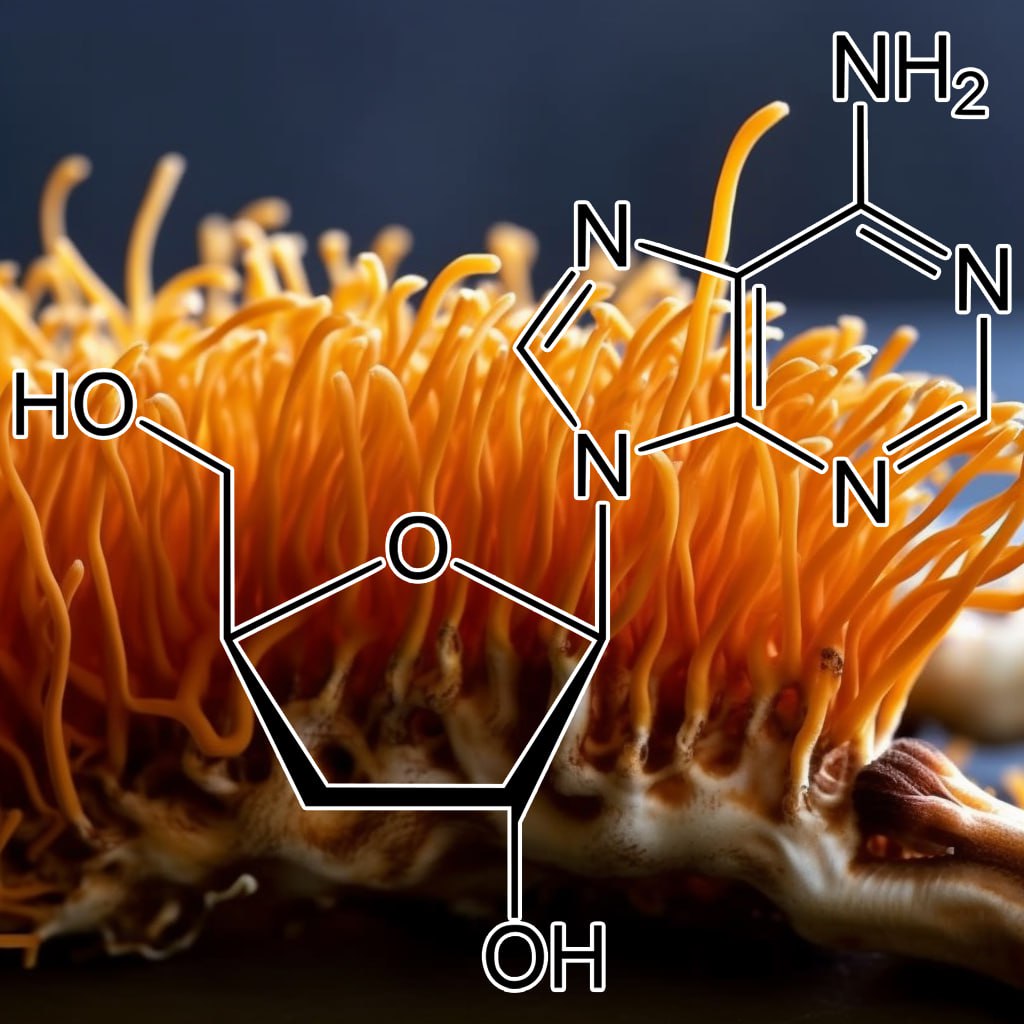




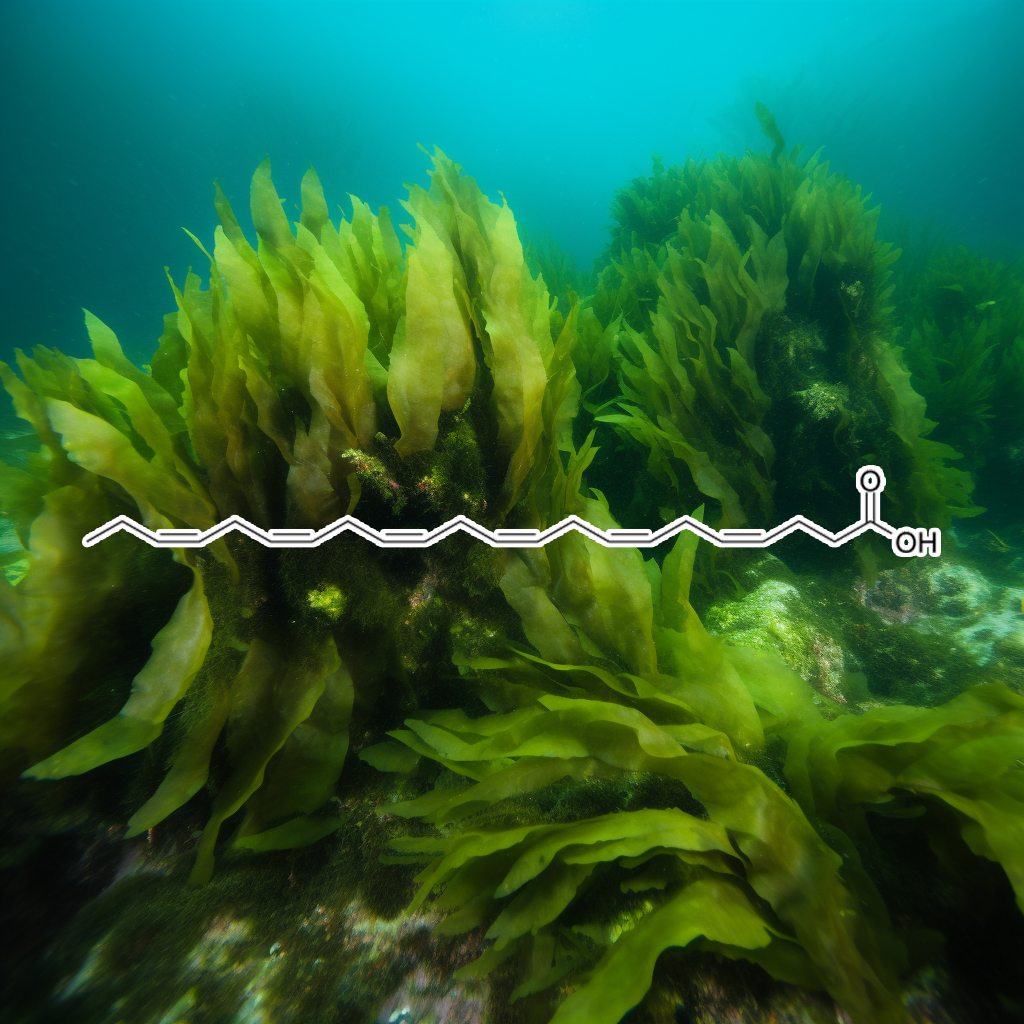


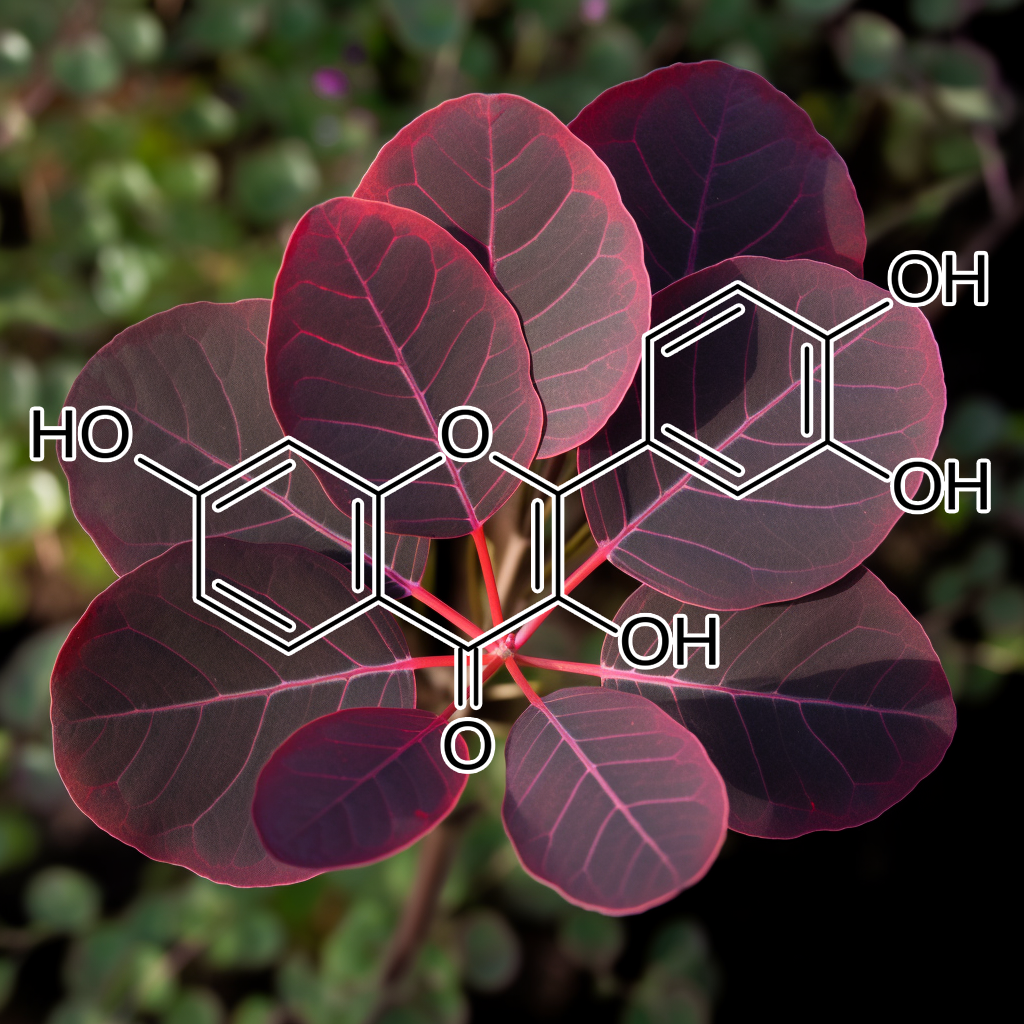



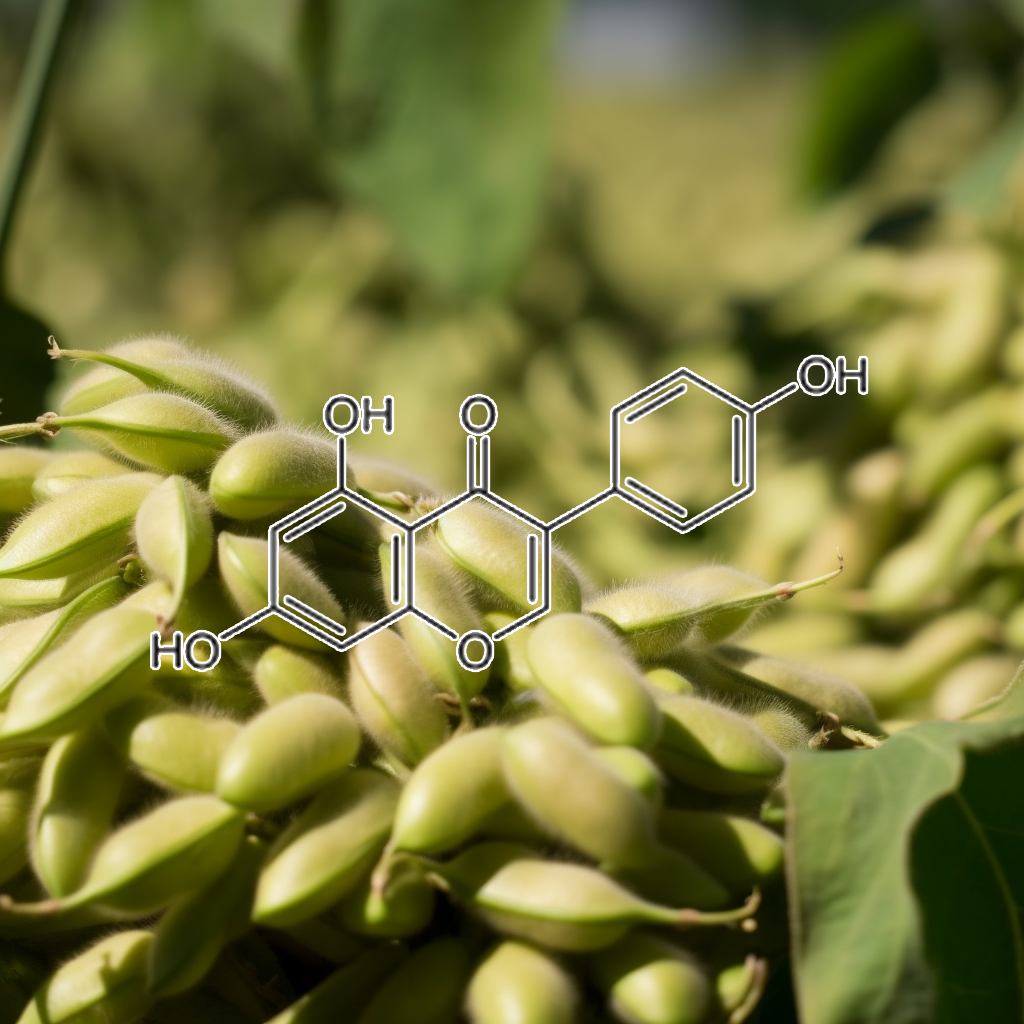

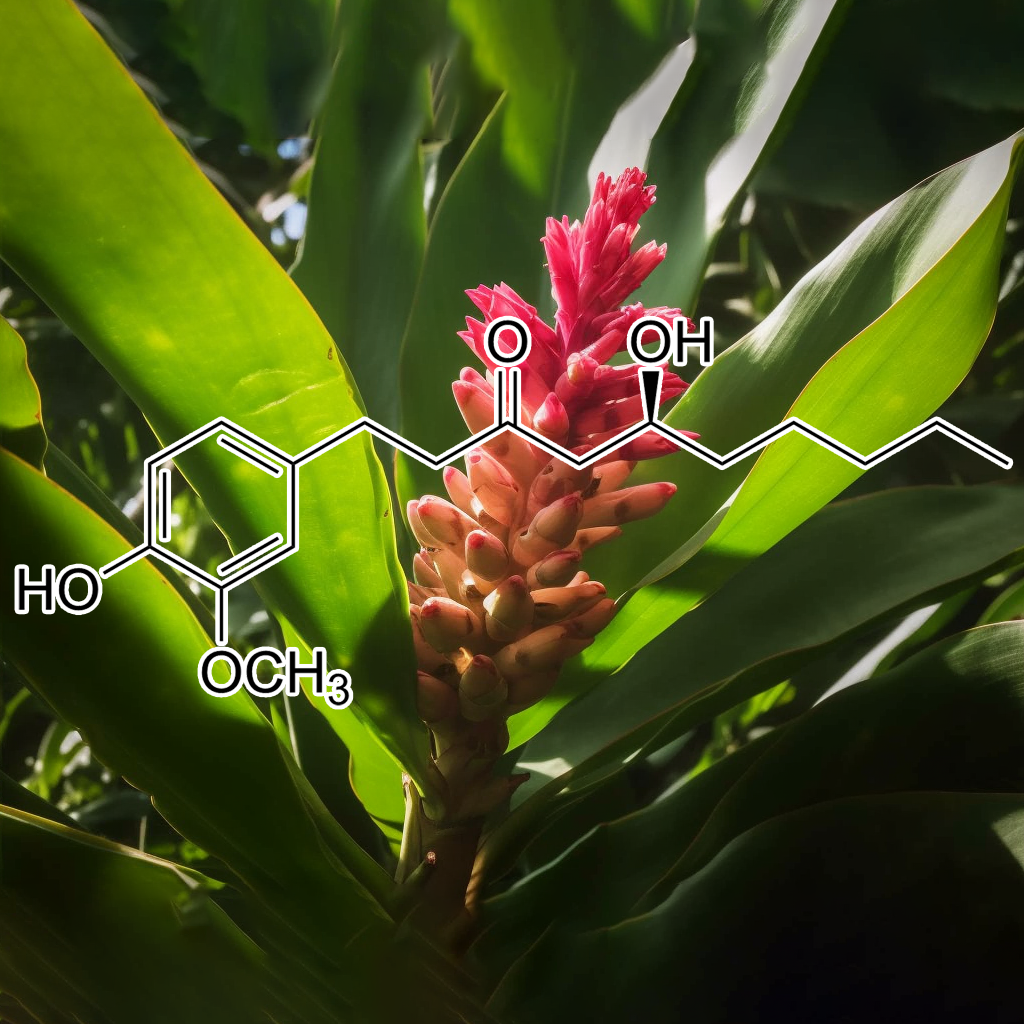



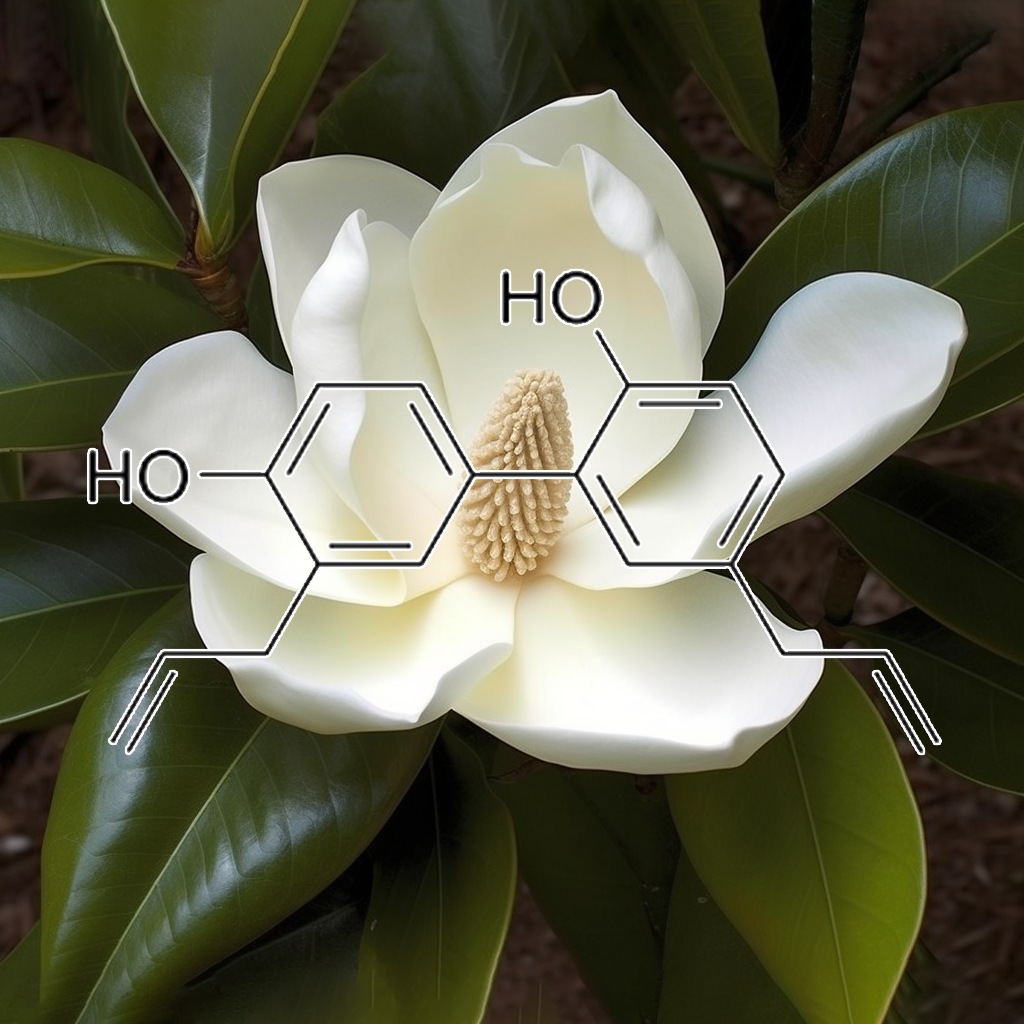
















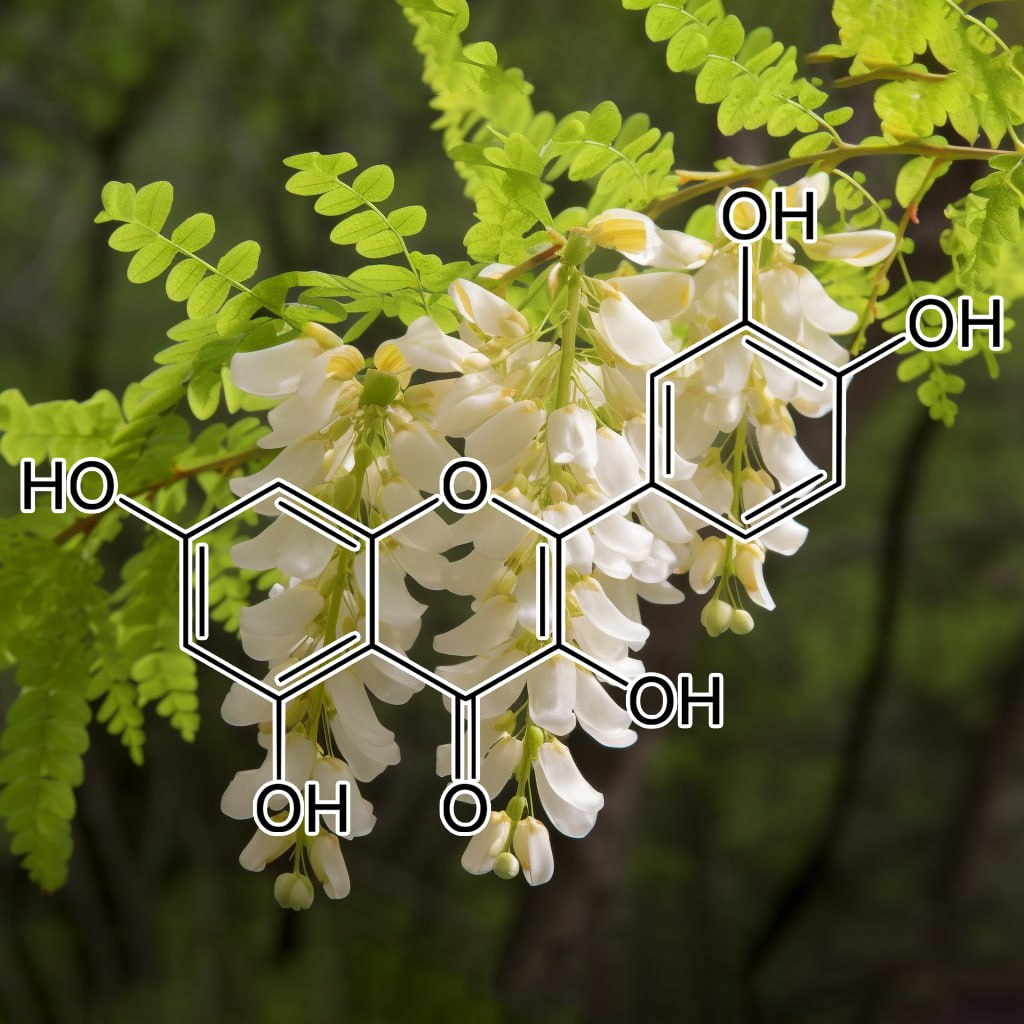













ziva avitan –
WOWZA, if you haven’t tried Autophagy Activator yet you have to. I received it as part of the special running now.
I contacted Gavin through facebook thats how I found this magician, my main concern was my pre menopause hot flashes, I would wake up 3/4 times at night sweating really bad; took me a long time to fall back asleep and again woke up sweating, just AWFUL nights; I didn’t wanna reach for hormones that my doctor recommended.
Let me tell you its been 10 days now, no hot flashes anymore, lost 10 lbs, lots of energy I’m not hungry to the point you look at food and think, “Will I ever crave bad food AGAIN??”scary?
My husband think I’m gone die soon cos im not eating like I used to ?but I eat what Gavin recommends- sardines greens, beets and more from the list,
I’ll message him every time I have questions and he answers no mater what time it is.
Cant wait to see what else I will benefit out of the blends!!!!
Thank you very much Gavin !!!
Rich Ryan –
This is Gavin’s most incredible blend yet. If you take this blend and then try and go stuff your face, you’re going to have a bad time. You’re not going to get your money’s worth at all-you-can-eat buffets anymore. If you try and force it, then things get very uncomfortable. Your body simply rejects big meals. I tried to power down a big dinner the other night and forgot I had taken this blend that morning. I felt so sick and uncomfortable trying to force myself to eat more food. Unreal! I’ve always been like Garfield with food, but not with this blend. It’s the first time in my life that I don’t feel like binge eating anymore. Incredible! Take a dose in the morning, eat keto (low or zero carb) and you’ll barely feel hungry. Food just doesn’t interest anymore. I’ve never come across an appetite suppressant blend like this. You’re going to have to plan your daily meal carefully otherwise you won’t be able to finish it. It cuts your food intake by about half.
Tanya Boldoczki –
First I want to say that I am fortunate to take a large majority of the blends offered. It is therefore difficult to pinpoint one specific result to one specific blend, but I do believe that ALL of the blends have contributed to the great results which I am about to share.
I think often times we notice more when things are wrong or bad rather than taking notice when things are good. But if you are aware and present, if you start to pay attention, you will see that these blends impact SO MANY areas of your life.
Here are a few examples of how these blends have impacted me. Perhaps Gavin can comment on the specific blend associated
1. I used to struggle with cold sores on my mouth and nose (herpes virus). I would get them every month or two due to stress or too much sun. I believe it has almost been a year since having one. Even when the conditions arose to get one I might feel the sensation of one but magically they would never appear and the feeling would dissipate quickly.
2. My skin has greatly improved. I had an age spot on my hand (I WISH I would have taken a before and after picture because it is incredible). I was self conscious about it because it made me look and feel older than I was. It is now gone. In addition, the sun spots and freckles on my arms and legs are much less. Even my aesthetician has had to increase my facial frequency because she said my cell turnover is just so much higher than it used to be. Another interesting thing that happened – and this would have to do with rapid healing but I recently had to have stitches. When I went in to have them removed the doctor commented that he had never seen anything like it. My skin and wound had healed so quickly and nicely that it had completely healed OVER the stitches. He had to access them for removal with an incision. ?
3. I stopped taking thyroid medicine when I started taking blends. This has probably been two years now. I recently started taking luteolin from Interstellar and after a new blood test, my Thyroid levels are the best they have ever been (although borderline) and quite honestly I feel no side effects of Hypothyroidism
4. I am happier and less stressed. This is subtle but noticeable. Even my husband has commented that I have a new energy and peace about me. And truthfully I just feel like smiling and laughing more.
There is more that I can say but these reviews can get lengthy.
….I did take Autophagy this morning. I’ve been doing longer fasts and plant based feeding windows to improve my gut bacteria and I’ve struggled a bit with hunger. Today is different. I am not hungry per usual.
Also just a little tip: Make a Matcha smoothie!! Wow! It’s my new staple. Nut milk, Stevia, flaxseeds, spinach, and a good scoop of Matcha. It’s life changing ?
A’oi Bartholomew –
I was in the middle of a paranoid schizophrenic meltdown…. I took the Trinity and Seven Sages formulas and it stopped my meltdown near instantaneously! I feel better now than I have felt in AGES! Profoundly grateful to Gavin for his life-altering blends and for his highly informative FB groups!! Thank you!!
Rhonda Wyatt –
Ok everyone this Autophagy Blend is life changing. I have been doing extended fasting for the past year. The first 3 days are always the hardest for me as I stay hungry and my moods are awful. The fourth day is when I finally get into the groove and can mellow out for the remainder of my fast. That being said I dont fast as often as I would like because of the mood swings in the beginning. This Autophagy Blend is a game changer. I have been taking it for two weeks, I take it four times a day and my last blend of the day I add an additional 1/8 tsp before going to bed. I never wake up hungry.
Since taking this Autophagy Blend I have gone back to doing 88/8 cycles back to back. No hungry, no mood swings, no cravings, no binges. I think this is Gavin’s best blend to date and I will never be without it. I feel more relaxed, probably because my mood swings have vanished and I am actually enjoying fasting. I have also had more energy during my fast. Not sure if its from the Autophagy blend or if its enhancing my other blends but I look forward to my 4-6 mile walk everyday now and during my walk instead of wishing I was done I find myself thinking about the positive results my walk is giving me , I am feeling stronger and my stamina has increased. I used to walk a mile in 20-22 minutes but now I am walking a mile 16-17.5 minutes and I do several sprints in between each mile. I am definitely experiencing more joy in each day. The only change I have made is adding the Autophagy Blend so I know this is the reason.
Trust me and just get it and try it if you want to up your game when fasting. I promise you will not be disappointed. This is a total game changer and I believe this blend will help me reach my next fitness level I have been struggling to achieve. Thank you Gavin you have outdone yourself on this one!
Alyssa Zinsman –
Ive been taking the new autophagy blend for a week and I love it! It’s the definition of appetite suppressant! I eat about half of what I normally would. I’m not craving junk or much of anything but water. It’s also clearing my bowels amazingly!! I feel this is the answer to still enjoy food but have your portions in check with this blend. Definitely will have this in my daily blend routine for life.
Thank you for all you do!!
Teri –
I am grateful to be able to have tried most of the blends. My first one was peel. After doing keto faithfully for over a year I was stalled no matter what I did. The peel was a miracle and bumped me to the next level. The weight fell off and I reached my goal. This remains one of my favorites. I added blends for other issues along the way and each really targets something different. Overall my mood, sleeping, brain fog, fatigue etc have all improved so much.
When I lost my job of 23 years my first thoughts were how will I pay my mortgage and how will I afford the blends. May seem like a strange reaction to some but I couldn’t fathom going through such a difficult situation without the blends knowing all those mood swings and anxiety would return. Thankfully I didn’t have to and a year later it all work out awesomely.
Now for the new blend autophagy…OMG what an amazing addition. I have always had to deal with weight issues and binge eating. It will be my life long battle. Sometimes I get off track and struggle to get back. This happened lately and I was having a hard time no matter what I tried. I got autophagy last week and again it proved to deliver success. Normally I always feel hungry, even when sticking to my regimen truth is I could always eat. This blend shut that down. For once in my life I wasn’t hungry. It doesn’t make you jittery or anxious it just shuts down the hunger. In 6 days I was able to lose the 9 pounds I gained falling off track. This stuff is a game changer and I never want to be without it. Thank you Gavin for all the research and guidance it is truly appreciated!!
Serhat Dereli –
Autophagy review:
This blend is truly a creation. I cannot give enough credit for this blend alone in this review, as it really is something you need to experience for yourselves! The Autophagy blend has changed how I feel since since the first dose, I’ve noticed a huge decrease in my appetite and an intense sense of well-being each day I take it, my sleep is a lot more restful and I’m a lot more in tune, focused and awake during the day, even on days where I may not have slept enough. This blend is really something special and has had such a huge positive impact on me in such a short period of time using it, I can understand why it’s sold out before its been put on sale even! I’ve noticed each day of using the Autophagy blend my appetite is decreasing to a point where fasting is now so much easier to do for extended periods of time, they have minimised the side effects of the first 24hours of the fast, to a point that makes fasting a breeze to maintain. The blends start to work immediately I find and provide me with an uplifting sense of well-being which motivates and pushes me to start my day on the right path! Cannot thank Gavin enough for this amazing blends and I can’t wait for time to unveil the many health benefits this blend will further provide me with.
DeJa Diana Mitchell Stelzer –
After following Gavin on Facebook for a few months, I decided to jump in. I purchased the largest package of blends.
I am 61 years young. I have been health minded all of my adult life and I have managed to stay off of all medications.
Still life happens! I have been in several serious auto accidents starting at 6 years old. I have had several closed head injuries, much scaring within the fascia throughout much of my body.
20 years ago I was in auto accident which left me with fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue as well as a host of other issues.
Over time with a healthy diet, fasting, herbs and supplements many of the issues have improved and I have been able to manage.
I am always looking for solutions and improvement!
I began taking the blends just a few months ago, ( May 2019)
Within a few weeks the fibromyalgia symptoms had improved 90%.
A month into taking the blends I began 22/2,44/4 66/6 and 88/8.
I needed to lose 20 pounds to be at my lowest healthy weight. With the blends, fasting is SO easy and I dropped the 20 pounds in 1 month.
About the same time I added Super Nova, with this blend the chronic fatigue became a thing of the past for me.
Next I added Luteolin, I notice within three days of adding Luteolin that my flexibility increased dramatically.
The following month I added Super Hair blend.
I have always been blessed with good hair,
However my hair is the thickest, strongest and shiniest it has ever been.
I added Autophagy blend a few weeks ago.
This blend COMPLETELY takes hunger away.
The first couple of weeks I only took it once a day because that’s all I needed to eliminate hunger. However in the last week I began taking it 4 times a day. I knew this blend did other things besides eliminating hunger so I decided to experiment. After the first day of taking Autophagy 4 times a day, I began feeling areas of my body heating up to the point of slight burning.
It wasn’t painful but enough to take notice.
Every area that I felt this heating up, is an area of internal scaring. So I KNOW healing is taking place!
My skin is softer, smoother and is more toned. Age spots are fading. Wrinkles and lines are diminishing.
My experience with the Interstellar Blends is the Blends rebuild your body from the inside out.
Things within my body that I hoped would be repaired is being repairing.
Things that I didn’t know needed to be repaired is repairing.
And things that I thought couldn’t be repaired is being repaired.
My friends comments are…
You look great, you looked good before, but you look great now!
Your getting younger!
You glow!
You Sparkle!
The transformation that takes place is not only physical, it’s also mentally, emotionally and spiritually.
In 2017 I had a great and unexpected loss, leaving me experiencing more grief, sadness and sorrow than I thought was possible to endure. I managed to function and continue on with life by focusing on graditute.
A few weeks of taking Interstellar Blends, I noticed that even though I was still experiencing sadness the emotional pain attached to the sadness was gone. This is HUGE. I didn’t even know that this was possible.
Two months into taking Interstellar Blends I attended my twin Grandsons birthday party.
I share these Grandsons with my first husband which was also attending the party.
The ending of my first marriage took place 36 years ago, however it was filled with trauma that continue both for my (now grown) son and myself for several years. Even though much time has past, and much healing and forgiveness has taken place. I still always experienced a sense of dread when I am going to be in the presence of my first husband. After leaving the birthday party I became aware this time there was NO dread.
This is HUGE.
I am SO grateful for Gavin’s BRILLIANCE and his COURAGE to share it with the world, so that we may BENEFIT!
Joy Mollnar –
I received the Autophagy and peel blends just a few days ago and all I can say is WOW. I have been suffering from arthritis due to old injuries from years of weight lifting, auto accidents, painting murals, etc… This had caused me to to put ME on the back burner. After seeing so many others benefit from the blends, I finally gave in. I chose the autophagy blend because I read about the appetite suppressant effects it had on others. The Peel blend was chosen bc I want the glowing skin that all blend users are raving about!
The first morning I took it, I mixed both with just a bottle of water. It was an almost immediate rush of energy. Not the nasty stimulant kind either. I went on to complete a full day of working outside in 98 degrees. I actually forgot to eat and was not hungry all day! I had to actually force myself to eat dinner. This is unheard of as I LOVE to eat, lol.
It is now day four since I’ve been using the blends and my appetite has shrunk, my energy levels are through the roof, my aches and pains have drastically gone down, and I am up and at em in the morning with a new zest for life.
I also wanted to point out that I have suffered from tightness in the chest for years now. I chalked it up to anxiety and kind of just expected it to always be there. Especially at night. I would literally feel my heart beat through my ears until I fell asleep. Wellll folks, it’s so weird because that feeling is completely gone! Poof! Even if I try to stress myself out on purpose to emulate it, my heart is just steady as ever. No tightness whatsoever!
I can’t even wait to see what other ailments melt away. These blends are kick ass!
Gavin has put so much thought and research into every single ingredient. There is no way I’d ever be able to afford to buy or even FIND every single one by itself. This blend is a masterpiece, perfectly orchestrated like a piece of fine ass music ?
Bravo Gavin! Bravo
Judi Bahr –
Today is day 14 for me on Autogaphy. Early on I wasn’t sure I was feeling immediately what others felt, I just knew from my first dose I lost my appetite. GONE… just GONE!! Over the past 2 weeks it has had a cumulative effect on me. I’m not hungry, staying on point when I have something to accomplish, clear thoughts, my sleep is more restful, ( in the midst of personal turmoil) which for me is a small miracle in itself. I’m quite surprised how I’m handling it! I don’t know how he blends these, but I understand how he can’t keep it in stock! At times the thought of eating another bite… makes me nauseous. Me??? Not want want to eat? My husband wants to know who took his wife???? No mood swings, no cravings, fasting is much easier, mental clarity.. energy….the list can go on….try this… you seriously will not be sorry.
18 months ago, I had never heard of dry fasting! ( where was my head ?????) I had been doing intermittent fasting/low carb and having small results. A dear friend was a member of Gavin’s group and added me. I was just blown away by what I was reading! Shortly after I joined I asked her if she had used any of Gavin’s blends. She had not…. but I decided to try them. Peel & Spice were the first I tried. Having just had a total hip replacement, I hoped they would help with healing….Damn!! Let just say I’m older than Gavin…. and I felt after 2 days on these 2 I could go to the club and keep up, if my new hip would cooperate of course. At my staple removal my surgeon commented how well I was healing! Could it be… the blends??? ?
I decided after I was released from my surgeon, I was going to try more blends, no 2 ways about it. When I went for my 3 month check up, my Dr could not believe how the incision had healed!
I decided that I was going to try & address my depression. Again … great results..off of anxiety meds and antidepressants after literally YEARS!!!! My only child suffered a near fatal accident when he was 18 and I had been on those meds since that time. He is now 36.. Do the math. In a matter of months I felt I could safely wean myself. I ordered more blends….and could only hope for similar results…. when I had blood work done 4 months after sticking my toe in the” BLEND sea”.. these were my initial results…
Dropped 11 pounds, completely off of blood pressure medication I’d been taking for 15 years, my cholesterol dropped 54 points. My physician attributed that drop to the “new statin” she had prescribed until I told her I never had the RX filled!!!!
When my hubby saw my results he asked if he could try My blends. I wasn’t sure I wanted to share, but relented. ? He has been prediabetic for years.
Wellllll … yep you guessed it.. Our personal PCP as well as his Dr’s at the VA told him he could no longer be considered pre diabetic. SCORE…. Of course we both made changes to our eating habits, small changes, we eat differently, and different foods but the common denominator for us was the blends!!!
This has been a tough year for me… 2 surgeries, my fathers passing, major surgery or hubby ( he had his hip replaced!!.. such a copy cat!) but I’m handling it. Some days more than others, and a friend who kicks my butt when I need it…
And Gavin..
You will never know how much you have helped me personally. I don’t know when the hell you sleep, because no matter when I contact you.. you always answer me. Without missing a beat. Your willingness to help virtual strangers is a gift to all of us, and I will be eternally grateful. Thank you for making this your life’s work. You’ll never completely understand my gratitude.
Thank you, thank you, thank you
Adele –
I’ve known Gavin for some time now. As a matter of fact, I started out buying the original blend. Over the years, I’ve added thermo, trinity, spice, peel, shilajit, pine pollen, matcha, luteolin and now most importantly Autophagy Activator. What I’ve come to trust and love about the blends is that I know Gavin well enough to understand that not only does he put the time in to research what will work best but the products that he uses top quality products in his blends.
He’s always been there to answer my questions no matter how silly and to also support me when I’ve needed assistance. Working with him, in conjunction with a functional medicine doctor has been the best thing for me but little did I know that the best thing was going to get better when I added Autophagy Activator. I cannot believe how easy it is too fast when I take this blend. AND… when I decide to break the fast, I get full and satisfied very easily.
If you’re looking for the support that you need to get your health on track, I recommend that you talk to Gavin and get up to speed about his various blends. He will not only recommend what he feels is best but he will support you in your adventure to wellness – whatever that means for you.
Arielle Hall –
Hi my name is Arielle and I am 29 years old. My parents have been using these blends for several months now. My husband and I would always joke / harass them that they were either doing drugs or selling them and that Gavin was their dealer lol we did not understand what these “blends” were.
Back in 2017 my husband and I wanted to get pregnant so I went to the doctors and learned I had a 9 cm cyst and was told that I wouldn’t be able to get pregnant and had to go on birth control first to regulate my hormones. But instead I quit grains, caffeine and sugar and in just 5 weeks my cyst had shrunk to 6 cm and I got pregnant! At 10 weeks pregnant, I got hospitalized with a kidney infection and was put on fever reducers and antibiotics. When I left the hospital I did not fill my prescriptions and I went to a Chiropractor/Holistic Dr. instead and he performed muscle testing on me and I learned that I had heavy metals in my system which is why my hands and feet had swelled up my whole life, and I had a toxic amount of chlorine in my lower abdomen from using tampons which, is why I got frequent UTI’s which, is also how I got the kidney infection. I was put on pharmaceutical grade, whole food supplements that detoxed my body from the heavy metals and toxic chemicals and had the absolute healthiest pregnancy and Baby!
With all that said, my husband and I are talking about baby number two and I felt like I didn’t know how to even start getting my body ready like last time and definitely didn’t want to be pregnant and learning I’m not as healthy as I thought. My Mom suggested to Fast and let my body do the correcting. Whenever I tried fasting, I’d get to like 10/11am and then I am starving and then I’m so hungry I’d stuff my face and then my whole day is thrown off. My mom also told me about the Autophagy and I really didn’t think it was going to work. I had tried natural hunger suppressants before and felt like nothing ever worked.
Friday night I took 1/8 tsp. and went to bed. The next morning I had to wake up early to drive my son out to his Grandparents and I was so tired! I took a second dose 1/4 tsp. because I didn’t believe this powder was going to do anything magical. On my drive to my in-laws which, is about a 20 min. drive on the freeway, I noticed I felt super focused and alert! Here I am exhausted no coffee, no food and I’m feeling 100% focused! I played with my mind the whole drive wondering if this was just a placebo effect and kept trying to think of something delicious to get my appetite going but, nothing worked. On my way back there’s a Starbucks that I normally stop at before work and I laughed that I had no desire to stop. I kept thinking “Oh my God! I have to write in to this guy because if this stuff worked on me, it can work on anyone!”
I have been using it for almost 3 weeks now and have been doing 22/2 fast which, I would have never ever been able to do! last Saturday I was going to dinner with friends so, I had to adjust my time. I actually ended up Fasting 25 hours! and again, no headaches, no dizziness, no hunger pains, no nausea. I have quit coffee and sugar besides when I have my blend in a little bit of Cold brew. I feel alert and focused and on the right track to preparing for another pregnancy.
Now being a believer in the blends I am interested in other blends that Gavin has to offer and becoming more educated on the blends.
I am a Skin expert and I have clients every day telling me about how they were diagnosed with something and put on heavy medications and I’d love to educate people on these blends and like to refer them to other alternatives which, I would most definitely now let them know about Interstellar blends.
Rebecca Walker –
I have been taking Autophagy with Nebula first thing every morning for just over a week now! Wow! It is just amazing.
The autophagy makes my fasting much easier, I regularly just have one meal a day, I have noticed that I don’t need to eat as much in the meal.
Combined with the Nebula in the morning, it really is kick-ass fuel, I am more focussed, brain-fog disappears, more productive… the benefits keep on coming.
I don’t get an afternoon slump, if I feel tiredness creeping in I have some more Autophagy with Peel and I’m back up to speed until my feeding window.
I’m not sure if this is a side-effect of the Autophagy but I have lost around 7lbs weight without even trying. Glad I bought a big bag to keep me going!
Another benefit I have noticed is my hair seems to be growing much faster, again it will be interesting to see if this is because of the Autophagy.
I have been taking Gavin’s blends for over two years now, in that time I have sorted my mental health and now my physical health, feeling better than I have done for 10 years.
I’m 44 years old and still not a grey hair to be found, all my blood results show my body is in top form.
Fasting – Blends – Good Diet
Thank you, Gavin, for another Interstellar Blend!!!
Anastasia Aldaeva –
Since the early childhood, as I remember myself, I was eating uncontrollably through the day and night (literally). It was not matter what I was eating, it just have to be a lot and constant. The necessity and desire to battle the addiction and improve health condition brought me to blends. Food addiction created a cycle which was very difficult to break and which consumed a lot of energy (consistent thoughts about food- when to eat, what to eat, how to get rid of calories which I eat, cycle of tension-release-guilt-decision to stop it-tension again etc etc). I started to take Autophagy at the moment of being deeply depressed (sleeping 16 hours in a day and the rest of the time having uncontrollable appetite). I experience the full benefit and beauty of Autophagy starting from day 10 of taking it.
It made me feel that “I am enough” and do not have to permanently stuff myself and finally can focus on daily tasks. It broke the cycle of constant guilt. It gave me back energy which was consumed by constant self-control. Autophagy made fasting as easy as it never was before. 24-48 hours of dry fasting with physical exercises with Autophagy is effortless. It is not only helping to fast, heal, lose weight, but it helped me to be more effective and confident.
Another great benefit which made Autophagy to stand out is that after breaking fast (feeding window) I am not going crazy and unstoppable with eating as I feel that the effect of the blend is still quite strong even if it was taken 5-8 hours ago. This makes me sure that during refeeding I will not mess up with too much wrong food and will maintain the effects/healing which was achieved by and during fasting.
I cannot stress strong enough how smooth my fasting days are now and how many positive effects I gained with Autophagy. Definitely I would recommend to anyone who either wants to effortlessly fast for health benefits or those who battling food addiction to experience all the magic and science which Autophagy can bring into your life.
Curran J Coughlin –
I got this as a sample pack with my normal order that I usually get, I used this on and off with Peel and Spice. I did notice a boost in fat metabolism when I used it as well as suppressed appetite. When doing extensive research on these herbs there is no parallel to this blend anywhere on the market or for this particular purpose. So if you’re fasting, dry or water and you want something to boost your results try adding this into your regiment. P.S two others I have to rave about that will boost any of his blends are the Peel and the Spice which I personally take daily for amazing skin and mood 🙂
TS –
What can I say about the Autophagy blend but that when you give your body time IT WILL WORK!
I have a very resistant body to herbs and medications. It takes me a long time to notice effects of things. Or if I take super high doses THEN I notice changes more rapidly.
I was determined to see how the Autophagy worked with just a small dose 2-3 times per day. It took my body about 3 weeks to notice changes.
I noticed how relaxed I felt in each day of my fast. Not thinking about food or what I was planning to eat. My window would come and I would blow past it. Looking up and realizing I was 1-3 hours past when I had planned on eating.
I have always been a good faster. But I would think about food all during my fasting hours. I am happy to say I am not thinking of food during my fasting hours. And when I do eat my food I do not find myself wanting to snack AFTER my meal.
What a beautiful thing to not snack AFTER your dinner/meal! Being able to relax and go to bed full comfortable and happy.
For anyone who struggles with any kind of eating disorder or food addiction I would strongly suggest getting the following blends to ease your mind, your appetite and your journey. LUTEOLIN, TRINITY, SEVEN SAGES and AUTOPHAGY are THEEEEE perfect combination for anyone who has struggled.
Thank you again Gavin for another fabulous blend.
Roberta –
Over my lifetime I have water & juice fasted many times and for at least 10 years I have intermittent fasted without any problems of going without food for a prolong period of time.
I learned of dry fasting at the beginning of this year. Once again I had no problem doing cycles of 66/6 —at least when it came to cravings or becoming hungry but, I did feel very tired during the dry fast.
When I would come off of the fast, I was also very good at being regimented about being on a keto diet. I even had a couple of cheat days and had no problem regaining any of the weight loss.
In April I went through some highly emotional things in my life that continued through July. I stopped doing the longer dry fast and tried to go to a 22/2 fast—here is where I developed a problem. Once I would eat dinner and have to resume the next day not eating or drinking, I started becoming extremely hungry. I had not felt that feeling in many years and I would unfortunately end up eating.
I am so grateful that Gavin came out with the Autophagy blend because what I found was that it was helping me to abstain from eating when I was having a difficult time doing it on my own. Since I always knew that I did ok dry fasting without hunger or cravings, I didn’t think that I would use it during fasting but, would only use it when I came off the 22/2 to help control hunger.
During most of my dry fast that I did through this year at best I would only lose about 6-7 lbs. per cycle. I thought I would go ahead and finally try using the Autophagy during my fasting window; I’m glad I did because another benefit that I am so excited about is that it seems to have helped bump up my ketones. Normally in the past, I would hardly have a ketone reading.
Autophagy has brought up my ketones to a moderate point and it also has increased my weight loss to 11-12 lbs. per cycle and that is with very minimal exercise since I have a knee and leg issue going on at this time.
When I told my adult daughter about what Autophagy does, she was excited to horn in on some of mine to try lol.
She always had great difficulty even fasting past 10 a.m. without becoming very hungry or getting a headache. She found that she was able for the first time to do multiple 22/2’s easily. She loves it!
I believe that adding Autophagy to your blends is extremely beneficial and an important asset to achieving your goals.
Tricia Mendoza –
For the last week I’ve been taking Trinity, Autophagy and Seven Sages.
On a dry-fasting search one night, I came across your products from a link mentioned on a YouTube video. Boy, Am I glad I did 🙂
All I can say is WOW-EEH!!!!!
I didn’t even know I was low on energy until I tried your herbs. My brain feels alert like never before and my energy is sky-high, without the jittery feeling that you often get from caffeine. I can best describe it as an all-day grounded and happy state. An overall sense of confidence has taken root. Fasting has become easy and my food cravings, especially for sugar, have gone away.
It’s pure magic ..A game changer indeed !
Tricia M –
For the last week I’ve been taking Trinity, Autophagy and Seven Sages.
On a dry-fasting search one night, I came across your products from a link mentioned on a YouTube video. Boy, Am I glad I did 🙂
All I can say is WOW-EEH!!!!!
I didn’t even know I was low on energy until I tried your herbs. My brain feels alert like never before and my energy is sky-high, without the jittery feeling that you often get from caffeine. I can best describe it as an all-day grounded and happy state. An overall sense of confidence has taken root. Fasting has become easy and my food cravings, especially for sugar, have gone away.
It’s pure magic ..A game changer indeed !
Scott “Coop” Cooper –
I was a very early adopter of Gavins blends, I started when there was only the Original 20:1. I was also an early adopter of bulletproof coffee, living on the west coast I woke up around 3:30am to trade the markets and bp coffee was a big help. I started adding the blends and WOW!!!! What a jolt of electricity and energy, I was loving it. I soon dumped the MCT oil from the bp coffee and the blends compensated much better. I soon started to get all the blends as they were released or actually before. I was soon using Supernova then Nebula, Thermo, Trinity, and Seven Sages. Now I pretty much use them all because they work and keep me healthy!!!! How can you go wrong when you get a plethora of plants, in very high concentration, nourishing and replenishing your body!!
I find that Citrus, Peel and Spice go to town on my high, once, Blood Pressure and keep my heart healthy. My blood pressure is much lower now. I love the ACB and have now added Apigenin and Luteolin to my collection.
When I was on the 88/8 challenge, I found the blends to be indispensable. After Cycle1, Gavin sent me(I won) the about to be released Autophagy!! WOW Again! These blends and the Autophagy are the real deal!!! Amazing products that work. What was great is that the blends really go to town feeding the body. They feed the body so well that you do not get hungry!
Walking 5 to 10 miles a day is not a problem, with the hunger. In fact, soon the food cravings and the craving of just eating go away. You start finding other things to do with your time, instead of eating. Also, there is a feeling that you get when you feel your body using your fat as fuel. It’s like a pulling/sucking effect, where you feel your body dropping weight all the time. You do not get or feel bloated. Its a very motivating feeling.
Now, after the challenge, I can go 3 to 4 days without eating. I can stay in Keto and when I do eat, I cant even finish my salad. Seriously! Hunger disappears! I continue to drop weight and drop fat. My clothes fit much better and most importantly, I FEEL GREAT!!!
Zoe (verified owner) –
I recently discover intermittent fasting. I went to Facebook to check out fasting groups as I wanted to learn more. I like reading real life stories.
In my group search I found Gavin’s fasting group. There is so much to discover and learn. I started with 16:8.
When I was reading the success stories, I never imagined I could do a 20 hour fast or 24 hour fast.
Someone posted about the power of the Autophagy blend. I clicked on the website and read all of these glowing reviews.
It was a no brainier, I ordered Autophagy Activator hoping to be able to get to 20 or 24 hours fast. The order arrived promptly.The first day I noticed an increase in energy. I wasn’t sure it was from the blends or from my mindset, either way I felt over the moon that I discovered a secret to making fasting easy.
The first week I found ease in doing 20 and 24 hour fasts. No hunger, no side effects…simple and easy. Today I completed my first 48 hour fast. Again, it was easy, no hunger pains, nothing. I plan to do more of the 48 hours then extend it again.
I have read great reviews about the peel and spice blends and their power to reduce inflammation, I am going to add it to my daily supply. I am a believer. I appreciate people taking the time to write reviews and sharing their stories. It really helps people like me who are new and researching.
Janaya Parra –
I cannot believe how well these blends work! You barely feel like you’re fasting and when you finally eat, your hunger is mild. This is great for those of us who struggle with food addiction and binging. We always seem to self-sabotage our efforts once an eating window opens, but the AUTOPHAGY formula stops that from happening. It took me a long time to believe it would happen for me after watching so many people lose huge amounts of weight in such little time but once I gave it a try, I was amazed at how perfectly everything in the protocol works synergistically. I never thought I would be able to go 10 miles or more in one day but now it feels normal! In the beginning I thought 5 miles a day was pushing it.
The THERMO blend really warms you up so you’re able to walk in the frigid temperatures and withstand the ice baths. I couldn’t believe I was outside in 12 degrees and wasn’t freezing to death! The NIAGRA formula is a great one to take for PMS, I barely feel like anything is happening during most cycles now! I have fibroids which cause long, heavy periods but with this blend (and with the help of the others) it’s painless. I’m hoping these blends will shrink and eradicate the fibroids in time…we shall see!
Overall, I just feel a constant stream of energy and since it’s not the jittery high you get from weigh loss pills or energy drinks, I didn’t even realize it for a while. One day I thought, wow I’m never really exhausted like I used to be ALL THE TIME! My mood has been good and steady since starting the blends, no low points or bouts of depression like I used to have. I’m just mellow and energized, a big switch from the somber, sleepy person I used to be! I can’t describe how grateful I am that I stumbled upon this group and these magical herbs because I’m a customer for life!
Lori Chapman (verified owner) –
I’m a retired (disabled) pharmacist…I’ve been obese my entire life…27 years of hard flooring and standing 12-16 hours/day… plantar fasciitis, and arch pain in my feet drove me to anti-inflammatory meds and steroid injections in my ankles, between my toes, and in my arches so that I could continue to work. Improper alignment of spine from having to lean on pharmacy counter while working produced 2 bulging discs in my lower back, and produced aggravated knee pain from a previous auto injury. Several years ago I tore the ligaments in the arches of both of my feet… I was only able to be on my feet one hour MAX per day… I’ve endured years of physical therapy, (with the refusal to take pain medication), portable TENS unit & biofeedback techniques, ‘REALITY’ … I was unable to resume work, which brought on stress,(loss of income), mental health deterioration with temporary depression… I gained ~138lbs in one year. I chose to have gastric bypass surgery and lost ~137lbs since that time weight has ping-ponged up and down with countless attempts of conventional weight loss methods…As a result, I was left with adrenal fatigue, insulin resistance, a screwed up metabolism, and a host of other physical issues. I found modified Keto March 29,2019 and began my lifestyle change. I’ve experimented with IF, OMAD, water fasts of 24’s, 48’s, 72’s with the longest fast of 14 days. I was averaging a 2-3 lb. loss per week, and by July I hit a weight loss stall (total loss 3 lbs for the entire month). I searched the Internet for solutions and stumbled across a post from someone using Interstellar Blends (Devine intervention)…I began to thoroughly educate myself with the research Gavin provided with each blend…He announced that a new blend called Autophagy Activator was going to become available in October 2019…with my physical issues I thought what a great option to help my body heal itself. I have been taking the Autophagy blend for 10 weeks (with no other blends). My energy levels have greatly increased, my weight loss has increased with an average of 3-4 lbs per week! I used to walk with the aid of a cane with a max of 2,000-3,000 steps per day. I’m currently able to walk without my cane and have been able to increase my distance to 7,000-8,000 steps per day. I have lost 39.8 lbs since beginning the use of the Autophagy blend making my total weight loss to date 131.2 lbs. I’ve just recently purchased several more blends to help with my overall health and longevity. I’m choosing not to do dry fasting and I’m approaching my health and weight loss with a slow and steady approach…Quitting is not an option… been there done that.
Dana Beaurem (verified owner) –
I have to brag about another blend that is near and dear to me. AUTOPHAGY ACTIVATOR
I’d planned to break my fast for an event in which I was trying to think of ways to not go to because I was afraid of over indulging. I did my research on what blends could help me mentally and physically during my break and I kept coming across Autophagy Activator. I made my shake and tripled the dose of Autophagy and prior to dinner i took a shot and ordered a nice salad; i didn’t even ieat the entire salad. When i got home my mood was sooooo calm and relaxing; I slept amazing with absolutely no cravings the entire day. I have started my rehydrating phase and preparing for my 88 hour dry fast and still no cravings. The AUTOPHAGY ACTIVATOR will be my go to blend between cycles. Gavin I can’t thank you enough for teaching me about these amazing herbs. The studies of these blends are helping me understand what mistakes I made throughout my life and prepare me for further life longevity. Thank you
Alice tyre (verified owner) –
First, a little background. I am 56 year old female living a fasting forward life for about 6 months now. Twenty years ago, main stream medical removed 90% of my thyroid and i have been struggling ever since; with weight, with being tired, with gut issues–and thats just the stuff I know about because five years after that I stopped going to western med doctors. I still struggle with weight, but am getting it under control with fasting.
Enter Gavin! So i stumbled upon this website totally by accident through a post on facebook group I belong to about fasting. And that was it. I spent the next couple weeks scouring everything i could–there is so much information here! I dry fast often and when I was reading about this new Autophagy Activator I just had to try it. I am a bit skeptical by nature, so one blend at a time is what I figure I would try because how else would I know if this particular thing was making a difference.
The blend arrived and I started almost immediately an open ended dry fast– I would just go until my body said otherwise. I took my first morning shot with Autophagy blend and just went about my business, just kind of forgot about it. 4 hours later, timer went off and I took second shot. And this is where things began to feel different. Im not even sure if this is what it is supposed to do, but I just felt “easy”– not really sure how else to put it, but like everything was right in the world. And I wanted to walk. So I did..for the next 2 hours, I just walked, almost in a meditative state. But I felt amazing! And for the next 3 days, I just took the blend as scheduled. I never had a minute of hunger or thirst. I didn’t have anything at all–no aches, no pains, nothing! So I’m hooked.
But that is not all. I reached out in the Interstellar telegram group about this hypothyroid business to see if any other members had these issues and what blends might be the best for me to use for this (yes, my “1 blend at a time” thing has gone by the wayside, lol.. I want whatever blends I need to address everything!!). And guess what? Gavin answered my post almost immediately. It’s kind of unheard of in business today. So thank you! Can’t wait to get it all under control.
Adrian Medina (verified owner) –
So it took me, almost, forever to, finally, buy some blends from Insterstellar. The craziest part is that, when I, finally, took them, I wondered why I took so long. I joined the page about a year ago and watched as so many people posted about the amazing benefits that every single blend provided them , including my friend that suggested them to me. She had already been taking different blends to alleviate some major and minor ailments. She ranted and raved about how responsive and helpful Gavin was (and still is) about any questions or concerns you may have pertaining to what you are trying to achieve.
As I look back at when I added the page, I can, honestly, say I never became skeptical or doubtful at the results people were getting because Gavin is THE EXAMPLE of what can be achieved. He lives it!!! In addition, there are so many better alternatives to the crap that we are prescribed every day. I knew this was the real deal and knew I was going to order some as soon as I could.
Fast forward to 2019…..Autophagy Activator and the “88/8” is shown to be nothing short of amazing. I reached out to Gavin a couple of times for questions and concerns and there he was in such quick fashion. To have that kind of response time from someone that was, surely, busy “saving the world” one blend at a time was FREAKING AWESOME!!! After a couple of questions answered, getting my priorites and money saved, I ordered PEEL, SPICE and TRINITY for my allergies and post nasal drip (I am a singer that works at a karaoke bar 5 nights a week) and Autophagy Activator for easier intermittent fasting. After taking these for a couple of weeks now, I must say, I have seen improvements in so many aspects in my body, mind and soul in leaps and bounds!!!!! My post nasal drip is, pretty much, nonexistent and I find fasting to be a cinch. I have been, gradually, working myself up to the “88/8” and can, positvely, say that I am getting there very quickly with the help of the Autophagy Activator. I can’t praise Gavin and his Interstellar blends enough. Thank you, Gavin, for everything you are doing to help this world and the people in it to be better. I can’t wait to see and implement into my life the new blends you will be releasing in the near future.
Michele Rakestraw –
I received Autophagy and a sample pack of Trinity last month. The Autophagy has helped tremendously in helping me get back to a low carb, intermittent fasting WOE.
It’s also given me much needed energy, which being a Mom of two, one being special needs, is greatly appreciated. I also feel more of a sense of well being with it. Looking very much forward to reordering.
Trinity I used on occasion when I felt stressed or needed a mental pick me up. Can’t wait to order more of that as well, along with some others.
Really appreciate that you offer these products Gavin, can’t thank you enough.
***** Michele Rakestraw
B.A. –
I’m loving autophagy activator SO much. I’ve been raving about it to all my friends and have even personified it by calling it “autophagy bae”. Now when I say “autophagy bae” my people all know who (not what – haha) I’m talking about. I recently started rolling 66/6 and it’s a must for following any of Gavin’s dry fasting protocols that include over 24 hours of dry fasting.
The ingredients are unparalleled!! Hundreds of ingredients that hit on autophagy (duh), oxidative stress, anti inflammation, lipolysis, mtor inhibition, anti obesity, anti diabetic, and leptin regulation. This is plant MEDICINE at its finest, people! You’re not going to find anything matching in one combined blend on the PLANET.
And when people have sticker shock at the price of the blends, they need to calm down and think about it. The list of ingredients and the recommended dosage demonstrate that you’re getting an incredible value. PLUS, Gavin is always willing to work with you – sometimes he is able to sell sample sizes (they still cost money obvi!) just for you to try to see if it will address your needs.
I’ve become a bonafide, unofficial spokesperson for Interstellar Blend. I can’t stop talking about them and guess what?! Friends and loved ones have taken note. Some have already become customers and started purchasing for themselves and their families!! The proof is in the evidence – the thorough descriptions of the blends on the website, the incredible authentic customer reviews and the amazing Facebook group.
I’ll say one last thing, JOIN the Facebook group, It’s so rich with info, reviews, feedback, protocols, weight loss challenges, maintenance regimens, Gavin’s top notch insight and guidance, and such a supportive community.
Cheers to longevity and prosperity with Interstellar!
FB @Bfb Fit
Kelly –
This blend really has been my BEST FRIEND for fasting! I’m not a fasting professional like many of the people here, but WOW has this stuff helped me keep my daily IF/OMAD intentions like a boss! At the beginning of the quarantine, I saw how easy it was going to be for me to just sit around and snack, so I decided to fast as a way of avoiding this behavior. Fortunately I had already ordered some Autophagy because a friend was saying how much it helped mitigate her appetite during prolonged dry fasts. SO GLAD I DID. For me there was a “loading phase” at first where I didn’t notice much of an effect on my appetite (but remember, I wasn’t actually doing extended fasts which is what I believe it’s designed for, and I was only taking 1/8tsp 2x/day). But once my body acclimated, I DEFINITELY noticed a totally different “attitude” about food. I felt way more nonchalant about it and really at ease and alert even after not eating for 20+ hours. I like Autophagy alone (and with green tea–I will also get Interstellar Matcha in my next order). But so far my favorite combo is Autophagy and Trinity togetheo get the effect that I want–happy, relaxed and not pressed about food. r. I am going to order more Autophagy and try it in combo with peel & spice too, but so far I like it with Trinity just fine. DEFFFFINITELY recommend for anyone who wants more painless, less distracted/food-focused fasting experiences (even if fasts are short like mine). Having done extended fasts and daily IF without Autophagy in the past, I would never want to do it again without this little gem. She’s a keeper!
Ada K. –
Love all the blends! They (samples) were gifted to me by a cousin and I was instantly blown away! I ordered Autophagy and love it! Ready to order ALL OF THEM! I look and feel 20 years younger; I feel like new person!
Nicole Ventura (verified owner) –
I have been taking the Autophagy blend for for 8 days now and LOVE IT!!!
Prior to discovering Interstellar blends and Autophagy Activator I would always start the day with the best of intentions but as the hours pass my will power would go down the drain and I would give in to my hunger. By the end of the day I would be full of garbage, feeling defeated and promise myself to be better the next day. It was never ending circle for me .
Until my order of Interstellar Blends arrived!!
Since taking Autopgahy Activator, hunger isn’t even an issue anymore. I immediately began fasting for 22 hours a day and it was EASY! I never in my life thought I would use the words fasting and easy in a sentence together. When I do finally eat I find myself getting full very quickly. Not only am I able to go longer periods of time without eating, but Autophagy Activator also keeps me from overindulging when I break my fast. Today I started my first 44/4 fast and I have no doubt that I will successfully complete it thanks to Gavin’s blends.
These blends have been an absolute game-changer. Gavin has been super helpful and is always available to answer questions. I have learned so much from reading through the numerous studies and scientific data he provides and am fascinated by it all. If appetite suppression is your goal I HIGHLY RECOMMEND Autophagy Activator. You will not be disappointed.
Shaya (verified owner) –
This has by far been the best for helping my fasting. I started using it about three times a day but down to two now. Moring, I will do coffee, and night I will do some sort of tea, make sure you mix it well to really break it in. I usually use this along will Thermo, Trinity, Nebula, or Supernova. This will for sure help your fasting and make it easier to get through the night without any cravings or wanting to break early.
I think its also key to stay active and move when you take these blends. I will usually try to run in the morning and after work, and try to stay on my feet throughout the day. Sitting around and taking the blends won’t help anything. I fund that these are a good catalyst to a healthy routine but don’t just think you can sit around and take them and they magically work. Im looking forward to getting more of this and trying some other blends to add into my routine.
Scotty –
Autophagy Activator is the key to make fasting a breeze! I used to have a rough time going more than 10 hours without eating, now 18-24 hour fasts are EASY! No hunger at all I sometimes forget im even fasting!
Not only does Autophagy Activator make you not hungry, it keeps you from over eating as well! I used to fast for long periods of time then eat anything and everything afterwards basically
making the fast useless. Now thats never a problem, a normal healthy keto meal fills me up super quick and i NEVER overeat!
When i began taking this blend I was 180 pounds, in 2 months i was able to get all the way down to 150 pounds and stay there! Anyone that has trouble feeling hungry while fasting or has a problem with overeating, THIS is it!!
Amanda Collins (verified owner) –
Autophagy Activator really helps to curb your appetite while fasting, I have no cravings for food and feel amazing! I use this blend along with, Thermo, Trinity, Nebula, Spice and Peel. I will not fast without this blend!
michalfilipkowski@yahoo.com (verified owner) –
This blend I was most excited for, because I was telling myself that this is my cure for cravings and over eating, that this blend will help me with fasting and that I will start doing 22/2 in no time.
Once it came and I started using it, I found out that it didn’t work the way I WANTED, I still had cravings, I’d still overeat here and there, and I still was pretty hungry, wasn’t able to do 22/2 in no time as I initially thought.
But I explained myself that these are herbs, not drugs like from big pharma that mask the problem but damage you elsewhere, to see if blends work we have to give them time, we also like stuff that works straight away otherwise we drop it so I let my disappointed thought go, it wasn’t righteous or smart. We either want something to work straight away, and if it doesnt work straight away, we are taught to drop it and do something else, never breaking from that cycle going from one solution to the other, always unhappy. so I did gave myself few more days and after 7-10 days I did saw that I can easily get fuller, if I cant fit any more food in my stomach I simply stop eating, if I see sweets I like in the shop and Im still fasting, I simply say to myself that this is wrong for me to 1-break my fast early and 2-break it with such a toxic piece of shit, which I never heard myself say in my head before, I’d always buy it, eat it and blame myself afterwards.
Autophagy seem to did something spectacular, maybe Im not able to do 22/2 yet but I can feel like my brain is getting rewired to respect fasting and respect what I put in my belly, Im learning to control myself more and my fasting window isn’t a feast, I don’t eat to make up my calories and stuff myself with everything I love and fancy at the time, I clear out stuff from the fridge and Im not fussy, I eat whats there to eat and I don’t overdo it. Im not a slave to food anymore.
this is much more important than what I was initially expecting, and it was wrong for me to have such high expectations, but after I gave it time I know this blend was only warming up and with my will power and my brain getting rewired with these blends, I will make it work and I will eventually enter the 22/2 club, cause Im staying as an interstellar customer for ever, Im not giving up and Im way ahead of my old self, time to become limitless, sky is the limit!